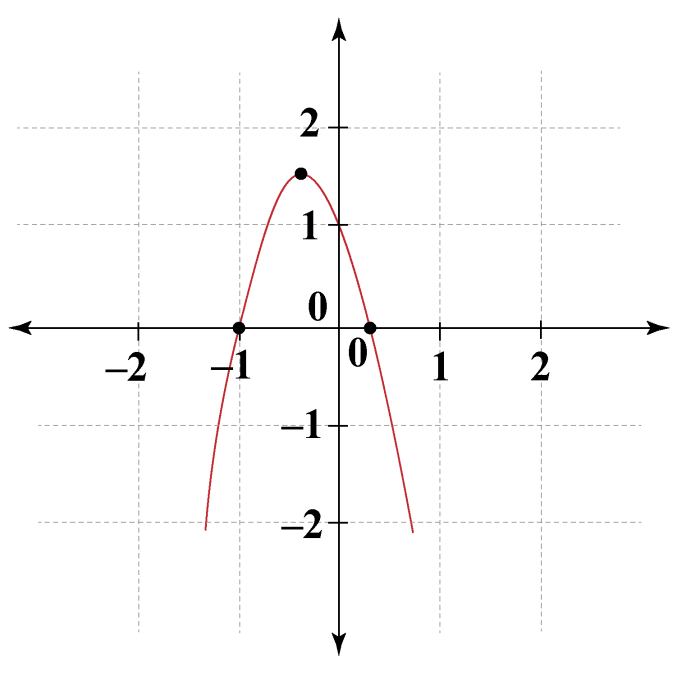
Robaxin vs Amrix similarities and differences explores the nuances of these muscle relaxants. Understanding their shared goals and distinct mechanisms of action is key for informed decisions about treatment. This comparison delves into chemical structures, potential side effects, dosages, and clinical applications, ultimately helping readers grasp the critical distinctions between these often-prescribed medications. This comprehensive…
Tag: pain relief
Vertex Painkiller Opioid Alternative Options
Vertex painkiller opioid alternative presents a compelling pathway to pain management, moving beyond the limitations of traditional opioid-based solutions. This exploration delves into the science, safety, and efficacy of these emerging alternatives, offering a comprehensive overview for those seeking effective and potentially safer pain relief options. Opioid painkillers, while sometimes effective, often come with a…
Alcohol & Arthritis Drugs Is It Forbidden?
Is alcohol forbidden when taking arthritis drugs? This crucial question impacts many people living with arthritis, demanding careful consideration of potential interactions. Different arthritis medications interact with alcohol in various ways, and understanding these interactions is vital for safe and effective treatment. This post will delve into the potential risks and benefits, providing valuable insights…
Massage Therapy Helps Relieve Pain A Deep Dive
Massage therapy helps relieve pain, offering a holistic approach to managing discomfort. This exploration delves into various massage techniques, their physiological effects, and the types of pain they can address. We’ll examine specific muscle groups and areas often targeted for relief, along with a comparative analysis of different massage styles. Beyond the basics, we’ll investigate…
Lower Back Pain After Sleeping A Deep Dive
Lower back pain after sleeping is a common complaint, affecting countless individuals. This detailed exploration delves into the multifaceted causes, from poor sleep posture to underlying medical conditions. We’ll uncover the symptoms, diagnostic processes, and effective treatment options, providing you with actionable strategies for prevention and self-care. Understanding the nuances of this prevalent issue is…
Safe OTC Pain Relievers During Pregnancy
Safe OTC pain relievers to take while pregnant are crucial for managing discomfort during pregnancy. Each trimester brings unique aches and pains, from morning sickness to backaches and headaches. Choosing the right, safe over-the-counter medication is vital for both your well-being and the health of your developing baby. This guide will explore the different types…
Ibuprofen Dosage How Much Is Safe?
Ibuprofen dosage how much you can safely take – Ibuprofen dosage: how much you can safely take is a crucial aspect of responsible pain and fever management. Understanding the appropriate dosage for both adults and children, along with potential side effects and interactions, is essential. This comprehensive guide delves into the various facets of ibuprofen…
Tylenol vs Advil for Headache Relief
Tylenol vs Advil for treating a headache is a common question for those seeking pain relief. Both are over-the-counter options, but they differ in their active ingredients and how they work. Understanding these differences can help you choose the best medicine for your headache. This comparison explores the efficacy, side effects, and safety considerations of…
Celebrex vs Ibuprofen Which Pain Reliever?
Celebrex vs ibuprofen how to decide which you should use – Celebrex vs ibuprofen: how to decide which you should use. Choosing between these common pain relievers can be tricky. Both ibuprofen and celecoxib are effective, but they work differently in the body and have varying side effects. This guide will walk you through the…
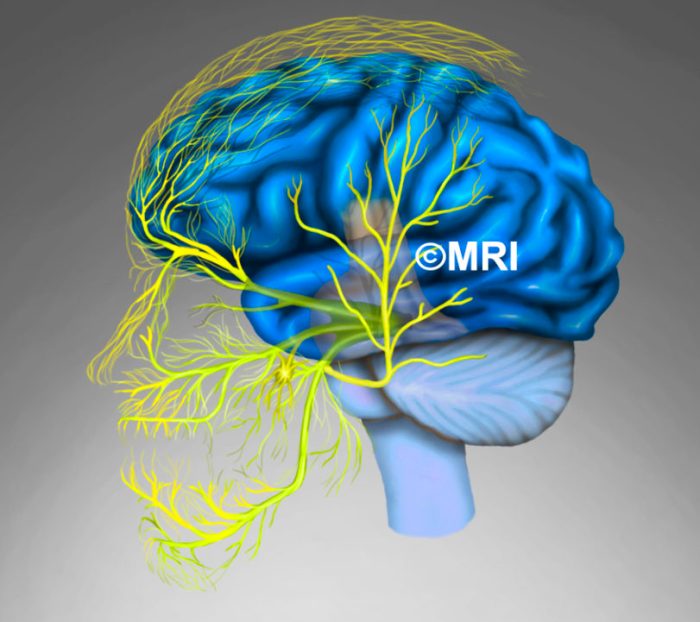
Nerve Block for Migraine A Deep Dive
Nerve block for migraine offers a potential pathway to relief from debilitating headaches. This treatment targets specific nerves believed to be contributing to migraine pain, potentially offering long-term relief or a reduction in attack frequency. Understanding the procedure, efficacy, and potential complications is crucial for informed decision-making. Let’s explore the various types of nerve blocks,…