OTC medications migraine tension are a common first line of defense against those pesky headaches. This guide delves into various over-the-counter options, from understanding their mechanisms of action to potential side effects and crucial safety precautions. We’ll also explore alternative and complementary treatments, self-management strategies, and specific considerations for different populations. Let’s navigate this world of headache relief together.
This comprehensive overview of OTC medications for migraine and tension headaches provides a practical approach to understanding these common pain relievers. We’ll cover everything from dosage guidelines to potential interactions and important safety precautions. We’ll compare different medications and discuss alternative treatment options, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your headache management.
Overview of OTC Migraine and Tension Headaches
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are often the first line of defense against migraine and tension headaches. These readily available remedies can provide relief for many individuals experiencing these common ailments. Understanding the various types of OTC medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects can empower you to make informed choices about your headache treatment.OTC pain relievers work in different ways to reduce headache pain.
Some target the inflammatory processes, while others directly impact the pain signals in the brain. Knowing the specifics of how these medications function can help you decide which might be most suitable for your individual needs. The information presented here provides a comprehensive overview of common OTC medications for migraines and tension headaches, including dosage guidelines and potential side effects.
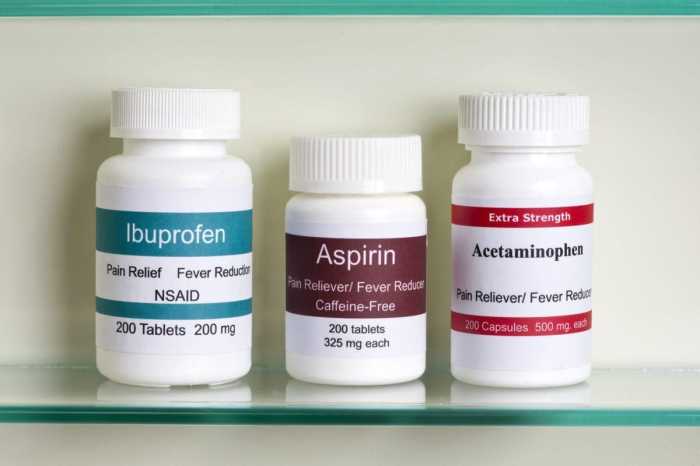
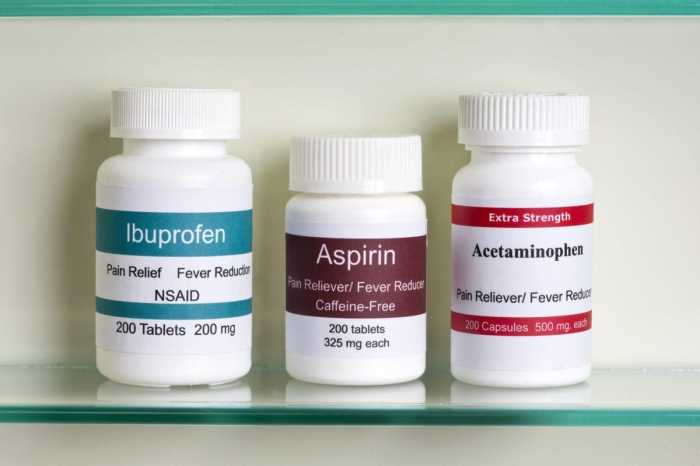
Common OTC Medications
A variety of OTC pain relievers are available for treating migraine and tension headaches. These medications typically contain active ingredients that reduce pain and inflammation. Choosing the appropriate medication often depends on individual factors such as the type of headache and the severity of symptoms.
Dosage Guidelines and Mechanisms of Action
| Medication | Dosage | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen (Tylenol) | 650 mg every 4-6 hours, up to 4 grams per day | Reduces pain signals in the brain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. It also has antipyretic (fever-reducing) properties. | Nausea, vomiting, liver damage (with excessive use), allergic reactions (rare). |
| Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) | 200-400 mg every 4-6 hours, up to 1200 mg per day | Reduces pain and inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. | Stomach upset, nausea, heartburn, allergic reactions (rare), kidney problems (with excessive use). |
| Aspirin | 325-650 mg every 4-6 hours, up to 4 grams per day | Reduces pain and inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. It also has antiplatelet effects. | Stomach upset, nausea, heartburn, bleeding (with excessive use), allergic reactions (rare), Reyes syndrome (in children). |
| Naproxen (Aleve) | 220 mg every 6-8 hours, up to 1000 mg per day | Reduces pain and inflammation by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis. | Stomach upset, nausea, heartburn, allergic reactions (rare), kidney problems (with excessive use). |
| Combination Medications (e.g., Excedrin Migraine) | Follow package directions | Contain a combination of acetaminophen, aspirin, and caffeine. Caffeine constricts blood vessels, which can reduce pain. | Potential side effects of the individual components. May cause increased heart rate or anxiety in some individuals. |
Important Considerations
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using OTC medications, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are pregnant or breastfeeding. Individual responses to medication can vary, and careful monitoring of symptoms is essential. If headaches are frequent or severe, it’s important to seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Comparison of OTC Medications: Otc Medications Migraine Tension
Deciding on the right over-the-counter (OTC) medication for a migraine or tension headache can be tricky. Different medications work in various ways and have different side effects, making personal experience and careful consideration crucial. This section delves into the comparative effectiveness of common OTC pain relievers, highlighting factors influencing medication choice and potential interactions.Understanding how various OTC medications address the root causes of these headaches is essential.
Some target inflammation, while others focus on pain signals in the brain. This understanding allows for more informed decisions about which medication might be most suitable for an individual’s specific headache type and symptoms.
Effectiveness of Different OTC Medications
Various OTC medications offer varying degrees of effectiveness for migraines and tension headaches. Ibuprofen and naproxen sodium are commonly used for both types, often providing significant pain relief for tension headaches. For migraines, these medications may not be as effective, and stronger pain relievers like acetaminophen or stronger combinations might be necessary. Acetaminophen, while effective for pain relief, may not address the underlying inflammation associated with some headaches.
Combination medications containing both acetaminophen and another pain reliever, such as ibuprofen, often provide broader pain relief.
Over-the-counter medications for tension headaches and migraines can be a lifesaver, but sometimes, it’s easy to overlook the potential risks of certain supplements. For example, while exploring natural remedies, some people consider incorporating raw milk into their diets. However, the safety and efficacy of consuming raw milk are a significant area of debate, as evidenced by resources like is raw milk safe.
Ultimately, consulting a doctor about your specific needs remains the best course of action when considering any alternative therapies for migraine relief.
Factors Influencing Medication Choice
Individual sensitivity to medications plays a critical role in choosing the right OTC pain reliever. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions or other adverse effects with certain medications. Pre-existing health conditions, such as stomach ulcers or kidney problems, can also influence the suitability of particular medications. Specific symptoms, such as throbbing pain (migraine) versus dull, persistent pain (tension), can also guide the selection.
For instance, someone experiencing throbbing pain might benefit more from a medication targeting the underlying inflammatory response associated with migraines.
Potential Interactions Between OTC Pain Relievers and Other Medications
It’s crucial to be aware of potential interactions between OTC pain relievers and other medications. Some medications, especially those affecting blood clotting or kidney function, may interact negatively with certain pain relievers. Always consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist before combining OTC pain relievers with prescription medications or supplements to avoid potential adverse effects.
Duration of Pain Relief
The duration of pain relief varies among OTC medications. Ibuprofen and naproxen sodium typically provide longer-lasting relief compared to acetaminophen. However, the duration can also depend on the individual’s response to the medication and the severity of the headache. In some cases, a second dose might be needed within a few hours if the pain persists.
Comparison Table of OTC Medications
| Medication | Effectiveness | Side Effects | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | Moderately effective for pain relief, less effective for inflammation-related headaches. | Generally well-tolerated, but can cause liver damage with excessive use. | Low |
| Ibuprofen | Effective for both migraine and tension headaches, targeting inflammation. | Potential for stomach upset, especially with prolonged use. | Moderate |
| Naproxen Sodium | Effective for both migraine and tension headaches, targeting inflammation, often longer-lasting relief. | Potential for stomach upset, increased risk of heartburn. | Moderate |
| Combination Medications (e.g., Acetaminophen and Ibuprofen) | Often more effective than individual medications due to combined mechanisms of action. | Potential for increased side effects when compared to individual medications. | Moderate to High |
Safety and Precautions
Taking over-the-counter (OTC) medications for migraine or tension headaches can be a helpful approach, but it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and precautions. Misuse or overuse of these medications can lead to serious complications. Always prioritize consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new medication regimen.Understanding the potential side effects, interactions with other medications, and contraindications is paramount to safe and effective use.
This section will delve into the important safety considerations to ensure responsible use of OTC migraine and tension headache medications.
Over-the-counter medications for tension headaches and migraines can be surprisingly helpful, but it’s important to be aware of potential interactions. For example, if you’re considering surgery, understanding how blood thinners function before, during, and after the procedure is crucial. blood thinners before during and after surgery can impact your overall health, so consulting a doctor is always recommended.
Ultimately, the best approach for managing migraine tension headaches still relies on exploring various OTC options and consulting your doctor for personalized advice.
Important Safety Precautions
Proper use of OTC medications requires awareness of potential risks. Always follow the dosage instructions carefully, and never exceed the recommended daily dose. Keep medications out of reach of children and pets. Be mindful of potential allergic reactions and promptly seek medical attention if any adverse effects arise.
Potential Risks of Overuse or Misuse
Repeated or excessive use of OTC pain relievers can lead to serious side effects. This includes the risk of developing gastrointestinal problems like ulcers or bleeding. Chronic misuse can also cause kidney damage or liver problems. Recognizing the potential for rebound headaches is also important.
Medication Interactions
Many OTC pain relievers can interact with other medications, both prescription and over-the-counter. This can significantly impact their effectiveness or potentially lead to harmful side effects. For instance, combining aspirin with blood thinners can increase the risk of bleeding. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are taking, including OTCs.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any new medication, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual health status, identify potential contraindications, and provide personalized advice on the appropriate medication and dosage. This is particularly important if you have underlying health conditions, such as liver or kidney problems.
Potential Contraindications and Warnings
- Aspirin: Avoid in individuals with a history of aspirin sensitivity or allergic reactions. It can cause stomach upset, ulcers, or bleeding. It is important to know that aspirin is not suitable for children with flu-like symptoms or chickenpox.
- Ibuprofen: Individuals with a history of gastrointestinal problems, kidney disease, or heart failure should use ibuprofen with caution and under medical supervision. Avoid in combination with other NSAIDs.
- Acetaminophen: Liver damage is a serious risk with excessive acetaminophen use. Never exceed the recommended daily dose. Be aware of potential interactions with alcohol.
- Combination Products: Products containing a combination of pain relievers may have specific warnings. Carefully review the label and consult with a healthcare professional if unsure about the suitability for your situation.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Beyond over-the-counter medications, various alternative and complementary approaches can play a role in managing migraine and tension headaches. These methods often focus on addressing the underlying causes and promoting overall well-being, rather than just treating the symptoms. While not a replacement for medical advice, they can be valuable adjuncts to existing treatment plans.These therapies aim to reduce triggers and promote relaxation, potentially offering a more holistic approach to headache management.
They may be particularly helpful for those seeking relief beyond the scope of over-the-counter pain relievers. Understanding the potential benefits and limitations of each is crucial for informed decision-making.
Natural Remedies
Natural remedies have been explored for centuries as potential headache treatments. Many individuals find relief from specific herbal supplements and dietary changes. However, it’s crucial to remember that rigorous scientific evidence for many natural remedies is still limited, and they should not be considered a substitute for conventional medical care.
- Acupressure and Acupuncture: These techniques involve applying pressure to specific points on the body (acupressure) or inserting thin needles into these points (acupuncture). Research suggests that these practices may reduce pain perception and improve blood flow, potentially alleviating headache symptoms. However, the evidence for their effectiveness in treating migraines and tension headaches is not always conclusive. Anecdotal reports often suggest benefits, but controlled studies are needed for definitive conclusions.
- Herbal Remedies: Various herbal remedies are promoted for headache relief, including feverfew, butterbur, and ginger. Feverfew, in particular, has shown some promise in reducing migraine frequency in some studies. However, the dosage and efficacy can vary greatly depending on the product and preparation. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies, as some can interact with other medications or have potential side effects.
- Dietary Changes: Diet plays a significant role in managing headaches. Certain foods and beverages, such as caffeine, alcohol, processed foods, and aged cheeses, can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals. Identifying and eliminating these triggers can significantly reduce headache frequency. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with adequate hydration, can support overall well-being and potentially mitigate headache episodes.
Lifestyle Modifications, Otc medications migraine tension
Lifestyle factors significantly influence headache frequency and severity. Implementing certain changes can lead to a noticeable reduction in symptoms.
- Stress Management Techniques: Chronic stress is a known trigger for many types of headaches. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and reduce the likelihood of headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can improve circulation and reduce muscle tension, which are often contributing factors to headaches. Regular exercise can also promote relaxation and reduce stress levels, contributing to a decrease in headache frequency. However, it’s crucial to start slowly and listen to your body.
- Adequate Sleep: Lack of sleep or inconsistent sleep patterns can significantly increase the risk of headaches. Prioritizing sufficient and quality sleep is essential for overall well-being and may contribute to a reduction in headache episodes. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule can be particularly helpful.
Combining Treatments
While alternative and complementary therapies can be beneficial, it’s crucial to remember they are not a replacement for conventional medical care. These methods can be used in conjunction with OTC medications for a more comprehensive approach to headache management. For example, someone experiencing a migraine might use an OTC pain reliever alongside stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing or mindfulness exercises.
Self-Management Strategies

Taking proactive steps to manage migraine and tension headaches is crucial for improving quality of life. By understanding triggers, implementing relaxation techniques, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of these headaches. This section delves into practical strategies for effective self-management at home.Effective headache management involves a multifaceted approach that goes beyond just medication.
Dealing with migraine tension headaches can be tough, and sometimes over-the-counter medications are just what the doctor ordered. Knowing how to manage a common cold is also helpful, as many of the same self-care strategies, like getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated, apply to both conditions. For a deeper dive into common cold self care, check out this helpful guide from Valley Ridge Health: common cold self care.
Ultimately, understanding how to treat both conditions effectively involves careful consideration of individual needs and symptoms, and a reliable resource for over-the-counter migraine medications can prove invaluable.
It requires recognizing personal triggers, developing coping mechanisms, and creating a supportive environment. This proactive approach empowers you to take control of your headaches and improve your overall well-being.
Relaxation Techniques and Stress Management
Stress is a significant contributor to both migraine and tension headaches. Implementing relaxation techniques can help reduce stress levels and prevent or alleviate headache episodes. These techniques are readily available and can be integrated into daily routines.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. This process can help release physical tension and reduce anxiety, leading to a decrease in headache frequency.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Slow, deep breathing techniques can activate the body’s relaxation response, lowering heart rate and blood pressure. This can be particularly helpful during a headache episode.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practicing mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. Meditation techniques can help quiet the mind and reduce stress, potentially lessening the occurrence of headaches.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Regular practice can contribute to a healthier lifestyle and help prevent headaches.
Importance of a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is a cornerstone of headache prevention. The choices you make daily significantly impact your overall health, influencing the frequency and intensity of headache episodes.
- Balanced Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with sufficient protein intake, can contribute to better overall health, potentially decreasing the likelihood of headaches.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps reduce stress, improves blood circulation, and promotes overall well-being, thereby potentially lessening the occurrence of headaches.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is vital for bodily functions. Dehydration can trigger or worsen headaches. Staying well-hydrated can prevent headaches.
- Sufficient Sleep: Adequate sleep allows the body to repair and restore itself. Sleep deprivation is a frequent trigger for headaches.
Creating a Headache Diary
Keeping a headache diary is a powerful tool for identifying patterns and triggers. This allows for a more personalized approach to managing headaches.A headache diary should include details about the headache, including the date, time, duration, intensity, location, and any associated symptoms. Record factors like stress levels, sleep duration, food intake, and activities. This organized record helps identify patterns, triggers, and potential remedies.
A well-maintained headache diary can significantly contribute to better self-management.
Sleep Hygiene and Hydration
Sleep and hydration are fundamental components of overall health and play a significant role in headache prevention.
- Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment can improve sleep quality. Poor sleep hygiene can be a significant headache trigger.
- Hydration: Maintaining adequate hydration by drinking sufficient water throughout the day is crucial. Dehydration can lead to headaches. Carry a water bottle and sip water regularly throughout the day.
Information for Specific Populations
Knowing which over-the-counter (OTC) medications are best suited for your unique needs and health conditions is crucial. This section delves into specific considerations for different populations, helping you make informed decisions about migraine and tension headache relief. Understanding the potential interactions and risks associated with certain medications is vital for safe and effective self-management.Taking into account factors like pre-existing conditions, concurrent medications, and age-related sensitivities is paramount when choosing OTC remedies.
This detailed analysis will equip you with the knowledge to navigate these decisions safely and effectively.
Guidance for Individuals with Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions may need to exercise caution when using OTC migraine and tension headache medications. Conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, or liver or kidney problems can interact with certain medications. Always consult your doctor before using any new medication, especially if you have pre-existing health issues.
Use in Children and Pregnant Women
Carefully consider the use of OTC medications in children and pregnant women. Children may require lower doses and different formulations than adults. Pregnant women should avoid medications whenever possible, and always consult with their healthcare provider before taking any medication during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Precautions for Individuals with Allergies
Individuals with allergies should be cautious about using OTC medications. Some medications contain ingredients that can trigger allergic reactions. Always check the label for ingredients and potential allergens before taking any medication. If you have a known allergy to a specific ingredient, do not use the medication. Severe allergic reactions require immediate medical attention.
Considerations for the Elderly
Elderly individuals may have different sensitivities to medications. Their bodies may process medications more slowly, increasing the risk of side effects. Consult a doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice. Start with the lowest effective dose and closely monitor for any adverse reactions.
Specific Considerations Table
| Population | Considerations | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions (e.g., high blood pressure, heart disease, liver/kidney problems) | Certain OTC medications may interact with existing conditions. | Consult a doctor before using any new medication. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. |
| Children | Lower doses and different formulations may be required. | Always consult a pediatrician before administering any medication to a child. Follow dosage instructions precisely. |
| Pregnant and breastfeeding women | Avoid medications whenever possible. | Consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication during pregnancy or breastfeeding. The potential risks to the developing fetus or infant must be carefully considered. |
| Individuals with allergies | Check the label for ingredients and potential allergens. | Do not use medications containing ingredients you are allergic to. Seek immediate medical attention for severe allergic reactions. |
| Elderly individuals | Medications may be processed more slowly, increasing the risk of side effects. | Start with the lowest effective dose and closely monitor for adverse reactions. Consult a doctor or pharmacist for personalized advice. |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, managing migraine and tension headaches with OTC medications requires careful consideration of individual needs and potential risks. This guide has provided a framework for understanding various options, comparing their effectiveness and side effects, and prioritizing safety. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions. By combining medication knowledge with self-care strategies, you can effectively manage your headaches and improve your overall well-being.




