Gallbladder disease causes and risk factors are multifaceted, encompassing lifestyle choices, genetics, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding these elements is crucial for proactive health management. This exploration delves into the interplay of diet, obesity, family history, and other influences that contribute to gallbladder issues. We’ll examine the role of various factors in increasing your risk and explore potential preventive strategies.
From the impact of dietary habits to the role of genetics, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the causes and risk factors of gallbladder disease. We’ll look at common symptoms, the pathophysiology of gallstones, and the various diagnostic methods used to identify the condition. By the end, you’ll have a clearer picture of the potential risks and how to approach prevention.
Introduction to Gallbladder Disease
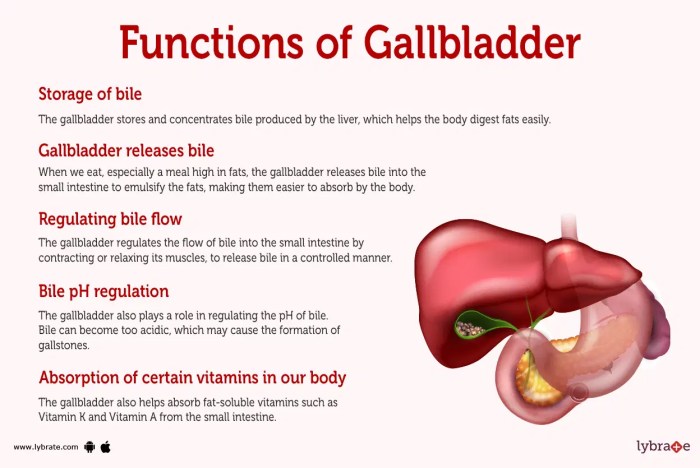
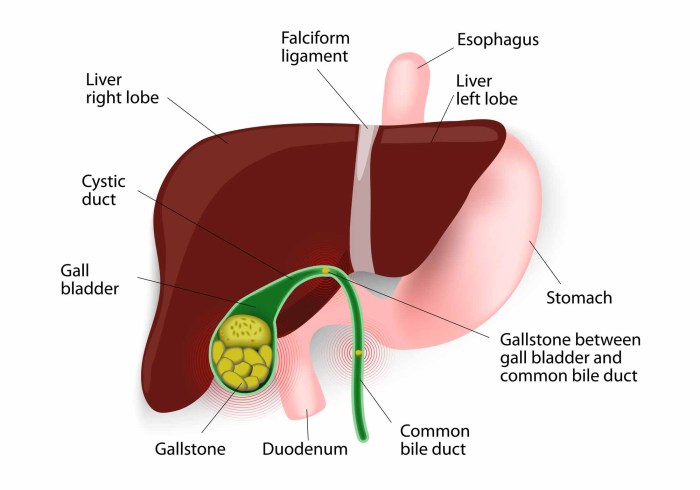
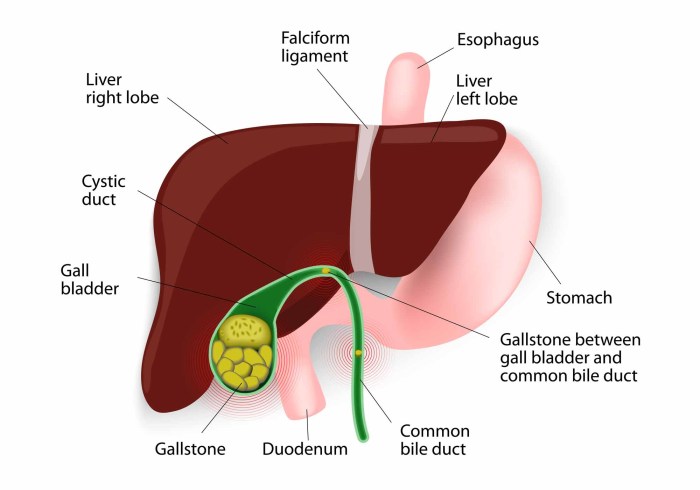
Gallbladder disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the gallbladder, a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. Its primary function is crucial for the digestion of fats, and its dysfunction can lead to discomfort and potentially serious complications. Understanding the workings of the gallbladder and the potential issues associated with it is vital for proactive health management.The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile, a fluid produced by the liver that aids in the breakdown and absorption of fats from the food we eat.
When food containing fats enters the small intestine, the gallbladder releases bile to emulsify these fats, making them easier for the body to absorb. Disruptions in this process can lead to various symptoms and complications.
Common Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease
Symptoms associated with gallbladder issues often manifest gradually and can vary in intensity. Common symptoms include persistent pain in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or right shoulder. This pain may be sharp, cramping, or dull and is frequently triggered or worsened by fatty meals. Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fever, and chills. It is important to note that not all individuals experience the same symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary significantly.
Types of Gallbladder Diseases
Gallbladder disease encompasses several conditions, the most common being gallstones (cholelithiasis). Other conditions include acute cholecystitis, chronic cholecystitis, and gallbladder cancer. Understanding these distinct conditions helps in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Overview of Gallbladder Diseases
| Type of Gallbladder Disease | Symptoms | Common Treatments | Further Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gallstones (Cholelithiasis) | Abdominal pain, often after meals, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and possible jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). | Dietary changes (reducing fat intake), medications to dissolve stones, and in some cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). | Gallstones are hard deposits that form within the gallbladder. They can vary in size and number. |
| Acute Cholecystitis | Severe, persistent abdominal pain, often accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. The pain may radiate to the right shoulder. | Hospitalization, intravenous fluids, antibiotics to combat infection, and often surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy). | Acute cholecystitis is a sudden inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct. |
| Chronic Cholecystitis | Recurring episodes of abdominal pain, often less severe than acute cholecystitis, but can lead to chronic symptoms. May include bloating, indigestion, and other gastrointestinal issues. | Dietary modifications, pain management, and possibly surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) if symptoms persist. | Chronic cholecystitis is a long-term inflammation of the gallbladder. It is often linked to gallstones, but can have other causes. |
| Gallbladder Cancer | Often presents with vague symptoms in the early stages, including abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and bloating. Later stages may show more severe symptoms. | Surgical removal of the gallbladder and possibly other treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the stage and extent of the cancer. | Gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious condition. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes. |
Risk Factors: Lifestyle: Gallbladder Disease Causes And Risk Factors
Our dietary choices and activity levels play a significant role in the development of gallbladder disease. Understanding how these lifestyle factors influence the risk is crucial for prevention and management. This section will explore the impact of diet, obesity, and physical activity on gallbladder health.Dietary habits significantly impact gallbladder function and the risk of developing gallstones. Certain dietary patterns can increase the likelihood of this condition, while others may offer some protection.
The relationship between specific dietary components and gallbladder disease risk is complex and often involves interplay with other factors.
Impact of Dietary Habits
Dietary habits have a profound influence on gallbladder function and the likelihood of developing gallstones. A diet high in saturated and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels, potentially leading to gallstone formation. Conversely, a diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables might offer some protective effect. Identifying the specific dietary patterns associated with higher risk can help individuals make informed choices.
- High-fat diets, particularly those rich in saturated and trans fats, are often linked to an increased risk of gallstones. These fats can increase cholesterol secretion into the bile, making it more prone to crystallization and stone formation. Examples include processed foods, fried foods, and red meat.
- Diets low in fiber can also contribute to gallbladder disease. Fiber aids in the movement of bile through the gallbladder, potentially reducing the risk of stagnation and subsequent stone formation.
- A diet high in refined carbohydrates, often found in sugary drinks and processed foods, can also increase the risk of gallstones. These foods can lead to insulin resistance and affect lipid metabolism, creating a conducive environment for gallstone development.
Obesity and Weight Management
Obesity is a significant risk factor for gallbladder disease. Excess weight can lead to changes in bile composition and increased cholesterol secretion, increasing the risk of gallstone formation. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce this risk. Weight loss, especially rapid weight loss, can also temporarily increase the risk of gallstones.
Effects of Different Types of Fat Intake, Gallbladder disease causes and risk factors
Different types of fat have varying effects on gallbladder health. Saturated and trans fats, often found in processed foods and animal products, are associated with a higher risk of gallstone formation. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, may have a more neutral or potentially protective effect. However, the overall dietary context is crucial, as an excessive intake of any type of fat can contribute to the problem.
Relationship Between Physical Inactivity and Gallbladder Disease
Physical inactivity is often linked to increased risk of developing gallstones. Regular exercise promotes healthy bile flow and reduces the likelihood of bile stasis, which can contribute to gallstone formation. Sedentary lifestyles contribute to weight gain and other factors that increase risk.
Comparison of Dietary Habits and Impact on Gallbladder Disease Risk
| Dietary Habit | Impact on Gallbladder Disease Risk | Examples | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-fat diet (saturated & trans fats) | Increased risk | Processed foods, fried foods, red meat | Increases cholesterol secretion, leading to potential gallstone formation. |
| Low-fiber diet | Increased risk | Processed foods, refined grains | Reduces bile movement, potentially leading to stagnation and gallstone formation. |
| High-refined carbohydrate diet | Increased risk | Sugary drinks, processed foods | Affects insulin resistance and lipid metabolism, creating a conducive environment for gallstone development. |
| Healthy diet (fiber, fruits, vegetables) | Potentially lower risk | Fruits, vegetables, whole grains | Promotes bile flow, potentially reducing gallstone formation. |
Risk Factors
Gallbladder disease, while often linked to lifestyle choices, isn’t solely determined by diet and exercise. Genetic predispositions, certain medical conditions, and hormonal fluctuations can also significantly impact your risk. Understanding these factors can help you take proactive steps to safeguard your gallbladder health.
Genetic Predispositions
Family history plays a crucial role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to gallbladder disease. Research consistently shows a strong correlation between having a close relative with the condition and an increased likelihood of developing it oneself. This suggests a genetic component influencing gallbladder function and susceptibility to disease. Inherited variations in genes that regulate bile production or gallbladder contraction can make some individuals more prone to developing gallstones.
For instance, individuals with a family history of gallstones may experience more frequent episodes or a more severe form of the disease compared to those without such a history.
Family History
A significant family history of gallbladder disease is a strong indicator of genetic predisposition. Individuals with a parent or sibling who has had gallbladder issues are at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves. This suggests that certain genetic traits are passed down, increasing the likelihood of gallstone formation or other gallbladder problems. It’s important to note that while family history is a risk factor, it doesn’t guarantee that someone will develop the disease.
Other lifestyle factors and environmental influences also contribute.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions are linked to an increased risk of gallbladder disease. Obesity, diabetes, and rapid weight loss are among these conditions. Obesity can lead to increased bile production, while diabetes can impact the way the body processes and uses glucose, potentially affecting gallbladder function. Rapid weight loss can also lead to an increased risk of gallstone formation due to changes in bile composition.
Furthermore, Crohn’s disease and cystic fibrosis are also associated with an elevated risk of gallbladder issues. Each condition can affect the gallbladder in unique ways, highlighting the complex interplay between various bodily systems.
Hormonal Influences
Hormonal fluctuations can influence gallbladder function and increase the risk of gallbladder disease. Pregnancy, for example, can lead to hormonal changes that alter bile composition, increasing the risk of gallstone formation. Oral contraceptives and other hormonal medications can also have a similar impact. These hormonal shifts can affect the way the gallbladder contracts and releases bile, increasing the likelihood of bile becoming concentrated and forming stones.
This emphasizes the dynamic nature of the gallbladder and its response to hormonal changes throughout a person’s life.
Impact of Medical Conditions
Different medical conditions affect gallbladder health in varying ways. Obesity can lead to a higher concentration of cholesterol in bile, increasing the risk of gallstones. Diabetes can impair glucose metabolism, potentially impacting the overall function of the gallbladder. Rapid weight loss, on the other hand, can result in changes in bile composition that increase the risk of gallstone formation.
These diverse impacts underscore the importance of considering the interplay between various factors when assessing gallbladder health.
Pregnancy and Gallbladder Issues
Pregnancy is often associated with an increased risk of gallbladder problems. The hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect bile composition and gallbladder function, potentially leading to gallstone formation. Furthermore, the pressure on the gallbladder due to the growing uterus can also contribute to the problem. This suggests that pregnancy can be a contributing factor to gallbladder issues, and monitoring is important for pregnant women.
Summary Table
| Genetic Factors | Medical Conditions | Hormonal Influences | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family history of gallbladder disease | Obesity | Pregnancy | Increased risk of gallstone formation |
| Inherited variations in genes related to bile production | Diabetes | Oral contraceptives | Alterations in gallbladder function |
| Genetic predisposition to gallstones | Rapid weight loss | Hormonal changes during pregnancy | Potential for complications |
| Specific genetic mutations | Crohn’s disease | Hormonal medications | Increased susceptibility to gallbladder issues |
Pathophysiology of Gallbladder Disease
Gallstones, a common culprit in gallbladder issues, form when the chemical balance of bile is disrupted. Understanding the underlying mechanisms is crucial for preventing and treating these conditions. The pathophysiology involves a complex interplay of factors, from the composition of bile to the inflammatory response within the gallbladder.The formation of gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, stems from imbalances in the components of bile.
Gallbladder disease, often stemming from factors like obesity and genetics, can be a real pain. While a healthy lifestyle plays a huge role in prevention, consider exploring the benefits of biodegradable sunscreen, which is gaining popularity for its environmental friendliness. Biodegradable sunscreen who needs it is a question worth asking if you’re looking to minimize your environmental impact while protecting your skin.
Ultimately, understanding the causes and risk factors for gallbladder disease can help you make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
This includes cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile salts. An excess of cholesterol or bilirubin, or an insufficient amount of bile salts, can lead to the precipitation of these substances, forming solid crystals that eventually aggregate into gallstones. Genetic predisposition and lifestyle factors, such as diet and obesity, play a significant role in altering the composition of bile and increasing the risk of stone formation.
Gallstone Formation Mechanisms
The formation of gallstones is a multifaceted process influenced by several factors. Excess cholesterol in bile, a common cause, can lead to the supersaturation of bile with cholesterol. This supersaturation surpasses the bile’s ability to dissolve the cholesterol, resulting in its precipitation and eventual crystallization. Similarly, an imbalance in the ratio of bile salts to cholesterol can also promote stone formation.
Furthermore, an increase in bilirubin, often due to liver dysfunction or hemolytic conditions, can contribute to gallstone formation. In some cases, the gallbladder’s inability to effectively contract and empty bile can lead to increased concentrations of bile components, increasing the likelihood of stone formation.
Types of Gallstones
Gallstones are broadly categorized into two main types: cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Each type exhibits unique characteristics influenced by the underlying chemical imbalances. Cholesterol stones, the most prevalent type, are typically yellow-green or light brown, and composed primarily of cholesterol. Pigment stones, conversely, are dark-colored, ranging from dark brown to black, and consist largely of bilirubin.
These stones can be further categorized based on their chemical composition and origin.
Inflammatory Processes in Gallbladder Disease
Inflammation, a critical aspect of gallbladder disease, is triggered by the presence of gallstones. The stones, obstructing the cystic duct, impede bile flow, leading to the accumulation of bile within the gallbladder. This accumulation can induce inflammation and potentially cause an acute attack of gallbladder pain, known as acute cholecystitis. Furthermore, the irritation caused by gallstones can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to the swelling and irritation of the gallbladder wall.
Gallbladder disease, often stemming from gallstones, can be a real pain. Factors like age, family history, and obesity play a role. Understanding these risks is crucial, and if you’re concerned about your health insurance options, knowing about catastrophic health insurance can be helpful too. What is catastrophic health insurance can provide a safety net if a serious illness like gallbladder issues arises.
Ultimately, recognizing the causes and risk factors for gallbladder disease empowers you to make informed choices about your health and potential insurance needs.
Role of Bile in Gallbladder Issues
Bile, a fluid produced by the liver, plays a crucial role in the digestion of fats. It emulsifies fats, making them easier for the body to absorb. However, imbalances in bile composition, such as an excess of cholesterol or bilirubin, can lead to the formation of gallstones. The presence of these stones can obstruct the cystic duct, leading to inflammation and pain.
Gallbladder disease, often stemming from gallstones, can sometimes present with concerning symptoms like loss of appetite and diarrhea. Understanding these symptoms is crucial, as they can be indicators of underlying issues, including gallbladder problems. Factors like a high-fat diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of gallbladder disease. Further research into potential causes, such as those explored in articles on loss of appetite and diarrhea , can help you better understand the complex relationship between these symptoms and potential gallbladder issues.
Furthermore, the stagnation of bile within the gallbladder due to obstruction can promote bacterial overgrowth, potentially exacerbating the inflammatory process.
Characteristics of Gallstones
| Type of Gallstone | Composition | Impact on Gallbladder | Further Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol Stones | Primarily cholesterol, with smaller amounts of bile salts and bilirubin | Often asymptomatic until they obstruct the cystic duct, causing inflammation and pain. | Most common type. |
| Pigment Stones | Predominantly bilirubin, often with calcium salts. | Can be associated with liver conditions or hemolytic anemia. Can cause chronic inflammation. | Less common than cholesterol stones. |
Inflammatory Response in the Gallbladder
The inflammatory response in the gallbladder, specifically acute cholecystitis, involves a cascade of cellular events. The obstruction of the cystic duct by gallstones leads to bile stasis and increased pressure within the gallbladder. This triggers the release of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines, which recruit immune cells to the site of inflammation. The infiltration of these cells further contributes to the inflammatory response, causing swelling, pain, and potential tissue damage.
The intensity of the inflammatory response varies depending on the severity and duration of the obstruction. The inflammatory response can progress to more severe conditions if left untreated.
Diagnostic Methods
Figuring out if you have gallbladder issues often involves a combination of tests. Doctors use a range of methods to pinpoint the problem, from simple blood work to more involved imaging techniques. Understanding these methods can help you feel more informed and involved in your health journey.
Common Diagnostic Tests
Several tests are commonly used to diagnose gallbladder problems. These range from basic blood tests to sophisticated imaging scans, each providing different pieces of the puzzle. A doctor carefully considers the results of these tests, along with your medical history and symptoms, to reach a diagnosis.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are frequently the first line of defense in evaluating gallbladder health. They help identify potential inflammation or infection in the body. Elevated levels of certain substances, like bilirubin or liver enzymes, might indicate gallbladder issues.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): This test measures various components of your blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Elevated white blood cell counts often signal infection, which could be related to gallbladder problems.
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): These tests assess the health of your liver. If your gallbladder is inflamed or blocked, it can affect your liver’s function, leading to elevated liver enzyme levels in the blood.
- Bilirubin Levels: Bilirubin is a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. High bilirubin levels can suggest issues with the gallbladder or bile ducts, as these are crucial for bilirubin processing.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques provide crucial visual information about the gallbladder and surrounding structures. They allow doctors to identify gallstones, blockages, or other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive procedure uses sound waves to create images of the gallbladder. It’s often the first imaging test performed because it’s readily available, relatively inexpensive, and doesn’t use radiation. The procedure involves applying a gel to the skin and moving a transducer over the area to create images of the gallbladder.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: CT scans use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. This provides a more comprehensive view than ultrasound, but it involves exposure to radiation. The procedure involves lying on a table that moves through a donut-shaped machine. The machine rotates around the body, taking multiple X-ray images.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI scans use powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. It offers excellent soft tissue contrast, which is valuable in visualizing potential gallbladder issues. The procedure involves lying inside a large, tube-shaped machine, which creates a magnetic field to allow the creation of detailed images.
- Cholescintigraphy (HIDA scan): This scan uses a radioactive tracer to assess gallbladder function. It’s particularly helpful in determining if the gallbladder is emptying properly. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein. The scan tracks the tracer as it moves through the biliary system. The scan helps evaluate gallbladder contraction and emptying.
Physical Examination
A physical examination, although not a definitive diagnostic test, can provide valuable clues. The doctor will evaluate signs like tenderness in the upper right abdomen, which might suggest gallbladder inflammation.
| Diagnostic Test | Procedure | Typical Results | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Sound waves create images of the gallbladder. | Images show gallstones, blockages, or other abnormalities. | Non-invasive, often first test performed. |
| CT Scan | X-rays create detailed cross-sectional images. | Detailed images of the gallbladder and surrounding structures. | More comprehensive than ultrasound, but involves radiation exposure. |
| MRI | Magnets and radio waves create detailed images. | High-quality images of soft tissues, useful in evaluating gallbladder. | Excellent soft tissue contrast, good for identifying issues. |
| Blood Tests (CBC, LFTs, Bilirubin) | Measure blood components and liver function. | Elevated white blood cells, liver enzymes, or bilirubin may suggest inflammation or blockage. | Initial indicators of potential gallbladder problems. |
Significance of Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are crucial in diagnosing gallbladder issues. They provide visual confirmation of gallstones, blockages, or other abnormalities that might not be apparent through physical examination or blood tests alone. This allows for more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
Role of Blood Tests
Blood tests are essential for identifying potential inflammation or infection in the body. Elevated levels of certain substances, like bilirubin or liver enzymes, could indicate issues with the gallbladder or bile ducts. They serve as important initial indicators.
Significance of a Physical Examination
A physical examination, although not a definitive diagnostic tool, can provide valuable clues. The doctor may check for tenderness in the upper right abdomen, a sign that might suggest gallbladder inflammation. This physical assessment helps to guide further testing and refine the diagnosis.
Prevention Strategies
Gallbladder disease, often characterized by gallstones, can lead to significant discomfort and potentially serious complications. Fortunately, proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Implementing lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and, in some cases, medical interventions, can be highly effective in preventing gallbladder issues.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits plays a crucial role in lowering the risk of gallstone formation and gallbladder disease. Maintaining a balanced approach to diet and exercise is paramount. Consistent physical activity and a healthy diet are not only crucial for overall well-being but also vital in mitigating the risk of this condition.
- Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling for at least 30 minutes most days of the week, helps in maintaining a healthy weight and reducing insulin resistance, both of which are associated with a lower risk of gallstones.
- Maintaining a healthy weight is a key factor in preventing gallbladder disease. Excess weight, especially abdominal fat, increases the risk of gallstone formation. Sustainable weight loss strategies, involving a balanced diet and regular exercise, are recommended.
Dietary Strategies
A balanced diet, rich in fiber and low in saturated and trans fats, can significantly impact gallstone formation. Specific dietary choices can minimize the risk.
- Increasing dietary fiber intake helps in slowing down the digestion process and promoting satiety. This can help prevent rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which are often associated with gallstone formation.
- Limiting the intake of saturated and trans fats is essential. These fats are often found in processed foods, fried foods, and red meat. Choosing healthier fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, is recommended.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day, rather than large meals, may help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of gallbladder problems.
Weight Management and Exercise
Weight management and regular exercise are crucial components in preventing gallstones and gallbladder disease. A combination of strategies is often most effective.
- Consistent exercise helps in burning calories and maintaining a healthy weight. This helps in reducing the risk of developing insulin resistance, a factor linked to an increased risk of gallstone formation.
- Sustainable weight loss strategies, achieved through a balanced diet and regular exercise, can dramatically reduce the risk of gallstone formation and other related issues. Gradual weight loss, aiming for a moderate rate, is generally recommended.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions play a vital role in preventing gallbladder disease in high-risk individuals. Specific medications or surgical procedures can prevent the formation of gallstones.
- Certain medications, such as ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), may help dissolve gallstones in some individuals. However, the effectiveness and appropriateness of these medications need to be evaluated by a healthcare professional based on individual circumstances.
- Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is a definitive treatment for gallstones and gallbladder disease. In cases where gallstones are causing significant symptoms or complications, cholecystectomy may be considered a preventive measure, especially in high-risk individuals.
Preventive Strategies Table
| Preventive Strategy | Effectiveness | Associated Benefits | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | High | Reduces risk of insulin resistance, promotes satiety | Requires consistent adherence |
| Regular Exercise | High | Maintains healthy weight, improves insulin sensitivity | Requires consistent effort |
| Weight Management | High | Reduces risk of gallstones, improves overall health | Requires long-term commitment |
| Medical Interventions (e.g., UDCA) | Moderate (variable) | May dissolve gallstones in some cases | Requires careful monitoring and professional guidance |
Role of Medications and Surgery
Medications like ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) can potentially dissolve small gallstones in some individuals. However, this is not a universal solution, and its effectiveness varies. Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is a definitive approach for preventing further issues associated with gallstones.
Cholecystectomy is generally recommended for individuals experiencing recurrent or severe symptoms related to gallstones, especially if medical management is not effective.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, gallbladder disease, while sometimes insidious, is often preventable through conscious lifestyle choices. Understanding the intricate interplay of risk factors, from dietary habits to genetic predispositions, empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. This knowledge allows for early detection and effective management of potential gallbladder issues, ultimately contributing to better overall well-being.