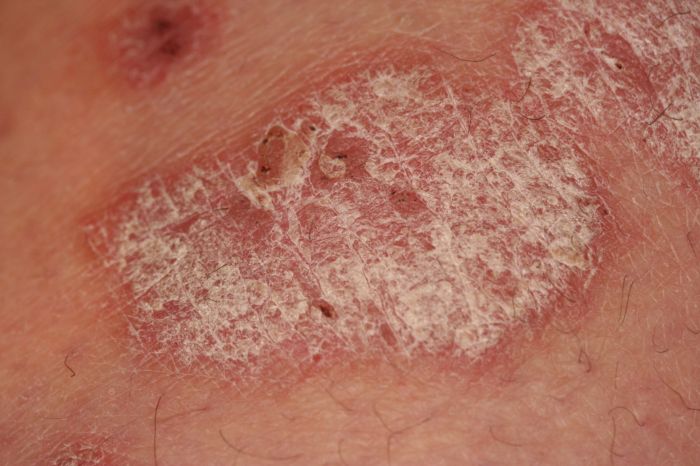
Do you have rosacea psoriasis or eczema – Do you have rosacea, psoriasis, or eczema? This guide dives deep into the symptoms, differences, and diagnostic considerations for these common skin conditions. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of each, comparing their appearances, triggers, and typical patterns. Understanding these conditions is crucial for proper self-care and seeking…
Tag: skin conditions
Itchy Hands and Feet Causes and Solutions
Itchy hands and feet can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience. This comprehensive guide delves into the various potential causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for this common ailment. Understanding the nuances of itchy hands and feet is key to finding relief and restoring comfort. From skin conditions to allergies and underlying health…
Skin Lesions Types, Pictures, Causes & Treatment
Types of skin lesion pictures causes and treatment is a comprehensive guide to understanding skin abnormalities. From identifying various lesion types and their characteristics, to exploring potential causes and effective treatments, this article provides a thorough overview. We’ll delve into the specifics of primary and secondary lesions, offering visual aids and descriptions to aid in…
Cosmetic Treatments for Psoriasis A Comprehensive Guide
Cosmetic treatments with psoriasis are gaining increasing attention as individuals seek solutions to improve not only the medical aspects of the condition but also its impact on their appearance. This comprehensive guide delves into various approaches, from topical medications to advanced procedures, considering both the physical and psychological well-being of those affected by psoriasis. We’ll…
Ask an Expert Self-Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis
Ask an expert self diagnose atopic dermatitis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of atopic dermatitis (AD), providing a crucial understanding of its symptoms, triggers, and the limitations of self-diagnosis. We’ll explore the crucial difference between self-assessment and a professional diagnosis, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. From…
Vitiligo vs Albinism Whats the Difference?
Vitiligo vs albinism what s the difference – Vitiligo vs albinism: what’s the difference? This exploration delves into the distinct characteristics, underlying mechanisms, and impacts of these conditions. Understanding the nuances between vitiligo and albinism is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective support. We’ll examine their physical manifestations, genetic origins, and the challenges faced by…
Psoriasis and Your Life A Deep Dive
Psoriasis and your life intertwine in profound ways, impacting everything from daily routines to emotional well-being. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of living with psoriasis, offering insights into its effects, treatment options, and the importance of coping strategies. We’ll navigate the challenges and triumphs of managing this condition, emphasizing the journey of adaptation…
Olive Oil for Eczema A Natural Approach
Olive oil for eczema: Is this ancient remedy a viable alternative to conventional treatments? This exploration dives deep into the potential benefits and drawbacks of using olive oil to manage eczema, examining scientific evidence, potential side effects, and practical application methods. We’ll uncover whether olive oil can truly soothe irritated skin and provide lasting relief….