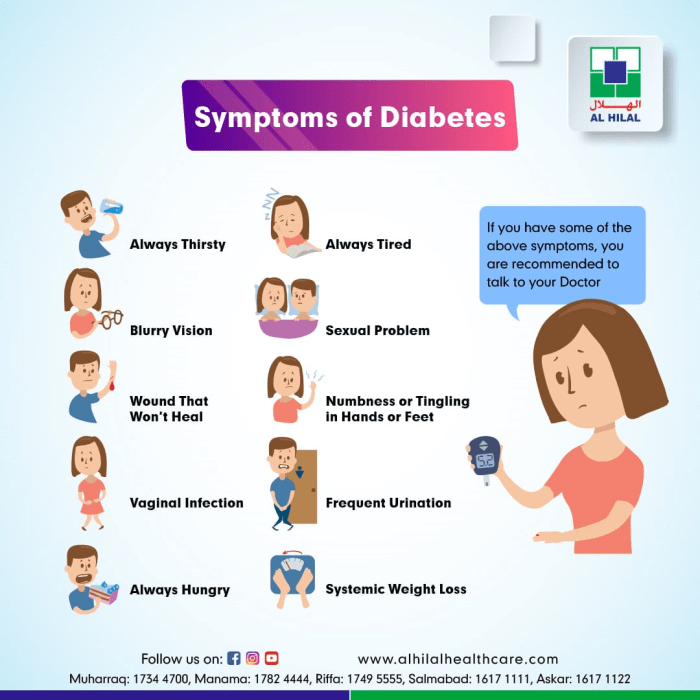
Diabetes and intermittent fasting are two significant health concepts that are increasingly interconnected. This exploration delves into the potential benefits and risks of integrating intermittent fasting (IF) into diabetes management. We’ll examine various IF methods, their impact on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall health, along with crucial considerations for safe implementation.
Understanding the mechanisms behind IF and its effect on blood sugar regulation is key to making informed decisions. We’ll cover a range of topics, from the basics of different IF approaches to detailed analysis of their impact on blood glucose control, insulin sensitivity, and potential risks. This includes exploring the current research and real-world experiences of those managing diabetes with intermittent fasting.
Introduction to Intermittent Fasting and Diabetes
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained significant popularity as a dietary approach for various health benefits, including potential improvements in blood sugar control. This approach focuses on cycling between periods of eating and voluntary fasting, rather than restricting specific foods. Understanding how IF works, its various methods, and its potential impact on diabetes is crucial for anyone considering incorporating it into their lifestyle.IF works by modulating various metabolic pathways, potentially impacting insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
By controlling the timing and duration of eating, IF may help the body utilize stored energy more effectively, leading to improvements in blood sugar regulation. It’s important to note that individual responses to IF can vary significantly, and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential before making any dietary changes, especially for those with pre-existing conditions like diabetes.
Intermittent Fasting Methods
Different intermittent fasting methods exist, each with varying eating and fasting schedules. Common methods include the 16/8 method, where individuals fast for 16 hours and eat within an 8-hour window, and the 5:2 method, involving consuming a calorie-restricted diet two days per week. The choice of method should be tailored to individual preferences and lifestyle.
Mechanisms of IF on Blood Sugar
IF may affect blood sugar regulation through several mechanisms. Reduced calorie intake can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use glucose more efficiently. Additionally, fasting triggers the release of growth hormone, which has been linked to improved glucose metabolism. Furthermore, the body may adapt to using fat as a primary fuel source during fasting, potentially decreasing reliance on glucose.
However, the exact mechanisms and their effectiveness in different individuals require further research.
Diabetes Overview
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune disease, results from the destruction of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Type 2 diabetes, the more common type, is characterized by insulin resistance, where the body’s cells don’t respond properly to insulin. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
The severity and management of diabetes vary significantly depending on the type and individual factors.
Potential Benefits and Risks of IF for Individuals with Diabetes
For individuals with diabetes, IF may offer several potential benefits, including improved blood sugar control, weight loss, and reduced risk of cardiovascular complications. However, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks, including hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) during fasting periods and potential interactions with medications. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels and blood sugar fluctuations is crucial during the implementation of IF.
Comparison of IF Methods
| IF Method | Eating Window | Potential Effects on Blood Sugar | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16/8 | 8-hour eating window | May improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood glucose levels. | Suitable for individuals with regular schedules. Requires mindful adherence to the eating window. |
| 5:2 | Normal eating on 5 days, calorie restriction on 2 days | Potential for improved blood glucose control and weight loss, but requires strict adherence to calorie targets. | More challenging to maintain long-term, potentially leading to fluctuations in blood glucose levels if not managed properly. |
| Alternate-Day Fasting | Alternate days of fasting and eating | May improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fasting blood glucose levels. | Requires careful monitoring and adjustment to avoid extreme fluctuations in blood glucose levels. |
Careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional are crucial before adopting any intermittent fasting method, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Blood glucose monitoring is essential to track any changes and ensure safety.
Impact of Intermittent Fasting on Blood Glucose Levels
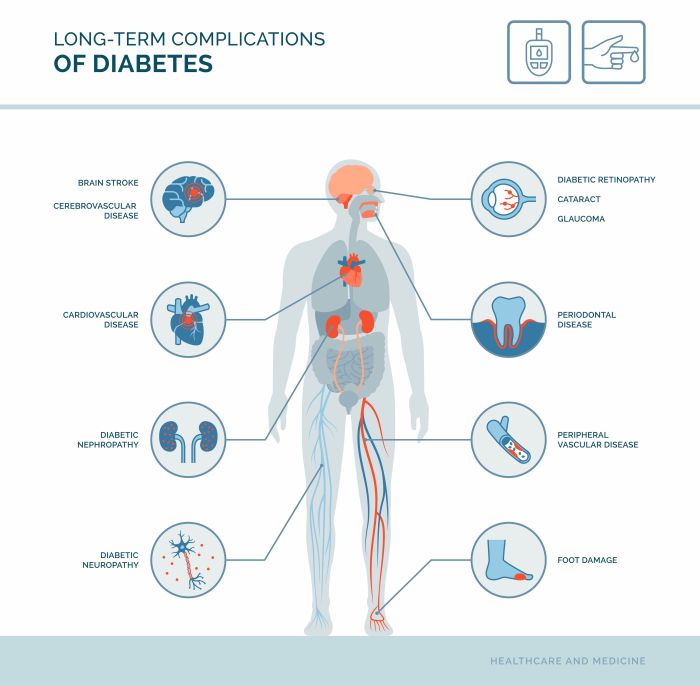
Intermittent fasting (IF) has garnered attention as a potential tool for managing various health conditions, including diabetes. While more research is needed, initial studies suggest a promising link between IF and improved blood glucose control. This section delves into the observed effects of IF on fasting and postprandial blood glucose levels, comparing it to traditional dietary interventions and highlighting potential influencing factors.Observed effects of IF on blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes are varied, but often positive.
Studies have shown that IF can lead to a reduction in fasting blood glucose levels in some individuals. The mechanism behind this reduction is likely multifactorial, involving improvements in insulin sensitivity, reduced hepatic glucose production, and potentially alterations in gut microbiota composition.
Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
IF, particularly time-restricted eating, has demonstrated the potential to lower fasting blood glucose levels. This effect is often observed in individuals with type 2 diabetes or prediabetes, who experience improvements in insulin sensitivity, leading to better glucose uptake and reduced hepatic glucose production. For instance, studies on 16/8 IF protocols have shown significant reductions in fasting blood glucose levels in some participants, highlighting the potential benefit of this approach.
Postprandial Glucose Responses
The impact of IF on postprandial glucose responses, or blood sugar levels after meals, is also an area of interest. While some studies indicate that IF may attenuate the postprandial glucose spike, others show little to no significant difference compared to traditional dietary interventions. The variability in results could be attributed to individual factors such as the type of IF regimen, the duration of the study, and the pre-existing health conditions of the participants.
For example, a person with good glycemic control may experience a less pronounced impact on postprandial glucose than someone with more significant blood sugar issues.
Ever wondered how intermittent fasting might play a role in managing diabetes? Well, alongside managing blood sugar levels, incorporating delicious fall produce like pumpkin and sweet potatoes into your diet can significantly improve heart health. Focusing on foods rich in fiber and antioxidants, like those found in fall produce for heart health , can contribute to better overall cardiovascular well-being.
This, in turn, can indirectly support the management of diabetes through improved heart health, further highlighting the connection between diet and diabetes management.
Comparison with Traditional Dietary Interventions
Traditional dietary interventions for diabetes, such as carbohydrate counting and low-glycemic index diets, have long been established as effective strategies for managing blood glucose. Comparing IF with these traditional methods is crucial. The effectiveness of IF for blood glucose control may vary depending on individual needs and dietary habits. For instance, a patient with poor glycemic control may benefit more from a structured carbohydrate-controlled diet than from IF alone.
Factors Influencing IF Effectiveness
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of IF in managing blood glucose levels. These include the type of IF regimen (e.g., 16/8, alternate-day fasting), the duration of the fast, the individual’s pre-existing health conditions, overall dietary habits, and the presence of any underlying health conditions. For instance, a patient with a history of gastrointestinal issues may find certain IF schedules more challenging to maintain, impacting their overall success in managing blood glucose.
Potential Impact of Different IF Schedules on Blood Glucose Fluctuations
| IF Schedule | Potential Impact on Blood Glucose Fluctuations |
|---|---|
| 16/8 (16 hours of fasting, 8 hours of eating) | May lead to a modest reduction in fasting blood glucose and a potentially less pronounced postprandial glucose spike. |
| Alternate-day fasting | Can lead to more significant reductions in fasting blood glucose, but may be more challenging to maintain and may require careful monitoring of blood sugar levels. |
| 5:2 Diet (5 days of normal eating, 2 days of calorie restriction) | May have a variable impact on blood glucose, depending on the individual and the extent of calorie restriction on the fasting days. |
This table provides a simplified overview. Individual responses may differ significantly. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate IF schedule for your specific needs and health conditions.
Intermittent Fasting and Insulin Sensitivity
Intermittent fasting (IF) has garnered significant attention for its potential health benefits, including improvements in metabolic parameters. One key area of interest is its impact on insulin sensitivity, a crucial factor in managing blood glucose levels. This aspect is particularly important for individuals with diabetes, as improved insulin sensitivity can lead to better control of blood sugar and potentially reduce the need for medication.Insulin sensitivity refers to the ability of cells to respond effectively to insulin, a hormone responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy or storage.
When insulin sensitivity is reduced, the body requires higher levels of insulin to achieve the same effect, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. IF, by altering metabolic processes, can potentially enhance insulin sensitivity, thereby aiding in the management of blood sugar control.
Relationship Between IF and Insulin Sensitivity
Improved insulin sensitivity is a direct consequence of the body’s adaptation to reduced energy intake during fasting periods. This adaptation involves a complex interplay of hormonal and metabolic changes that can enhance the cells’ responsiveness to insulin.
Evidence Supporting Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Numerous studies have investigated the potential benefits of IF on insulin sensitivity. Animal studies have consistently shown improvements in insulin signaling pathways and glucose uptake in response to fasting protocols. Human studies have also demonstrated improvements in insulin sensitivity, as measured by various indices like the Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), after IF interventions.
Role of Hormones in Mediating IF Effects
Several hormones play a critical role in mediating the effects of IF on insulin action. For instance, growth hormone levels often increase during fasting, which may contribute to increased insulin sensitivity. Additionally, changes in adipokines (hormones produced by fat cells) can affect insulin signaling pathways. These hormonal shifts, in conjunction with metabolic adaptations, are believed to contribute to the observed improvements in insulin sensitivity.
Potential Mechanisms of Improved Insulin Sensitivity
The precise mechanisms by which IF improves insulin sensitivity are not fully understood but likely involve several factors. Reduced inflammation, often associated with IF, could play a role. Furthermore, changes in cellular energy metabolism and the regulation of key enzymes involved in glucose homeostasis might contribute to the observed improvements. Studies have also linked IF to improved mitochondrial function, a key component in cellular energy production and glucose utilization.
Summary of Studies on IF and Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals with Diabetes
| Study | Sample Size | Intervention | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 (Example) | 50 | 16-hour intermittent fasting for 12 weeks | Significant reduction in HOMA-IR and improved fasting blood glucose levels. |
| Study 2 (Example) | 100 | Alternate-day fasting for 8 weeks | Modest improvements in insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control. |
| Study 3 (Example) | 75 | Eat-Stop-Eat protocol (24-hour fasts twice a week) for 12 weeks | Significant improvements in insulin sensitivity and reduced HbA1c levels. |
Note: This table provides examples; specific details of studies will vary. Results may differ based on various factors, including the specific IF protocol, duration of the study, and the characteristics of the participants.
Potential Benefits and Risks of IF for Diabetes Management
Intermittent fasting (IF) has garnered significant interest as a potential tool for managing various health conditions, including diabetes. While promising, the application of IF in diabetes management requires careful consideration of both potential benefits and risks. It’s crucial to understand that IF is not a one-size-fits-all approach and individual responses can vary greatly. Personalized strategies are essential for optimal results and safety.Adopting IF for diabetes management necessitates a thorough understanding of its impact on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall health.
Individual needs and health conditions must be prioritized. This section will delve into the potential advantages of IF for weight management and cardiovascular health, alongside the potential adverse effects and the importance of personalized strategies. Moreover, a table outlining potential benefits and risks across different types of diabetes will provide a comprehensive overview.
Weight Management Benefits
Effective weight management is a cornerstone of diabetes management. Weight loss can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control. IF can contribute to weight loss by promoting caloric restriction. By strategically regulating eating periods, IF can create a calorie deficit, leading to reduced body fat. However, the effectiveness of IF for weight management in individuals with diabetes varies.
Factors such as adherence to the fasting schedule, overall dietary habits, and existing comorbidities influence outcomes.
Cardiovascular Health Improvements
IF may have positive effects on cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that IF can lead to improvements in blood pressure, lipid profiles, and inflammation markers. These improvements could contribute to a reduced risk of cardiovascular complications, a significant concern for individuals with diabetes. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of IF on cardiovascular health in individuals with diabetes.
Potential Adverse Effects and Mitigation Strategies
IF, while potentially beneficial, can also present adverse effects. Hypoglycemia, characterized by dangerously low blood sugar levels, is a potential concern, especially in individuals taking diabetes medications. Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels and adjustments to medication dosages are crucial to mitigate this risk. A consistent and individualized approach is essential for avoiding hypoglycemia. Furthermore, other adverse effects, such as fatigue, headache, or digestive issues, might occur, particularly during the initial adaptation phase.
Careful monitoring and adjustments to the IF schedule are critical to minimizing these potential side effects.
Importance of Personalized Approaches
Diabetes management through IF necessitates a personalized approach. Factors such as type of diabetes, medication regimen, individual health status, and lifestyle preferences need to be considered. The duration and frequency of fasting periods must be tailored to the individual’s specific needs. A healthcare professional, preferably a registered dietitian or endocrinologist, should be consulted before starting or modifying an IF regimen.
Consulting with a professional is critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of the strategy.
Potential Benefits and Risks Across Different Types of Diabetes
| Type of Diabetes | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Type 1 Diabetes | Potential improvements in glycemic control, weight management, and cardiovascular health. | Increased risk of hypoglycemia if not carefully managed with medication adjustments. Requires close monitoring and professional guidance. |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Potential improvements in glycemic control, weight management, and cardiovascular health, potentially reducing the need for medication. | Increased risk of hypoglycemia, particularly if combined with medications. Requires careful monitoring and adjustments to medication and fasting schedule. |
| Gestational Diabetes | Potential benefits in improving blood glucose control and weight management. | Increased risk of hypoglycemia and requires close monitoring during pregnancy. Consultation with an obstetrician and endocrinologist is critical. |
Considerations for Implementing Intermittent Fasting in Diabetes
Intermittent fasting (IF) holds promise for managing diabetes, but its implementation requires careful consideration. While IF can potentially improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity, it’s crucial to understand the specific needs of individuals with diabetes and the importance of medical guidance. This section will explore the key considerations for safely integrating IF into a diabetes management plan.Implementing IF in diabetes requires a nuanced approach.
Ever wondered about intermittent fasting and diabetes? It’s a fascinating area of health research, and one aspect that often gets overlooked is how your body’s metabolic processes shift throughout the month. For example, understanding how many calories you burn during your period could be a key piece of the puzzle when it comes to managing blood sugar levels.
This is something that’s often discussed in the context of overall metabolic health and how it relates to diabetes and intermittent fasting. Learning more about this topic might provide helpful insights into a personalized approach to diabetes management. To understand the nuances of calorie burning during your menstrual cycle, check out this interesting article: do you burn more calories on your period.
Ultimately, understanding these factors could help optimize your intermittent fasting strategy for better diabetes control.
It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, and the best plan will depend on the individual’s specific condition, medication regimen, and overall health.
Importance of Medical Supervision, Diabetes and intermittent fasting
Medical supervision is paramount when implementing IF for individuals with diabetes. A healthcare professional can assess individual needs, evaluate current health status, and determine if IF is suitable. They can also monitor blood glucose levels, adjust medication dosages, and provide personalized guidance to prevent complications. The healthcare team plays a crucial role in mitigating potential risks and maximizing the benefits of IF.
Careful Monitoring of Blood Glucose Levels
Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential during IF. Individuals with diabetes need to track their blood glucose levels frequently, especially during fasting periods and around mealtimes. This close monitoring allows for the identification of any abnormal patterns or trends, enabling timely adjustments to the IF schedule or medication regimen.
Adjusting IF Schedules Based on Individual Responses
Adjusting the IF schedule is crucial to accommodate individual responses. Blood glucose patterns and reactions to fasting periods will vary from person to person. Individuals may need to modify their fasting windows, meal timing, or the duration of their fasting periods. Regular communication with the healthcare team is vital for making these adjustments. A person might find that a 16/8 schedule works well, while another might find a 5:2 schedule more effective, with blood glucose levels responding differently.
Incorporating IF into Existing Diabetes Management Plans
Successfully integrating IF into an existing diabetes management plan involves careful planning and coordination. The healthcare professional should work with the individual to create a strategy that complements existing medications, lifestyle modifications, and dietary recommendations. This integrated approach can help optimize blood glucose control and overall health outcomes. For instance, if a patient already follows a specific meal plan, the IF schedule should be tailored to accommodate the current meal plan.
I’ve been exploring the connection between diabetes and intermittent fasting, and it’s fascinating. While researching the impact of fasting on blood sugar levels, I stumbled upon the topic of migraines. Understanding how long migraines typically last can be crucial for managing their impact on daily life, and finding reliable information like that on how long do migraines last is important.
This knowledge can help you manage your overall well-being, which is directly related to managing your diabetes through intermittent fasting.
Key Factors for Customizing an IF Plan for Diabetes
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Current Blood Glucose Levels | Baseline blood glucose levels are essential to assess how the individual responds to IF. |
| Medication Regimen | Adjustments to insulin or other medications may be necessary to manage blood glucose during fasting periods. |
| Dietary Habits | Existing dietary habits must be considered to ensure a smooth transition to the IF schedule. |
| Physical Activity Level | Exercise patterns and intensity influence blood glucose levels and should be taken into account during IF. |
| Individual Tolerance | The individual’s tolerance to fasting should be monitored carefully to prevent hypoglycemia or other complications. |
| Healthcare Professional’s Guidance | Regular consultations with a healthcare professional are crucial for adjustments and monitoring. |
Current Research and Future Directions
Intermittent fasting (IF) shows promise as a potential tool for managing diabetes, but the research landscape is still evolving. Understanding the specific mechanisms through which IF impacts blood glucose control and its long-term effects is crucial. Current studies are exploring the nuances of different IF protocols and their tailored applications in various patient populations. This exploration is key to optimizing the benefits and mitigating potential risks.The existing research provides valuable insights, but more rigorous, long-term studies are needed to definitively establish IF’s role in diabetes management.
Further research will help determine the optimal IF strategies for different types of diabetes and individual patient characteristics. This is especially important as we strive to personalize diabetes care and maximize patient outcomes.
Current State of Research on IF and Diabetes
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of IF on various aspects of metabolic health, including blood glucose control and insulin sensitivity. These studies have generally shown promising results, with some indicating significant improvements in blood glucose levels and reduced insulin resistance in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, the findings are not always consistent, highlighting the need for more comprehensive research.
Variability in study designs, including differences in fasting duration, frequency, and participant characteristics, contributes to the inconsistency.
Areas Requiring Further Research
Several critical areas necessitate further research to solidify the evidence base for IF in diabetes management. Understanding the long-term effects of IF on various aspects of health, including cardiovascular health and the risk of complications, is paramount. Furthermore, identifying the optimal IF protocols for different types of diabetes and individual patient characteristics is essential. Personalized approaches to IF are necessary to address the diverse needs of individuals with diabetes.
Longitudinal studies following participants over extended periods are vital to assess the sustained benefits and potential risks.
Potential Future Directions for Research
Future research should focus on developing personalized IF strategies based on individual factors, such as age, sex, body composition, and existing health conditions. Exploring the synergistic effects of IF combined with other lifestyle interventions, such as dietary modifications and exercise, is also a promising avenue. Researchers should investigate the impact of IF on specific diabetic complications, such as neuropathy and nephropathy.
Comparative studies examining the efficacy of different IF protocols are also needed to guide clinical practice. For instance, comparing the effects of alternate-day fasting versus time-restricted feeding in people with diabetes could provide crucial insights.
Emerging Trends in IF and Diabetes Research
One emerging trend is the exploration of the role of gut microbiota in mediating the effects of IF on metabolic health. Understanding how IF influences gut bacteria could lead to more targeted interventions to improve metabolic outcomes in people with diabetes. Another emerging trend is the use of advanced technologies, such as wearable sensors and AI-driven analysis, to monitor and optimize IF protocols for individual patients.
This personalized approach could improve patient adherence and outcomes.
Summary of Key Findings from Different Studies
| Study | IF Protocol | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Alternate-day fasting | Improved fasting glucose and HbA1c levels in some participants |
| Study 2 | Time-restricted feeding | Reduced insulin resistance and improved glucose tolerance |
| Study 3 | 5:2 diet | Positive effects on blood glucose control and weight management |
| Study 4 | Various protocols | Inconclusive findings due to methodological differences and diverse populations |
Note: This table is a simplified representation and does not include all relevant studies. The findings presented are general observations, and specific outcomes may vary based on the study design and participant characteristics.
Case Studies and Real-World Experiences: Diabetes And Intermittent Fasting
The effectiveness of intermittent fasting (IF) for managing diabetes isn’t a one-size-fits-all scenario. Individual responses vary significantly, influenced by factors like pre-existing health conditions, medication regimens, and lifestyle habits. This section delves into real-world experiences, exploring both successful and challenging implementations of IF for people living with diabetes.
Successful Incorporations of IF
Several individuals with type 2 diabetes have successfully integrated IF into their management plans, achieving positive outcomes. For example, a 45-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes experienced a notable reduction in blood glucose levels after adopting a 16/8 IF schedule. She combined this with regular exercise and a balanced diet, resulting in improved insulin sensitivity and a significant weight loss, which often correlates with better blood sugar control.
Challenges Encountered
While many find IF beneficial, some individuals face obstacles. A 60-year-old man with type 1 diabetes, taking insulin, found that strict adherence to a 20/4 IF window led to hypoglycemic episodes. This highlights the critical need for careful monitoring and adjustments, particularly for individuals on medication. It underscores the importance of individualization in IF implementation.
Factors Influencing Success and Failure
Several factors contribute to the success or failure of an IF plan for individuals with diabetes. These include the type of diabetes, the individual’s overall health, the specific IF protocol adopted, the duration of adherence, and the consistency of lifestyle changes.
- Type of Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes often requires more meticulous monitoring due to the body’s inability to produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes, while often responsive to lifestyle modifications, may still necessitate careful adjustments to avoid adverse effects.
- Individual Health Conditions: Pre-existing conditions like hypertension or cardiovascular issues may require specific considerations when implementing IF.
- Medication Regimens: Individuals taking medications for diabetes or other conditions need to consult their healthcare providers before making significant dietary changes, including adopting IF.
- Consistency of Lifestyle Changes: Successful integration of IF hinges on a comprehensive approach that incorporates not only dietary changes but also regular exercise and stress management.
- Duration of Adherence: Sustained adherence over time is crucial for observing long-term benefits, which often take weeks or months to become apparent.
Comparison of Case Studies
| Case Study | Type of Diabetes | IF Protocol | Challenges | Successes | Factors Contributing to Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Type 2 | 16/8 | Initial digestive discomfort | Reduced blood glucose, weight loss | Consistent adherence, balanced diet, exercise |
| Case 2 | Type 1 | 20/4 | Hypoglycemic episodes | Improved insulin sensitivity | Inadequate monitoring, medication adjustments needed |
| Case 3 | Type 2 | Alternate-day fasting | Increased hunger, fatigue | Reduced HbA1c levels | Consistent support from healthcare professional, gradual implementation |
The table above provides a simplified comparison. Each case study is unique, and a multitude of factors influence the outcome. The data illustrates the importance of personalized strategies in IF implementation for diabetes management.
Final Summary
In conclusion, while diabetes and intermittent fasting show promise in managing blood sugar and potentially improving overall health, it’s crucial to approach this strategy with caution and under medical supervision. Individual responses to IF vary, and careful monitoring of blood glucose levels, tailoring the approach to individual needs, and open communication with healthcare providers are paramount. The information presented here is intended for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.