Can pregnant women eat shrimp? This crucial question confronts expectant mothers, navigating a world of nutritional needs and potential risks. Shrimp, a delicious and versatile seafood, offers a wealth of nutrients, but concerns about food safety and potential contaminants like mercury must be considered. This exploration delves into the nutritional value of shrimp, the potential risks of consumption during pregnancy, safe handling practices, alternative seafood options, and cultural variations in shrimp consumption.
Understanding the delicate balance between potential benefits and risks is essential for making informed choices. This comprehensive guide aims to equip pregnant women with the knowledge they need to enjoy shrimp safely and responsibly, while ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
Nutritional Value of Shrimp
Shrimp, a popular seafood choice, boasts a surprisingly impressive nutritional profile. Its delicate texture often masks a wealth of essential nutrients, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet, particularly for pregnant women seeking a nutritious and delicious protein source. This detailed look at shrimp’s nutritional value will help you understand why it’s such a healthy option.
Nutritional Profile of Shrimp
Shrimp is a lean protein source, packed with essential vitamins and minerals. It’s low in fat, making it a heart-healthy choice. Its high protein content supports growth and development, while other nutrients contribute to overall well-being.
Wondering if pregnant women can safely eat shrimp? While shrimp is generally a nutritious food, it’s crucial to consider potential contaminants. Recent EPA guidelines for PFAS limits in drinking water ( epa pfas limits drinking water ) highlight the importance of clean water sources, especially for expecting mothers. Ultimately, consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is key for personalized dietary advice about eating shrimp during pregnancy.
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving (approx.) | Potential Benefits for Pregnant Women |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 20-30 grams | Essential for fetal growth and development, tissue repair, and hormone production. |
| Iron | 1-2 milligrams | Crucial for red blood cell production, preventing anemia, which is common during pregnancy. |
| Selenium | Variable, but often significant | Supports thyroid function, important for healthy fetal development. |
| Vitamin B12 | 1-2 micrograms | Essential for nerve development and red blood cell formation, crucial for preventing neural tube defects. |
| Vitamin D | Trace amounts | Supports calcium absorption, vital for bone development in the fetus. |
| Choline | Significant amounts | Crucial for brain development in the fetus and for preventing neural tube defects. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Variable, but often present | Support brain and eye development in the fetus. |
Comparison to Other Seafood
Compared to other seafood options, shrimp generally provides a good balance of nutrients. For example, salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, while tuna is a good source of protein and vitamin D. However, shrimp offers a unique combination of nutrients, making it a versatile choice.
Potential Health Benefits for Pregnant Women
The nutritional profile of shrimp makes it a beneficial food for pregnant women. The protein supports the growth and development of the baby, while vitamins and minerals like iron and vitamin B12 are crucial for the mother’s health and the baby’s development.
Nutritional Differences Between Cooked and Raw Shrimp
The cooking method can slightly alter the nutritional content of shrimp. While raw shrimp contains all the essential nutrients, cooking methods can impact some of the vitamins and minerals. Raw shrimp can contain higher levels of some vitamins and minerals, depending on the preparation method. Cooking, while reducing some nutrients, often enhances palatability and safety.
Wondering if pregnant women can safely eat shrimp? It’s a common question, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. While shrimp is generally considered safe, it’s crucial to consider other factors, like food safety and potential allergies. Knowing when a child’s headache warrants concern is also important. For instance, if a child is experiencing frequent or severe headaches, seeking professional medical advice, like that found on this helpful resource about headache in kids when to worry , is essential.
Ultimately, the best approach to making informed decisions about food choices during pregnancy is to consult with a healthcare provider. This will help ensure you’re making the healthiest choices for you and your developing baby.
| Nutrient | Cooked Shrimp | Raw Shrimp | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Similar | Similar | Protein content remains largely consistent. |
| Vitamin B12 | Slightly lower (depending on cooking method) | Slightly higher (depending on cooking method) | Slight changes may occur, but overall B12 is present in significant amounts. |
| Iron | Similar | Similar | Iron bioavailability might vary slightly, but overall content remains consistent. |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Similar | Similar | Cooking methods may not significantly affect Omega-3 levels. |
Potential Risks Associated with Shrimp Consumption During Pregnancy
Enjoying shrimp during pregnancy can be tempting, but certain precautions are crucial to ensure a safe and healthy experience. While shrimp offers nutritional benefits, potential risks exist, particularly regarding foodborne illnesses. Understanding these risks empowers expectant mothers to make informed choices and minimize potential complications.
Foodborne Illnesses from Raw or Undercooked Shrimp
Consuming raw or undercooked shrimp poses a significant risk of foodborne illnesses. These illnesses can stem from bacteria that thrive in contaminated seafood. Proper cooking methods are essential to eliminate these harmful microorganisms.
Risks of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Contamination
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a bacteria commonly found in seafood, including shrimp. Infection can lead to symptoms like diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, which can be particularly problematic during pregnancy. Proper handling and cooking procedures are critical in preventing Vibrio parahaemolyticus contamination.
Risks for Pregnant Women with Pre-existing Health Conditions
Pregnant women with pre-existing health conditions, such as weakened immune systems, may be more susceptible to complications from foodborne illnesses. For instance, individuals with compromised immune systems may experience more severe symptoms from infections. It’s vital to prioritize safe food handling practices.
Warnings for Pregnant Women at Increased Risk
Certain pregnant women may be at higher risk of complications from shrimp consumption. These include individuals with weakened immune systems, those with chronic illnesses, and those who have a history of foodborne illness. It’s crucial for these individuals to take extra precautions. For example, pregnant women with compromised immune systems should opt for thoroughly cooked shrimp. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice.
Summary of Potential Risks and Preventive Measures
| Potential Risk | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|
| Foodborne illnesses (e.g., Vibrio parahaemolyticus) from raw or undercooked shrimp | Ensure shrimp is cooked thoroughly to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C). Avoid eating raw or undercooked shrimp. |
| Complications for pregnant women with pre-existing health conditions | Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Prioritize safe food handling practices. |
| Increased risk of severe illness for individuals with weakened immune systems | Avoid consuming raw or undercooked shrimp. Ensure thorough cooking. |
Safe Handling and Preparation of Shrimp
Shrimp, a delicious and nutritious food, can be a wonderful addition to a pregnant woman’s diet. However, proper handling and preparation are crucial to ensure safety and avoid potential risks. This section focuses on the safe practices for purchasing, storing, and preparing shrimp, emphasizing the importance of preventing foodborne illnesses.Safe handling practices are paramount to preventing foodborne illnesses, especially during pregnancy when the immune system might be slightly compromised.
Understanding these practices allows pregnant women to enjoy shrimp while minimizing potential risks.
Purchasing Shrimp
To ensure the quality and safety of shrimp, purchase them from reputable sources. Look for shrimp that are firm and free from unusual odors. Avoid shrimp that are slimy, discolored, or have an off-putting smell. When purchasing frozen shrimp, ensure the packaging is intact and free of damage, as this can compromise the product’s quality and safety.
Storing Shrimp
Proper storage is essential for maintaining the freshness and safety of shrimp. Fresh shrimp should be stored in the refrigerator at 40°F (4°C) or below. Frozen shrimp should be stored in the freezer at 0°F (-18°C) or below. Use the FIFO (First In, First Out) method to ensure you use the oldest shrimp first. Ideally, fresh shrimp should be consumed within one to two days of purchase.
Preparing Shrimp
Thorough preparation of shrimp helps ensure food safety. Shrimp should be washed thoroughly under cold running water before cooking. Discard any shrimp that appears damaged or shows signs of spoilage. Using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw shrimp and other foods prevents cross-contamination.
Cooking Shrimp
Proper cooking temperatures are vital to eliminate any potential pathogens. Cook shrimp until they reach an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C). This temperature is crucial for ensuring the complete elimination of harmful bacteria.
Avoiding Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination is a significant risk in food preparation. To avoid it, use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw shrimp and other foods. Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water before and after handling raw shrimp. Clean surfaces that come into contact with raw shrimp with hot, soapy water.
Safe Shrimp Cooking Guide
- Thoroughly wash the shrimp under cold running water.
- Pat the shrimp dry with paper towels.
- Prepare the cooking surface and any necessary seasonings.
- Heat the cooking oil or butter in a pan over medium-high heat.
- Add the shrimp to the pan and cook for 2-3 minutes per side, or until pink and opaque.
- Remove the shrimp from the pan and serve immediately.
Flowchart for Safe Shrimp Preparation

Alternatives and Recommendations for Pregnant Women

Pregnant women have unique dietary needs, and careful selection of seafood is crucial for both maternal and fetal health. While shrimp may pose some risks, many other seafood options are safe and offer significant nutritional benefits. This section explores alternative choices, their nutritional profiles, and the importance of a balanced diet and professional guidance.Choosing the right seafood during pregnancy is important to ensure both mother and baby receive essential nutrients without potential risks.
Different types of seafood offer a range of nutritional benefits, and it’s vital to understand these differences to make informed choices.
Safe Seafood Alternatives
A variety of seafood options are considered safe for pregnant women, providing essential nutrients without the potential risks associated with certain types. These alternatives offer valuable protein, vitamins, and minerals crucial for the developing baby.
- Salmon: Salmon is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, crucial for brain development in the fetus. It also contains vitamin D and B vitamins, supporting overall maternal health. Wild-caught salmon is generally preferred over farmed due to potential concerns about pollutants in some farmed varieties. Always ensure the salmon is cooked thoroughly to eliminate any potential risk.
- Tuna (in moderation): Tuna is a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, due to potential mercury content, it’s recommended to consume tuna in moderation. Avoid albacore (white) tuna, and opt for light tuna canned in water. One to two servings per week are usually sufficient.
- Catfish: Catfish is a low-mercury option, providing a good source of protein. Ensure it’s cooked properly.
- Cod: Cod is a lean protein source with low mercury content. It’s a good option for pregnant women seeking a variety of fish.
- Haddock: Similar to cod, haddock is another low-mercury fish option rich in protein.
- Shrimp Alternatives: While shrimp isn’t a recommended option, consider other seafood with similar nutritional profiles, like the ones mentioned above.
Nutritional Comparison of Seafood
Different seafood choices offer varied nutritional profiles. The table below highlights the approximate nutritional value of some safe seafood options, providing a quick comparison. Note that nutritional values can vary depending on the specific fish and preparation methods.
Wondering if pregnant women can safely eat shrimp? While generally safe, it’s crucial to consider potential foodborne illnesses. Nutritional needs during pregnancy are unique, and certain precautions are always wise. This is especially true when considering conditions like myasthenia gravis vs ALS, where dietary choices can be further complicated. For detailed insights on managing nutrition in such cases, check out this informative resource on myasthenia gravis vs als.
Ultimately, consulting a healthcare professional is key for personalized advice regarding shrimp consumption during pregnancy.
| Seafood | Protein (grams per 3 oz serving) | Omega-3 Fatty Acids (mg per 3 oz serving) | Vitamin D (mcg per 3 oz serving) | Other Key Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | 20-25 | 1000-1500 | 1-2 | Vitamin B12, Selenium |
| Tuna (light, canned in water) | 20-25 | 50-100 | Trace | Vitamin B12, Iron |
| Catfish | 18-22 | 50-100 | Trace | Vitamin B12, Niacin |
| Cod | 16-20 | 50-100 | Trace | Vitamin B12, Iodine |
| Haddock | 18-22 | 50-100 | Trace | Vitamin B12, Iodine |
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for both maternal and fetal well-being during pregnancy. It should include a variety of nutrient-rich foods beyond seafood. Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to ensure adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional, Can pregnant women eat shrimp
Individual dietary needs vary greatly. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or registered dietitian, is highly recommended for personalized advice. They can assess your individual needs and provide tailored recommendations based on your specific health conditions and dietary preferences. They can also advise on portion sizes and ensure that your diet aligns with your overall health goals during pregnancy.
Cultural and Regional Variations in Shrimp Consumption
Shrimp, a globally appreciated delicacy, holds a significant place in countless culinary traditions. Its versatility and delicious flavor have led to a wide array of preparation methods and consumption patterns, reflecting the rich tapestry of cultures across the globe. Understanding these differences is crucial, particularly for pregnant women considering shrimp consumption.Different cultures approach shrimp consumption with varied perspectives on safety and preparation, influencing the potential risks associated with its consumption during pregnancy.
These cultural nuances extend to the specific dishes prepared, the frequency of consumption, and the general attitudes toward seafood during pregnancy.
Diverse Culinary Applications of Shrimp
Shrimp is a staple ingredient in countless cuisines worldwide, featuring prominently in various dishes. Its versatility allows for incorporation into both simple and elaborate meals. The methods of preparation vary considerably, reflecting regional preferences and culinary traditions.
- In Southeast Asia, shrimp is often used in curries, stir-fries, and noodle dishes. These preparations typically involve robust flavor profiles, utilizing spices and herbs unique to the region. Examples include Thai green curry with shrimp, Vietnamese spring rolls with shrimp, and Indonesian shrimp satay. The use of fresh, local ingredients often contributes to the dish’s flavor and nutritional content.
- In Latin American cuisine, shrimp is frequently featured in vibrant sauces and stews. Dishes like shrimp ceviche (marinated in citrus juices), shrimp scampi (sauteed in garlic butter), and shrimp paella showcase the diverse culinary applications of shrimp in this region. The preparation methods emphasize the freshness of the shrimp and often incorporate local vegetables and herbs.
- In parts of Asia, including China and Japan, shrimp is a key component of many festive dishes and celebrations. These preparations frequently incorporate traditional techniques and ingredients that enhance the flavor and visual appeal of the meal. For instance, Chinese stir-fries and Japanese tempura highlight the preparation methods specific to the region, reflecting cultural preferences for different cooking styles.
Cultural Influences on Shrimp Preparation Methods
Cultural preferences significantly impact the methods used to prepare shrimp. These differences in approach often influence the potential health implications, particularly regarding the safety and preparation of the seafood.
- Certain cultures favor raw or lightly cooked shrimp, like ceviche in Latin America, while others prefer shrimp cooked to higher temperatures. This variability in preparation methods can influence the safety profile of the food, affecting the risk of bacterial contamination.
- The choice of spices, herbs, and sauces used in shrimp dishes also varies considerably. These additions can significantly impact the overall flavor and nutritional profile of the food, while also potentially influencing the risks of foodborne illnesses. For example, certain spices can reduce the risk of bacterial growth, while others may have a negligible effect.
- Cultural practices surrounding seafood consumption, including the types of shrimp commonly consumed and the methods of handling, can significantly influence the potential health implications for pregnant women. The risk factors may differ across cultures.
Potential Cultural Influences on Shrimp Risks
Cultural practices and traditions surrounding shrimp consumption can potentially influence the risks associated with its consumption during pregnancy. Factors like the frequency of consumption, preparation methods, and cultural beliefs about seafood can impact the overall safety profile of the food.
- Cultural practices regarding the handling and storage of shrimp can influence the risk of foodborne illnesses. For example, inadequate refrigeration or improper storage conditions can lead to bacterial growth, increasing the risk of food poisoning.
- Different cultures may have varying levels of awareness about the risks of eating raw or undercooked seafood. This lack of awareness can lead to higher risks of foodborne illnesses for pregnant women in some regions.
- The type of shrimp commonly consumed in a region may also play a role. Certain species may have a higher risk of contamination compared to others.
Impact of Mercury Content on Shrimp: Can Pregnant Women Eat Shrimp

Shrimp, a delicious and nutritious seafood, can be a valuable part of a balanced diet. However, concerns about mercury content arise, especially for pregnant women. Understanding the potential risks and how to make informed choices is crucial for a healthy pregnancy.Mercury, a naturally occurring element, can accumulate in certain marine life, including shrimp. While shrimp generally have lower mercury levels compared to some other fish, the concentration can vary based on several factors.
The environment in which the shrimp are raised and the age of the shrimp itself can affect the mercury levels present.
Potential Risks of High Mercury Intake During Pregnancy
High levels of mercury exposure during pregnancy can pose risks to the developing fetus. The neurological development of the baby is particularly vulnerable. Mercury can cross the placenta and affect the brain and nervous system of the unborn child. Symptoms of potential damage can range from developmental delays to learning disabilities, although the exact manifestation of these effects can vary.
Safe Choices for Limiting Mercury Intake
Pregnant women should prioritize consuming shrimp that have lower mercury levels. A variety of safe seafood options exist.
- Choose shrimp from reputable sources. Look for sustainably harvested shrimp from regions known for lower mercury contamination. Reading labels and checking for certifications from reputable organizations can help determine the origin and sustainability of the seafood.
- Limit consumption. Even with lower mercury levels, moderation is key. Consuming shrimp in moderation as part of a balanced diet is a safer approach.
- Variety in seafood consumption is crucial. Don’t rely solely on shrimp. Integrating a variety of seafood types, including those with lower mercury levels, into your diet will help maintain a balanced intake.
Selecting Shrimp Lower in Mercury Content
Several factors contribute to the mercury content in shrimp.
- Location of capture. Shrimp from certain regions, especially those with high industrial pollution or contaminated water sources, tend to have higher mercury levels. Opting for shrimp from cleaner, less polluted waters is recommended.
- Size of shrimp. Larger shrimp may have accumulated more mercury over their lifespan. Smaller shrimp, while still a part of a healthy diet, generally have lower mercury content.
- Method of harvesting. Sustainable fishing practices, where fishers follow regulations to avoid overfishing and minimize environmental impact, contribute to lower mercury levels in the shrimp.
Comparing Mercury Content in Different Types of Shrimp
The mercury content in shrimp can vary significantly based on several factors. It is crucial to remember that this is not an exhaustive list and individual shrimp may have varying levels. The table below provides a general comparison but should not be used as a definitive guide. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations.
| Shrimp Type | Potential Mercury Content (Estimated) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Wild-caught shrimp from pristine coastal waters | Low | Often have lower mercury levels due to their environment. |
| Farm-raised shrimp from controlled environments with minimal pollution | Lower | Can be a safer option if the farm practices sustainable methods. |
| Wild-caught shrimp from polluted waters | High | Should be avoided during pregnancy due to higher mercury levels. |
| Imported shrimp from regions with unknown or poor environmental standards | Variable | Risk of high mercury levels increases, so caution is warranted. |
Last Recap
In conclusion, the answer to whether pregnant women can eat shrimp isn’t a simple yes or no. It’s about understanding the nutritional benefits, acknowledging the potential risks, and prioritizing safe preparation methods. By carefully considering the factors discussed – from nutritional value and potential contaminants to cultural variations – pregnant women can make informed decisions that support their health and the well-being of their developing baby.
Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.

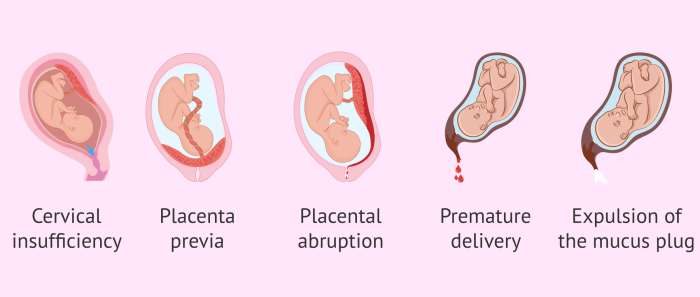

![Your Guide to Safe Exercise During Pregnancy [INFOGRAPHIC] Pregnancy massage benefits contraindications and safety](https://healthytipp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/motives-bleeding-second-third-trimester-1.png)