Skin pain in psoriasis is a significant concern for many sufferers, impacting their daily lives and overall well-being. This detailed exploration delves into the various types of pain, their mechanisms, and the factors that exacerbate them. We’ll also examine the profound impact on daily routines, mental health, and social interactions. Further, we’ll discuss diagnosis, management strategies, patient experiences, potential underlying causes, and successful case studies.
Finally, we’ll present practical pain relief strategies.
Psoriasis-related skin pain can manifest in different ways, from mild discomfort to severe agony. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management. This exploration will cover everything from the different types of psoriasis and their pain characteristics to the psychological and social implications. The following sections will also cover the diagnostic process, treatment options, patient perspectives, potential underlying causes, case studies, and strategies for pain relief.
Understanding Psoriasis-Related Skin Pain
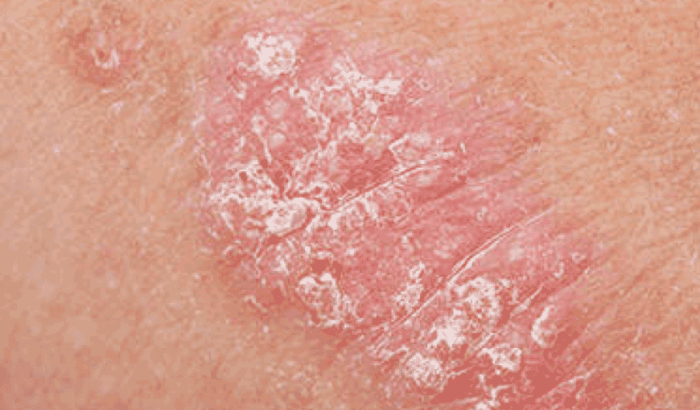
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune disease, is often accompanied by skin pain, ranging from mild discomfort to severe agony. This pain can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, affecting their daily activities and emotional well-being. Understanding the different types of pain, the underlying mechanisms, and exacerbating factors is crucial for effective management and treatment strategies.Psoriasis-related skin pain arises from a complex interplay of inflammatory processes, nerve involvement, and individual factors.
The inflammation characteristic of psoriasis can directly irritate nerve endings in the skin, leading to pain signals. Additionally, the skin lesions themselves, such as plaques and scales, can be tender and susceptible to injury, further contributing to pain.
Types of Psoriasis-Related Skin Pain
Psoriasis skin pain manifests in various forms, each with its unique characteristics. The pain can range from a dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations. Some patients experience burning or itching, while others describe a tingling or prickling sensation. The intensity of the pain can fluctuate depending on factors like the severity of the psoriasis flare-ups, the location of the affected skin, and the individual’s pain tolerance.
Mechanisms of Psoriasis-Related Skin Pain
Several mechanisms contribute to the development of skin pain in psoriasis. Inflammation plays a pivotal role, triggering the release of inflammatory mediators that can irritate nerve endings and increase pain sensitivity. The presence of skin lesions, including plaques and scales, can directly compress or irritate nerve fibers, leading to pain signals. Furthermore, the altered skin barrier function in psoriasis can make the skin more susceptible to injury and external stimuli, exacerbating pain.
The heightened sensitivity of the nervous system in psoriasis may also contribute to the experience of pain.
Factors Exacerbating Psoriasis Skin Pain
Several factors can exacerbate skin pain in psoriasis patients. Environmental triggers, such as exposure to extreme temperatures, certain fabrics, or irritants, can aggravate existing skin lesions and increase pain. Stress and emotional distress can also play a significant role, as stress hormones can worsen inflammation and increase pain perception. Certain medications, such as some topical treatments or systemic therapies, may also contribute to skin irritation and pain.
Furthermore, infections, such as skin infections, can increase the inflammatory response and lead to increased pain.
Comparison of Psoriasis Types and Pain Characteristics
| Psoriasis Type | Pain Description | Location | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plaque Psoriasis | Dull ache, burning, or itching; can be sharp or stabbing. | Usually on elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. | Moderate to severe, often fluctuating. |
| Pustular Psoriasis | Burning, throbbing, or sharp pain; often accompanied by tenderness. | Can occur anywhere on the body; often affecting hands and feet. | High; can be debilitating and require hospitalization. |
| Inverse Psoriasis | Burning, itching, or stinging pain; may be accompanied by redness and inflammation. | Folds of the skin, such as the groin, armpits, and under breasts. | Moderate, often accompanied by intense itching. |
| Erythrodermic Psoriasis | Intense burning, itching, and pain; can be widespread and debilitating. | Widespread over the entire body. | Extremely severe; life-threatening in some cases. |
Impact of Skin Pain on Daily Life
Living with psoriasis often involves more than just the visible skin condition. The persistent pain associated with psoriasis can significantly impact various aspects of daily life, from simple tasks to emotional well-being and social interactions. Understanding these effects is crucial for developing effective management strategies and support systems for those affected.The chronic nature of psoriasis-related skin pain can lead to a cascade of challenges that extend far beyond the physical discomfort.
This pain can disrupt daily routines, impacting work, social life, and overall quality of life. The psychological toll of managing this condition can be substantial, and the potential for social isolation should not be overlooked. This discussion delves into the multifaceted impact of psoriasis-related pain on individuals’ lives.
Psoriasis skin pain can be tough, especially when accompanied by other skin issues. Sometimes, that pain is connected to dry patches on the face, which can be incredibly irritating. Learning more about how dry patches on the face affect the skin might actually offer some clues about the root causes of your psoriasis pain. Ultimately, understanding these different factors can help you better manage your psoriasis symptoms.
Impact on Daily Activities and Routines
Psoriasis pain can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild discomfort to intense throbbing or burning sensations. This pain can make simple tasks, such as dressing, showering, or even sleeping, difficult and uncomfortable. Individuals may experience limitations in their mobility and range of motion, affecting their ability to perform everyday activities. For example, someone with severe psoriasis affecting their hands might find it challenging to hold utensils or perform tasks at work.
Dealing with the itchy, burning skin pain of psoriasis can be tough. Finding the right products can make a big difference, and for some, that might include exploring options like skyn non latex condoms for potential relief from irritation. While there’s no magic bullet, choosing the right materials for intimate contact can help minimize friction and further skin discomfort associated with psoriasis flare-ups.
These limitations can lead to decreased productivity and a reduced sense of independence.
Psychological Effects of Chronic Skin Pain, Skin pain in psoriasis
Chronic pain, like that associated with psoriasis, can have profound psychological effects. The constant discomfort can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and frustration. The fear of flare-ups, the emotional toll of managing the condition, and the perceived stigma can contribute to feelings of isolation and low self-esteem. The emotional distress associated with psoriasis pain can affect relationships and overall mental well-being.
Individuals may experience decreased self-confidence and social withdrawal due to the pain and discomfort.
Social Implications of Skin Pain
The social implications of psoriasis-related skin pain are significant. The visible nature of the condition, combined with the pain and discomfort, can lead to social isolation and discrimination. Individuals may avoid social situations, fearing judgment or negative reactions from others. This can result in feelings of shame, embarrassment, and a reduced sense of belonging. Furthermore, individuals might struggle to maintain relationships, as their partners or family members may not fully understand the impact of the pain and its associated challenges.
Summary Table of Effects
| Area of Life | Effect of Pain |
|---|---|
| Work | Reduced productivity, missed workdays, difficulty concentrating, limitations in performing job tasks. This can lead to financial strain and feelings of inadequacy. |
| Social Interactions | Avoidance of social gatherings, reduced participation in activities, feelings of isolation and embarrassment, potential for discrimination and prejudice. |
| Personal Care | Difficulty with showering, dressing, and other self-care tasks. This can affect hygiene and overall well-being. |
| Sleep | Disrupted sleep patterns due to discomfort and pain. This further impacts mood and overall health. |
| Emotional Well-being | Increased anxiety, depression, frustration, and low self-esteem. This can negatively impact relationships and daily functioning. |
Diagnosis and Management of Skin Pain in Psoriasis
Understanding the skin pain associated with psoriasis is crucial for effective management. This pain can range from mild discomfort to debilitating agony, significantly impacting a person’s quality of life. Effective diagnosis and treatment plans require a multifaceted approach, considering both the physical manifestation of the condition and the individual patient’s experience.Accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies are essential for managing psoriasis-related skin pain.
This involves recognizing the unique characteristics of the pain, considering potential underlying factors, and employing a range of interventions to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Diagnostic Process for Skin Pain
The diagnostic process for evaluating skin pain in psoriasis patients typically begins with a thorough clinical evaluation by a dermatologist. This involves a detailed patient history, including the location, duration, intensity, and character of the pain. Physical examination focuses on the affected skin areas, looking for signs of psoriasis plaques, inflammation, and any other potential contributing factors.Furthermore, the dermatologist will assess the patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions that could be contributing to the pain or interacting with psoriasis treatments.
This comprehensive evaluation helps determine the cause of the pain and rule out other potential diagnoses. In some cases, additional diagnostic tests, such as skin biopsies, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options for Skin Pain
A variety of treatment options are available to manage skin pain in psoriasis patients. These options are categorized to facilitate a clear understanding of the various approaches.
- Topical Medications: Topical medications, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and calcineurin inhibitors, are often the first line of treatment for managing mild to moderate psoriasis-related skin pain. These medications can help reduce inflammation and irritation in the affected areas, thereby alleviating pain. Examples of topical corticosteroids include hydrocortisone and betamethasone valerate, while vitamin D analogs like calcipotriene and tacalcitol, and calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are also effective in reducing inflammation and pain.
- Systemic Therapies: For patients with severe psoriasis and significant skin pain, systemic therapies may be necessary. These therapies, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics, target the underlying immune response driving the inflammatory process, leading to a reduction in pain and improvement in overall psoriasis symptoms. These medications often have more significant side effects compared to topical options and are typically prescribed under the guidance of a rheumatologist or dermatologist.
- Alternative Therapies: Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and dietary modifications, can also play a supportive role in managing psoriasis-related skin pain. These therapies aim to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. However, it is essential to note that alternative therapies should be considered complementary to, not replacements for, conventional medical treatments.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, including dermatologists, rheumatologists, and pain management specialists, play a critical role in managing psoriasis-related skin pain. They work collaboratively to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the psoriasis and the associated pain. Dermatologists are often the primary point of contact, managing the skin condition and prescribing topical medications. Rheumatologists may be involved for systemic treatments, and pain management specialists can help manage chronic pain, offering additional strategies for pain relief.
Organizing Treatment Options
A clear and concise organization of treatment options can be beneficial for patients and healthcare providers. A table format can effectively present the different approaches:
| Treatment Category | Examples | Mechanism of Action | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Medications | Corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogs, Calcineurin inhibitors | Reduce inflammation and irritation | Effective for mild-to-moderate pain, potential for skin thinning with prolonged use |
| Systemic Therapies | Methotrexate, Cyclosporine, Biologics | Target underlying immune response | More potent, greater potential side effects, require close monitoring |
| Alternative Therapies | Acupuncture, Massage, Dietary modifications | Promote relaxation, stress reduction | Complementary to conventional treatments |
This structured approach allows for easy comparison and selection of appropriate treatment strategies based on the individual patient’s needs and severity of pain.
Patient Experiences with Skin Pain: Skin Pain In Psoriasis

Living with psoriasis can be incredibly challenging, and one of the most distressing aspects for many patients is the persistent skin pain. This pain can range from mild discomfort to excruciating agony, significantly impacting daily life and overall well-being. Understanding the diverse experiences of psoriasis sufferers is crucial for developing effective management strategies and providing compassionate care.The experience of skin pain in psoriasis is highly individualistic, varying in intensity, location, and type.
While the underlying cause is often related to inflammation, the subjective experience is shaped by psychological factors, pre-existing conditions, and individual pain thresholds. This section delves into the realities of psoriasis-related skin pain, offering firsthand accounts that illuminate the impact on patients’ lives.
Patient Descriptions of Skin Pain
Patients describe psoriasis-related skin pain using a wide range of terms. Some common descriptions include:
- Burning: Patients often report a sensation of intense heat or burning in affected areas.
- Itching: The relentless itch associated with psoriasis can be incredibly bothersome, often leading to scratching and further skin damage.
- Sharp or stabbing pain: In some cases, psoriasis can cause sharp or stabbing pain, particularly during flares or when skin lesions are inflamed.
- Aching or throbbing pain: This type of pain may be more persistent and diffuse, impacting a larger area of the body.
- Tenderness or pressure sensitivity: Certain areas of affected skin may be unusually sensitive to touch or pressure, causing pain upon minimal contact.
Impact on Daily Life
The chronic nature of psoriasis and the accompanying skin pain can significantly impact various aspects of daily life. These impacts range from physical limitations to emotional distress.
- Sleep disturbances: Severe skin pain can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased energy levels.
- Social isolation: Some patients feel self-conscious about their condition and avoid social situations due to the pain and visible lesions. This can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Reduced physical activity: The discomfort and pain can limit mobility and participation in physical activities.
- Work productivity: Chronic pain can negatively impact work productivity, potentially leading to missed workdays or reduced job performance.
- Emotional well-being: Living with chronic skin pain can take a toll on emotional well-being, leading to anxiety, depression, and feelings of hopelessness.
Importance of Patient-Centered Care
Effective management of psoriasis-related skin pain necessitates a patient-centered approach. This involves actively listening to patients’ experiences, understanding their individual needs, and tailoring treatment plans accordingly.
- Empathetic communication: Healthcare providers must actively listen to patients’ descriptions of their pain and validate their experiences.
- Personalized treatment plans: Treatment strategies must be tailored to individual needs and preferences, considering factors such as the severity of pain, location of lesions, and overall health.
- Collaboration between patient and provider: Open communication and collaboration are essential for successful pain management. Patients should feel empowered to actively participate in decisions about their care.
- Multidisciplinary approach: Involving other healthcare professionals, such as psychologists or social workers, can further enhance the patient’s support network.
Patient Testimonials
The following quotes highlight the diverse experiences of psoriasis patients:
“My skin pain was so severe that I couldn’t sleep, and the constant itching drove me to distraction.”
“I felt isolated and ashamed of my condition. The pain made it hard to participate in social activities.”
“The pain affected my work performance. I missed many days due to the discomfort and lack of concentration.”
“The emotional toll of living with psoriasis was just as significant as the physical pain.”
“My doctor’s empathy and willingness to listen to my concerns made a huge difference in my ability to manage my pain.”
Exploring Potential Causes
Psoriasis skin pain isn’t always solely due to inflammation. Other factors can contribute, potentially making the experience more complex and challenging to manage. Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for developing a comprehensive treatment plan.Beyond the well-known inflammatory process, various contributing factors can intensify the discomfort associated with psoriasis. These include nerve involvement, infections, and even the presence of other medical conditions.
Dealing with the constant skin pain of psoriasis can be incredibly isolating. It’s easy to feel like you’re carrying a heavy burden, and that can sometimes lead to feelings of loneliness and fear of being alone. This can be a surprisingly common side effect, and understanding those anxieties is key to managing the condition. The emotional toll of psoriasis can be significant, and it’s important to seek support and resources like those found at fear of being alone to help navigate these difficult feelings.
Ultimately, acknowledging and addressing these feelings is crucial to finding relief and better managing the skin pain associated with psoriasis.
A thorough medical evaluation is essential to pinpoint the specific cause and tailor the most effective approach to pain management.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Many medical conditions can coexist with psoriasis, potentially influencing or exacerbating skin pain. Conditions like diabetes, hypothyroidism, and certain autoimmune diseases can impact nerve function, leading to chronic pain. Proper diagnosis of such co-morbidities is crucial to provide targeted treatment strategies. A careful review of a patient’s medical history and current medications is vital.
Nerve Involvement and Neuropathic Pain
Psoriasis can sometimes affect nerve endings, leading to neuropathic pain. This type of pain often differs from the typical inflammatory pain associated with psoriasis, presenting as burning, shooting, or tingling sensations. The exact mechanism linking psoriasis and nerve involvement isn’t fully understood, but studies suggest inflammatory mediators released during psoriasis flares may contribute to nerve damage. Careful neurological assessments can help differentiate between inflammatory and neuropathic pain components.
Infections and Skin Conditions
Skin infections, such as bacterial or fungal infections, can coexist with psoriasis, causing additional pain and discomfort. Superimposed infections can make the skin more susceptible to pain and inflammation. Careful examination of the skin lesions, including checking for signs of infection (e.g., redness, swelling, pus), is necessary.
Mechanical Factors
Certain mechanical factors can contribute to skin pain in psoriasis. For example, scratching or picking at the lesions can lead to further irritation and pain. Tight clothing or jewelry rubbing against affected areas can also increase discomfort. Patients should be educated on proper skin care techniques, including avoiding harsh scrubbing and choosing appropriate clothing.
Importance of a Comprehensive Medical Evaluation
A thorough medical evaluation is essential to rule out other conditions and determine the precise cause of the skin pain. This process involves a detailed medical history, physical examination, and potentially diagnostic tests.
Steps Involved in a Comprehensive Medical Evaluation
- Detailed Medical History: Gathering information about the patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, medications, and allergies, is the first step. This includes a detailed history of psoriasis, including its duration, severity, and location.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the skin, focusing on the affected areas, is crucial. The examination should include evaluating the characteristics of the lesions (e.g., size, shape, color), as well as assessing for any signs of infection or other conditions.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the suspected underlying causes, diagnostic tests might be necessary. These tests can include blood tests to check for infections, autoimmune markers, or other medical conditions, and nerve conduction studies to evaluate nerve function.
Illustrative Cases of Skin Pain Management
Managing skin pain associated with psoriasis requires a multifaceted approach, tailoring treatment to the individual patient’s needs and the specific characteristics of their condition. Different factors influence the effectiveness of interventions, including the severity of psoriasis, the location of the lesions, and the presence of comorbidities. This section presents a case study illustrating a successful approach to skin pain management in a psoriasis patient.Successful skin pain management hinges on a proactive and collaborative approach between the patient and healthcare professionals.
This involves careful assessment of the patient’s pain, understanding the triggers and contributing factors, and then developing a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the psoriasis and the associated pain.
Case Study: A Successful Management Strategy
A 35-year-old female presented with moderate plaque psoriasis affecting her elbows, knees, and scalp. She experienced significant pain, particularly in the affected areas, which significantly impacted her daily activities. Her pain was described as a persistent, throbbing ache, aggravated by temperature changes and friction.
Initial Assessment and Treatment Plan
The initial assessment included a thorough examination of the skin lesions, a detailed evaluation of the patient’s pain, and a review of her medical history. The patient reported that stress and changes in weather patterns often exacerbated her pain. The treatment plan initially focused on topical corticosteroids to manage the psoriasis and reduce inflammation. Additionally, a topical analgesic cream was prescribed to provide immediate relief from the pain.
Combination Therapy and Monitoring
Recognizing the importance of addressing both the psoriasis and the pain, a combination therapy approach was implemented. This included topical corticosteroids for the psoriasis, along with a low-dose oral anti-inflammatory medication for systemic inflammation and pain management. Regular follow-up appointments were scheduled to monitor the response to treatment.
Factors Contributing to Positive Outcome
Several factors contributed to the positive outcome:
- Patient Compliance: The patient diligently followed the prescribed treatment regimen, including applying topical medications as directed and attending follow-up appointments. This adherence to the plan was critical for achieving optimal results.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the skin lesions and pain levels allowed for adjustments to the treatment plan. This iterative approach ensured the treatment remained effective and addressed any emerging issues.
- Addressing Lifestyle Factors: Recognizing the impact of stress and weather changes, the patient was encouraged to incorporate stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and yoga, and to adjust her clothing to minimize friction on the affected areas.
- Combination Therapy: The combination of topical and oral medications addressed both the inflammatory component of the psoriasis and the pain sensation. This multi-pronged approach was crucial for long-term relief.
Significance of Monitoring and Adjustments
Monitoring and adjusting the treatment plan is essential for optimizing outcomes in psoriasis-related skin pain. Regular evaluations allow healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of the chosen therapies and make necessary modifications to improve treatment efficacy and minimize potential adverse effects. This iterative process ensures the treatment remains targeted and relevant to the individual patient’s evolving needs.
Pain Relief Strategies for Psoriasis
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition, often presents with painful skin inflammation. Effective pain relief strategies are crucial for managing discomfort and improving quality of life for those living with this condition. These strategies go beyond simply masking the symptoms; they address the underlying causes and triggers of the pain, leading to long-term relief and better overall well-being.Effective pain relief for psoriasis involves a multifaceted approach, combining topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and potentially, medical interventions.
Understanding how these strategies interact and addressing individual needs are key to achieving lasting results.
Topical Treatments for Skin Pain
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against psoriasis-related skin pain. These therapies directly target the affected skin, reducing inflammation and providing localized relief. Various options exist, each with unique mechanisms of action and potential side effects.
- Corticosteroids: These potent anti-inflammatory agents can significantly reduce inflammation and associated pain. However, prolonged use can lead to skin thinning and other side effects. Prescription strength is often required.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: These topical medications work by suppressing the immune response, thereby reducing inflammation and pain. They are often prescribed for less severe cases or when corticosteroids are not suitable.
- Vitamin D Analogues: These topical treatments can help modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation, often effectively managing pain. They are a valuable option for long-term use.
- Moisturizers: Maintaining skin hydration is crucial. Moisturizers help prevent dryness and cracking, which can exacerbate pain and discomfort.
Lifestyle Modifications for Pain Management
Managing psoriasis-related skin pain extends beyond topical treatments. Lifestyle choices can significantly impact pain levels and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, including pain. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels effectively.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein may contribute to overall health and reduce inflammation. Avoiding trigger foods, such as processed foods or those high in sugar, may also help.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin hydration, which can be beneficial in reducing itching and dryness associated with psoriasis.
- Sun Exposure (with Caution): Controlled sun exposure can sometimes help reduce inflammation. However, prolonged or unprotected sun exposure can be harmful. Consult a dermatologist for guidance.
Managing Flare-Ups and Pain Triggers
Identifying and managing triggers can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of psoriasis flare-ups, which often come with increased pain.
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a journal can help pinpoint specific triggers, such as certain foods, stress levels, or environmental factors.
- Avoiding Triggers: Once triggers are identified, avoiding them is crucial for managing pain and preventing future flare-ups.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practicing stress-reducing techniques can help minimize the impact of stress on psoriasis symptoms.
Practical Strategies for Pain Reduction
This table offers a practical guide to managing pain in different situations.
| Situation | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Dry, itchy skin | Use a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer regularly. |
| Skin cracking and bleeding | Apply a barrier cream to protect the skin and prevent further irritation. |
| Severe flare-up | Consult a dermatologist for stronger topical treatments or systemic medications. |
| Stress-related pain | Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. |
| Pain from clothing friction | Wear loose-fitting, soft clothing to minimize irritation. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, skin pain in psoriasis is a multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive understanding. We’ve explored the various types of pain, their causes, impact on daily life, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and patient experiences. We’ve also delved into potential underlying causes and successful management strategies. Ultimately, effective pain management requires a holistic approach that considers the physical, emotional, and social aspects of the patient’s experience.




