How much protein in an egg? This question is more than just a simple query; it’s a window into the incredible nutritional powerhouse that is the humble egg. From understanding the protein content differences between the egg white and yolk to exploring the impact of cooking methods, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of egg protein. We’ll examine the science behind egg protein, its role in various diets, and its overall health benefits.
Get ready to uncover the fascinating truth about the protein in an egg.
This in-depth exploration of egg protein content covers everything from the basics of protein types to the factors influencing the amount present. We’ll dissect the nutritional value beyond protein, comparing eggs to other protein sources, and examining the effects of various cooking methods. Furthermore, we’ll investigate how egg protein fits into different dietary needs and goals, along with a discussion of the health benefits and potential drawbacks.
Egg Protein Content Overview
Eggs are a fantastic source of protein, making them a popular choice for breakfast, snacks, and meal additions. Understanding the distribution of protein within the egg—specifically in the white and yolk—is crucial for tailoring your protein intake. This section provides a comprehensive overview of egg protein content, including measurement methods and a breakdown by egg component.
Average Protein Content in a Whole Egg
The average whole egg contains approximately 6 grams of protein. This amount varies slightly depending on factors such as the breed of hen and the egg’s size. The protein in eggs is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids our bodies need but cannot produce.
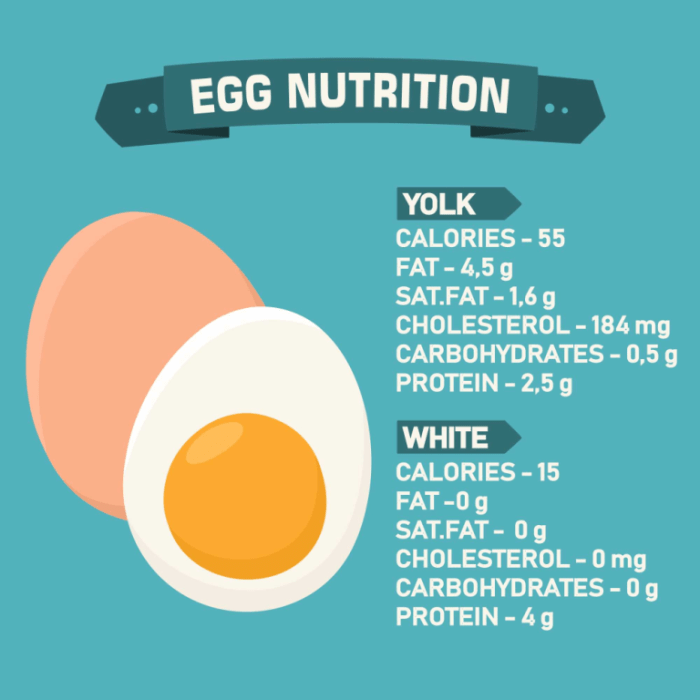
Protein Content Differences: Egg White vs. Yolk
Egg whites are predominantly protein, while egg yolks contain a mix of protein, fat, and other nutrients. This difference in composition significantly impacts the protein content of each part.
Measurement Methods
Protein content is often measured in grams and as a percentage of the total egg weight. Grams provide a specific amount of protein, while percentages offer insight into the protein’s proportion within the egg. For example, a 50-gram egg with 6 grams of protein means 12% of the egg is protein.
Protein Content Breakdown
| Egg Part | Protein Content (grams) | Percentage of Total Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Whole Egg | 6 | 100% |
| Egg White | 3.6 | 60% |
| Egg Yolk | 2.4 | 40% |
Note: Values are approximate and can vary slightly.
Protein Types in Eggs

Eggs, a nutritional powerhouse, are packed with essential proteins crucial for various bodily functions. Understanding the different types of proteins within an egg and their specific roles provides a deeper appreciation for their nutritional value. This exploration will delve into the primary protein types, their individual functions, and their overall biological significance.The proteins in eggs are not a single entity but a complex mixture of various types, each contributing to the egg’s overall nutritional profile and the body’s diverse needs.
These proteins, when digested and absorbed, become essential building blocks for tissues, enzymes, and hormones, demonstrating the egg’s multifaceted nutritional contribution.
Primary Protein Types
Eggs contain a variety of proteins, but some are more prominent than others. These key proteins play vital roles in supporting various physiological processes within the body.
- Ovalbumin: This is the most abundant protein in egg white, accounting for approximately 54% of the total egg white protein. Ovalbumin’s primary function is as a storage protein, providing amino acids readily available for the developing chick during embryonic development. In humans, ovalbumin contributes to overall protein synthesis and repair of tissues. Its presence in egg white makes it a significant source of dietary protein.
- Ovotransferrin: Ovotransferrin, also known as egg transferrin, is a crucial protein found in egg white and yolk. It plays a vital role in iron transport and absorption. This protein’s ability to bind iron is essential for efficient iron utilization within the body. Ovotransferrin’s presence enhances the nutritional value of eggs by improving iron bioavailability.
- Ovomucoid: This protein, found primarily in egg white, is an inhibitor of proteolytic enzymes. Its function is to prevent premature digestion of the egg’s proteins during storage or cooking. This protective role ensures the egg’s nutritional integrity until it is consumed.
- Ovoinhibitor: This protein is another important component of egg white, acting as an inhibitor for trypsin, a digestive enzyme. This inhibition is crucial to maintain the integrity of the egg’s proteins during development and preservation, protecting the embryo and ensuring nutritional quality for consumption.
Protein Structure and Function Comparison
Understanding the structural characteristics and the functional roles of these proteins provides insights into their significance in various biological processes.
| Protein Type | Structure | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Ovalbumin | Globular protein, with a compact, folded structure. | Storage protein, providing amino acids for embryonic development and general protein synthesis. |
| Ovotransferrin | Globular protein, with a high affinity for iron. | Iron transport and absorption, crucial for oxygen transport and cellular processes. |
| Ovomucoid | Globular protein, with a complex structure that inhibits proteolytic enzymes. | Inhibits proteolytic enzymes, protecting the egg’s protein from premature digestion. |
| Ovoinhibitor | Globular protein, specifically inhibits trypsin. | Inhibits trypsin, a digestive enzyme, preventing premature digestion of egg proteins. |
Factors Affecting Protein Content
While the protein content of an egg is generally consistent, several factors can influence the amount of protein present. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone interested in optimizing their egg consumption for dietary needs. These variations are not necessarily indicative of a significant difference in nutritional value, but rather reflect natural variations in hen health and production.Egg protein content isn’t a static value; it can vary based on a range of influences.
Factors like the hen’s diet, overall health, and even the egg’s size can affect the final protein profile. These natural variations should be considered when evaluating egg nutritional information.
Egg Size and Breed
Egg size is a significant factor in protein content. Larger eggs, containing more egg white and yolk, will generally have a higher protein content than smaller ones. This is due to the increased volume of the egg itself, not necessarily a difference in the protein composition of the egg white or yolk. The breed of hen also plays a role, though the effect is often less pronounced than size.
Different breeds may have slightly different protein levels, but this is usually overshadowed by the influence of egg size.
Hen’s Diet and Health
The hen’s diet directly impacts the protein content of the eggs it produces. A diet rich in protein-rich foods will naturally lead to a higher protein content in the egg. Conversely, a diet lacking in sufficient protein will result in eggs with lower protein levels. Factors like the quality of feed and the availability of essential nutrients are crucial.
Furthermore, the hen’s overall health is critical. Illnesses or stress can negatively affect egg production and thus the protein content of the eggs. A healthy hen is more likely to produce eggs with a higher protein content, as her body is functioning optimally.
Impact of Different Factors, How much protein in an egg
| Factor | Potential Impact on Protein Content |
|---|---|
| Egg Size | Larger eggs generally have higher protein content due to increased volume. |
| Hen Breed | Minor differences in protein content may exist between breeds, but often less significant than egg size. |
| Hen’s Diet | A diet rich in protein sources will result in eggs with higher protein content. |
| Hen’s Health | Illnesses or stress can negatively impact egg production and thus the protein content of the eggs. |
Nutritional Value Beyond Protein
Eggs, celebrated for their protein content, offer a surprisingly comprehensive nutritional profile extending far beyond their amino acid richness. Beyond the essential building blocks for muscle growth and repair, eggs are a powerhouse of vitamins and minerals vital for maintaining overall health. This comprehensive look delves into the nutritional landscape of eggs, highlighting their diverse contribution to well-being.Eggs are more than just a source of protein; they are a nutrient-dense food packed with vitamins and minerals that play crucial roles in various bodily functions.
Understanding these components and how their composition varies based on factors like hen’s diet and laying stage provides a more complete picture of their nutritional value.
Vitamins in Eggs
Eggs are excellent sources of various essential vitamins, notably those crucial for metabolic processes, immune function, and vision. These vitamins contribute significantly to overall health and well-being. For example, vitamin D supports calcium absorption, crucial for strong bones, while vitamin B12 is vital for red blood cell formation.
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision, cell growth, and immune function. Eggs contain a form of vitamin A called retinol, which the body can readily absorb. A deficiency can lead to impaired vision and weakened immunity.
- Vitamin D: Plays a critical role in calcium absorption, crucial for bone health. Vitamin D deficiency can result in weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- B Vitamins: Eggs are a good source of various B vitamins, including riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), and biotin (B7). These vitamins are vital for energy production, nerve function, and red blood cell formation.
Minerals in Eggs
Eggs are a significant source of several essential minerals, playing vital roles in maintaining healthy bodily functions. Minerals like iron contribute to oxygen transport, while phosphorus is crucial for bone formation and energy metabolism.
- Iron: Eggs provide heme iron, which is more easily absorbed by the body than non-heme iron found in plant-based foods. Iron is essential for oxygen transport and red blood cell production. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia.
- Phosphorus: Crucial for bone formation, energy metabolism, and DNA synthesis. Eggs are a good source of phosphorus, which helps to maintain healthy bones and teeth.
- Selenium: An antioxidant mineral that supports thyroid function, immune system health, and protects cells from damage. Eggs contain a good amount of selenium.
- Zinc: Essential for immune function, wound healing, and cell growth. Eggs are a source of zinc, a crucial nutrient for overall health.
Variability in Egg Nutritional Composition
The nutritional composition of eggs can vary depending on several factors, including the hen’s diet and the stage of laying. For instance, hens fed diets rich in specific nutrients will lay eggs with higher concentrations of those nutrients. Similarly, the nutritional content can fluctuate slightly throughout the laying cycle.
| Nutrient | Potential Variations |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Eggs from hens fed on a diet rich in carotenoids, like green leafy vegetables, might have a higher vitamin A content. |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Hens fed diets rich in flaxseed or fishmeal will lay eggs with higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Protein | Protein content might fluctuate slightly depending on the hen’s feeding regime and the laying stage. |
Protein Comparison to Other Foods
Eggs are a powerhouse of protein, but how do they compare to other common protein sources? This section delves into the protein content of eggs relative to meat, beans, and dairy, highlighting the nutritional value and bioavailability differences. Understanding these comparisons helps in creating well-rounded and balanced diets.
Ever wondered how much protein a humble egg packs? It’s a surprisingly good source, you know. Learning how to care for a popped pimple, though, is a different kind of protein-packed challenge. Fortunately, proper care for a popped pimple, like following the steps in this guide how to heal a popped pimple , can prevent infection and promote quicker healing.
And that means you’ll be back to enjoying the protein-rich goodness of eggs in no time!
Protein Content Comparison
Different foods offer varying amounts of protein per serving. A crucial aspect to consider is the amount of protein per 100 grams of food, providing a standardized measure for comparison. This approach allows for a fair evaluation of protein density across diverse food groups.
| Food Group | Protein Content (g/100g) | Nutritional Value |
|---|---|---|
| Eggs | 12-13 | Excellent source of essential amino acids, choline, and vitamins. |
| Lean Beef (e.g., sirloin) | 20-30 | Good source of iron, zinc, and B vitamins, but higher in saturated fat in some cuts. |
| Chicken Breast | 20-30 | Good source of protein, low in fat, and rich in various vitamins and minerals. |
| Kidney Beans | 8-9 | Excellent source of fiber, iron, and various minerals, often part of vegetarian diets. |
| Milk (whole) | 3.5-4 | Good source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein, often consumed as part of a balanced diet. |
| Greek Yogurt | 10-12 | High protein content, often fortified with probiotics and calcium, suitable for various dietary needs. |
Bioavailability of Egg Protein
The bioavailability of protein refers to how efficiently the body absorbs and utilizes the protein from a food source. Eggs have a high protein bioavailability, meaning the body absorbs and utilizes a significant portion of the protein for building and repairing tissues. This efficiency makes eggs a highly valuable protein source.
“Egg protein is considered a complete protein, containing all essential amino acids in the right proportions for optimal human use.”
Protein in Other Foods
While eggs offer a significant amount of high-quality protein, other food groups also contribute essential nutrients. Lean meats, particularly chicken and beef, are excellent sources of protein, iron, and other essential minerals. Beans, a staple in many cuisines, provide a substantial amount of protein, fiber, and important nutrients for a balanced diet. Dairy products, such as milk and yogurt, contribute protein, calcium, and other essential vitamins.
Cooking Methods and Protein Impact: How Much Protein In An Egg
Flipping an egg in a pan, whisking it into a fluffy omelet, or gently simmering it until perfectly cooked—each cooking method alters the egg’s protein structure, impacting its digestibility. Understanding these changes is key to maximizing the nutritional benefits of this versatile food. This exploration delves into how different cooking methods affect egg protein, examining the impact on structure, digestibility, and bioavailability.Different cooking methods significantly alter the structure of egg proteins, impacting their digestibility.
Heat induces changes in the proteins, primarily through a process called denaturation. This process alters the protein’s shape and interactions, which in turn affects how easily our bodies can break down and absorb the protein. The extent of these changes varies depending on the cooking method, temperature, and duration.
Protein Denaturation and Digestibility
Protein denaturation is a crucial aspect of cooking eggs. Denaturation occurs when heat disrupts the hydrogen bonds and other weak interactions holding the protein’s complex structure together. This unfolding of the protein exposes previously hidden amino acid chains, making them more accessible to digestive enzymes. This increased accessibility generally enhances digestibility. However, excessive denaturation can lead to the formation of tough, insoluble protein aggregates, potentially hindering digestion.
Comparative Analysis of Cooking Methods
The table below presents a comparative analysis of protein content and digestibility across various cooking methods. Note that precise measurements of digestibility can vary depending on factors like individual physiology and specific cooking techniques.
| Cooking Method | Protein Structure Impact | Digestibility (Estimated) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiled | Proteins are relatively intact, with moderate denaturation. | High | A soft-boiled egg retains a significant portion of its original protein structure. |
| Scrambled | Moderate to significant denaturation, depending on temperature and time. | High | The whisking and cooking process unfolds proteins, increasing digestibility. |
| Fried | Significant denaturation, particularly on the surface exposed to direct heat. | High, potentially slightly lower than scrambled | The surface proteins of a fried egg are more exposed to heat, leading to greater unfolding. |
| Omelet | Moderate to high denaturation, depending on the cooking process. | High | The folding and gentle cooking of an omelet maintain a good balance of structure and denaturation for digestion. |
Impact of Temperature and Time
Cooking temperature and duration directly influence the extent of protein denaturation. Higher temperatures and longer cooking times generally lead to more significant protein unfolding. For instance, a hard-boiled egg, cooked at a higher temperature for a longer duration, will have more denatured proteins compared to a soft-boiled egg. This is reflected in the texture difference. This greater denaturation can lead to a slightly higher level of digestibility, but also potentially to the formation of less digestible protein aggregates if the cooking is excessive.
Bioavailability of Egg Proteins
Cooking does not significantly affect the bioavailability of egg proteins. Bioavailability refers to the proportion of a nutrient that the body can absorb and utilize. The essential amino acids in egg proteins are readily available and efficiently absorbed regardless of the cooking method. The impact of cooking methods primarily affects the digestibility of the protein, not its overall nutritional value.
The body efficiently breaks down and utilizes the proteins regardless of the preparation method.
Egg Protein in Different Diets
Eggs are a remarkably versatile and nutritious food, making them a valuable addition to a wide array of dietary patterns. Their high protein content, essential amino acids, and bioavailability make them a popular choice for athletes, those looking to build muscle, and individuals seeking a complete protein source. Understanding how eggs fit into different dietary needs and restrictions is crucial for making informed choices.The nutritional value of eggs, particularly their protein profile, makes them a compelling option for various dietary goals.
Their suitability for different dietary preferences and restrictions, however, varies. This section explores the role of egg protein in vegetarian and vegan diets, along with suggestions for incorporating eggs into diverse dietary patterns. We’ll also compare eggs to other protein sources and highlight any potential limitations for specific dietary needs.
Eggs are packed with protein, a crucial nutrient for overall health. Knowing how much protein is in an egg can be helpful for meal planning, especially if you’re considering conditions like polycythemia and the associated risks with coronavirus COVID-19 complications, as discussed in more detail in this insightful article on polycythemia and coronavirus COVID-19 risks, complications, and considerations.
While a single egg provides a good dose of protein, it’s important to remember a balanced diet is key, and understanding your individual needs is always important.
Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
Eggs are a complete protein source, containing all essential amino acids. This makes them a valuable addition to vegetarian diets, which often lack a sufficient source of complete proteins. However, vegans, who avoid all animal products, cannot consume eggs. Alternative protein sources, such as tofu, legumes, and quinoa, become crucial for meeting protein requirements.
Incorporating Eggs into Different Dietary Patterns
Eggs can be easily incorporated into a variety of dietary patterns. For example, scrambled eggs with vegetables can serve as a quick and nutritious breakfast or a light lunch. Omelets can be filled with various ingredients, allowing for flexibility in dietary preferences. Baked goods, such as muffins and cakes, can also benefit from the addition of eggs, enhancing their texture and flavor.
Suitability for Different Dietary Preferences and Restrictions
The suitability of eggs for various dietary preferences and restrictions depends on individual needs. For those following a gluten-free diet, eggs are a safe and convenient option. Individuals with specific allergies, such as egg allergies, must avoid eggs altogether. For those following a low-fat diet, eggs can still be included, but portion control is key. Likewise, for those with dietary restrictions related to cholesterol, careful consideration of portion sizes and overall dietary intake is necessary.
Dietary Recommendations for Egg Consumption
| Dietary Need/Goal | Recommended Egg Consumption | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| General Health | 1-3 eggs per day | Provides a good source of protein and essential nutrients. |
| Muscle Building | 2-4 eggs per day | Increased protein intake supports muscle growth and repair. |
| Weight Management | 1-2 eggs per day | Balanced protein intake can help manage weight, but portion control is important. |
| Vegetarian | 2-3 eggs per day | A valuable source of complete protein to support balanced nutrition. |
| Vegan | 0 eggs per day | Eggs are excluded from a vegan diet due to their animal origin. |
Health Benefits and Drawbacks of Egg Protein
Eggs, a ubiquitous breakfast staple, offer a wealth of nutrients, including high-quality protein. Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of egg consumption is crucial for incorporating them safely and effectively into a balanced diet. The nutritional profile of eggs, coupled with their versatility in cooking, makes them a valuable food source.Egg protein, being a complete protein, provides all nine essential amino acids our bodies need.
However, like any food, egg consumption carries potential health implications, both positive and negative. This section delves into the benefits and concerns surrounding egg consumption, including its impact on muscle growth and repair.
Potential Health Benefits
Eggs are a powerhouse of nutrients beyond protein. Their high nutritional value extends to vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. This contributes to various health benefits.
- Improved Muscle Growth and Repair: The complete protein profile in eggs supports muscle protein synthesis, a critical process for building and repairing muscle tissue. This is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals engaged in strength training. Consuming eggs post-workout can aid in recovery and muscle growth.
- Enhanced Eye Health: Eggs are rich in lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids crucial for maintaining healthy vision and reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration. These antioxidants protect the eyes from oxidative damage.
- Strong Bones: Eggs contain significant amounts of vitamin D and phosphorus, both essential for bone health and preventing osteoporosis. This makes eggs a valuable food source for individuals at risk of bone-related conditions.
- Healthy Cholesterol Profile (in moderation): While eggs contain cholesterol, the impact on blood cholesterol levels can vary from person to person. For many individuals, eggs can be consumed in moderation without significantly raising cholesterol levels. The key lies in a balanced diet and lifestyle, which includes consuming foods rich in fiber and healthy fats. For those with existing cholesterol concerns, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
Ever wondered how much protein a humble egg packs? It’s a surprisingly good source, and knowing the nutritional value is key for a balanced diet. While we’re on the topic of health, if you’re struggling with hidradenitis suppurativa and want to understand the potential genetic factors involved, check out this expert’s insights on ask an expert hidradenitis suppurativa genetic.
Ultimately, understanding the protein content in eggs can be a valuable piece of the puzzle for a healthy lifestyle.
Potential Drawbacks and Concerns
While eggs offer numerous benefits, certain concerns regarding their consumption exist.
- Cholesterol Content: Eggs contain cholesterol, which has been linked to increased risk of heart disease in some individuals. However, recent research suggests that dietary cholesterol’s impact on blood cholesterol levels is less significant than previously thought, and that other dietary factors play a more substantial role. Moderation is key, especially for those with existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Allergic Reactions: Egg allergies are relatively common, especially in children. Symptoms can range from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Individuals with egg allergies should avoid egg consumption entirely and seek medical advice.
- Salmonella Contamination: Raw or undercooked eggs can harbor Salmonella bacteria, posing a significant risk of foodborne illness. Thorough cooking of eggs to an internal temperature of at least 160°F (71°C) is crucial to eliminate this risk.
- Potential for Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as bloating or discomfort, after consuming eggs, particularly if they have pre-existing digestive conditions. This may vary depending on individual sensitivities and dietary habits. It is crucial to listen to your body and adjust your intake accordingly.
Impact on Muscle Growth and Repair
Eggs are an excellent source of high-quality protein, which is essential for muscle growth and repair.
Protein synthesis, a critical process for muscle growth and repair, is directly influenced by adequate protein intake. Eggs, due to their complete protein profile, provide all the essential amino acids needed for this process. Consuming eggs, especially after workouts, can contribute to optimal muscle recovery and growth. Furthermore, eggs provide other nutrients vital for overall health and athletic performance.
Practical Applications and Recipes
Eggs are a versatile and affordable protein source, perfect for a wide range of culinary applications. Understanding the protein content and nutritional value allows for strategic incorporation into various meals, catering to different dietary needs and preferences. From quick breakfasts to elaborate dinners, eggs are a key ingredient in many kitchens worldwide.This section dives into practical ways to utilize egg protein, offering diverse recipes and demonstrating the flexibility of this nutritional powerhouse.
We’ll explore how to incorporate eggs into your daily meals, focusing on both nutritional and culinary benefits.
Breakfast Dishes
Eggs are a staple in many breakfast routines, offering quick and satisfying meals. Their versatility allows for numerous preparation methods, from simple scrambled eggs to elaborate omelets.
- Scrambled Eggs with Veggies: A classic breakfast choice, easily customizable. Chopped vegetables like spinach, mushrooms, and onions add flavor and nutrients. Seasoning with herbs and spices enhances the taste profile. This is a great way to incorporate more vegetables into your diet.
- Omelets: Omelets are perfect for filling with various ingredients, like cheese, meats, and vegetables. The customizable nature makes them adaptable to diverse tastes and dietary requirements. They provide a good source of protein and healthy fats.
- Frittata: A baked egg dish, frittatas can be prepared with a variety of ingredients, making them suitable for a light lunch or brunch. The baked nature results in a firmer texture compared to scrambled eggs. The flexibility allows for a filling meal with multiple protein and vegetable options.
Lunch and Dinner Recipes
Eggs can be more than just a breakfast food. Their versatility extends to lunch and dinner meals, providing a protein-rich component in various dishes.
- Egg Salad Sandwiches: A simple yet satisfying lunch option. Combining hard-boiled eggs with mayonnaise, mustard, and seasonings provides a protein-packed and flavorful filling for sandwiches. The combination is a great way to add protein and nutrients to any lunch.
- Pasta with Pesto and Egg: A quick and easy pasta dish, perfect for a weeknight dinner. Pasta is a carbohydrate source that is balanced with egg protein and pesto, which is a healthy and flavorful sauce.
- Egg Curry: A flavorful and satisfying dish, often incorporating spices and vegetables. Eggs are a great addition to curries as they hold their shape and absorb flavors well. The curry can be made with various vegetables and spices.
Recipe Table
| Dish | Ingredients | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Scrambled Eggs with Spinach | Eggs, spinach, butter/oil, salt, pepper | Whisk eggs, sauté spinach, combine, cook until set. |
| Quiche Lorraine | Eggs, cheese, bacon, cream | Combine ingredients, bake in a pie crust until set. |
| Egg Fried Rice | Eggs, rice, vegetables, soy sauce | Scramble eggs, stir-fry with rice and vegetables. |
Closure
In conclusion, an egg is a surprisingly versatile and nutritious food. Its protein content, while varying slightly depending on factors like egg size and the hen’s diet, remains a significant contributor to a balanced diet. From the egg white’s lean protein to the yolk’s richness in essential nutrients, eggs provide a complete protein source. Understanding how much protein in an egg and its various nutritional components allows us to appreciate its value in various dietary approaches and cooking styles.
So, next time you crack an egg, remember the incredible nutritional story it holds!