Psoriatic arthritis differential diagnosis is crucial for accurate treatment. Understanding the subtle distinctions between PsA and similar conditions like reactive arthritis, lupus, or even osteoarthritis is key to effective management. This guide dives deep into the various facets of diagnosing PsA, exploring its clinical presentation, potential overlaps with other conditions, and the diagnostic tools used to differentiate it.
We’ll cover everything from symptoms and imaging findings to genetic and environmental factors that can play a role.
The complexities of PsA often make accurate diagnosis challenging. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the process by providing a thorough overview of common differential diagnoses. It highlights the key characteristics that distinguish PsA from other inflammatory conditions, offering insights into the diagnostic criteria and supporting tests. By understanding the nuances, healthcare professionals and patients can work together towards the best possible outcomes.
Introduction to Psoriatic Arthritis Differential Diagnosis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that often accompanies psoriasis, a skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. It’s a complex condition that can affect various joints and, in some cases, cause significant disability. Understanding PsA and its potential mimics is crucial for timely and effective treatment.Accurate differential diagnosis is paramount in PsA management. Misdiagnosis can delay appropriate treatment, potentially leading to irreversible joint damage.
Early and precise identification of PsA allows for the initiation of targeted therapies that can effectively control inflammation, slow disease progression, and improve patients’ quality of life. This process involves carefully considering the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and supporting laboratory and imaging results.
Figuring out what’s causing those joint pains can be tricky, especially with psoriatic arthritis differential diagnosis. It’s important to rule out other conditions, and sometimes that means looking at less obvious symptoms. For example, have you been coughing up mucus lately? Understanding the connection between respiratory issues like coughing up mucus, particularly in the context of COVID-19, can be vital for a complete picture.
coughing up mucus covid can be a confusing symptom, so proper investigation is key. Ultimately, a thorough differential diagnosis for psoriatic arthritis involves careful consideration of a patient’s complete health history and physical examination.
Clinical Presentation of Psoriatic Arthritis
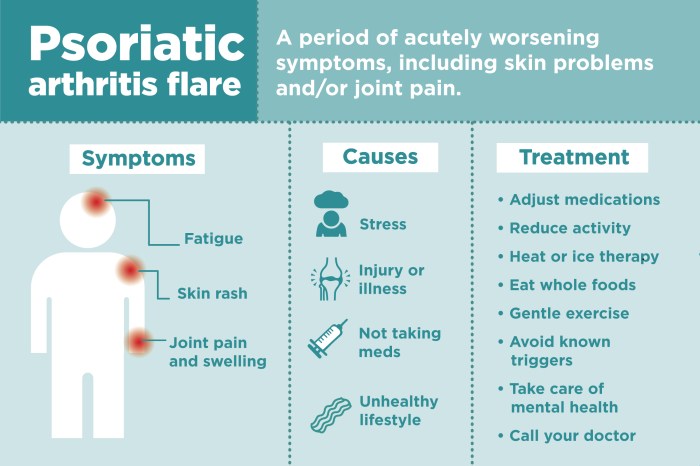
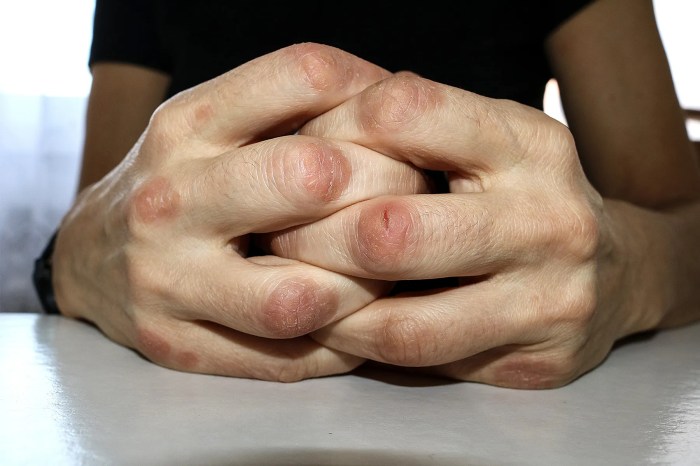
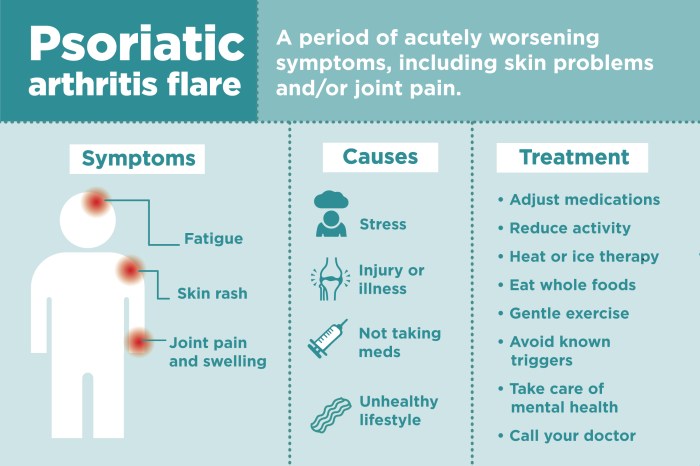
Psoriatic arthritis presents with a diverse range of symptoms, often affecting joints asymmetrically. Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and redness in the affected joints. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can fluctuate over time. In some cases, PsA can manifest as a spondylitis, affecting the spine, leading to stiffness and limited mobility. Nail changes, such as pitting and discoloration, are frequently observed in patients with PsA, alongside skin lesions if psoriasis is present.
Key Characteristics Distinguishing PsA from Other Conditions
PsA often exhibits distinct characteristics that help differentiate it from other forms of arthritis. For instance, the involvement of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, which are located at the ends of the fingers, is a key feature often observed in PsA. Dactylitis, a sausage-like swelling of the fingers or toes, is another distinguishing feature. Enthesitis, inflammation at the sites where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, is also frequently present in PsA, and can cause pain and tenderness in these areas.
Finally, the presence of psoriasis or a history of psoriasis is highly suggestive of PsA.
Comparison of PsA and Reactive Arthritis
| Characteristic | Psoriatic Arthritis | Reactive Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Pain, stiffness, swelling, redness in joints (often asymmetric), dactylitis, enthesitis, DIP joint involvement, nail changes (pitting, discoloration), skin lesions (psoriasis). | Pain, stiffness, swelling, redness in joints (often asymmetric), enthesitis, conjunctivitis, urethritis, or cervicitis. |
| Cause | Likely an autoimmune response triggered by a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors in patients with psoriasis. | Usually triggered by an infection in another part of the body, such as the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary tract. |
| Associated Conditions | Psoriasis, nail changes, skin lesions, enthesitis. | Urethritis, conjunctivitis, cervicitis, gastroenteritis. |
| Imaging Findings | Can show erosions and joint space narrowing on X-rays, characteristic of PsA. | Imaging findings may vary depending on the affected joints and tissues. |
The table above highlights key differences in the symptoms, cause, associated conditions, and imaging findings of PsA and reactive arthritis. Careful consideration of these factors can aid in distinguishing between the two conditions.
Common Differential Diagnoses
Pinpointing the precise cause of joint pain and inflammation is crucial for effective treatment. Many conditions can mimic the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), making accurate diagnosis a challenge. This section explores several common conditions frequently considered in the differential diagnosis of PsA.Understanding these conditions allows healthcare professionals to distinguish PsA from similar conditions, ensuring patients receive the appropriate care and treatment plan.
Reactive Arthritis
Reactive arthritis, often triggered by a bacterial infection, presents with inflammatory arthritis, typically affecting the lower extremities. Clinical features frequently include asymmetric arthritis, conjunctivitis (eye inflammation), and urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). Diagnostic criteria usually include a history of recent infection, alongside the characteristic inflammatory joint symptoms. The overlap with PsA can be significant, especially when skin manifestations are absent or less pronounced.
Patients with reactive arthritis might also experience enthesitis (inflammation at tendon/ligament attachment points), a hallmark symptom also seen in PsA. This shared feature underscores the importance of a thorough patient history and physical examination.
Infectious Arthritis
Infectious arthritis is caused by bacterial or viral pathogens directly affecting the joint. Symptoms typically include rapid onset of severe joint pain, swelling, and tenderness. Diagnostic criteria often involve synovial fluid analysis (examination of fluid within the joint) to detect signs of infection. The presence of fever, chills, and malaise further suggests an infectious etiology. The clinical presentation can vary, but severe, acute inflammation is a defining feature.
PsA, on the other hand, typically develops more insidiously, although rapid flares can occur. Distinguishing infectious arthritis from PsA relies on prompt diagnostic testing.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, is characterized by gradual cartilage breakdown within the joints. Clinical features commonly include progressive joint pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Diagnostic criteria often rely on radiographic imaging to detect joint space narrowing and bone spurs. Symptoms tend to be localized to specific joints, particularly weight-bearing joints like knees and hips.
While PsA can affect similar joints, the inflammatory component and potential for systemic manifestations (such as skin psoriasis) differentiate it. Overlap in symptoms may occur, especially in older individuals, which necessitates careful assessment of the patient’s history and physical examination.
Figuring out psoriatic arthritis’s differential diagnosis can be tricky. It often mimics other conditions, making accurate identification crucial. Understanding how to manage your sleep schedule, like resetting your circadian rhythm, can surprisingly play a role in overall health and well-being, potentially influencing the symptoms of psoriatic arthritis. This is because a consistent sleep cycle supports a healthy immune response, which can impact the course of the disease.
So, incorporating strategies for how to reset circadian rhythm might help, along with ongoing medical monitoring, in managing the differential diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis effectively.
Gout
Gout, a metabolic disorder, involves the deposition of uric acid crystals in the joints. Clinical features include acute, intense, and often excruciating joint pain, particularly in the big toe (podagra). Diagnostic criteria frequently include the presence of needle-shaped urate crystals in synovial fluid or characteristic tophi (deposits of urate crystals under the skin). The episodic nature of gout attacks, often triggered by dietary factors or certain medications, is a key differentiating characteristic.
PsA, conversely, typically displays a more chronic, persistent inflammation. Differentiating gout from PsA relies on evaluating the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and specific diagnostic tests.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic inflammatory condition primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints. Clinical features commonly include low back pain, stiffness, and progressive limitation of spinal mobility. Diagnostic criteria often rely on radiographic findings of sacroiliitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joints) and may involve genetic testing for HLA-B27. PsA can occasionally affect the spine, but the distinctive spinal involvement of ankylosing spondylitis is not a common feature of PsA.
The gradual progression of symptoms and the tendency for spinal fusion distinguish ankylosing spondylitis from PsA. Overlap can exist in the early stages, necessitating a detailed patient history and physical examination, particularly in cases involving axial joint involvement.
Table of Differential Diagnoses
| Differential Diagnosis | Key Symptoms | Distinguishing Features |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive Arthritis | Asymmetric arthritis, conjunctivitis, urethritis, recent infection | Associated with recent infection, often resolves with treatment of infection. |
| Infectious Arthritis | Severe, acute joint pain, swelling, fever, chills | Rapid onset, presence of infection in synovial fluid. |
| Osteoarthritis | Progressive joint pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion | Degenerative joint disease, often affects weight-bearing joints. |
| Gout | Acute, intense joint pain (often in big toe), tophi | Episodic attacks, associated with hyperuricemia, urate crystals in synovial fluid. |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | Low back pain, stiffness, limited spinal mobility | Primarily affects spine and sacroiliac joints, often associated with HLA-B27. |
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Pinpointing psoriatic arthritis (PsA) amidst a multitude of potential diagnoses demands a multifaceted approach. Accurate diagnosis hinges on a thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, physical examination findings, and results from various diagnostic tests. These tests help distinguish PsA from other inflammatory arthritides, infections, and other rheumatic conditions.A crucial aspect of the diagnostic process involves ruling out other conditions that share overlapping symptoms.
The diagnostic tests serve as valuable tools in this process, providing objective evidence that helps refine the differential diagnosis. The significance of each test lies in its ability to identify specific markers or characteristics associated with PsA, thereby facilitating a more precise diagnosis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging plays a critical role in evaluating PsA, offering insights into joint structure and inflammation. X-rays, for example, reveal bony erosions and joint space narrowing, characteristic features of PsA progression. These radiographic changes may not be immediately apparent, and their presence typically indicates a more advanced stage of the disease. The sensitivity of X-rays for detecting early PsA changes is somewhat limited, necessitating the use of more advanced imaging techniques.Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides a more detailed assessment of soft tissue structures, including tendons, ligaments, and joint capsules.
MRI excels in detecting inflammation and bone marrow edema, which are frequently observed in PsA. MRI can identify early inflammatory changes that might be missed by X-rays. Furthermore, MRI can distinguish PsA from other conditions characterized by similar joint involvement. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the extent and distribution of the inflammatory process.
Laboratory Investigations, Psoriatic arthritis differential diagnosis
Blood tests are valuable tools in assessing systemic inflammation and identifying potential markers associated with PsA. Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels are often elevated in inflammatory conditions. However, these markers are not specific to PsA and can be elevated in various inflammatory conditions. A complete blood count (CBC) can reveal anemia or other blood abnormalities that may accompany PsA.
Elevated inflammatory markers (ESR and CRP) can indicate an inflammatory process, but they are not specific to PsA.
The presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies is often helpful in differentiating PsA from rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The absence of RF and anti-CCP antibodies helps to rule out RA.
Diagnostic Tests and Their Relevance
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Significance in Distinguishing PsA |
|---|---|---|
| X-rays | Visualize bone structure, detect erosions, and assess joint space narrowing. | Demonstrates characteristic bony changes in PsA, but may not show early signs. |
| MRI | Detailed visualization of soft tissues, tendons, ligaments, and bone marrow. | Identifies inflammation and bone marrow edema, which can be helpful in early diagnosis and monitoring disease progression. |
| ESR/CRP | Measure systemic inflammation. | Elevated levels may indicate inflammation, but not specific to PsA. |
| CBC | Assess blood cell counts and overall blood health. | May reveal anemia or other blood abnormalities associated with PsA. |
| RF/anti-CCP | Identify antibodies associated with RA. | Absence of RF and anti-CCP antibodies helps rule out RA. |
Clinical Presentation and Symptoms
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) presents with a diverse range of musculoskeletal symptoms, making differential diagnosis challenging. Understanding the wide spectrum of these symptoms, including their varied patterns and extra-articular manifestations, is crucial for accurate identification and appropriate management. The symptom duration and pattern also play a significant role in distinguishing PsA from other conditions.Accurate diagnosis relies on recognizing the distinctive characteristics of PsA’s clinical presentation.
This includes recognizing the common patterns of arthritis, the range of musculoskeletal symptoms, and the possibility of extra-articular manifestations. Understanding these elements is essential for differentiating PsA from other inflammatory arthritides.
Musculoskeletal Symptoms in Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis can manifest with a broad range of musculoskeletal symptoms. These symptoms vary significantly in their severity and distribution. Pain, stiffness, and swelling are common complaints, affecting joints in different patterns. Some individuals experience symmetric joint involvement, while others exhibit asymmetric involvement, affecting a single joint or a group of joints.
Types of Arthritis Presentations
Psoriatic arthritis can manifest in various forms of arthritis. These include:
- Distal Interphalangeal (DIP) Joint Involvement: Inflammation often affects the small joints of the fingers and toes, leading to pain, swelling, and tenderness. This is a frequent characteristic of PsA, often presenting before other joint symptoms.
- Proximal Interphalangeal (PIP) and Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) Joint Involvement: Inflammation in these joints can also occur, resulting in pain, swelling, and stiffness. The pattern may resemble rheumatoid arthritis in some cases.
- Spondylitis (Axial Involvement): Psoriatic arthritis can also affect the spine, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. This presentation may mimic ankylosing spondylitis.
- Asymmetrical Arthritis: A hallmark of PsA, the inflammation often affects joints on one side of the body more than the other.
Extra-Articular Manifestations
Beyond the musculoskeletal system, PsA can involve other body systems. These extra-articular manifestations can significantly impact a patient’s overall well-being and complicate the diagnostic process.
- Nail Involvement: Psoriasis often presents with nail changes, including pitting, discoloration, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. These changes can occur in patients with PsA.
- Skin Involvement: Skin lesions, a hallmark of psoriasis, may be present in individuals with PsA, although not always apparent.
- Eye Involvement: Uveitis, an inflammation of the eye, is a potential complication of PsA. This can lead to eye pain, redness, and blurred vision.
- Cardiovascular Involvement: Increased risk of cardiovascular disease has been associated with PsA, particularly in individuals with concurrent metabolic conditions.
- Other Manifestations: PsA can also manifest in other organs, including the liver, lungs, and kidneys, though less frequently. These should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
Symptom Duration and Pattern in Differential Diagnosis
The duration and pattern of symptoms are crucial in differentiating PsA from other conditions. For example, a history of a gradual onset of symmetric joint involvement with morning stiffness might suggest rheumatoid arthritis. In contrast, the presence of asymmetrical involvement, especially in the DIP joints, along with nail changes, strongly suggests PsA.
Clinical Presentations of PsA
| Clinical Presentation | Description | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Peripheral Arthritis | Inflammation in the joints of the limbs (hands, feet, etc.). | Asymmetrical involvement, DIP joint involvement, nail changes. |
| Axial Arthritis | Inflammation in the spine and sacroiliac joints. | Back pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion. |
| Mucocutaneous Presentation | Simultaneous skin and nail involvement. | Psoriasis, nail pitting, dactylitis. |
| Enthesitis | Inflammation at the attachment points of tendons and ligaments. | Heel pain, Achilles tendon pain, buttock pain. |
Imaging Findings in Differential Diagnosis: Psoriatic Arthritis Differential Diagnosis
Imaging plays a crucial role in differentiating psoriatic arthritis (PsA) from other inflammatory arthropathies. Radiographic and MRI findings, when interpreted alongside clinical and laboratory data, significantly aid in accurate diagnosis. The specific patterns observed can offer insights into the disease’s extent, severity, and potential complications.
Typical Radiographic Findings in PsA
Radiographic evaluation often reveals characteristic changes in PsA, including erosions, new bone formation (osteophytes), and joint space narrowing. These changes are frequently asymmetrical, meaning they affect joints on one side of the body more than the other. Furthermore, PsA frequently affects the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints, a characteristic feature not commonly seen in other inflammatory arthropathies. These changes are typically progressive over time and can lead to significant joint damage if left untreated.
Radiographs can also show evidence of enthesitis, inflammation at the sites where tendons or ligaments attach to bone, a hallmark feature of PsA.
Imaging Characteristics of Other Inflammatory Arthropathies
Other inflammatory arthropathies, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and reactive arthritis, present with distinct radiographic features. RA, for instance, typically shows symmetric joint involvement, with erosions and joint space narrowing often affecting multiple joints simultaneously. AS primarily affects the spine, with characteristic findings of syndesmophytes (new bone formation along the ligaments of the spine). Reactive arthritis may present with asymmetric involvement, often affecting the lower extremities.
Comparison and Contrast of Radiographic Features
Distinguishing PsA from other conditions relies on the pattern of joint involvement and the presence of specific features. PsA often exhibits asymmetric involvement, particularly in the DIP joints, and a predilection for enthesitis. RA, in contrast, is more likely to show symmetric joint involvement. AS predominantly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. Careful attention to the location and distribution of joint damage is vital in distinguishing these conditions.
The presence of characteristic radiographic features in conjunction with clinical presentation helps in accurate diagnosis.
Role of MRI in Assessing PsA
MRI offers superior visualization of soft tissues, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment of the extent and severity of PsA. MRI can detect inflammation in the synovium (the lining of the joint capsule), enthesitis, and bone marrow edema, which may not be evident on radiographs. This detailed information helps assess the disease activity and extent of damage in joints and surrounding tissues, guiding treatment strategies.
Furthermore, MRI is helpful in evaluating the severity of inflammation in areas difficult to access with X-rays.
Table of Imaging Findings
| Condition | Typical Radiographic Findings | MRI Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) | Asymmetric joint involvement, particularly DIP joints; erosions, osteophytes; enthesitis | Synovitis, enthesitis, bone marrow edema, tendonitis |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Symmetric joint involvement; erosions, joint space narrowing | Synovitis, periarticular soft tissue edema |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) | Sacroiliitis, syndesmophytes, spine involvement | Sacroiliitis, enthesitis, epidural fibrosis |
| Reactive Arthritis | Asymmetric joint involvement, enthesitis | Synovitis, enthesitis, inflammation in affected joints |
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Understanding the interplay of genetics and environment is crucial in the differential diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). While a genetic predisposition certainly increases the risk, environmental triggers can either initiate or exacerbate the disease. This interplay is not unique to PsA but is seen across a spectrum of inflammatory arthropathies.Genetic factors play a significant role in determining susceptibility to inflammatory conditions, including PsA.
Certain genes are associated with a higher risk of developing PsA and other related inflammatory arthropathies. Furthermore, environmental exposures can influence the expression of these genes, potentially leading to disease onset or progression. This complex interaction is the subject of ongoing research.
Genetic Predisposition to Inflammatory Arthropathies
PsA, along with other inflammatory arthropathies, is associated with specific genetic markers. These markers are often located within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region of the genome. Variations in these genes can predispose individuals to the development of PsA. For example, certain HLA-B27 alleles are strongly linked to an increased risk of ankylosing spondylitis. This is a key distinction in differential diagnosis.
Genetic predisposition is not a guarantee of disease development; environmental factors often play a pivotal role. Furthermore, the specific genes involved can vary across different types of inflammatory arthropathies.
Environmental Triggers for PsA
Environmental factors can influence the onset and severity of PsA. Certain infections, such as streptococcal infections, have been implicated as potential triggers. Furthermore, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing PsA, as well as more severe disease progression. Environmental exposures to certain chemicals or toxins may also play a role, although the exact mechanisms remain under investigation.
The interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers is complex.
Figuring out psoriatic arthritis can be tricky, involving a whole bunch of potential diagnoses. It’s important to consider other possibilities like inflammatory conditions, and even connections to things like migraine and multiple sclerosis. Understanding the complex interplay between different health issues is key for proper diagnosis, which is crucial in effectively treating psoriatic arthritis, similar to exploring the migraine and multiple sclerosis connection.
Further investigation into the various potential causes is vital for accurate differential diagnosis.
Role of Genetic Testing in Differential Diagnosis
Genetic testing can be a valuable tool in differentiating PsA from other inflammatory arthropathies. While specific genetic tests for PsA are not yet widely available for routine clinical use, the identification of certain HLA genes can aid in the diagnosis and risk assessment. Testing for HLA-B27, for instance, can help distinguish ankylosing spondylitis from other conditions. It is important to note that genetic testing is not always conclusive and should be interpreted in conjunction with clinical findings and other diagnostic procedures.
Environmental Factors in Other Inflammatory Arthropathies
Environmental triggers are not unique to PsA. For example, infections have been linked to the development of reactive arthritis, a form of inflammatory arthritis. Similarly, certain environmental factors, such as occupational exposures to certain chemicals, may play a role in triggering or exacerbating other inflammatory arthropathies. Research into these environmental triggers is ongoing and aims to identify potential preventative measures.
Table: Genetic and Environmental Factors in Arthropathies
| Arthropathy | Genetic Factors | Environmental Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Psoriatic Arthritis | HLA-Cw6, HLA-B27 (less frequently), other genes | Infections (e.g., streptococcal), smoking, environmental toxins |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | HLA-B27 | Infections (e.g., gut infections), certain occupational exposures |
| Reactive Arthritis | HLA-B27, other genes | Infections (e.g., Chlamydia, Salmonella), trauma |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Multiple genes, including HLA-DRB1 | Environmental factors, potentially infections, diet |
Treatment Approaches and Management
Navigating the complexities of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and its many potential mimics requires a nuanced approach to treatment. A tailored strategy is crucial, as the underlying inflammatory mechanisms and disease progression can vary significantly between individuals and even between different forms of inflammatory arthropathies. Effective management hinges on a thorough understanding of both the specific diagnosis and the patient’s unique response to various therapeutic options.Effective treatment for PsA and other inflammatory arthropathies aims to reduce pain, inflammation, and joint damage.
This often involves a multi-pronged approach encompassing medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies. The choice of treatment will be heavily influenced by the severity and extent of the disease, as well as the patient’s overall health and potential comorbidities.
Common Treatment Strategies
Various treatment strategies are employed for inflammatory arthropathies, reflecting the distinct characteristics of each condition. These range from simple lifestyle adjustments to powerful biological therapies. Understanding the common approaches, their potential benefits, and limitations is crucial for informed decision-making.
Similarities and Differences in Therapeutic Approaches
While the specific medications and dosages may differ, many inflammatory arthropathies share overlapping treatment goals. These include reducing inflammation, controlling pain, preventing joint damage, and improving overall function. However, the underlying causes and disease mechanisms can differ, leading to varying responses to particular treatments. For example, while nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are frequently used in various inflammatory conditions, their effectiveness can differ depending on the specific diagnosis.
Some conditions may respond more favorably to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), while others may benefit more from targeted therapies.
Importance of Tailoring Treatment to the Specific Diagnosis
Precise diagnosis is paramount for successful treatment of inflammatory arthropathies. Treating a patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with a treatment plan intended for psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may not yield the desired outcomes and could even lead to complications. The specific characteristics of each condition, including the inflammatory pathways involved, influence the choice of treatment and its potential efficacy.
For example, a patient with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) may require different treatment strategies compared to a patient with reactive arthritis.
Treatment Options Summary Table
| Condition | Non-pharmacological Interventions | Pharmacological Interventions (NSAIDs) | Pharmacological Interventions (DMARDs) | Biological Therapies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Exercise, weight management, physical therapy | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Methotrexate, Sulfasalazine, Leflunomide | TNF inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, IL-12/23 inhibitors |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | Exercise, weight management, physical therapy | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Methotrexate, Hydroxychloroquine, Leflunomide | TNF inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors |
| Ankylosing Spondylitis | Exercise, physical therapy, posture correction | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Sulfasalazine, Methotrexate | TNF inhibitors |
| Reactive Arthritis | Rest, physical therapy | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Sulfasalazine, Methotrexate | TNF inhibitors (in severe cases) |
Summary
In conclusion, navigating the intricate world of psoriatic arthritis differential diagnosis requires a multifaceted approach. Careful consideration of clinical presentation, symptom duration, imaging findings, and potential genetic and environmental factors are all essential. By understanding the key characteristics that distinguish PsA from other inflammatory arthropathies, we can improve diagnostic accuracy and ultimately optimize patient care. This comprehensive guide provides a valuable resource for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking a deeper understanding of this complex condition.