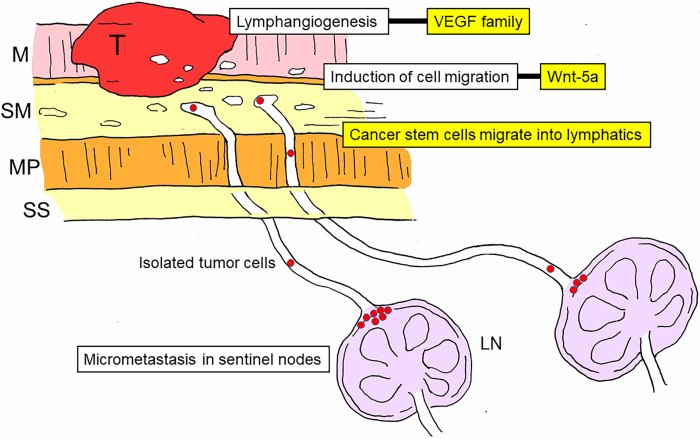
De novo metastatic breast cancer presents a unique challenge, representing breast cancer that spreads to other parts of the body from the start, without any prior evidence of local or regional spread. This contrasts with other forms of metastatic breast cancer, and understanding its distinct characteristics, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals.
This comprehensive overview delves into the complexities of this aggressive disease.
This exploration will cover the defining characteristics, potential risk factors, diagnostic processes, treatment approaches, and overall prognosis for individuals facing this diagnosis. The information presented aims to provide a clear and informative understanding of de novo metastatic breast cancer, from its early stages to ongoing research and support resources.
Defining De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer
De novo metastatic breast cancer is a particularly aggressive form of the disease, characterized by the presence of cancer spread to distant organs at the time of initial diagnosis. Understanding this distinction is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment strategies, as it significantly impacts prognosis and treatment approach compared to other breast cancer types. This form of the disease poses unique challenges for clinicians and patients alike.
Definition and Key Characteristics
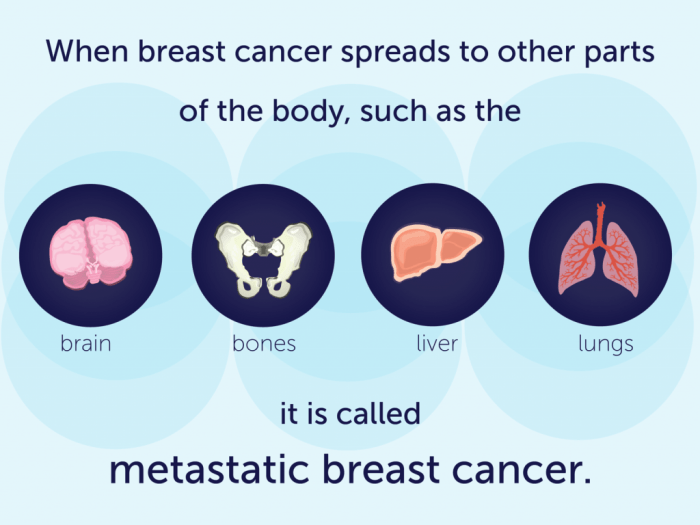
De novo metastatic breast cancer is defined as breast cancer that has spread to distant sites (like the lungs, liver, bones, or brain) at the time of initial diagnosis. Crucially, this means the cancer has already metastasized without any evidence of local or regional disease. This contrasts with other breast cancers where the tumor initially grows locally, then may eventually spread to other areas.
The absence of a detectable primary tumor in some cases further complicates diagnosis and treatment planning.
Prognostic Differences
The prognosis for de novo metastatic breast cancer tends to be less favorable than for non-de novo metastatic breast cancer. Patients with de novo disease often face a shorter time to progression and poorer overall survival rates. This is likely due to the more advanced nature of the disease at diagnosis. For example, a patient with de novo metastatic breast cancer might have a 5-year survival rate significantly lower than a patient with non-de novo metastatic breast cancer who was initially diagnosed with a localized tumor.
Role of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment play a critical role in influencing the course of the disease in all forms of breast cancer, including de novo metastatic. While early detection of the primary tumor isn’t always possible for de novo cases, prompt diagnosis and initiation of appropriate systemic therapy can still positively impact outcomes. Aggressive, multidisciplinary approaches are often necessary to maximize the chances of remission and improve quality of life.
Early detection and treatment of de novo metastatic breast cancer often involve a combination of chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and hormone therapies, tailored to the specific genetic profile of the tumor.
Comparison of De Novo vs. Non-De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer
| Presentation | Treatment Strategies | Survival Rates | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| De novo: Distant metastases present at initial diagnosis. Often no detectable primary tumor. | Aggressive systemic therapy (chemotherapy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy) tailored to tumor characteristics. Often requires close monitoring and multidisciplinary team approach. | Generally lower 5-year survival rates compared to non-de novo. Survival varies based on tumor subtype, treatment response, and patient factors. | De novo presents with immediate distant spread. Non-de novo initially involves localized disease, followed by spread. Prognosis tends to be poorer for de novo. |
| Non-de novo: Initial diagnosis of localized or regional breast cancer, followed by later metastasis. | Combination of local therapies (surgery, radiation) and systemic therapies. Treatment strategies tailored to the extent of disease at the time of metastasis. | Higher 5-year survival rates compared to de novo, as disease is often detected at an earlier stage. | Non-de novo metastasis occurs after initial diagnosis and treatment of localized disease. |
Risk Factors and Etiology
Decoding the complex tapestry of de novo metastatic breast cancer (DMBC) requires understanding the interplay of various risk factors. While the exact cause remains elusive, pinpointing potential contributors helps in targeted preventative strategies and more effective treatments. This exploration delves into the known and suspected risk factors, highlighting genetic predispositions, environmental influences, and demographic variations.
Genetic Predispositions and Family History
Inherited mutations in certain genes, particularly BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly elevate the risk of developing breast cancer, including DMBC. These mutations increase the likelihood of faulty DNA repair mechanisms, making cells more susceptible to uncontrolled growth. Family history of breast cancer, especially at a young age or in multiple family members, is a crucial indicator. Individuals with a strong family history may benefit from genetic testing to identify potential mutations and proactively manage their risk.
De novo metastatic breast cancer is a tough beast to tackle, often presenting with unusual symptoms. While the primary focus is on the cancer itself, it’s important to be aware of other potential issues that can arise. For instance, patients might experience symptoms like those associated with kidney stones, such as sharp pain in the back or side, symptoms of kidney stones can be easily confused with the cancer’s effects.
It’s crucial to maintain open communication with your healthcare team to ensure all possible causes are considered, especially in cases of de novo metastatic breast cancer.
Environmental Factors
Environmental exposures can also play a role in the development of DMBC, although the precise mechanisms are not always clear. Exposure to certain chemicals, radiation, and lifestyle factors may contribute to the disease’s progression. For example, prolonged exposure to hormone-disrupting chemicals, a diet lacking in essential nutrients, and a sedentary lifestyle may increase the risk. Further research is necessary to fully understand the intricate relationship between environmental factors and DMBC.
Prevalence of Risk Factors Across Demographics
| Risk Factor | Description | Impact | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family History of Breast Cancer | Presence of breast cancer in first-degree relatives (mother, sister, daughter). | Strong association with increased risk. | Higher frequency in families with multiple cases or early-onset breast cancer. |
| BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutations | Inherited mutations in genes responsible for DNA repair. | Significantly increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer. | Prevalence varies by ethnicity and geographic location, but estimated at ~10% of breast cancer cases. |
| Age | Increased age correlates with higher risk of breast cancer in general. | Significant correlation with overall risk, especially post-menopause. | Highest incidence in women over 50 years old. |
| Early Menarche/Late Menopause | Starting menstruation at a young age or experiencing menopause at a later age. | Increased exposure to estrogen over a longer period. | Reported to be a contributing factor, but the impact varies. |
| Obesity | Excess body fat. | Associated with elevated estrogen levels and inflammation. | Higher prevalence in certain ethnic groups and socioeconomic classes. |
The table above provides a snapshot of potential risk factors and their estimated prevalence. It’s crucial to remember that these are correlations, not definitive causes. A detailed assessment, including genetic testing and lifestyle factors, is essential for individual risk assessment.
Hierarchy of Risk Factors
While the exact ranking of risk factors is still being refined, the strongest correlations often include family history, particularly if it involves multiple family members or early-onset breast cancer. Inherited genetic mutations like BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations demonstrate a very high impact on the likelihood of DMBC. Environmental factors, while not as strongly associated, can still influence risk. Age, early menarche, and late menopause are also considered factors, but their impact can vary depending on other risk factors.
Obesity is another factor, albeit less impactful than genetic predispositions. Further research is needed to refine this hierarchy and fully understand the intricate relationship between these factors and DMBC.
Diagnosis and Staging: De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer
Navigating the complexities of de novo metastatic breast cancer requires a meticulous approach to diagnosis and staging. Early and accurate identification allows for timely intervention and personalized treatment strategies. This process involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging techniques to determine the extent of the disease.
Diagnostic Procedures
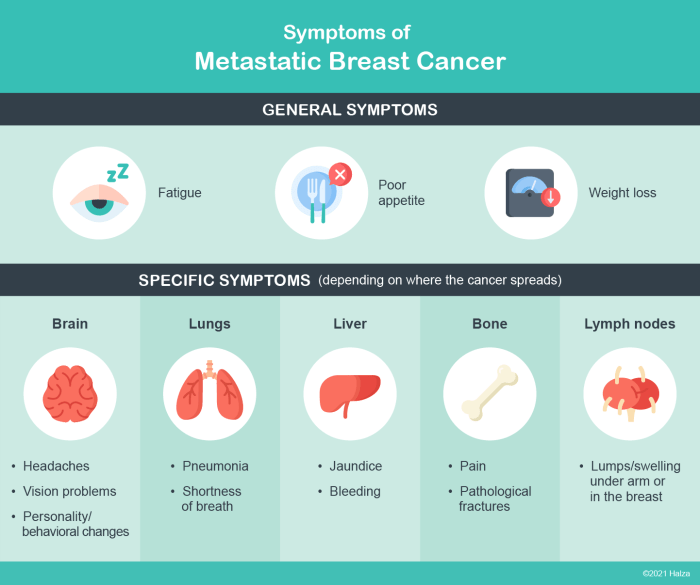
The diagnostic journey for de novo metastatic breast cancer begins with a thorough clinical evaluation. This includes a detailed patient history, focusing on symptoms, family history, and any prior breast cancer diagnoses. Physical examination is crucial to identify any palpable abnormalities, such as enlarged lymph nodes or masses in other parts of the body. Subsequent laboratory tests, such as blood tests and tumor markers, aid in assessing the disease’s progression and potential spread.
Biopsy is often required to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of breast cancer present.
Imaging Techniques
A battery of imaging techniques plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and staging de novo metastatic breast cancer. These techniques provide crucial insights into the extent of the disease and its spread to various sites. Mammography, ultrasound, and MRI are frequently used for evaluating the primary breast tumor. For detecting distant metastases, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and bone scans are commonly employed.
These scans provide detailed images of internal organs and bones, enabling identification of potential metastatic lesions.
Staging Elements
Staging involves a comprehensive assessment of the disease to determine its extent and guide treatment. Key elements considered during staging include tumor size, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastases. Tumor size is often measured in centimeters. Lymph node involvement refers to the presence of cancer cells in lymph nodes, which indicates the potential for the cancer to spread.
Distant metastases, or the presence of cancer in organs beyond the primary site, significantly impact staging and prognosis.
Flowchart of Diagnostic Process
Initial Symptoms (e.g., bone pain, unexplained weight loss, persistent cough) | v Clinical Evaluation (history, physical exam) | v Laboratory Tests (blood tests, tumor markers) | v Imaging Studies (mammography, ultrasound, MRI, CT, bone scan) | v Biopsy (if needed) | v Pathological Analysis | v Staging (tumor size, lymph node involvement, distant metastases) | v Final Diagnosis and Treatment Plan
Staging Systems
Various staging systems exist for metastatic breast cancer. These systems categorize the disease based on specific criteria, providing a standardized framework for assessing prognosis and treatment planning.
| Stage | Criteria | Characteristics | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Limited to a single organ or site, small tumor size, minimal lymph node involvement | Early-stage disease with a favorable prognosis | Targeted therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, surgery |
| Stage II | Cancer has spread to more organs or sites, or the tumor is larger, with more lymph node involvement | Intermediate-stage disease with a slightly less favorable prognosis than Stage I | Combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy |
| Stage III | Extensive spread of the cancer to multiple organs or sites, larger tumor size, extensive lymph node involvement | Advanced-stage disease with a less favorable prognosis | Combination of chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and hormonal therapy |
| Stage IV | Cancer has spread extensively to multiple organs or sites, often with a poor prognosis | Most advanced stage, with significant spread | Palliative care, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormonal therapy, and immunotherapy to manage symptoms and extend survival |
Treatment Approaches
Navigating the complexities of de novo metastatic breast cancer requires a multifaceted approach. Treatment strategies are tailored to individual patient needs, considering factors like the specific subtype of breast cancer, the extent of metastasis, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. A collaborative effort between oncologists, surgeons, and other healthcare professionals is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Treatment for de novo metastatic breast cancer aims to shrink tumors, control disease progression, and improve quality of life. This often involves a combination of therapies, carefully chosen and monitored to maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects. Understanding the nuances of these therapies is essential for informed decision-making.
Standard Treatment Options
Standard treatment options for de novo metastatic breast cancer typically involve a combination of therapies. The initial approach often includes chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and/or hormonal therapies. The specific combination and duration of treatment are determined based on the individual’s tumor characteristics and overall health.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs work by targeting rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells. This approach can be highly effective in shrinking tumors and reducing the spread of disease. Common chemotherapy regimens for metastatic breast cancer include anthracyclines, taxanes, and others. The selection of chemotherapy agents and the specific regimen are based on the tumor’s characteristics and the patient’s overall condition.
For instance, a patient with a HER2-positive tumor might receive a regimen that includes a targeted therapy in addition to chemotherapy. The potential side effects of chemotherapy, such as nausea, hair loss, and fatigue, can be managed with supportive care.
Targeted Therapies
Targeted therapies are designed to specifically target certain molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth. These therapies can be effective in treating specific types of breast cancer, such as those driven by mutations in the HER2 receptor or in other pathways. Examples of targeted therapies include trastuzumab (Herceptin) for HER2-positive tumors and others for specific genetic mutations. These therapies may be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy or hormonal therapies.
De novo metastatic breast cancer is a tough diagnosis, and finding ways to boost your overall well-being is crucial during treatment. While there’s no magic bullet, exploring different lifestyle choices can be helpful. For example, some people find that incorporating cold showers into their routine can be beneficial for stress reduction and general health, as detailed in this helpful article about are cold showers good for you.
Ultimately, it’s essential to remember that everyone’s journey with de novo metastatic breast cancer is unique, and personalized approaches to health and wellness are key.
Side effects can vary depending on the specific drug and the individual patient.
Hormonal Therapies
Hormonal therapies are often effective for hormone receptor-positive breast cancers. These therapies work by blocking the hormones that fuel the growth of these tumors. Examples include tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors, and others. The choice of hormonal therapy depends on factors like the patient’s menopausal status and the specific hormone receptors present in the tumor. These therapies may be used as initial therapy, in combination with other therapies, or as a maintenance therapy.
Side effects of hormonal therapies can include hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and others.
Combination Therapies
Combination therapies, which involve using two or more different types of treatment simultaneously, are frequently employed in treating de novo metastatic breast cancer. These combinations can increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the risk of resistance to single-agent therapies. For instance, a combination of chemotherapy and a targeted therapy might be more effective than either therapy alone.
The decision to use combination therapy is made based on the patient’s specific tumor characteristics and overall health. Careful monitoring of side effects is essential in these cases.
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects of cancer treatments is a critical aspect of patient care. A multidisciplinary approach involving oncologists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals is often employed to develop individualized strategies for managing side effects. These strategies can include supportive care, medications to alleviate specific symptoms, and lifestyle adjustments. For example, nausea can be managed with antiemetic medications, while fatigue can be addressed through lifestyle modifications and supportive care.
Regular communication between the patient and their healthcare team is vital to ensure optimal symptom management.
Comparing Treatment Regimens
Treatment regimens for de novo metastatic breast cancer are tailored to individual patients. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, including the tumor’s characteristics (hormone receptor status, HER2 status, genetic mutations), the extent of metastasis, and the patient’s overall health. A detailed discussion with the patient’s oncologist is necessary to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. Clinical trials are also important sources of information on new and emerging therapies.
Comparison tables, while helpful, should be discussed with a physician to understand the nuances of each treatment approach and how it applies to the specific patient’s situation.
De novo metastatic breast cancer is a tough beast, isn’t it? One aspect often overlooked is the impact of diet. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including avoiding foods high in sodium, like processed foods and some restaurant meals , could potentially play a role in managing the disease. It’s a complex area, and more research is needed, but taking steps towards a balanced diet is definitely worth considering in the fight against de novo metastatic breast cancer.
Prognosis and Survival
Navigating the landscape of de novo metastatic breast cancer (MBC) is challenging, but understanding prognosis and survival is crucial for patients and their families. While the diagnosis can be daunting, advancements in treatment and supportive care are improving outcomes and quality of life. A personalized approach tailored to each patient’s specific tumor characteristics and overall health is vital.
Current Prognosis and Survival Rates
The prognosis for de novo MBC varies significantly. Factors such as the stage of the disease at diagnosis, the specific type of breast cancer, the patient’s age, and overall health play a crucial role. While there’s no single answer, current estimates suggest that survival rates depend on the individual’s circumstances. Some studies have shown 5-year survival rates ranging from 10-30% depending on the factors mentioned.
It’s important to note that these are general averages, and individual experiences differ widely.
Factors Influencing Survival Outcomes
Several factors influence survival outcomes for patients with de novo MBC. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and personalized care plans.
- Tumor characteristics: The specific subtype of breast cancer, the presence of hormone receptors, HER2 status, and the extent of the tumor’s spread at diagnosis are critical. For example, patients with hormone receptor-positive tumors might have slightly better outcomes compared to those with triple-negative breast cancer.
- Patient characteristics: Age, overall health, comorbidities, and the patient’s response to treatment all impact survival. A patient with a pre-existing cardiovascular condition, for example, may face different challenges in tolerating certain chemotherapy regimens compared to a younger patient with no significant health issues.
- Treatment approach: The choice and efficacy of treatment protocols, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, hormone therapy, and surgery, play a pivotal role. Access to advanced treatment options and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen are key components of successful outcomes.
Examples of Successful Outcomes and Interventions
Successful outcomes in de novo MBC often involve a combination of factors. While complete remission is rare, achieving prolonged periods of stable disease and improved quality of life are achievable goals.
- Targeted therapies: For patients with HER2-positive breast cancer, targeted therapies like trastuzumab have shown remarkable success in extending survival time and controlling the progression of the disease. This is particularly evident in cases where the therapy is incorporated into a multi-pronged approach involving chemotherapy and other supportive interventions.
- Immunotherapy: Emerging immunotherapy approaches show promise in some patients, particularly those with specific tumor characteristics. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the effectiveness of immunotherapies in conjunction with other treatments to improve outcomes.
- Early detection and aggressive treatment: While not always possible in de novo cases, early diagnosis and swift, multidisciplinary treatment strategies are essential for potentially extending survival and improving the quality of life. The involvement of specialists in oncology, radiology, and surgical oncology is crucial in these cases.
Challenges in Improving Outcomes
Despite advancements, challenges remain in improving outcomes for patients with de novo MBC.
- Resistance to treatment: Tumor cells can develop resistance to various therapies, necessitating a continuous search for novel treatment strategies.
- Heterogeneity of the disease: The diverse nature of breast cancer subtypes and their varied responses to treatments create challenges in tailoring effective therapies.
- Late-stage diagnosis: The diagnosis of MBC often occurs at a later stage, which negatively impacts the effectiveness of treatment. This underscores the importance of early detection and awareness.
Role of Supportive Care in Improving Quality of Life
Supportive care plays a vital role in improving the quality of life for patients with de novo MBC. This involves addressing physical, emotional, and social needs.
- Palliative care: Palliative care focuses on providing comfort and managing symptoms related to the disease and its treatment, including pain management and emotional support.
- Nutritional counseling: Nutritional support can help maintain strength and well-being, especially during treatment. This often involves managing side effects of treatment and maintaining a healthy diet.
- Mental health support: Dealing with a life-threatening illness can be emotionally challenging. Mental health support, such as counseling and support groups, is crucial for managing stress, anxiety, and depression.
Research and Future Directions
Unraveling the complexities of de novo metastatic breast cancer (DMBC) demands a multifaceted approach, encompassing meticulous research, innovative clinical trials, and a deep understanding of the disease’s underlying mechanisms. The relentless pursuit of effective treatments and improved outcomes hinges on a continuous cycle of investigation and adaptation. The need for new therapeutic strategies is urgent, given the limited options currently available for this aggressive subtype.
Latest Research Trends
Recent research into DMBC has focused on identifying molecular signatures and genetic alterations that distinguish it from other forms of breast cancer. These studies aim to understand the unique biological pathways driving the early and rapid metastasis in DMBC patients. Researchers are investigating the role of specific gene mutations, epigenetic modifications, and immune responses in the development and progression of this aggressive disease.
For example, studies have shown that certain mutations in the tumor suppressor gene, BRCA1, may be more prevalent in DMBC cases compared to other subtypes.
Promising Areas of Investigation
Several promising areas of investigation are emerging. One area focuses on developing targeted therapies that specifically inhibit the growth and spread of DMBC cells based on identified molecular drivers. Immunotherapy approaches are also being explored, aiming to harness the body’s immune system to fight the cancer cells. Further research is needed to determine the most effective combination therapies for DMBC.
Another area of interest is the identification of predictive biomarkers that can identify patients at high risk of developing DMBC early on, enabling preventative strategies and timely interventions.
Clinical Trial Imperative
The need for well-designed clinical trials is paramount to translate research findings into effective treatments. These trials should investigate the efficacy and safety of novel therapies, including targeted agents, immunotherapies, and combination regimens. Trials should also evaluate the use of predictive biomarkers to select patients most likely to benefit from specific therapies. The inclusion of diverse patient populations in clinical trials is critical to ensure that the results are generalizable and applicable to a broader range of individuals.
Furthermore, long-term follow-up studies are essential to assess the long-term efficacy and potential side effects of new treatments.
Future Research Directions
Future research should focus on understanding the early stages of DMBC development, identifying the specific molecular pathways driving metastasis, and developing more personalized treatment strategies. The development of liquid biopsies for early detection and monitoring of DMBC is also a critical area for research. Furthermore, exploration of novel combinations of existing therapies and new targeted agents hold great promise for improving outcomes.
The development of effective prevention strategies, including lifestyle modifications and screening protocols, is also an important area for future investigation.
Summary Table of Key Research Findings and Ongoing Trials
| Research Area | Findings | Implications | Future Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Characterization | Identification of unique genetic profiles and signaling pathways in DMBC | Potential for developing targeted therapies and personalized treatment strategies | Further research to identify predictive biomarkers and optimize therapeutic targets |
| Immunotherapy | Early success in some patients, but further investigation required for wider application | Immunotherapy could be a valuable addition to treatment regimens | Development of combination therapies and exploration of immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| Targeted Therapies | Some success in inhibiting specific molecular pathways | Potential for more effective and less toxic treatments | Combination therapies and tailoring therapies based on individual genomic profiles |
| Early Detection | Development of liquid biopsies and other non-invasive diagnostic methods | Improved ability to detect DMBC at earlier stages | Large-scale clinical trials to validate diagnostic accuracy and impact on survival |
Patient Experiences and Support
Facing a de novo metastatic breast cancer diagnosis is incredibly challenging, impacting not only physical health but also emotional and psychological well-being. The uncertainty surrounding treatment options, the potential for long-term side effects, and the emotional toll on patients and their families are significant factors to consider. Navigating this journey requires access to comprehensive support systems.
The emotional and psychological impact of this diagnosis is multifaceted. Patients may experience feelings of fear, anxiety, anger, and despair. The diagnosis often disrupts daily life, relationships, and career plans. The knowledge that the disease has spread beyond its initial site can be devastating, creating a sense of helplessness and loss of control. Moreover, the emotional distress can extend to family members who are deeply affected by witnessing the patient’s struggle.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
The emotional and psychological distress associated with de novo metastatic breast cancer is significant. Patients may experience a wide range of feelings, from fear and anxiety to grief and despair. The uncertainty surrounding treatment options, the potential for long-term side effects, and the emotional toll on patients and their families are all crucial factors to address. Furthermore, the diagnosis can lead to social isolation as patients may struggle to maintain relationships and social connections.
Understanding and acknowledging these emotional responses is essential for effective support and care.
Resources Available to Support Patients and Families, De novo metastatic breast cancer
Numerous resources are available to support patients and families coping with de novo metastatic breast cancer. These resources can provide crucial emotional support, practical guidance, and information about available treatment options.
- Support Groups: Support groups offer a safe space for patients to connect with others facing similar experiences. Sharing stories, coping mechanisms, and experiences can provide invaluable emotional support and reduce feelings of isolation. Many local cancer centers and community organizations host support groups specifically for breast cancer patients. Online support groups can also be beneficial, connecting patients across geographical boundaries.
- Counseling and Therapy: Professional counseling and therapy can help patients and families navigate the emotional challenges of the disease. Therapists can provide coping strategies, emotional support, and guidance in adjusting to the changes brought about by the diagnosis. Mental health professionals specializing in cancer care are often available through hospitals and community centers.
- Financial Assistance Programs: Financial burdens can add to the stress of a cancer diagnosis. Many organizations offer financial assistance programs to help patients and families cover medical expenses, travel costs, and other related financial needs. Information about these programs can be found through local cancer centers and social work departments.
Examples of Support Groups and Community Resources
Numerous support groups and community resources exist to assist patients and families. These vary greatly in format and location, but often provide valuable emotional support and practical assistance. Examples include:
- Local Cancer Centers: Many cancer centers have dedicated support groups, workshops, and educational programs for patients and their families. These centers typically offer a range of services, including counseling, support groups, and access to specialists.
- Community-Based Organizations: Local organizations often organize support groups and events to connect patients and their families. These organizations often have volunteers and trained staff who can provide emotional support and practical assistance. They often partner with local healthcare providers.
- Online Forums and Support Communities: Online platforms dedicated to breast cancer patients and their families provide a virtual space for support and connection. These online communities can offer valuable insights and support, allowing patients to connect with others who understand their experiences.
Patient Perspectives
“The diagnosis was devastating. But connecting with other patients in the support group was incredibly helpful. Knowing I wasn’t alone and hearing about others’ journeys gave me strength and hope.”
– Jane Doe, Breast Cancer Survivor
Importance of Emotional Support
Providing emotional support is crucial in the journey of a patient with de novo metastatic breast cancer. It involves acknowledging the patient’s emotions, listening without judgment, and offering practical assistance when needed. Recognizing and addressing the emotional needs of patients and their families is essential for promoting well-being and fostering a supportive environment. This support extends beyond medical care to encompass the psychological and social aspects of the patient’s life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, de novo metastatic breast cancer is a formidable challenge, demanding a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment. While the prognosis can be challenging, ongoing research and evolving treatment strategies are offering hope for improved outcomes. Ultimately, understanding this unique form of breast cancer, including its risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, is essential for providing the best possible care and support to those affected.