Ringworm vs eczema symptoms: Understanding the differences between these skin conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Both can cause frustrating itching, redness, and scaling, making it challenging to distinguish them at first glance. This comprehensive guide will explore the overlapping symptoms, unique characteristics, and diagnostic considerations for each condition, helping you gain a clearer picture of the underlying causes and effective treatments.
Ringworm, a fungal infection, often presents as a circular rash with raised borders and central clearing. Eczema, on the other hand, can manifest in various ways, from dry, cracked skin to inflamed, oozing patches. This exploration delves into the nuances of each condition, highlighting the key differences and similarities to aid in proper identification.
Introduction to Ringworm and Eczema: Ringworm Vs Eczema Symptoms
Ringworm and eczema are both common skin conditions that can cause discomfort and itching. While they share some overlapping symptoms, they have distinct causes and characteristics. Understanding the differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.Ringworm, despite its name, isn’t caused by a worm at all. It’s a fungal infection that appears as itchy, red, and often ring-shaped rashes on the skin.
Eczema, on the other hand, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can manifest in various forms and affect different areas of the body.
Defining Ringworm and Eczema
Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, or nails. The characteristic circular rash often has a raised border and clear center. These fungal infections are typically caused by dermatophytes, a type of fungus that thrives in warm, moist environments. The infection is spread through direct contact with infected individuals or animals, or indirectly through contaminated surfaces.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation, dryness, and itching. It encompasses a range of types, including atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and dyshidrotic eczema. The exact cause of eczema isn’t fully understood, but a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and immune system dysfunction are thought to play a role.
Common Affected Areas
Both ringworm and eczema can affect various areas of the body. Knowing the typical locations can aid in distinguishing between the two conditions.
Comparison Table: Ringworm vs Eczema Locations
| Body Part | Ringworm | Eczema | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalp | Yes, often presenting as patchy, scaly areas. | Less common, though possible, especially in children. | Ringworm on the scalp can be easily mistaken for dandruff. |
| Groin (Jock Itch) | Yes, particularly in moist areas. | Possible, but often characterized by more widespread inflammation. | Jock itch is a common form of ringworm. |
| Feet (Athlete’s Foot) | Yes, often affecting spaces between toes. | Possible, but typically involves more dryness and cracking. | Athlete’s foot is a type of ringworm infection. |
| Face | Possible, but less common than other locations. | Common, particularly in infants and children. | Facial eczema can manifest as redness, dryness, and scaling. |
| Hands | Possible, but often limited to areas with moisture. | Very common, often causing dryness, cracking, and intense itching. | Hand eczema can be triggered by various irritants. |
| Body | Possible, often in a circular pattern. | Possible, can manifest as patches of dry, inflamed skin. | Generalized body eczema can be difficult to pinpoint. |
Overlapping Symptoms
Ringworm and eczema, while distinct conditions, can sometimes share similar symptoms, leading to confusion in diagnosis. This overlap can make it challenging to differentiate between the two without a proper examination by a healthcare professional. Understanding these shared characteristics is crucial for accurate identification and appropriate treatment.Identifying the subtle differences between these skin conditions is not always straightforward. Many people experience similar itching, redness, and scaling, making self-diagnosis unreliable.
This section delves into the common symptoms shared by ringworm and eczema, highlighting potential misconceptions and emphasizing the importance of professional medical advice.
Common Misconceptions
A common misconception is that the presence of itching, redness, and scaling automatically points towards one specific condition. In reality, these symptoms can manifest in both ringworm and eczema, making visual differentiation difficult. It’s crucial to remember that visual assessments alone are not sufficient for accurate diagnosis. Accurate diagnosis necessitates a detailed evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and potentially, laboratory tests.
Shared Symptoms, Ringworm vs eczema symptoms
Itching, redness, and scaling are common to both ringworm and eczema. The location, pattern, and overall presentation of these symptoms, however, can offer clues, but not definitive ones. For example, ringworm often presents with a ring-like shape, while eczema can appear as dry, inflamed patches. Nevertheless, these overlapping symptoms necessitate professional medical evaluation for a precise diagnosis.
Symptom Summary Table
| Symptom | Ringworm | Eczema | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Itching | Often intense, especially during the night | Variable intensity, often worse at night or when skin is dry | Both conditions can cause significant discomfort due to itching. |
| Redness | May appear as a well-defined red ring | Skin can appear red, inflamed, and sometimes blistered | Redness is a common sign in both, but the pattern may differ. |
| Scaling | Can appear dry, flaky, and sometimes with a yellowish tint | Scaling can be present, ranging from fine to thick, dry patches | Both conditions can present with scaling, but the texture and appearance can differ. |
| Pattern | Often circular or ring-shaped | Can be patchy or widespread, sometimes affecting specific body areas | While both can be localized, ringworm’s distinctive ring shape is a helpful, though not foolproof, indicator. |
Distinguishing Features
Ringworm, a common fungal infection, often presents with telltale signs that help differentiate it from other skin conditions, including eczema. Understanding these distinctive characteristics is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. While some symptoms can overlap, specific visual patterns and characteristics help pinpoint ringworm.
Circular or Ring-Like Shape
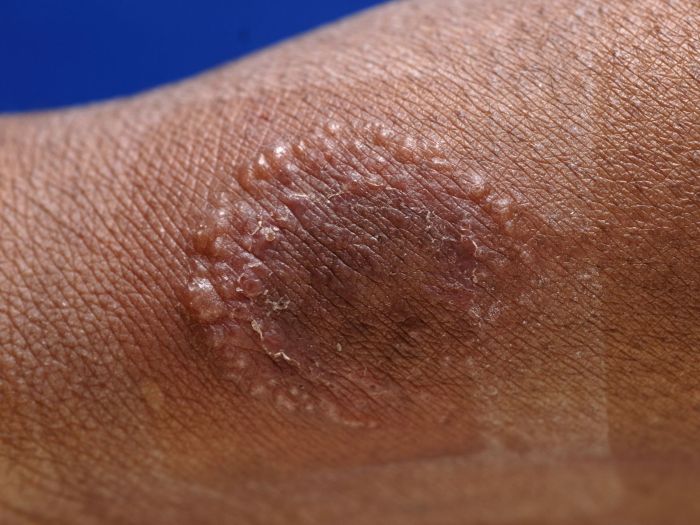
Ringworm infections typically manifest as a circular or ring-like rash. The affected area expands outward, giving the characteristic ring shape. The edges of the ring often appear raised and inflamed, creating a border around the central area. This expanding ring pattern is a key visual indicator of ringworm.
Raised Borders and Central Clearing
A significant characteristic of many ringworm infections is the presence of raised borders around the ring-like lesion. These raised borders are often scaly and slightly red or inflamed. The center of the ring often appears clear or less inflamed compared to the surrounding border, creating a distinctive ring-like appearance. This combination of raised borders and central clearing is frequently observed in ringworm.
Potential for Spread
Ringworm is contagious and can spread to other parts of the body if not treated properly. The fungus can easily spread through contact with infected skin or contaminated surfaces. Therefore, prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent further spread. Carefully following treatment instructions and avoiding scratching the affected area is important to prevent the infection from spreading.
Trying to tell ringworm from eczema can be tricky, right? Different rashes have similar symptoms, making diagnosis a bit of a puzzle. Fortunately, there’s a memory trick that can help you remember the key differences – like using keyword mnemonics to help you remember the key features of each condition. Check out memory tip 1 keyword mnemonics for a great way to organize these details in your mind.
This can really make a difference in distinguishing between the two skin conditions and getting the right treatment.
Identifying Ringworm Patterns
The characteristic patterns created by ringworm on the skin can aid in identification. The ring shape, with the raised border and central clearing, is a common visual cue. Furthermore, the ringworm rash often appears as a series of rings or patches, with one ring growing larger than another. Observing these patterns can help distinguish ringworm from other skin conditions.
Visual Characteristics of Ringworm
| Feature | Description | Illustration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Circular or ring-like, with an expanding border. | Imagine a circle on the skin, with the edges of the circle being slightly raised and inflamed, and the center being relatively clear or less inflamed. | The ring may appear as a single ring or multiple rings, with one ring growing larger than another. |
| Borders | Raised, scaly, and often inflamed. | Visualize the edges of the ring being elevated and having a slightly rough texture. | The raised borders often appear reddish or pinkish. |
| Central Area | Clear or less inflamed compared to the surrounding border. | Imagine the center of the ring being less red and irritated than the edges. | This central clearing is a distinguishing feature. |
| Spread | May spread to other areas of the body if not treated promptly. | Visualize the ring expanding outwards, creating multiple rings or patches. | Follow proper hygiene and treatment instructions to prevent further spread. |
Distinguishing Features
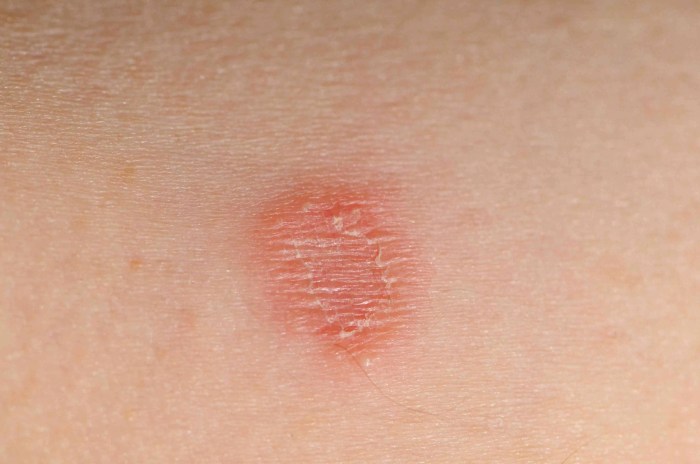
Identifying ringworm and eczema can be tricky, especially when symptoms overlap. Understanding the unique characteristics of each condition helps in accurate diagnosis. This section focuses on the distinguishing features of eczema, delving into its various presentations, inflammatory role, and different types.Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, manifests in diverse ways. The appearance of eczema can vary greatly, depending on the specific type and individual factors.
Dryness, cracking, and oozing are common features, but the specific presentation can provide crucial clues for diagnosis.
Eczema Appearances
Eczema’s diverse presentations are often characterized by inflammation, dryness, and potential for cracking and oozing. These symptoms can vary depending on the type of eczema and individual factors. Understanding these varied presentations is crucial for differentiating eczema from other skin conditions.
- Dryness: A hallmark of many eczema types, dryness often presents as rough, scaly skin, particularly on areas like the elbows, knees, and behind the knees. This dryness can be accompanied by itching and discomfort. In severe cases, the skin can become very tight and painful. This is often seen in atopic dermatitis, a common form of eczema.
- Cracking: The skin’s dryness can lead to cracking, especially in areas subjected to friction or pressure. These cracks can become fissures and may bleed, increasing the risk of infection. The severity of cracking can vary greatly, from minor surface cracks to deeper, more pronounced fissures.
- Oozing: Some eczema types, particularly in acute stages, may exhibit oozing. This often presents as a weeping or leaking of fluid from the affected area. The fluid can be clear or yellowish, and it can lead to crusting and scaling of the skin. This is frequently seen in atopic dermatitis flares.
Role of Inflammation in Eczema
Inflammation is a crucial component in eczema. It’s the body’s immune response to an irritant, allergen, or unknown trigger. This response leads to the characteristic symptoms. The inflammatory process plays a significant role in the development and progression of eczema.
Inflammation triggers the release of chemicals that can cause redness, swelling, itching, and dryness.
The inflammation in eczema can manifest in various ways, influencing the skin’s appearance and function. Chronic inflammation can lead to thickening and changes in the skin’s structure, making it more susceptible to damage and infection.
Types of Eczema
Eczema isn’t a single entity; it encompasses several types, each with unique characteristics. Understanding these different types helps in targeted treatment and management. The underlying causes and specific presentations vary between types.
| Eczema Type | Description | Typical Appearance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | A chronic, relapsing skin condition often associated with a family history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. | Dry, itchy, inflamed skin; often appears on the folds of the elbows and knees, face, and neck. Can be characterized by oozing, cracking, and scaling. | The most common type of eczema. |
| Contact Dermatitis | Inflammation of the skin triggered by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. | Redness, itching, and inflammation at the site of contact. Can also exhibit blistering or oozing. | Reaction to specific substances, like chemicals or plants. |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms, soles, and sides of the fingers and toes. | Itchy, small blisters, often clustered. | Often triggered by stress or sweating. |
| Nummular Eczema | Rounded, coin-shaped patches of inflamed, itchy skin. | Round or oval patches, dry, scaly, and often thickened. | Can be persistent and difficult to treat. |
Diagnostic Considerations
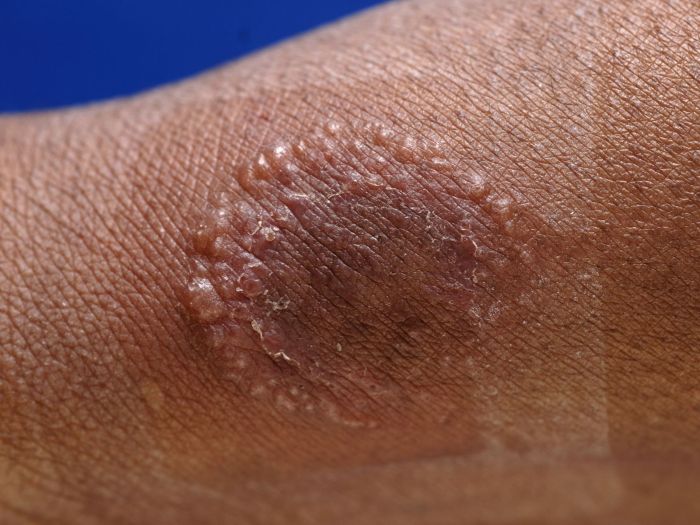
Accurate diagnosis of ringworm and eczema is crucial for effective treatment. Incorrect diagnoses can lead to ineffective treatments, prolonged discomfort, and potentially unnecessary use of strong medications. A healthcare professional’s expertise is essential in differentiating these conditions, given the potential for overlapping symptoms. A proper diagnosis hinges on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and sometimes, further testing.The diagnostic process involves more than just identifying the visible signs.
A doctor must consider various factors, including the location, appearance, and duration of the rash, alongside the patient’s overall health and any potential underlying conditions. This multifaceted approach ensures the most accurate and appropriate treatment plan.
Importance of a Medical Professional’s Diagnosis
A healthcare professional possesses the knowledge and expertise to accurately interpret the complex interplay of symptoms and factors associated with ringworm and eczema. They can differentiate between similar-appearing skin conditions and identify any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the symptoms. Their experience in assessing various skin lesions, combined with the patient’s medical history, provides the best chance for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods
A comprehensive diagnostic approach often includes several methods. Skin scraping is a common technique, involving the removal of a small sample of skin for microscopic examination. This allows for the visualization of fungal elements, which are indicative of ringworm. The potassium hydroxide (KOH) test is another valuable tool. A skin sample is treated with KOH, which helps to break down skin cells, making fungal hyphae (the thread-like structures of fungi) more visible under a microscope.A doctor may also perform a physical examination to assess the skin’s texture, look, and location of the rash.
Figuring out if it’s ringworm or eczema can be tricky, as their symptoms can overlap. Both can cause itchy, red patches, but the specific location and appearance can sometimes offer clues. Interestingly, while we’re on the topic of skin conditions, did you know there’s a fascinating connection between caffeine consumption and breast health? Research suggests a potential link, but more study is needed.
For more insights into this topic, check out this article on the link between caffeine breast health. Regardless of the underlying cause, it’s always best to consult a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for skin conditions like ringworm or eczema.
They may ask questions about the duration of the rash, any recent exposures to allergens or irritants, and any other relevant symptoms. This multifaceted approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying cause of the skin condition.
Potential for Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis is a possibility in any medical field. With conditions like ringworm and eczema, misdiagnosis can occur due to the similarity in some symptoms. For example, certain types of eczema can exhibit ring-like patterns, mimicking ringworm. Conversely, ringworm can sometimes present with symptoms that overlap with eczema. Therefore, relying solely on visual cues can lead to errors.
A thorough evaluation by a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare professional is essential.
Significance of Medical History and Patient Reports
The patient’s medical history and detailed description of symptoms are vital components of the diagnostic process. A history of recent illnesses, medications, or exposures to potential irritants or allergens can offer crucial insights into the underlying cause of the skin condition. Patient reports, such as the duration of the rash, its progression, and any associated symptoms (itching, pain, or discomfort), provide valuable context for the healthcare professional.
Trying to figure out if it’s ringworm or eczema can be tricky, as their symptoms can overlap. Both often present with itchy, red patches on the skin. However, understanding the common symptoms of low back pain, like stiffness and radiating pain, can help differentiate these skin conditions from musculoskeletal issues. For a deeper dive into the various presentations of low back pain, check out this helpful resource: common symptoms of low back pain.
Ultimately, accurate diagnosis of ringworm or eczema still requires a proper medical evaluation, so don’t hesitate to consult a doctor if you’re unsure.
These details help rule out or support various possibilities.
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods
| Method | Description | Ringworm Applicability | Eczema Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin Scraping | Removal of a small skin sample for microscopic examination. | Helpful in identifying fungal elements. | Can help rule out fungal infection, but not specific to eczema. |
| KOH Test | Treating a skin sample with KOH to reveal fungal hyphae. | Highly effective in detecting fungal elements. | May be used to rule out fungal infection, but other tests might be needed to confirm eczema. |
| Physical Examination | Visual assessment of skin texture, appearance, and location of the rash. | Useful for identifying characteristic ring-shaped lesions. | Essential for observing skin inflammation, dryness, and other eczema-related characteristics. |
| Medical History and Patient Reports | Gathering information about the patient’s past illnesses, medications, and reported symptoms. | Can help determine potential exposure to fungal sources. | Provides insight into potential triggers and patterns associated with eczema. |
Treatment Approaches
Understanding the appropriate treatment for ringworm and eczema is crucial for effective management. Choosing the right approach depends on several factors, including the severity, type, and location of the condition. Different treatments can have varying degrees of effectiveness and potential side effects, making personalized care essential.Effective treatment often involves a combination of strategies, tailored to address the specific needs of the individual.
For instance, mild cases might respond well to topical treatments, while more severe cases may require oral medications or a combination of therapies. A healthcare professional can guide you in developing a personalized treatment plan.
Ringworm Treatment
Ringworm, caused by fungal infections, typically responds well to antifungal medications. Topical antifungal creams are frequently the first line of treatment for mild to moderate cases. These creams contain ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine, which directly target and eliminate the fungi. The duration of treatment often depends on the severity and location of the infection, and usually lasts from a few weeks to several months.In more severe cases or when topical treatments are insufficient, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed.
These medications, taken by mouth, provide a broader reach and are more effective in treating deeper or more widespread infections. Examples include terbinafine and griseofulvin. Oral medications typically have a longer treatment duration compared to topical creams. Important considerations include potential side effects, drug interactions, and patient compliance.
Eczema Treatment
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, often requires a multifaceted approach to treatment. The goal is to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Moisturizers play a vital role in maintaining skin hydration and preventing dryness, a common trigger for eczema. They help create a protective barrier and reduce the itching and discomfort associated with the condition.Topical corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation and itching.
Their strength and frequency of use depend on the severity of the eczema. Mild to moderate cases may respond well to over-the-counter or low-potency corticosteroids, while more severe cases may require prescription-strength medications. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and application instructions carefully. In some cases, other topical therapies like calcineurin inhibitors or immunomodulators might be considered.
These medications can help reduce the immune response that contributes to the inflammation.
Treatment Comparison
Different treatment approaches for ringworm and eczema have unique characteristics and effectiveness. While antifungal creams and oral medications are effective for ringworm, topical corticosteroids and moisturizers are frequently used for eczema. The effectiveness of each treatment can vary based on the individual’s response, the severity of the condition, and the type of fungus or eczema involved.
Treatment Variations by Severity
The intensity of treatment often depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of ringworm or eczema might respond well to topical therapies, whereas severe cases may necessitate oral medications or a combination of topical and systemic treatments. A healthcare provider can evaluate the severity of the condition and recommend the most appropriate course of action.
Table of Common Treatment Options
| Condition | Treatment | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ringworm | Topical antifungal creams | Creams containing antifungal agents like clotrimazole or miconazole applied to the affected area. | Effective for mild to moderate cases; treatment duration varies. |
| Ringworm | Oral antifungal medications | Oral medications such as terbinafine or griseofulvin taken by mouth. | More effective for severe or widespread infections; longer treatment duration; potential side effects. |
| Eczema | Moisturizers | Hydrating creams or lotions applied regularly to maintain skin moisture and prevent dryness. | Essential for managing eczema; helps create a protective barrier. |
| Eczema | Topical corticosteroids | Creams or ointments containing corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. | Available in varying strengths; follow prescribed dosage and application instructions. |
Prevention and Management
Ringworm and eczema, while distinct conditions, share some overlapping symptoms and can be challenging to manage. Effective prevention and ongoing management strategies are crucial for minimizing flare-ups and improving quality of life for those affected. Understanding the specific preventative measures and consistent management approaches for each condition can significantly reduce the impact of these skin issues.Preventing and managing these conditions involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on both external factors and internal well-being.
A proactive approach, combining hygiene practices, avoidance of triggers, and consistent monitoring, is essential for long-term control.
Ringworm Prevention
Preventing ringworm often involves minimizing contact with potential sources of infection. Maintaining good hygiene practices, particularly handwashing, is paramount. Avoid sharing personal items like towels, clothing, or hats with others, especially those known to have ringworm. Prompt treatment of infected individuals is vital to prevent further spread within communities or families. Identifying and isolating infected individuals, combined with proper cleaning of potentially contaminated surfaces, plays a key role in preventing the spread of the fungus.
Eczema Prevention
Eczema management heavily relies on identifying and avoiding triggers. Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics. Maintaining consistent skin hydration is also crucial. Applying moisturizing creams or ointments regularly can help prevent dryness and cracking, reducing the likelihood of flare-ups. Identifying and eliminating specific allergens or irritants that trigger eczema can drastically reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Stress management techniques can also play a role in preventing eczema flare-ups in some individuals.
Ongoing Management Strategies
Effective management of both ringworm and eczema requires ongoing monitoring and proactive intervention. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist or healthcare professional are essential for both conditions. Prompt treatment of any new or worsening symptoms is critical to prevent complications. Identifying patterns of flare-ups and understanding triggers can aid in developing personalized management strategies. Early intervention and consistent follow-up care can significantly improve outcomes.
Symptom Management and Flare-Up Prevention
Managing symptoms and preventing flare-ups involves a combination of strategies. For ringworm, adhering to prescribed antifungal medications and avoiding scratching are crucial. For eczema, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using appropriate moisturizers, and managing stress are key components. Regular application of prescribed topical treatments, along with avoiding triggers, can help manage both conditions effectively. A personalized management plan, tailored to individual needs and triggers, can optimize treatment outcomes and minimize flare-ups.
Prevention and Management Summary Table
| Condition | Prevention Tip | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ringworm | Avoid contact with infected individuals | Minimizing exposure to the fungus that causes ringworm is essential to prevent infection. | Do not share personal items like towels or hats with others who have ringworm. |
| Ringworm | Practice good hygiene | Maintaining cleanliness, particularly handwashing, is crucial in preventing the spread of ringworm. | Wash hands thoroughly after touching potentially contaminated surfaces. |
| Eczema | Avoid irritants | Identifying and eliminating substances that trigger eczema flare-ups is key. | Switch to fragrance-free soaps and detergents. |
| Eczema | Maintain skin hydration | Regular moisturizing helps maintain skin barrier function, reducing dryness and irritation. | Apply moisturizer several times a day, especially after bathing. |
| Both | Monitor symptoms | Regularly checking for signs of worsening or new symptoms is vital. | Report any changes in rash appearance or intensity to a healthcare professional. |
| Both | Follow prescribed treatment | Adherence to prescribed medications and therapies is essential for effective management. | Take antifungal medications as directed for ringworm. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, while both ringworm and eczema can produce similar symptoms, crucial differences exist in their appearance, cause, and treatment. A proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is essential for effective management. By understanding the unique characteristics of each condition, individuals can work towards effective treatment and prevent future outbreaks. This detailed comparison provides a valuable resource for anyone seeking to understand the nuances of these common skin conditions.