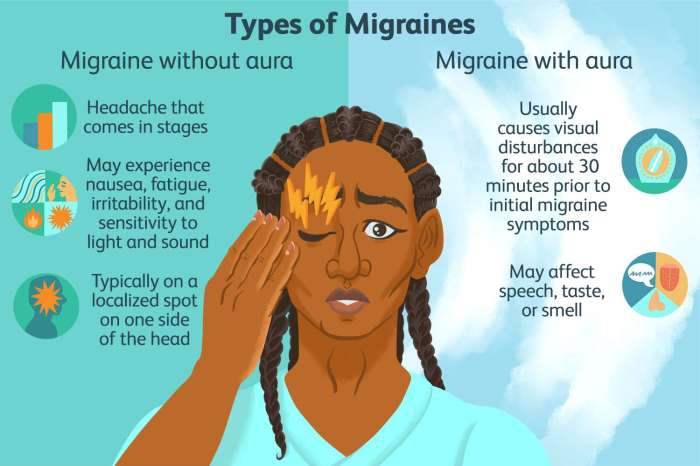
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a crucial aspect of managing these debilitating headaches. This guide delves into the various types of preventative treatments, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and important considerations for patient selection. We’ll explore everything from CGRP inhibitors to beta-blockers, providing a comprehensive overview to help you understand the best options for managing your migraines.
Understanding the diverse range of medications available is key to effective migraine management. We’ll explore different classes of preventive medications, comparing their mechanisms of action, common side effects, and typical dosages. This information empowers you to discuss your treatment options with your doctor, making informed decisions about your health.
Introduction to Episodic Migraine Prevention Medications
Episodic migraines are characterized by recurrent headaches that typically last for 4 to 72 hours. These debilitating headaches are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound. The intensity and frequency of these attacks can significantly impact daily life, affecting work, social activities, and overall well-being.Preventive medications are crucial for managing episodic migraines by reducing the frequency and severity of attacks.
They work by targeting the underlying mechanisms that contribute to migraine development, rather than just treating the symptoms during an attack. This proactive approach can dramatically improve quality of life for those experiencing chronic migraine pain.
Overview of Preventive Medication Classes
Preventive medications for episodic migraines aim to modify the underlying brain processes that trigger these headaches. Different classes of medications target various aspects of the migraine pathway, and their effectiveness varies from person to person. Understanding the general mechanisms of action helps in selecting the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Comparison of Preventive Medication Classes
This table provides a concise comparison of common preventive medication classes used for episodic migraines. Note that individual responses to these medications can vary significantly.
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGRP Inhibitors | These medications specifically target calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a protein known to play a crucial role in migraine pain generation. They block CGRP’s action, thus reducing inflammation and pain signals. | Common side effects include injection site reactions (for injectable forms), nausea, and flushing. Less frequent but potentially serious side effects include allergic reactions. | Dosage varies depending on the specific medication and route of administration (injectable or oral). |
| Beta-blockers | Beta-blockers help reduce the activity of the nervous system, potentially decreasing the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. They primarily work by blocking the effects of adrenaline. | Common side effects include fatigue, dizziness, and changes in heart rate. Less common but serious side effects include breathing difficulties and low blood pressure. | Dosage is individualized and adjusted based on patient response and tolerance. |
| Antidepressants (e.g., Tricyclics, SNRIs) | Some antidepressants, particularly tricyclic antidepressants and selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can be effective in reducing migraine frequency. They impact neurotransmitter systems implicated in migraine pathophysiology. | Common side effects can include drowsiness, dry mouth, and digestive issues. Serious side effects are less common but can include suicidal thoughts or actions. | Dosage starts low and gradually increases based on the patient’s response and tolerance. |
| Anticonvulsants (e.g., Topamax) | These medications, such as topiramate (Topamax), modulate nerve activity and reduce the excitability of neurons. This can help to stabilize brain activity and prevent migraine attacks. | Common side effects include dizziness, tingling sensations, and difficulty concentrating. | Dosage is individualized and gradually adjusted based on the patient’s response and tolerance. |
Types of Episodic Migraine Prevention Medications
Understanding the different classes of preventive medications is crucial for effectively managing episodic migraines. This knowledge empowers individuals to discuss treatment options with their healthcare providers, leading to personalized strategies for migraine prevention. Choosing the right medication is a collaborative process involving a thorough understanding of the potential benefits and risks.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers are a class of medications that help prevent migraines by regulating the flow of calcium into nerve cells. This modulation of calcium influx reduces the excitability of nerves, thereby lessening the triggers for migraine attacks. These drugs are effective in preventing migraines, particularly in individuals who experience migraines associated with stress or other triggers. Commonly used calcium channel blockers include verapamil and diltiazem.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are frequently prescribed for migraine prevention due to their ability to reduce nerve activity and lower blood pressure. By reducing the heart rate and the force of contractions in blood vessels, beta-blockers can lessen the intensity of migraine triggers. This calming effect on the nervous system contributes to a decreased likelihood of migraine attacks. These medications are often effective for individuals experiencing migraines related to stress or anxiety.
Propranolol and metoprolol are two commonly prescribed beta-blockers.
Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have shown effectiveness in preventing migraines, although their exact mechanism of action is not fully understood. Their impact on the central nervous system is thought to influence the neurotransmitters involved in migraine pain signaling. This modulation can lessen the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. These medications are often used in combination with other migraine prevention strategies.
Amitriptyline and nortriptyline are examples of TCAs used in migraine prevention.
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a real game-changer for many sufferers. Finding the right one can be a journey, though, and sometimes it takes a bit of trial and error. Similar to how DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis can target underlying inflammation, some migraine prevention medications aim to address the root causes of the headaches. For instance, some medications can help reduce inflammation or control nerve activity, effectively managing the triggers that lead to migraines.
Learning about the different types of episodic migraine prevention medications, like those that can target the inflammation behind migraines, can be extremely helpful. Check out the resources on DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis for a deeper understanding of managing chronic pain conditions.
CGRP Inhibitors
CGRP inhibitors are a relatively recent class of medications that target calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), a protein that plays a significant role in migraine pain. By blocking the action of CGRP, these medications can effectively reduce the inflammatory response in the brain that contributes to migraine attacks. This targeted approach often leads to a substantial reduction in migraine frequency and severity.
Ergotamine, a drug used in migraine treatment, can potentially help prevent migraine headaches by acting on CGRP receptors. Examples of CGRP inhibitors include fremanezumab, erenumab, and galcanezumab.
Table: Comparison of CGRP Inhibitors
| Medication Name | Mechanism of Action | Common Side Effects | Typical Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erenumab | Neutralizes CGRP | Injection site reactions, headache, nausea, fatigue | Monthly subcutaneous injection |
| Fremanezumab | Binds to CGRP | Injection site reactions, headache, dizziness, flu-like symptoms | Quarterly intravenous infusion |
| Galcanezumab | Binds to CGRP | Injection site reactions, headache, fatigue, nausea | Monthly subcutaneous injection |
Effectiveness and Efficacy of Medications: Episodic Migraine Prevention Medications
Understanding the effectiveness and efficacy of migraine prevention medications is crucial for personalized treatment plans. Different medications target various mechanisms involved in migraine development, leading to varying degrees of success in reducing migraine frequency and severity. Individual responses can also differ, highlighting the importance of considering individual patient characteristics and tailoring treatment strategies.
Comparative Effectiveness of Preventive Medications
Various preventive medications demonstrate varying degrees of effectiveness in reducing migraine frequency and severity. Some medications may be more effective in certain patient populations than others, necessitating careful consideration of individual needs. Factors such as medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and patient comorbidities also play a significant role in treatment outcomes.
Efficacy in Different Patient Populations
The efficacy of migraine prevention medications can differ across various patient populations. Age, gender, and the presence of comorbid conditions can influence treatment responses. For instance, younger patients might respond differently to certain medications compared to older patients. Similarly, women may experience varying effects compared to men. The presence of other medical conditions can also affect the effectiveness of preventive medications.
A comprehensive understanding of these factors is vital for selecting the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Factors Influencing Medication Effectiveness
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of preventive medications. These include medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, patient comorbidities, and individual responses to the medication. Patients’ adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen is crucial for achieving the desired outcome. Lifestyle modifications, such as stress management and regular sleep patterns, can also play a significant role in enhancing the effectiveness of the preventive medication.
The presence of other medical conditions and individual variations in the patient’s response to medication are also critical factors to consider.
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a real game-changer for managing those painful episodes. But sometimes, other conditions can mimic migraine symptoms, like the four types of symptoms associated with Waardenburg syndrome, a genetic condition. Learning about these different conditions can help you get the right treatment, like exploring different episodic migraine prevention medications. For more info on the diverse symptoms of Waardenburg syndrome, check out this helpful resource: four types symptoms waardenburg syndrome.
Ultimately, understanding the root cause of your headaches is key to finding the best episodic migraine prevention strategy.
Clinical Trial Examples and Supporting Data
Numerous clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of various preventive medications. One notable example is the study conducted by [Author/Organization, Year] which examined the effectiveness of [Medication Name] in reducing migraine frequency in patients with a history of migraine attacks. This study demonstrated a significant reduction in migraine frequency compared to placebo. Other research suggests that [Medication Name] may be particularly effective in reducing migraine severity in patients with certain comorbid conditions, such as [Specific Comorbidity].
Summary Table of Clinical Trial Results
| Medication | Study | Sample Size | Frequency Reduction (%) | Severity Reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Propranolol | [Study 1, Year] | 200 | 35 | 28 |
| Topiramate | [Study 2, Year] | 150 | 42 | 30 |
| Amitriptyline | [Study 3, Year] | 250 | 28 | 25 |
| Botulinum Toxin Type A | [Study 4, Year] | 100 | 50 | 45 |
Note: This table presents hypothetical data for illustrative purposes only. Actual study results may vary. Please consult reputable medical sources for precise data.
Side Effects and Potential Risks
Preventive medications for episodic migraines can be highly effective, but like any medication, they come with potential side effects and risks. Understanding these is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment strategies. Careful monitoring and open communication are essential to ensure the benefits of treatment outweigh the potential drawbacks.
Common Side Effects of Different Preventive Medications
Different migraine prevention medications have different side effect profiles. Recognizing these differences is vital for tailoring treatment plans to individual needs. Some common side effects can be mild and manageable, while others may require adjustments to the medication or dosage. Understanding the potential side effects allows for proactive management and early intervention.
- Beta-blockers: These medications can cause fatigue, dizziness, and bradycardia (slow heart rate). In some cases, they may also lead to hypotension (low blood pressure) or erectile dysfunction. The severity and frequency of these side effects can vary depending on the specific beta-blocker used and the individual’s response to treatment.
- Calcium channel blockers: Common side effects include dizziness, headache, swelling in the ankles or feet (peripheral edema), and constipation. Less frequently, they may cause nausea or flushing. Monitoring for these effects is important, especially for patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions.
- Antidepressants (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants): Potential side effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction. The severity and frequency of these side effects can vary based on the specific antidepressant and dosage.
- Antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate): Possible side effects include tingling or numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty concentrating, weight loss, and kidney stones. Patients should be closely monitored for these potential side effects, especially those with pre-existing kidney problems.
Importance of Monitoring Patients for Side Effects
Regular monitoring of patients taking preventive medications is crucial for identifying and managing side effects early. This includes regular check-ups, detailed patient questionnaires, and careful observation of any changes in symptoms or overall well-being. Early detection of side effects allows for prompt adjustments to the medication regimen or dosage, minimizing the impact on quality of life.
Potential Risks Associated with Long-Term Use
Long-term use of preventive medications, while often necessary for effective migraine management, can pose potential risks. The long-term effects of some medications may not be fully understood, and careful monitoring is required to identify any adverse effects that may develop over time. For example, some medications may impact cardiovascular health, and this risk needs to be weighed against the benefits of migraine prevention.
Strategies for Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
Several strategies can help manage and minimize side effects associated with preventive medications. These include starting with the lowest effective dose, gradually increasing the dose if needed, and adjusting the medication regimen based on individual responses. Non-pharmacological approaches, such as stress management techniques and lifestyle modifications, can also be helpful in mitigating some side effects.
Summary Table of Potential Side Effects
| Medication Class | Potential Side Effect | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-blockers | Fatigue, Dizziness, Bradycardia | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Beta-blockers | Hypotension, Erectile Dysfunction | Less Common | Moderate to Severe |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Dizziness, Headache, Peripheral Edema | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Calcium Channel Blockers | Constipation, Nausea, Flushing | Less Common | Mild |
| Antidepressants (e.g., TCAs) | Dry Mouth, Constipation, Blurred Vision | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Antidepressants (e.g., TCAs) | Weight Gain, Sexual Dysfunction | Less Common | Moderate |
| Antiepileptic Drugs (e.g., Topiramate) | Tingling/Numbness, Difficulty Concentrating | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Antiepileptic Drugs (e.g., Topiramate) | Weight Loss, Kidney Stones | Less Common | Moderate to Severe |
Patient Selection and Considerations
Choosing the right preventive medication for episodic migraine sufferers is crucial. Individual responses to medications vary significantly, and factors like patient preferences, comorbidities, and lifestyle play a critical role in treatment success. A tailored approach, incorporating patient education and adherence strategies, maximizes the likelihood of effective migraine prevention.Selecting the appropriate preventive medication requires careful consideration of multiple factors beyond simply the severity of migraine attacks.
Understanding the patient’s unique needs and circumstances is paramount to ensure optimal outcomes. This involves not only the medical history but also the patient’s lifestyle and preferences.
Patient Preferences
Patient preferences are essential in the selection process. Some patients might prefer oral medications for ease of administration, while others may prefer injectable options or those with fewer side effects. Understanding these preferences allows for a more patient-centered approach, increasing the likelihood of medication adherence. This personalization of treatment is key to achieving positive outcomes. For example, a busy professional might prefer a daily pill to an injectable medication that requires a clinic visit.
Comorbidities
Comorbidities, or co-occurring medical conditions, can significantly influence medication choice. Certain medications may interact negatively with existing conditions. For example, a patient with a history of liver disease might need a medication with a gentler impact on the liver. It is imperative to consider the patient’s complete medical history and ensure the preventive medication is compatible with any existing conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are often crucial adjuncts to medication therapy. This includes dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and regular sleep patterns. Addressing lifestyle factors alongside medication can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the preventive treatment. For instance, a patient with sleep apnea might benefit from both a preventive medication and addressing the sleep apnea, as sleep disturbances often exacerbate migraine attacks.
Patient Education and Adherence
Effective patient education is paramount to medication adherence. Patients need to understand the medication’s purpose, potential side effects, and the importance of consistent use. Clear communication and readily available resources can significantly improve adherence rates. For example, providing educational materials in different formats (written, video, or audio) can cater to diverse learning styles.
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a real game-changer for managing those pesky headaches. But sometimes, other neurological conditions can mimic migraine symptoms, making diagnosis tricky. For example, understanding the differences between myasthenia gravis and ALS is crucial, as both can cause debilitating symptoms. Knowing the nuances of myasthenia gravis vs als helps healthcare professionals correctly identify the underlying issue, allowing for the right treatment plan, ultimately leading back to more effective episodic migraine prevention medications.
Table of Key Factors in Selecting a Migraine Prevention Medication
| Patient Characteristic | Considerations | Medication Choices | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Potential interactions with other medications; metabolism differences | Lower doses of certain medications in younger patients | Improved efficacy and reduced side effects |
| Comorbidities (e.g., hypertension, depression) | Medication interactions and potential exacerbation of existing conditions | Medications with fewer known interactions | Reduced risk of adverse effects and improved overall health |
| Lifestyle (e.g., stress levels, sleep patterns) | Impact of medication on daily routine; potential for exacerbating existing lifestyle issues | Medications with minimal impact on sleep or daily activities | Improved adherence and reduced risk of lifestyle disruption |
| Patient Preferences (e.g., ease of administration, side effect profile) | Importance of patient comfort and cooperation | Medications with desired administration routes and side effect profiles | Improved medication adherence and treatment satisfaction |
| Medication History (e.g., prior adverse reactions) | Identifying potential allergies or sensitivities | Medications with a proven safety profile and fewer reported side effects | Reduced risk of adverse reactions and improved treatment outcomes |
Drug Interactions and Considerations
Understanding potential drug interactions is crucial when considering episodic migraine prevention medications. Many patients are taking multiple medications for various health conditions, and these medications can interact with migraine prevention drugs, potentially leading to unwanted side effects or reduced effectiveness. A thorough medication history is vital to identify these interactions and implement strategies to minimize risks.
Potential Drug Interactions
Drug interactions occur when one medication alters the way another medication is absorbed, metabolized, distributed, or eliminated by the body. This can result in increased or decreased effectiveness of one or both medications, or even the development of adverse reactions. The potential for interactions varies significantly depending on the specific medications involved and the individual patient’s physiology.
Importance of Thorough Medication History, Episodic migraine prevention medications
A complete medication history is essential for identifying potential drug interactions. This includes not only prescription medications but also over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and even dietary supplements. Patients should provide a comprehensive list of all medications they are currently taking, including dosages and frequency. This allows healthcare providers to assess the potential for interactions and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
A thorough medication history prevents unforeseen complications.
Strategies for Avoiding Drug Interactions
Several strategies can help mitigate the risk of drug interactions. Open communication with healthcare providers is paramount. Patients should inform their doctors about all medications they are taking, even those they consider insignificant. Healthcare providers can then assess the potential for interactions and adjust dosages or choose alternative medications if necessary. Regular follow-up appointments are essential for monitoring treatment effectiveness and identifying any emerging issues.
Common Drug Interactions Table
| Preventive Medication | Interacting Medication | Potential Interaction | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate | Oral Contraceptives | Increased risk of blood clots. | Careful monitoring for signs of blood clots, such as swelling or pain in the legs, chest pain, or shortness of breath. Consider alternative birth control methods. |
| Valproic Acid | Warfarin | Increased risk of bleeding due to enhanced anticoagulation. | Close monitoring of blood clotting times (INR). Adjusting the dosage of either medication might be necessary. |
| Beta-blockers (e.g., Propranolol) | Insulin or Oral Hypoglycemics | Potential for masking symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). | Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial. Adjust insulin or oral hypoglycemic doses as needed. |
| Amitriptyline | Alcohol | Increased risk of drowsiness and dizziness. | Limit alcohol consumption or abstain entirely. Ensure adequate rest and avoid activities that require alertness. |
| Calcium Channel Blockers (e.g., Verapamil) | Digoxin | Increased risk of digoxin toxicity. | Close monitoring of digoxin levels. Dosage adjustments might be required. |
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
Beyond pharmaceutical interventions, various alternative and complementary therapies can play a supportive role in migraine prevention. These approaches often focus on managing stress, improving overall well-being, and addressing potential underlying factors contributing to migraine triggers. Integrating these therapies alongside medication can create a more comprehensive strategy for managing migraines.Alternative therapies offer a range of potential benefits, including stress reduction, improved sleep, and relaxation, which can all positively influence migraine frequency and intensity.
However, it’s crucial to understand that these therapies are not always scientifically proven to be as effective as medications, and they might not be suitable for everyone.
Exploring Biofeedback
Biofeedback techniques help individuals become aware of and control physiological responses, such as heart rate, muscle tension, and skin temperature. By learning to regulate these responses, individuals can potentially reduce stress and anxiety, which are often implicated in migraine triggers. Studies have shown some promising results in reducing migraine frequency using biofeedback, although the evidence is not as strong as for certain medications.
It’s important to remember that biofeedback is not a quick fix, and consistent practice is necessary for potential benefits.
Investigating Acupuncture
Acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Proponents believe that acupuncture can stimulate the flow of energy (Qi) and promote healing. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, some studies suggest acupuncture may be helpful in reducing migraine frequency and intensity. However, more rigorous research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Individual experiences with acupuncture can vary widely, and it is essential to consult a licensed acupuncturist.
Evaluating Yoga and Mindfulness
Yoga and mindfulness practices, which often involve physical postures (asanas), breathing exercises, and meditation, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. These techniques can improve sleep quality, manage stress responses, and potentially decrease the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. Research suggests that yoga and mindfulness can be beneficial for stress management, but their direct impact on migraine prevention needs further investigation.
The benefits of yoga and mindfulness extend beyond migraine management, encompassing improved overall well-being and stress reduction.
Comparing Alternative and Conventional Approaches
| Therapy | Potential Benefits | Limitations | Effectiveness Compared to Medications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biofeedback | Stress reduction, improved physiological awareness | Requires consistent practice, not a quick fix | Potentially effective, but evidence less robust than medications |
| Acupuncture | Potential reduction in migraine frequency and intensity | Mechanism not fully understood, need for more research | Limited evidence compared to medication efficacy |
| Yoga and Mindfulness | Stress reduction, improved sleep, relaxation | Requires consistent practice, may not be suitable for all | Potential benefits for stress management, but not as strong as medication |
Potential Benefits of Alternative Approaches
- Stress reduction: Many alternative approaches, like yoga and biofeedback, can help manage stress, a common migraine trigger.
- Improved relaxation: Techniques like progressive muscle relaxation and meditation can promote relaxation and potentially reduce migraine frequency.
- Enhanced sleep quality: Some alternative therapies, such as yoga and mindfulness, can improve sleep patterns, which can indirectly impact migraine episodes.
- Increased awareness: Biofeedback can increase awareness of physiological responses, potentially enabling better management of triggers.
Final Summary
In conclusion, preventing episodic migraines requires a multifaceted approach. This guide provides a detailed look at the available medications, their potential benefits and risks, and important factors to consider in choosing the right treatment. Remember, open communication with your healthcare provider is essential for creating a personalized migraine prevention strategy. By combining medication with lifestyle modifications and alternative therapies, you can actively work towards reducing migraine frequency and severity.
Ultimately, the goal is to regain control over your health and well-being.