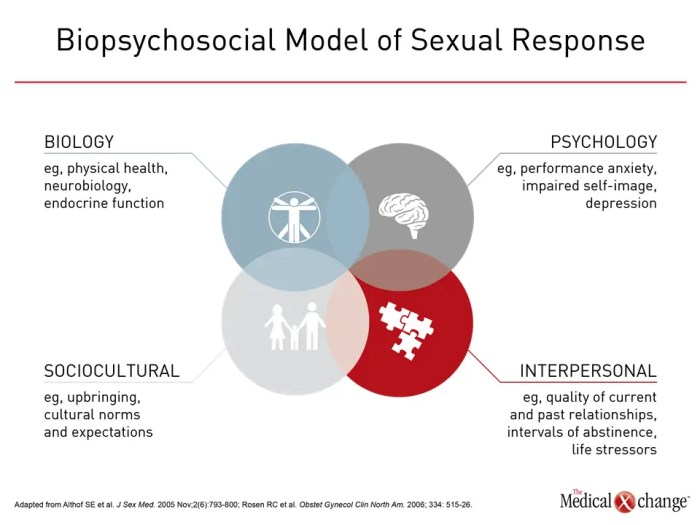
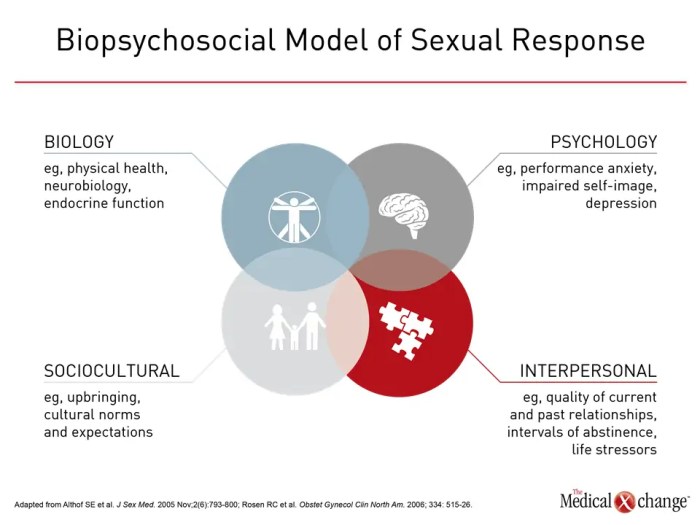
Hypoactive sexual desire disorder symptoms causes diagnosis treatment and coping is a multifaceted issue affecting many individuals. This in-depth exploration delves into the complexities of this condition, examining its symptoms, potential causes, diagnostic processes, available treatments, and effective coping strategies. We’ll cover the nuances of low libido versus HSDD, exploring the biological, psychological, and relational factors that contribute to this condition.
We’ll also examine the various treatment approaches, from pharmacological interventions to lifestyle modifications and relationship-focused therapies.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of HSDD, empowering readers with knowledge and resources to navigate this sensitive topic. We’ll address common questions and misconceptions, offering practical insights into diagnosing, treating, and coping with HSDD. We’ll explore illustrative case studies, highlighting both successful treatment journeys and the challenges individuals may face. By understanding the various perspectives, you’ll gain a better understanding of this often-misunderstood condition.
Understanding Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD)
Hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is a condition characterized by a persistent or recurrent deficiency or absence of sexual fantasies, thoughts, or desires. It’s a significant concern impacting a person’s sexual well-being and potentially their relationships. Understanding its nuances is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.This condition is distinct from simply having a low libido, which can fluctuate based on various factors such as stress, fatigue, or relationship issues.
HSDD, however, involves a more sustained and persistent lack of sexual desire, causing significant distress or interpersonal problems.
Diagnostic Criteria for HSDD
The diagnosis of HSDD relies on specific criteria Artikeld in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria emphasize the persistent nature of the deficiency and its impact on the individual’s life. Crucially, the low sexual desire must be present for a significant duration (e.g., at least six months) and cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Furthermore, the low desire cannot be better explained by another medical or mental health condition.
Differentiating HSDD from Other Sexual Dysfunctions
Understanding HSDD requires differentiating it from other sexual dysfunctions. The following table contrasts HSDD with other common conditions:
| Characteristic | Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder (HSDD) | Female Orgasmic Disorder | Female Sexual Arousal Disorder | Sexual Pain Disorders |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Issue | Persistent or recurrent lack of sexual desire, fantasies, or thoughts. | Difficulties achieving orgasm. | Difficulties achieving or maintaining sexual arousal. | Pain during sexual activity. |
| Impact | Significant distress or interpersonal problems. | Significant distress or interpersonal problems. | Significant distress or interpersonal problems. | Significant distress or interpersonal problems. |
| Duration | At least 6 months. | At least 6 months. | At least 6 months. | At least 6 months. |
| Underlying Factors | Can be related to medical, psychological, or relationship factors. | Can be related to medical, psychological, or relationship factors. | Can be related to medical, psychological, or relationship factors. | Can be related to medical, psychological, or physical factors. |
This table highlights the key differences in the core issues, impact, and duration of these conditions, aiding in proper identification and treatment. Careful consideration of these distinctions is crucial for effective intervention.
Symptoms of HSDD
Understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) involves recognizing its multifaceted symptoms. It’s crucial to remember that these symptoms aren’t always indicative of a disorder, and many factors can influence sexual desire. However, persistent and distressing low sexual desire can significantly impact a person’s well-being and relationships. The symptoms can vary greatly, both in intensity and presentation, making accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment essential.
Common Symptoms
A wide range of emotional and behavioral aspects characterize HSDD. These symptoms can encompass a lack of interest in sexual activity, difficulty experiencing sexual arousal, and a reduced desire for sexual intimacy. Individuals may report feeling emotionally detached from sexual experiences, or exhibit a general disinterest in sexual thoughts or fantasies. This can manifest in various ways, impacting their overall sexual functioning and satisfaction.
Symptoms Across Age Groups and Demographics
The experience of HSDD varies across different age groups and demographics. Younger individuals may experience a general lack of interest in sexual activity, potentially due to developmental factors, life stressors, or a lack of sexual experience. In contrast, older adults may face decreased libido due to hormonal changes, chronic health conditions, or the impact of medications. Cultural backgrounds and personal experiences also play a significant role in shaping the manifestation of these symptoms.
For instance, societal pressures or personal beliefs can influence an individual’s perception and expression of their sexual desire.
Symptoms in Men and Women
While the core issue of low sexual desire is consistent, the ways in which it manifests can differ between men and women. Men with HSDD may report a reduced frequency of sexual thoughts or fantasies, a lack of spontaneous sexual interest, or difficulty initiating sexual activity. Women may experience a similar decrease in sexual interest, but they might also report a diminished capacity for sexual arousal, lubrication, or orgasm.
These differences highlight the importance of considering individual experiences and not relying on generalized assumptions.
Talking about hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and coping strategies can be tough, but it’s important to remember you’re not alone. Just like tackling the grime in those hard-to-reach spots during spring cleaning (check out the 10 dirtiest places to hit during spring cleaning ), addressing HSDD takes a multifaceted approach. Finding the right support and understanding the various facets of the disorder is key to effective management and healing.
Ultimately, prioritizing your mental and physical well-being is crucial in dealing with HSDD.
Symptom Severity Levels
The severity of HSDD symptoms can be assessed using a tiered approach. The following table Artikels varying levels of symptom intensity, providing a general framework for understanding the potential impact on an individual’s life.
| Severity Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Mild | Occasional lack of interest in sex, minor impact on overall well-being. |
| Moderate | Regular periods of decreased sexual desire, noticeable impact on sexual relationships and personal satisfaction. |
| Severe | Persistent and significant absence of sexual desire, causing substantial distress and impacting daily life. Difficulty maintaining relationships and emotional well-being. |
Causes of HSDD
Understanding the causes of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is crucial for effective treatment and support. It’s not a simple issue, often stemming from a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and relational factors. Pinpointing the root causes allows for a more personalized approach to addressing the disorder.The factors contributing to HSDD are multifaceted and often intertwined. While a single cause might not fully explain the condition, a combination of elements frequently leads to decreased sexual desire.
Understanding these factors can empower individuals to address the underlying issues and work towards restoring a healthy sexual life.
Biological Factors
Biological factors significantly influence sexual desire. Hormonal imbalances, particularly a decrease in testosterone levels in both men and women, can contribute to a reduced libido. Medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, and certain neurological conditions can also impact sexual function and desire. Medications, including antidepressants and some blood pressure medications, can also sometimes reduce sexual desire as a side effect.
Genetic predispositions may also play a role, though further research is needed in this area.
Psychological Factors
Psychological factors can significantly impact sexual desire. Stress, anxiety, and depression can all negatively affect libido. Past trauma, whether physical or emotional, can also contribute to decreased sexual desire. Body image issues, low self-esteem, and negative experiences related to sexuality can also play a role in the development of HSDD. A history of sexual abuse or assault can profoundly affect sexual desire and functioning.
Relationship Issues
Relationship problems can be a major contributor to HSDD. Communication breakdowns, conflicts, and a lack of intimacy can negatively impact sexual desire. Feeling emotionally disconnected from a partner can make it challenging to feel sexual attraction or desire. Dissatisfaction with the relationship itself can also be a significant factor in reduced sexual desire. Difficulties in intimacy and trust can also significantly affect sexual desire.
Stress and Other Factors
Chronic stress, whether from work, family, or other sources, can significantly impact sexual desire. Financial strain, relationship conflicts, and major life changes can all contribute to stress-induced HSDD. A lack of sleep and poor overall health can also negatively impact sexual desire. Furthermore, substance abuse, including alcohol and drug use, can have a detrimental effect on sexual function and desire.
Interplay of Contributing Factors
| Factor | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Biological | Hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, medications | A woman experiencing a drop in estrogen levels due to menopause, or a man with a thyroid condition experiencing reduced testosterone. |
| Psychological | Stress, anxiety, depression, past trauma, body image issues | A person experiencing significant work-related stress leading to decreased libido, or someone with a history of sexual abuse struggling with intimacy. |
| Relationship Issues | Communication breakdowns, conflicts, lack of intimacy | A couple experiencing frequent arguments leading to a diminished desire for sexual activity, or a feeling of emotional detachment impacting sexual desire. |
| Stress and Other Factors | Chronic stress, poor health, substance abuse | A person under immense financial strain struggling to maintain sexual desire, or someone with a poor diet and lack of sleep experiencing reduced libido. |
Diagnosis of HSDD
Understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) begins with a thorough and compassionate evaluation. It’s crucial to remember that HSDD is not simply a lack of desire; it’s a complex condition with various potential contributing factors. A proper diagnosis requires careful consideration of the individual’s medical history, lifestyle, and emotional well-being. This process ensures that the underlying cause is identified, enabling effective and personalized treatment.Diagnosing HSDD involves a multifaceted approach, moving beyond a simple questionnaire.
It necessitates a comprehensive evaluation that delves into the individual’s complete health picture. This includes considering potential medical conditions, psychological factors, and relationship dynamics. Ultimately, a healthcare professional will work with the patient to understand the specific circumstances and arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Medical History Evaluation
A detailed medical history is fundamental to the diagnostic process. This includes inquiring about any pre-existing medical conditions, such as hormonal imbalances, chronic illnesses, or past surgeries. Furthermore, it involves exploring the patient’s current medications, as certain drugs can impact sexual desire. Understanding the patient’s lifestyle, including sleep patterns, diet, and exercise routine, is also important. Additionally, a thorough review of past and current psychological health, including any previous mental health diagnoses or ongoing stress, is essential.
Physical Examination, Hypoactive sexual desire disorder symptoms causes diagnosis treatment and coping
A physical examination, while not always directly related to sexual desire, can uncover potential underlying medical conditions. The examination may include checking for any physical signs or symptoms that might suggest a hormonal imbalance or other health concerns that could affect sexual function. This examination helps in ruling out any medical conditions that could be contributing to the decreased sexual desire.
Examples of such conditions could include thyroid issues or diabetes.
Questions a Healthcare Professional Might Ask
A healthcare professional will likely ask a series of questions to gain a deeper understanding of the patient’s situation. These questions are designed to gather comprehensive information, not to be judgmental. Some examples include:
- Have you experienced any changes in your sexual desire over time?
- Are there any particular situations or circumstances that seem to trigger or diminish your sexual desire?
- What is your current relationship status, and how has it affected your sexual desire?
- Have you experienced any recent life changes, such as job loss, relationship problems, or financial stress?
- Have you noticed any changes in your mood or energy levels?
- What is your current use of medications or supplements, including over-the-counter drugs?
These questions are intended to gather information about the patient’s experience and identify potential contributing factors. This comprehensive approach allows the healthcare professional to build a holistic picture of the patient’s health and well-being.
Diagnostic Process Steps
The diagnostic process for HSDD is a systematic evaluation. It’s not a one-size-fits-all approach; it’s tailored to the individual patient.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gather detailed medical history, including current medications, previous illnesses, and lifestyle factors. |
| 2 | Conduct a thorough physical examination to rule out any underlying medical conditions. |
| 3 | Assess psychological factors, including stress levels, relationship dynamics, and any previous mental health diagnoses. |
| 4 | Administer validated questionnaires to assess the severity and nature of sexual desire concerns. |
| 5 | Review laboratory tests (if necessary) to check for hormonal imbalances or other potential medical causes. |
| 6 | Discuss treatment options based on the diagnosis, involving both medical and psychological interventions. |
This structured approach ensures that all relevant aspects of the patient’s health are considered during the diagnostic process. This enables a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the individual’s situation, leading to a more effective and personalized treatment plan.
Dealing with low libido can be tough, and understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and coping strategies is key. Sometimes, physical factors like a concussion can also play a role in reduced desire. Learning how to recognize the signs of a concussion is crucial, as detailed in this helpful guide: how to tell if you have a concussion.
Ultimately, seeking professional medical advice for HSDD, including a thorough evaluation, is the best way to address any underlying concerns and develop a personalized approach to managing your sexual health.
Treatment Options for HSDD: Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder Symptoms Causes Diagnosis Treatment And Coping
Understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing that a single treatment rarely suffices. Treatment strategies are tailored to individual needs and may combine pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods. A thorough evaluation of the underlying causes, including medical conditions, psychological factors, and relationship dynamics, is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.Effective treatment for HSDD often involves a collaborative effort between the patient, their partner (if applicable), and healthcare professionals.
The goal is to address the root causes of the disorder and promote a healthy and fulfilling sexual relationship.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological interventions aim to increase libido by influencing hormone levels or addressing related conditions. These interventions are often used in conjunction with other therapies, as they don’t always address the underlying psychological or relationship factors.
- Hormone Therapy: In some cases, low levels of estrogen or testosterone may contribute to HSDD. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) aims to restore hormonal balance. This therapy may involve estrogen creams, oral medications, or testosterone patches. The effectiveness of HRT varies greatly among individuals, and it’s important to discuss potential side effects, such as breast tenderness, mood changes, or increased risk of blood clots with a healthcare professional.
- Other Medications: In some instances, other medications, such as antidepressants, may have a negative impact on libido. Adjusting medication dosage or switching to an alternative medication may be necessary in such cases. Consulting a physician is essential to explore the potential link between medication and decreased libido.
Non-Pharmacological Treatments
Non-pharmacological approaches address psychological, relationship, and lifestyle factors contributing to HSDD.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps identify and modify negative thoughts and behaviors related to sexuality. Techniques such as relaxation exercises and communication skills training can be beneficial for improving sexual satisfaction.
- Couple’s Therapy: Communication issues, relationship conflicts, or differing expectations regarding intimacy can contribute to HSDD. Couple’s therapy can help resolve conflicts, improve communication, and foster a more supportive environment for sexual expression.
- Lifestyle Changes: Addressing lifestyle factors like stress, poor sleep, or unhealthy diet can positively impact sexual desire. Promoting healthy habits, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet, may improve overall well-being and potentially increase sexual desire.
Comparison of Treatment Modalities
A table summarizing the pros and cons of various treatment options can aid in decision-making.
| Treatment | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hormone Therapy | Potential for increased libido, restoration of hormonal balance. | Potential side effects (e.g., breast tenderness, mood changes, increased risk of blood clots), variable effectiveness. |
| CBT | Addresses psychological factors, modifiable behaviors, improves communication. | Can be time-consuming, requires patient commitment and active participation. |
| Couple’s Therapy | Addresses relationship dynamics, improves communication, fosters support. | Requires commitment from both partners, may not be effective for all relationship issues. |
| Lifestyle Changes | Promotes overall well-being, achievable independently. | May not directly address underlying psychological or hormonal issues. |
Potential Side Effects of Medication
It’s crucial to understand that medications used to treat HSDD may have potential side effects. These should be carefully discussed with a healthcare professional before initiating any treatment. Common side effects may include nausea, headaches, or changes in mood. Monitoring for adverse effects is essential during treatment.
Coping Strategies for HSDD

Navigating hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) can be emotionally challenging, impacting self-esteem and relationships. However, effective coping strategies can significantly improve quality of life. This section delves into practical techniques for managing emotional distress, enhancing communication, and prioritizing self-care to better manage HSDD.Coping with HSDD involves a multifaceted approach, addressing emotional well-being, relationship dynamics, and individual self-care. Successful management necessitates understanding the interconnectedness of these areas and implementing strategies that cater to individual needs and preferences.
Managing Emotional Distress
Emotional distress is a common experience for individuals with HSDD. It often stems from feelings of inadequacy, shame, or anxiety about sexual performance or desire. Recognizing and validating these feelings is the first step toward managing them effectively. Strategies for emotional regulation, such as mindfulness practices and journaling, can be beneficial. Seeking support from therapists or support groups can provide a safe space to discuss concerns and develop coping mechanisms.
Improving Communication within Relationships
Open and honest communication is crucial for navigating HSDD within relationships. Partners need to understand the condition’s impact and be supportive rather than judgmental. Active listening, empathy, and a willingness to explore solutions together are essential. Couples therapy can be immensely helpful in learning effective communication skills and establishing shared goals. Joint exploration of alternative intimacy activities and mutual understanding of individual needs are important aspects of successful communication.
Importance of Self-Care and Stress Reduction
Prioritizing self-care is vital for managing HSDD. Stress, anxiety, and other lifestyle factors can exacerbate the condition. Implementing stress-reducing techniques like exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature can significantly improve overall well-being and potentially enhance sexual desire. A balanced lifestyle, including adequate sleep and a healthy diet, forms a strong foundation for emotional and physical health.
Coping Mechanisms Table
| Category | Coping Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional | Mindfulness Meditation | Focusing on the present moment to reduce anxiety and stress, promoting emotional regulation. |
| Emotional | Journaling | Writing down thoughts and feelings to gain self-awareness and process emotions related to HSDD. |
| Emotional | Seeking Professional Support (Therapy) | Working with a therapist to address emotional distress and develop coping strategies. |
| Emotional | Support Groups | Connecting with others experiencing similar challenges for mutual support and understanding. |
| Relationship | Open Communication | Discussing concerns, needs, and desires with your partner openly and honestly. |
| Relationship | Couples Therapy | Seeking professional guidance to improve communication and relationship dynamics. |
| Relationship | Exploring Alternative Intimacy | Discovering non-sexual activities that foster connection and intimacy. |
| Physical | Regular Exercise | Physical activity can reduce stress, improve mood, and potentially enhance libido. |
| Physical | Healthy Diet | Nourishing the body with a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being. |
| Physical | Adequate Sleep | Ensuring sufficient rest is essential for emotional and physical health. |
| Physical | Stress Reduction Techniques (Yoga, etc.) | Practicing relaxation techniques like yoga or deep breathing exercises to manage stress. |
Illustrative Case Studies (Hypothetical)
Understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) requires looking beyond just the symptoms. Case studies, while hypothetical, can illuminate the complexities of diagnosis and treatment, and the challenges individuals face in seeking help. They also illustrate how a personalized approach is crucial for success.These hypothetical cases will explore successful treatment approaches, highlight diagnostic and therapeutic hurdles, and illustrate the importance of patient-provider communication in navigating HSDD.
A Successful Treatment Approach
A 35-year-old woman, Sarah, presented with HSDD. Her initial evaluation revealed a history of relationship difficulties and significant stress stemming from a recent career change. Rather than focusing solely on medication, her therapist employed a multifaceted approach. This involved addressing the underlying stress through cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques, promoting open communication with her partner through couples therapy, and exploring potential hormonal imbalances.
Regular check-ins with her therapist and partner’s involvement in therapy proved crucial. Sarah experienced a noticeable increase in her sexual desire and a renewed sense of intimacy with her partner after several months of consistent therapy. This case highlights the importance of considering the psychological and relational factors contributing to HSDD, alongside potential biological influences.
A Challenging Aspect of Diagnosis or Treatment
Consider the case of Mark, a 45-year-old man experiencing HSDD. His medical history included a recent heart attack and several other chronic conditions. Diagnosing HSDD in this context proved challenging. The potential impact of medications for his other conditions, as well as the physiological changes related to his medical history, needed careful consideration. Furthermore, the potential for the condition to be a side effect of medication or a symptom of a related underlying medical condition added to the complexity.
Understanding hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and coping strategies can be a journey, but it’s important. While exploring this, it’s fascinating to consider the intricate workings of your body, like the incredible facts about your colon, which plays a crucial role in overall health. facts about your colon Ultimately, understanding HSDD involves a multifaceted approach, considering physical and psychological factors, and finding what works best for you.
This requires open communication, support, and potentially professional guidance.
Effective diagnosis required thorough medical evaluations to rule out any underlying medical conditions or medication side effects, followed by a comprehensive psychological assessment to determine the psychological factors involved. This scenario emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to diagnosis, recognizing the potential for interplay between physical and psychological factors.
Challenges in Seeking Help
Many individuals with HSDD face significant challenges in seeking professional help. Shame, embarrassment, and fear of judgment are common obstacles. Lack of awareness about HSDD as a legitimate medical concern also plays a role. Additionally, some individuals may struggle to find healthcare providers who are knowledgeable and experienced in treating sexual health issues. They might also worry about the cost of treatment and the potential for stigmatization.
These obstacles emphasize the importance of creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment for individuals seeking help. Promoting open communication and providing accessible resources can facilitate the process of seeking and receiving appropriate care.
Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is paramount in addressing HSDD. Consider this scenario: A 28-year-old woman, Emily, felt uncomfortable discussing her sexual concerns with her physician. Her physician, recognizing the sensitivity of the topic, adopted a gentle and empathetic approach. She encouraged Emily to describe her concerns in her own words and ensured her questions were answered thoroughly and without judgment.
By creating a safe space for discussion and using open-ended questions, the physician facilitated open communication. This approach, characterized by empathy, active listening, and non-judgmental language, is crucial in building trust and fostering a supportive therapeutic relationship. This approach encourages patients to feel comfortable disclosing their concerns and enables healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s situation.
Prevention and Risk Factors
Understanding the potential risk factors for hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) is crucial for proactive measures. While not all individuals experiencing HSDD will fit neatly into these categories, recognizing common threads can help identify individuals at risk and implement strategies for prevention or mitigation. This section will Artikel potential risk factors and present lifestyle modifications to reduce the likelihood of developing HSDD.
Identifying Potential Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of HSDD. These factors often intertwine, making it challenging to isolate any single cause. Chronic stress, for example, can negatively impact both physical and psychological well-being, potentially leading to reduced libido. Similarly, certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or diabetes, can influence hormone levels, which are directly linked to sexual desire.
Strategies for Preventing or Mitigating Risk Factors
Proactive steps can help mitigate the risk factors associated with HSDD. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is paramount. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can support overall well-being, including hormonal balance. Regular exercise, including cardiovascular activity and strength training, can help manage stress and improve mood, positively impacting libido. Adequate sleep is equally important, as sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal cycles and contribute to reduced desire.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce the Likelihood of HSDD
Lifestyle modifications play a vital role in reducing the risk of developing HSDD. Prioritizing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or meditation, can significantly impact overall well-being. Maintaining open communication with a partner about sexual needs and desires can strengthen the relationship and foster a supportive environment. Seeking professional help for underlying medical conditions, such as hormonal imbalances, can address the root cause of potential HSDD.
Table Summarizing Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
| Risk Factor | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| Chronic stress | Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Prioritize sufficient sleep and relaxation. |
| Medical conditions (e.g., thyroid disorders, diabetes) | Regular check-ups and adherence to medical treatment plans. Open communication with healthcare providers about sexual health concerns. |
| Relationship issues | Maintain open communication and healthy relationship dynamics. Seek couples therapy if needed. |
| Medication side effects | Discuss potential sexual side effects with a physician when starting new medications. Explore alternative medication options if possible. |
| Poor diet and lack of exercise | Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Incorporate regular physical activity into the daily routine. |
| Sleep deprivation | Establish a regular sleep schedule. Create a relaxing bedtime routine. Address underlying sleep disorders if present. |
Last Word
In conclusion, hypoactive sexual desire disorder symptoms causes diagnosis treatment and coping is a complex issue requiring a multifaceted approach. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the condition, touching upon the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and various treatment options. Remember, seeking professional help is crucial, and a collaborative effort between patients and healthcare providers is key to achieving positive outcomes.
Open communication, self-care, and understanding the nuances of the condition are essential components of successful coping strategies. This discussion emphasizes the importance of empathy, support, and personalized care in addressing HSDD.