Prevent fall risk in older adults uspstf guidelines offer crucial insights into reducing the significant threat of falls among seniors. Understanding the recommendations from the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers to proactively address this public health concern. Falls can lead to serious injuries, impacting both physical and mental well-being, and placing a substantial economic burden on individuals and society.
This comprehensive overview examines the USPSTF’s approach to fall prevention, including risk factors, assessment methods, interventions, and the crucial role of environmental modifications. It also explores pharmacological considerations and the importance of community resources in supporting fall prevention efforts. The discussion will delve into the details of the USPSTF recommendations and how they can be implemented to create a safer and healthier environment for older adults.
Introduction to Fall Prevention in Older Adults (US Preventive Services Task Force): Prevent Fall Risk In Older Adults Uspstf
Falls are a significant concern for older adults, impacting their health, independence, and quality of life. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has issued recommendations regarding fall prevention strategies, aiming to reduce the substantial burden of falls on individuals and the healthcare system. These recommendations provide evidence-based guidance for clinicians and policymakers to help older adults maintain their mobility and safety.The USPSTF recommendations are grounded in the substantial health and economic implications of falls.
The USPSTF guidelines on preventing falls in older adults are really important, but sometimes, you might wonder about other health issues. For example, if you’re experiencing blood clots in your period, it’s definitely worth checking out why. Understanding those issues can help you better manage your overall health and well-being, just like following the USPSTF recommendations for fall prevention.
For more information on blood clots in periods, you can check out this helpful resource: why are there blood clots in my period. Ultimately, taking proactive steps towards fall prevention is key for maintaining independence and quality of life in later years.
Falls can lead to serious injuries, including fractures, head trauma, and even death. These injuries often result in prolonged hospital stays, rehabilitation needs, and long-term disability, placing a substantial financial burden on both individuals and the healthcare system. Preventing falls through proactive interventions can significantly mitigate these negative outcomes.
USPSTF Recommendations on Fall Prevention, Prevent fall risk in older adults uspstf
The USPSTF recommends interventions for fall prevention in older adults aged 65 and older who are at increased risk of falling. These interventions typically involve a combination of strategies aimed at improving strength, balance, and gait, along with environmental modifications. The USPSTF emphasizes the importance of tailored interventions based on individual risk factors.
Rationale Behind the Recommendations
The USPSTF’s recommendations stem from a comprehensive review of available scientific evidence. Falls are a multifaceted problem, and the interventions considered by the USPSTF aim to address the complex interplay of physical, environmental, and social factors that contribute to falls. The recommendations are focused on maximizing effectiveness while minimizing potential harms and costs associated with the interventions.
Key Factors Considered by the USPSTF
Several key factors influenced the USPSTF’s recommendations:
- Evidence Strength: The Task Force meticulously evaluated the strength of evidence supporting the effectiveness of various fall prevention interventions. They prioritized interventions with robust and consistent evidence demonstrating a positive impact on fall rates.
- Risk Factors: The USPSTF recognized the importance of identifying individuals at high risk of falling. Factors such as age, pre-existing conditions (e.g., arthritis, osteoporosis), medication use, and cognitive impairment are considered when assessing individual risk.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The recommendations were developed with an awareness of the financial implications of fall prevention interventions. Interventions were assessed for their potential to generate positive outcomes in relation to their associated costs.
- Implementation Considerations: The Task Force acknowledged the need for interventions that are practical and feasible to implement in various healthcare settings. This involved evaluating factors such as availability of resources, training needs, and potential barriers to adoption.
Comparison with Other Guidelines and International Perspectives
A comprehensive comparison across various guidelines and international perspectives highlights potential similarities and differences in approach.
| Aspect | USPSTF Recommendations | Other Relevant Guidelines (e.g., CDC, WHO) | International Perspectives (e.g., European guidelines) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Population | Older adults (≥65) at increased fall risk | Similar, often with emphasis on community-based programs | May have slightly different age cutoffs or focus on specific populations |
| Intervention Types | Multifactorial interventions, including exercise, medication review, environmental modifications | May emphasize specific types of exercise or environmental interventions | May incorporate specific local considerations or cultural factors |
| Evidence Strength Requirements | High standards for evidence-based interventions | Varying levels of evidence criteria | May align with European guidelines or standards |
Risk Factors Associated with Falls in Older Adults
Falls are a significant concern for older adults, often leading to injuries, reduced mobility, and decreased quality of life. Understanding the multifaceted factors contributing to fall risk is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. This section delves into the primary risk factors, categorizing them for clarity and highlighting their interplay in increasing fall likelihood.Falls in older adults are not a simple event, but rather a consequence of multiple factors interacting in complex ways.
Identifying and addressing these risk factors is crucial to developing effective prevention programs.
Physical Risk Factors
Factors related to physical health significantly contribute to fall risk. These include diminished strength and balance, impaired vision, and chronic health conditions.
- Muscle Weakness and Loss of Balance: Age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) and reduced flexibility decrease stability, making it harder to maintain balance during everyday activities. This is often compounded by decreased proprioception (the body’s awareness of its position in space), which further increases the risk of losing balance and falling. For example, an older adult with weak leg muscles might struggle to stand up from a chair or navigate uneven terrain, increasing their risk of tripping and falling.
- Impaired Vision: Reduced visual acuity, depth perception, and contrast sensitivity can significantly impair the ability to perceive obstacles and maintain balance. This is especially relevant in low-light conditions or when navigating unfamiliar environments. For example, an older adult with cataracts may not be able to see a step or a rug, leading to a fall. Similarly, problems with glare can make it difficult to see obstacles in outdoor settings.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Conditions like arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and diabetes can affect balance, coordination, and strength, increasing the risk of falls. For instance, individuals with arthritis may experience pain and stiffness in their joints, making it difficult to move around safely. Similarly, individuals with Parkinson’s disease may experience tremors and postural instability, increasing their risk of falls.
Environmental Risk Factors
The home environment plays a significant role in fall risk. Unsafe or poorly designed environments can create tripping hazards, and lack of appropriate assistive devices can further complicate safety.
- Unsafe Home Environment: Cluttered pathways, inadequate lighting, loose rugs, and stairs without railings are common environmental hazards. These factors increase the risk of tripping, stumbling, and falling. For instance, a loose rug in a hallway can cause an older adult to trip and fall. Similarly, poor lighting in a bedroom or bathroom can hinder visibility and increase the risk of falling.
- Lack of Assistive Devices: Proper assistive devices, such as grab bars in bathrooms and supportive footwear, can substantially reduce fall risk. The absence of these aids can significantly increase the chance of falling. For example, a lack of grab bars in the shower can make getting in and out of the shower a hazardous activity.
Cognitive Risk Factors
Cognitive decline, including problems with memory, attention, and decision-making, can contribute to fall risk.
- Cognitive Impairment: Difficulties with attention, memory, and processing information can impact an individual’s ability to react to potential hazards and maintain balance. For example, an older adult with dementia might forget where they placed an object, leading them to trip over it. Similarly, difficulties with processing information can impact their ability to react quickly to unexpected situations, increasing their risk of falling.
Interaction of Risk Factors
The likelihood of a fall increases significantly when multiple risk factors coexist. For example, an older adult with impaired vision, a cluttered home environment, and some cognitive decline will have a much higher fall risk compared to someone with only one of these factors. This compounding effect necessitates a holistic approach to fall prevention.
Prevalence of Risk Factors
| Risk Factor | Age Group (Approximate) | Prevalence (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Weakness/Balance Issues | 65-74 | 20-30% |
| Muscle Weakness/Balance Issues | 75-84 | 30-40% |
| Muscle Weakness/Balance Issues | 85+ | 40-50% |
| Vision Impairment | 65-74 | 15-25% |
| Vision Impairment | 75-84 | 25-35% |
| Vision Impairment | 85+ | 35-45% |
| Environmental Hazards | 65-74 | 10-20% |
| Environmental Hazards | 75-84 | 15-25% |
| Environmental Hazards | 85+ | 20-30% |
Note: Prevalence estimates are approximate and may vary based on specific studies and populations.
Assessment and Screening Methods for Fall Risk
Identifying older adults at high risk of falls is crucial for implementing preventative strategies. Accurate assessment helps target interventions to reduce fall-related injuries and improve quality of life. Various tools and methods exist, each with strengths and limitations. Understanding these tools and their appropriate application is key to effective fall prevention programs.
Assessment Tools for Fall Risk
A multi-faceted approach to fall risk assessment is essential, as no single tool captures all relevant factors. This holistic approach considers physical abilities, cognitive function, environmental hazards, and medication side effects. This comprehensive evaluation provides a more complete picture of an individual’s fall risk, allowing for tailored interventions.
Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test
The TUG test assesses mobility and balance. Participants rise from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and return to the chair. The time taken is measured. A longer time indicates a higher risk of falls. The TUG test is widely used due to its simplicity and quick administration.
It can be used in various settings, from healthcare facilities to community centers. For example, an individual taking 15 seconds to complete the TUG test might be considered at higher risk for falls than someone completing it in 10 seconds.
Berg Balance Scale
The Berg Balance Scale (BBS) is a more comprehensive assessment of balance and mobility. It evaluates various balance tasks, including standing, turning, and reaching. Higher scores indicate better balance. The BBS provides a more detailed understanding of an individual’s balance abilities, which is valuable for developing personalized fall prevention strategies. For instance, a score of 20 on the BBS might indicate a higher risk of falls than a score of 25, reflecting a more significant need for interventions focused on improving balance.
Other Assessment Tools
Other useful assessment tools include the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI), the Functional Reach Test (FRT), and various questionnaires. Each tool focuses on specific aspects of balance, mobility, or cognitive function. The DGI assesses gait and balance during dynamic movements. The FRT measures the forward reach distance. Questionnaires often assess an individual’s history of falls and current medication use.
Choosing the appropriate tools depends on the specific needs of the individual and the resources available.
Comparison of Assessment Tools
| Assessment Tool | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Timed Up and Go (TUG) | Simple, quick, inexpensive, and widely available. | Limited in assessing specific balance issues. |
| Berg Balance Scale (BBS) | Comprehensive assessment of balance and mobility, provides more in-depth information. | More time-consuming to administer than the TUG test. |
| Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) | Focuses on dynamic movements during gait, which is a crucial aspect of fall risk. | May require specialized training for accurate administration. |
| Functional Reach Test (FRT) | Easy to perform, assesses forward reach, which is relevant to preventing falls. | Only assesses one aspect of balance. |
| Questionnaires | Useful for gathering background information about falls, medication, and personal factors. | Reliance on self-reported information can be inaccurate. |
Rationale for a Multi-Faceted Approach
A multi-faceted approach to fall risk assessment acknowledges the complexity of falls. Individual circumstances, including medical history, medications, and environmental factors, all contribute to fall risk. No single test can capture all these influences. By combining various assessment methods, healthcare professionals can develop a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s fall risk and design effective interventions.
Interventions and Strategies for Fall Prevention
Falling is a significant concern for older adults, impacting their independence and overall well-being. Fortunately, many strategies can effectively reduce the risk of falls. These interventions encompass a multifaceted approach, targeting both individual factors and environmental hazards. Understanding and implementing these strategies is crucial for promoting a safer and more fulfilling life for older adults.
Exercise Programs
Physical activity plays a vital role in maintaining strength, balance, and flexibility, all crucial for preventing falls. Targeted exercise programs, specifically designed for older adults, can significantly reduce fall risk. These programs often incorporate strength training, balance exercises, and cardiovascular activities.
- Strength Training: Exercises that build muscle mass and strength improve the ability to maintain upright posture and resist falls. Examples include weightlifting, resistance band exercises, and bodyweight exercises like squats and lunges.
- Balance Exercises: Activities like Tai Chi, yoga, and simple balance exercises (e.g., standing on one leg) enhance proprioception and improve the ability to recover from unexpected movements.
- Cardiovascular Activities: Improving cardiovascular fitness increases endurance and improves overall physical function, making it easier to respond to unexpected situations.
Environmental Modifications
Creating a safe home environment is paramount for fall prevention. Identifying and mitigating potential hazards in the home can drastically reduce the risk of falls.
- Lighting Improvements: Adequate lighting in all areas of the home, including hallways, stairs, and bathrooms, is essential. Consider using brighter bulbs, motion-sensor lights, and strategically placed lamps to ensure clear visibility.
- Removing Hazards: Removing tripping hazards such as loose rugs, clutter, and uneven surfaces is critical. Ensure proper placement of furniture and walkways to avoid obstructions.
- Bathroom Modifications: Installing grab bars in the shower and bathroom can significantly improve safety and balance during bathing or using the toilet.
- Stair Modifications: Secure handrails, well-lit stairs, and non-slip surfaces on stairs are crucial for safe navigation. Consider adding a stair lift if necessary.
Medication Review
Certain medications can increase the risk of falls in older adults. A thorough review of medications by a healthcare professional is essential to identify potential risks and adjust prescriptions if necessary.
- Identifying Potential Risks: Medications that can affect balance, coordination, or alertness (e.g., sedatives, diuretics, some antidepressants) should be carefully assessed.
- Dosage Adjustments: In some cases, adjusting medication dosages or switching to alternative medications can significantly reduce fall risk.
- Educating Patients: Patients should be educated about the potential side effects of their medications and the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms.
Evidence-Based Fall Prevention Programs
Numerous evidence-based fall prevention programs exist, demonstrating the effectiveness of comprehensive interventions. Examples include programs targeting specific populations or incorporating a range of strategies.
- Tai Chi: Tai Chi has demonstrated success in reducing falls due to its focus on balance, coordination, and mindfulness.
- Strength and Balance Training: Structured programs combining strength and balance exercises have shown effectiveness in reducing falls among older adults.
- Home Modification Programs: Programs that focus on identifying and modifying home hazards, combined with education, are highly effective in fall prevention.
Comparison of Intervention Approaches
Different approaches to fall prevention vary in their effectiveness. A comprehensive approach combining various strategies often yields the best results.
| Intervention Approach | Rationale | Effectiveness | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise Programs | Improves strength, balance, and flexibility | High | Tai Chi, strength training, balance exercises |
| Environmental Modifications | Reduces tripping hazards and enhances safety | High | Improved lighting, removal of clutter, bathroom modifications |
| Medication Review | Identifies and addresses potential medication risks | Moderate to High | Medication adjustment, education |
Role of the USPSTF in Fall Prevention Initiatives

The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) plays a crucial role in shaping health policy and practice. Their recommendations, based on rigorous evidence reviews, significantly influence how healthcare providers approach preventive care. This is especially important for issues like fall prevention in older adults, where proactive measures can drastically reduce the risk of serious injury and improve quality of life.The USPSTF’s recommendations regarding fall prevention aren’t just theoretical; they have tangible impacts on healthcare systems.
They guide the development of guidelines, inform insurance coverage decisions, and empower healthcare providers with evidence-based strategies. This influence extends to community-based programs, impacting the types of interventions offered and the resources allocated.
The USPSTF guidelines for preventing falls in older adults are really important. While those guidelines often focus on things like exercise and home modifications, I’ve been exploring natural remedies like arnica, which is believed to help with joint pain and inflammation. The benefits of arnica could potentially play a role in reducing fall risk by improving mobility and reducing pain, making it a fascinating avenue to explore alongside conventional preventative measures.
Ultimately, a multi-faceted approach, combining expert advice with potential natural supplements, is key to maintaining independence and safety for older adults.
USPSTF’s Promotion and Dissemination of Information
The USPSTF promotes fall prevention through various channels. They publish detailed recommendations on their website, providing accessible information for healthcare professionals, patients, and the public. These resources explain the importance of fall prevention and offer actionable strategies. These resources also detail the risk factors associated with falls in older adults, aiding in early identification and intervention. The information is readily available and updated regularly, ensuring it remains current with the latest research findings.
Influence on Healthcare Practices and Policies
USPSTF recommendations significantly impact healthcare practices. Clinicians often integrate these guidelines into their patient care, leading to increased screening for fall risk and the implementation of preventive strategies. Insurance policies, recognizing the value of fall prevention, may cover some of these interventions, further encouraging their adoption. These guidelines have contributed to the development of standardized assessment tools and protocols, fostering consistency in fall prevention strategies across different healthcare settings.
Policies at the state and national level are also impacted, influencing community-based initiatives and programs.
Importance of Community-Based Fall Prevention Programs
Community-based fall prevention programs are essential for reaching a broad range of older adults. These programs often incorporate education, exercise, and environmental modifications, providing practical and accessible support for those at risk. The USPSTF recognizes the critical role of these programs, influencing their development and implementation through recommendations and resources. These programs are crucial for addressing the needs of diverse communities and for ensuring that everyone has access to fall prevention strategies.
USPSTF Recommendations Regarding Primary Care Integration
The USPSTF advocates for the integration of fall prevention into primary care settings. They recognize that routine screening and interventions during routine checkups can be highly effective. This integration ensures that fall prevention is not treated as a separate issue, but as an integral part of overall care for older adults. Such integration is critical for early identification and proactive management of fall risk factors.
By integrating fall prevention into primary care, the USPSTF aims to promote preventative healthcare practices and improve the overall health and well-being of older adults.
Key Recommendations for Healthcare Providers
| Recommendation | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Screen older adults for fall risk during routine visits. | Early detection allows for timely intervention and management of risk factors. |
| Provide individualized interventions based on assessed risk. | Tailored interventions address specific needs and increase effectiveness. |
| Recommend exercise programs that improve balance and strength. | Physical activity is a crucial component in fall prevention. |
| Assess home environments for safety hazards. | Modifying home environments reduces tripping hazards and falls. |
| Refer to specialists as needed. | Specialized care may be necessary for certain risk factors. |
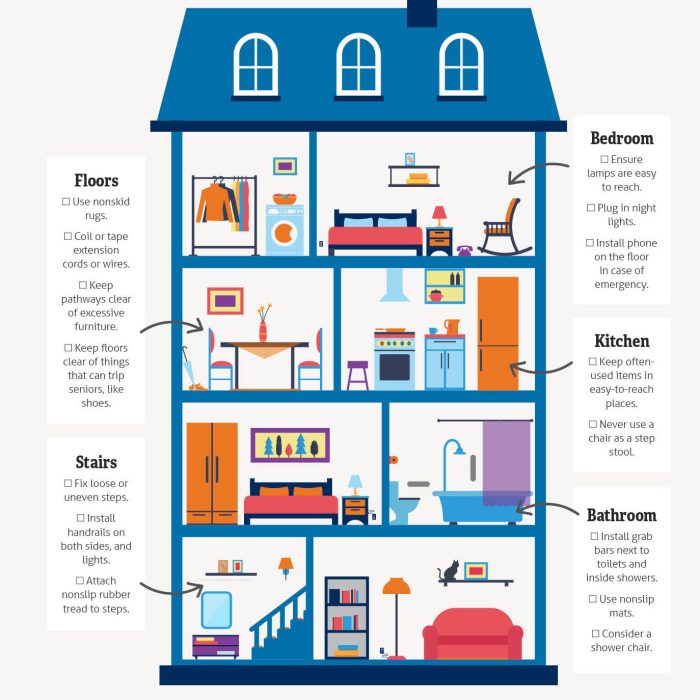
Environmental Modifications to Reduce Fall Risk
Creating a safe home environment is crucial for preventing falls in older adults. Falls are a significant concern for seniors, often leading to injuries, decreased mobility, and a reduced quality of life. Proactive steps to modify the home environment can significantly mitigate these risks, empowering older adults to maintain their independence and safety.Home environments can contain hidden dangers that contribute to falls.
Identifying and addressing these hazards is key to preventing falls and promoting safe living spaces.
Common Household Hazards
Many common household items can become fall hazards for older adults. Slippery floors, inadequate lighting, and cluttered walkways are just a few examples. Understanding these hazards and implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of falls.
- Slippery surfaces, such as those in bathrooms or kitchens, often present significant risks.
- Poor lighting, especially in hallways or stairwells, can make it difficult to see obstacles and increase the chance of tripping.
- Cluttered pathways, with items placed haphazardly, can obstruct movement and cause falls.
- Stairs without adequate handrails or proper lighting are significant fall risks.
- Loose rugs or carpets can easily cause tripping and falls.
- Lack of grab bars in bathrooms or showers is a frequent cause of falls.
Importance of Home Assessments
Home assessments are essential to identify specific fall risks within a particular home. A professional home assessment can pinpoint areas of concern and offer tailored solutions. This personalized approach is key to effective fall prevention. The assessment should evaluate not only the physical environment but also the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
- Home assessments provide a detailed evaluation of the home environment.
- The assessment identifies potential hazards that may not be readily apparent to the resident.
- Assessments help to determine specific modifications needed to create a safe and secure environment.
- They are a valuable tool to prevent falls, especially for individuals with mobility limitations.
Specific Modifications for Fall Prevention
Numerous modifications can be made to reduce fall risk. Implementing these modifications can dramatically improve the safety and independence of older adults. Examples include installing grab bars, improving lighting, and removing tripping hazards.
- Installing grab bars in bathrooms and beside toilets provides crucial support and stability.
- Adding brighter lighting, particularly in hallways and stairwells, improves visibility and reduces the risk of falls.
- Removing loose rugs or carpets from high-traffic areas can eliminate tripping hazards.
- Installing handrails on both sides of stairs provides crucial support and reduces the risk of falls.
- Improving the lighting around the home reduces the risk of tripping on objects in the dark.
- Making pathways wider and free of clutter can prevent obstacles and make movement easier.
Tailoring Modifications to Individual Needs
Modifications must be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities. This personalized approach ensures maximum effectiveness and safety. A tailored approach also considers the individual’s physical limitations, lifestyle, and cognitive function.
Table of Common Home Hazards and Suggested Modifications
| Common Home Hazard | Suggested Modification |
|---|---|
| Slippery floors in bathroom | Install non-slip mats, grab bars near the shower/tub, and use a bath seat. |
| Poor lighting in hallways | Install brighter light bulbs or add motion-activated lights. |
| Cluttered walkways | Declutter pathways, and use storage solutions to keep items organized. |
| Loose rugs or carpets | Secure rugs with double-sided tape or use non-slip mats underneath. |
| Stairs without handrails | Install handrails on both sides of the stairs. |
| Lack of grab bars in bathrooms | Install grab bars near the toilet and shower/tub. |
Pharmacological Considerations in Fall Prevention
Medications are often a significant factor in falls among older adults. Many common prescriptions and over-the-counter drugs can impact balance, coordination, and alertness, increasing the risk of falls. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for proactive fall prevention strategies.Older adults often take multiple medications simultaneously. This polypharmacy can lead to drug interactions and side effects, which can significantly impair physical function and increase the likelihood of falls.
The USPSTF guidelines for preventing falls in older adults are crucial, but sometimes seemingly unrelated health issues can affect balance and mobility. For example, itchy hands and feet can cause discomfort and distraction , which can indirectly increase fall risk. Addressing underlying health conditions like this is vital for effective fall prevention strategies in older adults.
Careful medication management is therefore essential to maintain safety and well-being.
Potential Role of Medications in Fall Risk
Medications can directly affect balance and coordination through various mechanisms. Some drugs may lower blood pressure too rapidly, leading to dizziness and falls. Others can impair cognitive function, reducing alertness and reaction time. Still others can affect the central nervous system, increasing the risk of falls.
Medications Increasing Fall Risk in Older Adults
Several medication classes are frequently associated with an increased fall risk in older adults. These medications can affect balance, reaction time, and cognitive function.
- Antihypertensives: Blood pressure medications, especially those that lower blood pressure quickly, can cause dizziness and postural hypotension, leading to falls. This is particularly problematic in older adults, whose blood pressure regulation mechanisms may not be as efficient as in younger individuals. For example, a sudden drop in blood pressure from a medication taken before getting out of bed can increase the risk of a fall.
- Sedatives and Hypnotics: Drugs like benzodiazepines and other sedative medications can significantly impair balance and coordination. Reduced alertness and slowed reaction time make falls more likely. For example, an older adult taking a sleeping pill may experience difficulty getting out of bed or walking around safely.
- Antipsychotics: Some antipsychotic medications can cause side effects such as postural instability, parkinsonism, and tremors. These side effects directly impact balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls.
- Diuretics: Diuretics, often prescribed for hypertension or heart conditions, can lead to dehydration. Dehydration can worsen balance and increase the risk of falls. This is especially concerning for older adults, who may have difficulty maintaining fluid balance.
- Opioids: Opioids, used for pain management, can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and confusion. These effects can impair coordination and balance, significantly increasing the risk of falls.
Importance of Medication Review and Adjustment
Regular medication reviews are crucial for older adults, particularly those at risk of falls. A healthcare professional can assess the potential interactions and side effects of multiple medications, identifying those that might contribute to fall risk. Adjusting dosages or switching to alternative medications can often significantly reduce the risk of falls. Medication reviews should be a regular part of the preventive care process for older adults.
Examples of Medications Associated with Increased Fall Risk
Several specific medications are frequently associated with a heightened risk of falls in older adults. The following are some examples:
- Diazepam (Valium): A benzodiazepine frequently used to treat anxiety and muscle spasms. Its sedative effects can significantly impair balance and coordination.
- Lisinopril (Prinivil): An ACE inhibitor used to treat high blood pressure. Rapid blood pressure lowering can cause dizziness and falls.
- Verapamil (Calan): A calcium channel blocker used for hypertension and angina. Potential for dizziness and postural hypotension.
- Furosemide (Lasix): A loop diuretic often prescribed for fluid retention. Its effect on fluid balance can increase the risk of falls, especially if dehydration occurs.
Comparison of Fall Risk Associated with Different Medication Classes
| Medication Class | Mechanism of Fall Risk | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Antihypertensives | Rapid blood pressure drop, dizziness, postural hypotension | Lisinopril, Verapamil |
| Sedatives/Hypnotics | Impaired coordination, reduced alertness, slowed reaction time | Diazepam, Zolpidem |
| Antipsychotics | Postural instability, parkinsonism, tremors | Risperidone, Haloperidol |
| Diuretics | Dehydration, electrolyte imbalance | Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Opioids | Drowsiness, dizziness, confusion | Morphine, Oxycodone |
Community Resources and Support for Fall Prevention
Staying safe at home and in the community is crucial for older adults. Community resources play a vital role in preventing falls and promoting independence. These resources provide support, education, and practical strategies to reduce fall risk. From home modifications to social connections, a strong community network is essential in maintaining well-being and preventing falls.
Community Resources for Fall Prevention
Community-based programs are invaluable for supporting fall prevention initiatives. These programs can provide a range of services, from education and support groups to home assessments and exercise classes. They are often tailored to meet the specific needs of the community and address potential fall risks.
- Senior Centers and Community Centers: These facilities frequently offer exercise programs, health education workshops, and social activities that promote physical function and fall prevention awareness. Classes focusing on balance, strength training, and flexibility are especially helpful. These programs can also connect individuals with other resources in the community.
- Home Modification Programs: Some communities offer assistance with home modifications to reduce fall hazards. This can include installing grab bars, improving lighting, and removing tripping hazards. These programs often work in partnership with local contractors or volunteers to ensure safety modifications are completed properly.
- Fall Prevention Clinics: These clinics provide comprehensive assessments and interventions to address fall risk. They can involve a variety of professionals like physical therapists, nurses, and social workers. They offer tailored plans to address individual needs and can refer individuals to other community resources.
- Transportation Services: Transportation services are important for older adults to access medical appointments, social activities, and community resources. Reliable transportation can help prevent isolation and promote participation in fall prevention programs.
Role of Community Health Workers
Community health workers (CHWs) are valuable members of the community support network. They are often trusted members of the community who can provide culturally competent support and education about fall prevention. They are often the first point of contact and can help connect individuals with necessary resources and services.
- Cultural Sensitivity: CHWs often have deep understanding of the local culture and can communicate effectively with individuals from diverse backgrounds. This cultural awareness is crucial when addressing fall prevention, as different communities may have varying levels of access to resources and different cultural perspectives on health and wellness.
- Language Accessibility: CHWs often speak multiple languages, making it easier for individuals who do not speak the dominant language to access information and support.
- Building Trust: CHWs build trust within their communities, which is essential for encouraging participation in fall prevention programs and promoting adherence to strategies.
Promoting Adherence to Fall Prevention Strategies
Community programs can promote adherence to fall prevention strategies by providing ongoing support and encouragement. Education is essential. This includes providing clear instructions on how to implement the strategies, and the benefits of doing so. Support groups, and motivational strategies can also play a role in encouraging individuals to maintain their commitment.
Multidisciplinary Collaboration in Fall Prevention
Collaboration between different organizations, professionals, and community members is vital. A multidisciplinary approach ensures a comprehensive approach to fall prevention.
| Community Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Senior Centers | Offer exercise classes, workshops, and social activities. |
| Home Modification Programs | Provide assistance with home safety modifications. |
| Fall Prevention Clinics | Offer comprehensive assessments and interventions. |
| Transportation Services | Provide access to medical appointments and community resources. |
| Community Health Workers (CHWs) | Provide culturally competent support and education. |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, preventing falls in older adults is a multifaceted challenge requiring a collaborative approach involving healthcare providers, caregivers, and community members. The USPSTF’s recommendations, combined with targeted interventions and a focus on environmental safety, offer a strong foundation for reducing fall risk. By understanding the risk factors, utilizing appropriate assessment tools, and implementing effective interventions, we can significantly improve the quality of life for older adults and lessen the burden of falls on individuals and society.




