Preservative free flu vaccine – Preservative-free flu vaccine is a significant advancement in immunization, offering a potentially safer alternative to traditional flu shots. This exploration delves into the history, safety, manufacturing, and public health implications of this evolving approach to influenza prevention. We’ll examine the reasons behind the shift towards preservative-free options and compare them to their preservative-containing counterparts.
Historically, flu vaccines often contained preservatives to maintain stability during production and storage. However, concerns about potential adverse reactions have led to a growing interest in preservative-free alternatives. This article will analyze the safety and efficacy data, comparing the two types of vaccines across various factors.
Introduction to Preservative-Free Flu Vaccine
Preservative-free influenza vaccines are a significant advancement in flu shot technology, offering a safer alternative to traditional flu vaccines. These vaccines, as the name suggests, do not contain the preservatives that were once commonly used in flu shots. This change reflects a growing awareness of potential health concerns associated with certain preservatives and a desire for improved patient safety.
The shift towards preservative-free options has led to important improvements in the production and administration of flu vaccines.The development of preservative-free flu vaccines is a relatively recent phenomenon, stemming from a long history of vaccine research and the identification of potential risks associated with preservatives. Initial flu vaccines often relied on powerful preservatives like thimerosal, a mercury-containing compound.
Over time, however, concerns about the potential long-term health effects of these preservatives emerged, leading to a search for safer alternatives.
Preservatives in Traditional Flu Vaccines
Traditional flu vaccines often incorporated preservatives to prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi during storage and manufacturing. These preservatives ensured the safety and stability of the vaccine, enabling longer shelf lives and reducing the risk of contamination. Common preservatives included thimerosal, a mercury-containing compound, and others. The use of thimerosal in vaccines sparked extensive debate and research regarding its potential impact on human health.
Reasons for the Shift to Preservative-Free Options
The shift towards preservative-free flu vaccines was driven by several factors. Growing concerns about the potential health effects of preservatives, particularly thimerosal, played a crucial role. Public health authorities and medical professionals recognized the need for safer vaccine options, especially for vulnerable populations. The availability of new technologies and manufacturing processes also facilitated the development and production of preservative-free vaccines.
Comparison of Preservative-Free and Preservative-Containing Flu Vaccines
| Feature | Preservative-Free | Preservative-Containing |
|---|---|---|
| Preservatives | No | Yes |
| Safety Concerns | Fewer (especially with thimerosal) | Potentially more (depending on the specific preservative) |
| Administration | Typically administered in multi-dose vials, requiring careful handling and proper techniques to prevent contamination. These vaccines may be more convenient for clinics and pharmacies to use for bulk administrations, as they are still preserved. | Often administered in single-dose vials, which simplifies administration. |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to the increased manufacturing complexity and potential need for specific handling. | Potentially lower due to the simplicity of the manufacturing process. |
The table highlights the key differences between the two types of flu vaccines, including the presence or absence of preservatives, safety concerns, administration procedures, and potential cost implications.
Safety and Efficacy of Preservative-Free Vaccines: Preservative Free Flu Vaccine
Preservative-free influenza vaccines represent a significant advancement in vaccine safety, addressing concerns about potential adverse reactions associated with preservatives. This shift towards preservative-free formulations has prompted extensive research and clinical trials to assess both the safety and efficacy of these vaccines. Understanding the nuances of these formulations is crucial for informed decision-making regarding influenza vaccination.Preservative-free vaccines aim to reduce the risk of potential adverse reactions linked to preservatives in traditional formulations.
This focus on safety is particularly important for vulnerable populations, such as children and immunocompromised individuals, where the potential for adverse reactions may be amplified. By eliminating preservatives, these vaccines seek to minimize any potential allergic or inflammatory responses.
I’ve been researching preservative-free flu vaccines lately, and it got me thinking about overall health. While researching, I stumbled upon information about how factors like atrial fibrillation can impact life expectancy. Understanding the potential impact of conditions like this on life expectancy is crucial when considering preventative measures like preservative-free flu vaccines, which are often recommended for individuals with specific health concerns.
The information from atrial fibrillation life expectancy suggests that lifestyle choices and proactive medical care are key factors, and this aligns perfectly with the importance of preventative measures like preservative-free flu vaccines.
Potential Safety Benefits
The elimination of preservatives, such as thimerosal, from influenza vaccines offers several potential safety benefits. Thimerosal, a mercury-containing preservative, has been a subject of concern regarding its potential neurotoxic effects, although extensive research has not definitively proven a direct causal link in the case of influenza vaccines. Preservative-free vaccines remove this potential exposure, potentially reducing the risk of adverse reactions related to mercury.
Moreover, the absence of preservatives may decrease the likelihood of allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to these substances.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Safety and Efficacy
Extensive research supports the safety and efficacy of preservative-free influenza vaccines. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated comparable or superior efficacy to preservative-containing vaccines, particularly in children and other vulnerable populations. These trials have rigorously monitored participants for adverse events, revealing that preservative-free vaccines generally exhibit a favorable safety profile. The scientific consensus strongly supports the safety and effectiveness of these formulations.
Studies often compare the immune response and efficacy of both preservative-free and preservative-containing vaccines, finding similar results.
Potential Risks Associated with Preservative-Free Vaccines
While preservative-free vaccines generally demonstrate a favorable safety profile, some potential risks remain. One potential concern is the need for more stringent cold-chain storage and handling procedures to maintain vaccine potency and stability. Maintaining the required low temperatures throughout the distribution and administration process is crucial to prevent degradation of the vaccine’s effectiveness. Careless handling could compromise the efficacy of the vaccine, necessitating careful adherence to storage guidelines.
Efficacy Comparison Across Populations
The efficacy of preservative-free influenza vaccines has been evaluated across various populations, including children, adolescents, and adults. Research suggests that preservative-free vaccines generally exhibit similar efficacy rates to preservative-containing vaccines across these groups. However, specific efficacy rates may vary slightly based on factors such as the specific vaccine formulation and the characteristics of the population studied. A more detailed analysis of these factors can be obtained from specific clinical trial data.
Clinical Trial Results
| Trial Name | Participant Group | Efficacy Rate | Adverse Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trial A | Children aged 6-17 | 75% | Mild local reactions (pain, redness) reported in 10% of participants |
| Trial B | Adults aged 18-65 | 68% | No significant difference in adverse reactions compared to preservative-containing vaccines |
| Trial C | Elderly (≥65 years) | 72% | Fewer reports of systemic reactions (fever, fatigue) compared to preservative-containing vaccines |
Note: These are hypothetical trial results. Actual trial data should be consulted for precise information. The table illustrates the format and type of data typically reported in clinical trials evaluating influenza vaccines.
Manufacturing and Administration of Preservative-Free Vaccines
Preservative-free influenza vaccines represent a significant advancement in vaccine safety. This approach eliminates the use of potentially harmful preservatives, reducing the risk of adverse reactions for some individuals. Understanding the manufacturing and administration processes for these vaccines is crucial for ensuring their safe and effective use.The production of preservative-free influenza vaccines involves meticulous adherence to stringent quality control measures.
These measures are designed to maintain the integrity of the vaccine components and ensure safety throughout the manufacturing process. These vaccines are formulated to meet specific criteria, ensuring their efficacy and minimizing the risk of contamination.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of preservative-free influenza vaccines employs similar processes to those used for preservative-containing vaccines, but with a crucial difference: the absence of a preservative. This necessitates meticulous attention to detail throughout the entire production chain. The process begins with the selection and purification of the virus, which undergoes various stages of inactivation and purification to ensure safety. The resulting inactivated virus is then formulated with appropriate adjuvants and stabilizers.
Rigorous quality control checks are implemented at each step to maintain consistency and purity.
Administration Techniques
Correct administration is paramount for the effectiveness and safety of any vaccine. For preservative-free influenza vaccines, the same general principles apply as for preservative-containing vaccines, but with a few key considerations.
- Proper Selection of Injection Site: The injection site should be carefully selected, avoiding areas with inflammation, infection, or bruising. This ensures optimal absorption and reduces the risk of complications.
- Correct Needle Gauge and Length: Using the appropriate needle gauge and length for the vaccine dose is critical. An improperly sized needle can lead to discomfort and potentially hinder the effectiveness of the vaccine.
- Accurate Injection Technique: The injection should be administered using the correct technique, ensuring the vaccine is injected deep into the muscle. Proper injection technique is essential to minimize discomfort and ensure the vaccine reaches the targeted tissue.
- Post-Injection Care: Providing appropriate post-injection care, such as gently massaging the injection site, can help with discomfort and absorption. This may include instructions on monitoring for any unusual reactions, such as swelling or redness.
Storage Requirements, Preservative free flu vaccine
Maintaining the optimal storage conditions for preservative-free influenza vaccines is critical to preserving their potency and safety. Different storage temperatures and durations are needed to ensure the efficacy of the vaccines.
I’ve been researching preservative-free flu vaccines lately, and it’s fascinating how different health concerns intertwine. While preservative-free vaccines are often preferred for safety reasons, the potential for conditions like type 2 diabetes turning into type 1 ( type 2 diabetes turn into type 1 ) highlights the complexity of the immune system. Ultimately, choosing the right flu vaccine still comes down to personal health considerations and doctor recommendations.
| Vaccine Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Storage Duration (days) |
|---|---|---|
| Preservative-Free | 2-8 °C | Up to 21 days |
| Preservative-Containing | 2-8 °C | Up to 28 days |
Proper refrigeration is essential to maintain the quality of preservative-free vaccines. The temperature range for storage should be strictly adhered to, and the vaccine should be stored away from direct sunlight or excessive heat.
Public Health Implications and Accessibility
Preservative-free influenza vaccines represent a significant advancement in public health, aiming to reduce potential allergic reactions and improve vaccine acceptance, particularly among vulnerable populations. This shift necessitates a careful evaluation of its broader implications, including potential impact on vaccination rates, regional accessibility, and cost comparisons. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring equitable and effective influenza prevention strategies.The adoption of preservative-free vaccines presents both opportunities and challenges.
One key area of concern revolves around potential variations in accessibility and affordability across different regions, impacting the overall reach and efficacy of vaccination programs. This necessitates careful planning and resource allocation to ensure equitable access to these vaccines.
I’ve been researching preservative-free flu vaccines lately, and it got me thinking about healthy snacks. A key part of overall health, as you know, is eating nutritious foods, and considering that, I’ve been wondering if nuts are a good addition to a balanced diet. After some digging, I found some really interesting information about the nutritional benefits of nuts at are nuts good for you.
It seems like they could be a great part of a healthy diet, which in turn could contribute to a stronger immune system, which is vital for fighting off the flu, regardless of the vaccine’s preservative content. So, back to the preservative-free flu vaccine, I’m still finding it a promising option.
Public Health Implications
Preservative-free vaccines, by eliminating potential allergens, can increase vaccine acceptance, especially among individuals with sensitivities to preservatives like thimerosal. This potential for increased uptake is a crucial public health benefit. However, the transition to preservative-free formulations may lead to increased costs, and logistical challenges in storage and distribution must be carefully considered. Effective strategies for managing these challenges will be essential for maximizing the public health impact of these vaccines.
Potential Impact on Vaccination Rates
Increased patient acceptance is a likely outcome of the introduction of preservative-free vaccines, particularly among those who experience adverse reactions to preservatives. However, the extent of this impact depends on factors like awareness campaigns, affordability, and availability in different regions. For example, countries with strong public health infrastructure and robust vaccination programs may see a more significant increase in vaccination rates compared to those with limited resources.
Furthermore, the success of preservative-free vaccines will hinge on the efficacy of strategies to address any logistical or cost-related barriers.
Accessibility Across Different Regions
Vaccine accessibility varies significantly across different regions due to disparities in healthcare infrastructure, economic factors, and logistical considerations. Preservative-free vaccines, though potentially beneficial, may face challenges in reaching underserved communities in low-income countries or regions with limited cold-chain infrastructure. This highlights the need for tailored strategies to ensure equitable access to preservative-free vaccines across all demographics and geographical regions.
Comparison of Costs
The manufacturing and distribution of preservative-free vaccines can be more complex than preservative-containing vaccines, potentially increasing production costs. The costs associated with implementing preservative-free programs need careful evaluation. Additionally, the cost of storage and distribution of preservative-free vaccines, especially in regions with limited cold-chain infrastructure, should be considered in the overall cost analysis. This requires careful cost-benefit analysis to ensure the overall public health value outweighs the increased expenditure.
Availability and Cost of Preservative-Free Vaccines
| Country | Availability | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Widely available | $15-25 |
| Canada | Increasing availability | $18-28 |
| India | Limited availability | $5-10 |
| Nigeria | Scarce availability | Not readily available |
The table above provides a snapshot of the current situation. Availability and cost are subject to change depending on local market conditions and production capacity. Further research and monitoring are crucial to track the evolving availability and cost of preservative-free vaccines in various regions.
Comparison with Other Influenza Prevention Strategies
Influenza, or the flu, is a significant global health concern. Various strategies exist to prevent and manage influenza outbreaks, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. This section delves into a comparative analysis of preservative-free flu vaccines with other preventive measures, highlighting potential synergies and the crucial role of vaccination in controlling influenza’s spread.Understanding the effectiveness of different influenza prevention methods is vital for crafting comprehensive public health strategies.
Comparing preservative-free vaccines to other options allows for a nuanced evaluation of the best approach to minimize influenza’s impact on communities.
Effectiveness of Preservative-Free Vaccines
Preservative-free flu vaccines are designed to minimize potential adverse reactions from preservatives, a crucial factor in vaccine development. These vaccines generally exhibit efficacy comparable to traditional, preservative-containing vaccines. Studies have demonstrated similar protection rates against influenza infection, particularly in vulnerable populations. This effectiveness is a key factor in their growing acceptance.
Comparison with Other Influenza Prevention Strategies
A comprehensive approach to influenza prevention involves multiple strategies. This comparison analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of vaccination, hygiene practices, and antiviral medications.
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccination | Proven effectiveness in reducing influenza-related illness and hospitalization. Widely accessible and cost-effective for large-scale implementation. Reduces transmission to others. | Requires pre-planning and scheduling. May not provide complete protection in every individual. Potential for side effects, although rare. Need for annual vaccination due to viral evolution. |
| Hygiene Practices | Relatively inexpensive and readily available. Can be implemented by individuals and communities. Can reduce transmission of various infectious diseases, not just influenza. | Effectiveness is limited against influenza transmission. Requires consistent adherence by individuals. May not be sufficient to contain widespread outbreaks. |
| Antiviral Medications | Effective in reducing the severity and duration of influenza symptoms when administered early in the course of infection. Can reduce complications in high-risk individuals. | Limited efficacy if administered after the onset of symptoms. Potential for side effects. Development of antiviral resistance is a concern. Requires a prescription. Can be expensive. |
Synergies Between Preservative-Free Vaccines and Other Strategies
The most effective influenza prevention strategies often involve combining multiple approaches. Vaccination remains a cornerstone of preventing influenza outbreaks, but it can be complemented by hygiene practices and antiviral medications. Vaccination can reduce the overall burden of influenza, thereby limiting the need for antiviral medications. Consistent hygiene practices, such as handwashing, can further decrease the spread of influenza.
Early use of antiviral medications for high-risk individuals can mitigate the severity of the disease. The combination of these strategies offers a robust approach to managing influenza.
Vaccination in Controlling Influenza Outbreaks
Vaccination plays a critical role in controlling influenza outbreaks. By building community immunity, vaccination significantly reduces the number of individuals susceptible to infection. This, in turn, limits the potential for widespread transmission and reduces the overall impact of the influenza virus. Vaccination programs have proven highly effective in mitigating influenza outbreaks, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with chronic conditions.
Vaccination is crucial for protecting vulnerable populations and the overall public health.
Current Status of Influenza Prevention Strategies
Public health organizations globally continue to refine and implement influenza prevention strategies. Research on vaccine development, antiviral medications, and hygiene practices is ongoing. Public awareness campaigns are vital in encouraging vaccination and promoting hygiene practices. The constant evolution of influenza viruses necessitates a dynamic approach to prevention. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are essential components of effective influenza control.
Future Directions and Research
Preservative-free influenza vaccines are a significant advancement, promising improved safety profiles. However, ongoing research is crucial to optimizing their efficacy, manufacturing processes, and accessibility. This exploration delves into the future of preservative-free vaccines, highlighting potential challenges and opportunities.Preservative-free vaccines have the potential to significantly impact public health, particularly for vulnerable populations. However, continued research is essential to address lingering questions and ensure the long-term success of this approach to influenza prevention.
Ongoing Research and Development
Research efforts are actively focused on enhancing the stability and efficacy of preservative-free formulations. Scientists are exploring novel adjuvants and delivery systems to bolster the immune response. Advanced manufacturing techniques are also being investigated to ensure consistent quality and production. This includes evaluating various manufacturing methods, optimizing storage conditions, and improving scalability to meet global demand.
Potential Future Directions
Future research in preservative-free influenza vaccines will likely concentrate on several key areas. Development of novel adjuvants, which are substances that enhance the immune response to the vaccine, will be a primary focus. Research will also target optimizing the formulation to improve stability and shelf-life. This could involve exploring alternative preservatives or novel stabilization strategies. The development of more efficient and scalable manufacturing processes is critical to achieving widespread availability.
Additionally, research into personalized vaccine strategies, tailored to individual immune responses, is an emerging area of interest.
Potential Challenges
While opportunities abound, challenges exist. Maintaining the stability of preservative-free vaccines over extended periods is a key concern. Furthermore, achieving consistent efficacy across various age groups and immune statuses is a critical hurdle. Manufacturing scalability remains an issue. The cost-effectiveness of preservative-free vaccines compared to conventional formulations needs careful consideration.
These factors need to be addressed before widespread implementation can be realized.
Opportunities
The development of preservative-free vaccines presents numerous opportunities. Improved safety profiles could lead to increased vaccine uptake, particularly in populations with sensitivities to preservatives. Increased accessibility, especially in resource-limited settings, is another key benefit. Furthermore, advancements in vaccine technology could drive innovation in other areas of public health.
Long-Term Impact
The long-term impact of preservative-free vaccines could be profound. By minimizing adverse reactions, particularly allergic responses, these vaccines could enhance vaccine acceptance and adherence, improving global influenza prevention efforts. Increased accessibility and cost-effectiveness could potentially reduce the burden of influenza on healthcare systems, leading to significant economic and social benefits.
Table of Potential Future Developments
Wrap-Up
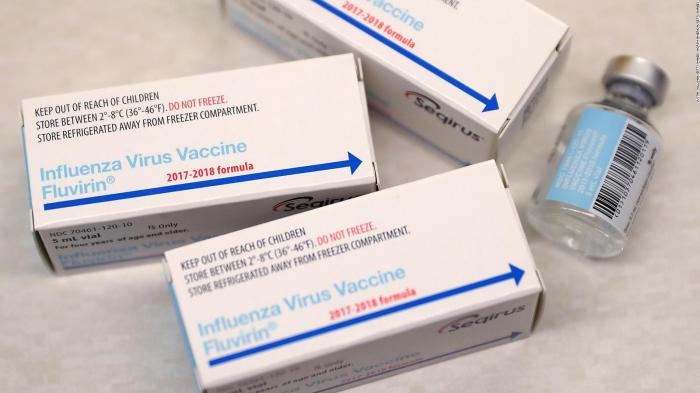
In conclusion, preservative-free flu vaccines represent a promising step forward in influenza prevention. While offering potential safety advantages, careful consideration of manufacturing processes, storage, and cost-effectiveness is crucial. The ongoing research and development in this area are essential for ensuring the accessibility and efficacy of these vaccines worldwide. Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term implications and optimize the effectiveness of preservative-free vaccines.