Hip labrum surgery is it the right treatment? This exploration delves into the complexities of hip labrum tears, examining the various treatment options, from conservative methods to surgical interventions. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures, providing a comprehensive overview of the factors that influence treatment decisions.
Understanding the nuances of hip labrum tears is crucial for informed decision-making. This guide will help you navigate the process, from initial diagnosis to recovery, equipping you with the knowledge to discuss treatment options with your healthcare provider.
Introduction to Hip Labrum Surgery
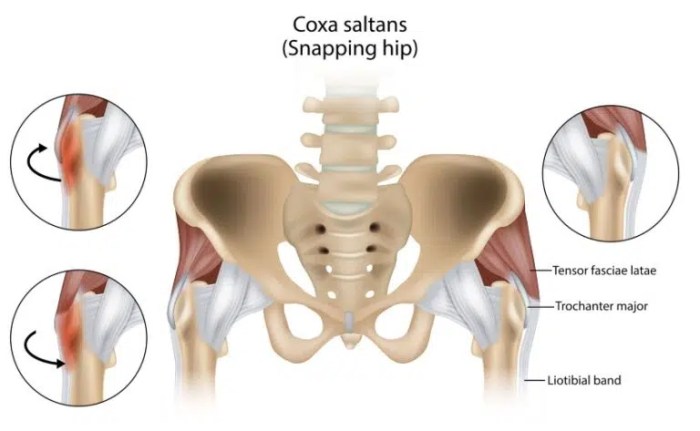
The hip labrum is a ring of cartilage that lines the socket of the hip joint. It acts as a gasket, deepening the socket and improving the joint’s stability. A tear in this cartilage, known as a hip labrum tear, can result in pain, instability, and decreased range of motion. Various factors can contribute to such tears, including repetitive stress, trauma, or underlying conditions.
Understanding the causes, function, and symptoms of hip labrum tears is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.Hip labrum tears can significantly impact the mechanics of the hip joint. The labrum’s primary role is to increase the contact area between the ball and socket, thus improving joint stability and reducing friction. Damage to the labrum can lead to abnormal movement patterns, increased wear and tear on the joint, and a predisposition to further injuries.
This disruption of normal joint mechanics is a key factor in the development of pain and disability.
Hip Labrum Tear Causes
Several factors can contribute to hip labrum tears. Repetitive stress, such as from sports activities or certain occupations, can gradually wear down the labrum. Trauma, like a fall or direct blow to the hip, can cause an acute tear. Underlying conditions like hip dysplasia, which affects the shape of the hip socket, can predispose individuals to labrum tears.
Furthermore, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to weaker or more susceptible labral tissue.
Hip Labrum Tear Symptoms
Common symptoms of hip labrum tears include pain, often felt in the groin, hip, or buttock area. The pain can vary in intensity and may be aggravated by specific movements, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs. Limited range of motion, clicking or popping sounds in the hip, and a feeling of instability or catching in the hip joint are also potential indicators.
Pain may also radiate down the leg.
Types of Hip Labrum Tears
Different types of hip labrum tears can affect the hip joint differently. The location of the tear plays a role in the resulting symptoms and treatment options. Here’s a comparison of the common types:
| Type | Location | Potential Symptoms | Treatment Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior | Front of the hip socket | Pain in the groin, difficulty with hip flexion (bending the hip), and potentially instability during walking. | May require surgical repair or conservative management depending on the severity. |
| Posterior | Back of the hip socket | Pain in the buttock or back of the hip, difficulty with hip extension (straightening the leg), and potential instability during certain movements. | Often requires surgical repair, especially if the tear is significant. |
| Superior | Top of the hip socket | Pain in the groin and upper hip region, potential for catching or clicking sensations, and reduced range of motion. | Treatment may range from physical therapy to surgery, depending on the severity of the tear. |
| Inferior | Bottom of the hip socket | Pain in the groin, potentially radiating down the inner thigh, difficulty with hip abduction (moving leg away from the body). | Surgical intervention may be necessary for significant tears. |
Diagnostic Procedures and Evaluation
Pinpointing the cause of hip pain, especially when a labral tear is suspected, requires a systematic approach. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment strategy. This often involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging studies, and potentially arthroscopy. Understanding the information each procedure provides is essential for making well-informed decisions.
Physical Examinations
Thorough physical examinations are the initial step in evaluating hip pain. Clinicians assess range of motion, palpating for tenderness, clicking, or grinding sensations. Specific tests, such as the impingement test and flexion abduction external rotation test, are used to evaluate for labral tears and other possible causes of pain. These tests help determine the location and nature of the pain, providing valuable clues about the potential involvement of the hip labrum.
Pain reproduction during specific movements, coupled with observed limitations in range of motion, can strongly suggest labral pathology.
Imaging Studies
Imaging plays a vital role in confirming suspected labral tears and evaluating the extent of the damage. Different imaging modalities offer varying levels of detail and information.
X-rays
X-rays are a fundamental initial step in evaluating the hip joint. They primarily assess for bony abnormalities, such as fractures, arthritis, or other bony injuries. X-rays provide a general overview of the hip structure, helping to rule out significant bony pathology. While not specifically designed to visualize soft tissues like the labrum, they can help identify potential contributing factors to the pain.
MRIs
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a powerful tool for visualizing soft tissues, including the labrum. MRI scans offer detailed images of the hip joint, showcasing the cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and the labrum itself. They can clearly identify labral tears, demonstrating their size, location, and degree of detachment from the underlying bone. An MRI can also reveal other soft tissue injuries that may coexist with a labral tear.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is an arthroscopic procedure that involves inserting a small camera into the hip joint through a small incision. This allows direct visualization of the joint structures, providing a high-resolution view of the labrum and other surrounding tissues. Arthroscopy is particularly useful for confirming the diagnosis and evaluating the extent of the labral tear in detail. It enables the surgeon to identify the precise location, size, and nature of the tear.
This direct visualization allows for precise assessment and can also guide surgical interventions, ensuring a tailored approach to the individual patient’s needs.
Importance of Proper Diagnosis
A precise diagnosis is crucial for developing the most effective treatment plan. An accurate assessment helps determine the severity of the tear and whether conservative or surgical intervention is necessary. Incorrect diagnoses can lead to inappropriate treatment choices, potentially prolonging the recovery period or causing further complications. Therefore, careful consideration of all diagnostic procedures is paramount in ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Summary Table of Typical Findings
| Imaging Modality | Typical Findings in Labral Tears |
|---|---|
| X-ray | May reveal signs of osteoarthritis, hip dysplasia, or other bony abnormalities. No direct visualization of the labrum. |
| MRI | Demonstrates labral tears as focal defects or detachment of the labrum from the underlying bone. Provides details on the size, location, and extent of the tear. May also show associated cartilage damage or other soft tissue injuries. |
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Hip labrum tears, while sometimes requiring surgical intervention, often respond well to non-surgical treatments. Conservative approaches can be highly effective in managing pain and restoring function, avoiding the risks and recovery time associated with surgery. These methods aim to reduce inflammation, promote healing, and improve mobility through targeted exercises and lifestyle modifications.Conservative treatment strategies focus on alleviating symptoms and promoting healing without the need for invasive procedures.
The effectiveness of each method can vary depending on the severity of the tear, the individual’s response to treatment, and the presence of any other contributing factors. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable course of action.
Physical Therapy, Hip labrum surgery is it the right treatment
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the non-surgical management of hip labrum tears. It’s a cornerstone of conservative treatment, focusing on restoring strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected hip joint. Exercises are tailored to address specific needs, and the progression of exercises is crucial for optimal results. The key is to gradually increase the intensity and complexity of the exercises as the patient’s condition improves.
Rest
Rest is an essential component of managing hip labrum tears, especially in the acute phase. It allows the injured tissues to heal and reduces further stress on the affected area. While complete bed rest might not always be necessary, avoiding activities that aggravate pain is crucial. This could involve modifying work tasks, avoiding high-impact sports, or adjusting daily routines to minimize hip strain.
Proper rest is vital for allowing the body to initiate the healing process.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with hip labrum tears. These medications can be particularly helpful in managing the initial inflammatory response, which often contributes to pain and discomfort. However, it’s essential to use these medications as directed by a healthcare professional, as they may have potential side effects, including gastrointestinal issues.
Considering hip labrum surgery? It’s a big decision, and figuring out if it’s the right treatment for you is key. While hip pain can be debilitating, understanding the common locations for skin conditions like eczema might offer some insight into the overall picture of your health. For example, knowing the most common location for eczema can help you identify potential triggers and improve your treatment plan.
Ultimately, a consultation with your doctor is crucial in deciding if hip labrum surgery is the right choice for your specific needs. most common location for eczema
Always consult with a doctor before taking any new medication, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.
Typical Physical Therapy Exercises and Stretches
| Exercise/Stretch | Description |
|---|---|
| Hip Flexor Stretch | Standing or seated, gently pull the knee towards the chest, holding for 20-30 seconds. |
| Hip Abduction Exercises | Side-lying with the affected leg raised, keeping the knee straight, to strengthen hip abductors. |
| Hip Extension Exercises | Prone position, raising the leg straight up to strengthen hip extensors. |
| Glute Bridges | Lying on the back, lifting the hips off the ground, contracting gluteal muscles. |
| Clamshells | Side-lying with knees bent, raising the top knee, targeting hip abductors. |
| Prone Hip Rotations | Lying on stomach, rotating the leg outward and inward, improving hip external and internal rotation. |
The specific exercises and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist will depend on the individual’s specific needs and the stage of healing.
Surgical Procedures for Hip Labrum Tears
Hip labral tears, often caused by repetitive stress, trauma, or a combination of factors, can lead to significant pain and dysfunction. Surgical intervention is sometimes necessary to restore hip joint stability and alleviate symptoms. This section will delve into the various surgical techniques employed for hip labral repair or reconstruction.Surgical procedures for hip labrum tears aim to address the underlying cause of the problem and restore the structural integrity of the labrum.
Different techniques exist, each with its own set of advantages and potential risks. Understanding these techniques allows patients and medical professionals to make informed decisions about the best course of action for their specific needs.
Arthroscopic Labral Repair
Arthroscopic labral repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that utilizes small incisions and specialized instruments to access and repair the damaged labrum. This approach is generally preferred for its smaller incision size, reduced recovery time, and decreased post-operative pain compared to open surgical techniques.The procedure typically involves the following steps:
- The surgeon makes small incisions in the hip joint, inserting a specialized camera (arthroscope) and small surgical instruments.
- The arthroscope allows visualization of the damaged labrum, enabling the surgeon to identify the extent of the tear.
- Using specialized instruments, the surgeon carefully cleans the area around the tear, removing any loose tissue or debris.
- Depending on the type of tear, the surgeon may use sutures, anchors, or other techniques to repair the labrum.
- The joint is flushed with saline solution to remove any residual debris.
- The incisions are closed, and a bandage is applied to the surgical area.
Open Labral Repair
Open labral repair is a more extensive surgical procedure, often reserved for cases where arthroscopic techniques are insufficient or not suitable. The surgeon makes a larger incision to directly access the hip joint, enabling a more comprehensive view and greater control over the repair.
- A larger incision is made in the hip joint, providing direct access to the damaged labrum.
- The surgeon carefully dissects the surrounding tissues to expose the labrum tear.
- The damaged labrum is cleaned and repaired using sutures, anchors, or other appropriate techniques.
- The surrounding tissues are carefully repositioned to restore normal joint anatomy.
- The incision is closed, and the surgical area is bandaged.
Comparison of Surgical Approaches
Arthroscopic surgery offers a less invasive approach, resulting in a quicker recovery, less pain, and smaller scars. However, it may not be suitable for all types of labral tears, particularly those involving significant bone damage or complex tear patterns. Open surgery, while more invasive, allows for greater visualization and control, which can be beneficial for complex repairs.
Surgical Instruments Used in Hip Labral Repair
The choice of surgical instruments depends on the specific procedure and the surgeon’s preference. Here’s a table outlining some common instruments used in hip labral repair procedures:
| Instrument | Description |
|---|---|
| Arthroscope | A small camera and light source used to visualize the hip joint interior. |
| Shaver | A tool for removing damaged or loose tissue from the joint. |
| Scissors | Used for precise tissue dissection. |
| Sutures | Used to repair the torn labrum. |
| Anchors | Used to secure sutures to the bone. |
| Graspers | Used to hold and manipulate tissues. |
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Hip Labrum Surgery: Hip Labrum Surgery Is It The Right Treatment
Recovering from hip labrum surgery is a journey, not a sprint. A diligent and structured rehabilitation program is crucial for a successful outcome. This involves a combination of pain management, targeted physical therapy, and gradual return to activities. Understanding the process and adhering to the prescribed protocol will significantly impact the recovery time and overall success of the surgery.The recovery period after hip labrum surgery is designed to restore hip function and strength while minimizing the risk of re-injury.
This phase involves a gradual increase in activity, starting with gentle movements and progressing to more challenging exercises. Patience and consistency are key components to a successful recovery.
Considering hip labrum surgery? It’s a complex decision, and the right treatment depends heavily on the individual’s specific case. Factors like the severity of the tear and the patient’s overall health play a crucial role. Understanding the potential costs, including those related to tariffs and OTC drug pricing fluctuations, can be critical when making your choice. For example, tariffs and OTC drugs can influence the price of necessary medications and supplies, which can impact the overall financial picture.
Ultimately, talking to a healthcare professional is key to determining if hip labrum surgery is the best path for you.
Pain Management
Effective pain management is essential for allowing patients to participate fully in their rehabilitation program. Strategies typically involve a combination of medication, physical therapy modalities, and lifestyle adjustments. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be sufficient for mild discomfort, while stronger medications might be necessary for more severe pain. Physical therapy modalities, such as ice packs, heat therapy, and electrical stimulation, can also help manage pain and inflammation.
Regular communication with the surgeon and physical therapist is crucial to ensure the pain management plan is optimized throughout the recovery process.
Physical Therapy Phases
A structured physical therapy program is tailored to each individual’s needs and recovery progress. It’s designed to gradually restore hip strength, flexibility, and range of motion. A typical progression of exercises and activities can be broken down into distinct phases.
| Phase | Focus | Duration (Approximate) | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 (Initial Post-Op) | Protecting the surgical site, managing pain, and regaining basic mobility. | 1-4 weeks | Gentle range of motion exercises, isometric exercises (contracting muscles without movement), and pain-free walking with assistive devices as needed. |
| Phase 2 (Early Strengthening) | Increasing hip strength and improving flexibility. | 4-8 weeks | Progressive resistance exercises (using light weights or resistance bands), balance exercises, and controlled walking. Activities such as stationary cycling and swimming can be incorporated. |
| Phase 3 (Advanced Strengthening) | Improving functional strength and preparing for return to activities. | 8-12 weeks | More challenging exercises, including plyometrics (jumping and hopping), sport-specific drills (if applicable), and functional exercises mimicking daily activities. Gradual return to impact activities, such as jogging or stairs, is also introduced. |
| Phase 4 (Return to Activity) | Full functional recovery and return to desired activity level. | 12+ weeks | Maintenance exercises to maintain gains, and progression to pre-injury activity levels. |
This table provides a general guideline. The duration of each phase may vary depending on the individual’s progress and the complexity of the surgery. Always follow the recommendations of your physical therapist and surgeon.
Return to Activity Timelines
The timeline for returning to various activities depends on the extent of the injury, the surgical procedure, and the individual’s progress through the rehabilitation program. Light activities like walking can often begin within a few days of surgery, while more strenuous activities, such as running or contact sports, typically require several months of recovery. It’s crucial to avoid overexertion and allow the body adequate time to heal to prevent re-injury.
Factors Influencing Recovery Time
Several factors can influence the recovery time after hip labrum surgery. These include the severity of the tear, the individual’s overall health, adherence to the rehabilitation program, and the surgeon’s expertise. Age, pre-existing conditions, and the patient’s motivation also play a significant role. For instance, a more extensive tear or a patient with underlying medical conditions may take longer to recover.
Furthermore, a strong commitment to the rehabilitation protocol is crucial for a faster and more complete recovery.
Potential Complications
Potential complications after hip labrum surgery are generally rare but include infection, blood clots, persistent pain, stiffness, or incomplete recovery. Addressing any concerns promptly with the surgeon is essential for effective management. Regular follow-up appointments and adherence to the recovery plan are critical in mitigating these risks. Open communication with the surgical team allows for proactive intervention if any complications arise.
Factors Affecting Treatment Decisions
Deciding whether hip labrum surgery is the right course of action isn’t a simple yes or no. It’s a nuanced evaluation considering various factors unique to each patient. A surgeon carefully weighs the potential benefits and risks against the patient’s individual circumstances to determine the most appropriate treatment path.Surgeons aren’t simply looking at the tear itself. They consider the patient’s overall health, activity level, and how the labrum tear impacts their daily life.
This holistic approach ensures the best possible outcome, balancing the need for intervention with the desire for a minimally invasive and effective solution.
Severity of the Tear
The extent of the hip labrum tear significantly influences treatment decisions. A small, stable tear might not require surgery, whereas a large, unstable tear causing significant pain and dysfunction may necessitate surgical intervention. Surgical repair aims to restore the labrum’s integrity and function, while non-surgical approaches focus on managing symptoms and promoting healing. The surgeon carefully assesses the tear’s size, location, and the presence of any associated damage to other structures in the hip joint.
Patient’s Activity Level
A patient’s activity level plays a crucial role in determining the best course of action. An individual leading a sedentary lifestyle might respond well to non-surgical treatments like physical therapy and activity modification. Conversely, an athlete requiring high-impact movements or frequent weight-bearing activities might benefit more from surgical repair to restore function and prevent further damage. A professional athlete with a large tear affecting their performance would likely be a strong candidate for surgery.
Overall Patient Health
Pre-existing medical conditions, such as arthritis or other joint problems, can influence the suitability of hip labrum surgery. The presence of other health concerns may necessitate a more conservative approach to avoid additional risks. For instance, a patient with significant cardiovascular issues might not be an ideal candidate for surgery, even with a severe labrum tear. A careful assessment of the patient’s medical history is essential to determine the safest and most effective treatment plan.
Patient’s Goals and Expectations
A key factor is the patient’s expectations and desired outcomes. Open communication between the patient and the surgeon is crucial to ensure mutual understanding and agreement on the treatment plan. A patient who desires complete restoration of function and the ability to return to their pre-injury activity level may be a better candidate for surgery. Conversely, a patient prioritizing symptom relief and improved quality of life might find non-surgical management more suitable.
Comparison of Surgical and Non-Surgical Options
| Feature | Non-Surgical Options | Surgical Options |
|---|---|---|
| Potential Benefits | Reduced risk of surgery-related complications, quicker recovery, and potentially more cost-effective. | Restoration of labrum integrity and function, potentially addressing underlying causes of pain and dysfunction, and returning to previous activity levels. |
| Potential Risks | Limited effectiveness in severe cases, potential for persistent pain, and possible need for future interventions. | Potential complications like infection, nerve damage, or blood clots, longer recovery period, and higher costs. |
| Recovery Time | Typically shorter than surgical recovery. | Typically longer recovery period, requiring a period of rehabilitation and physical therapy. |
| Success Rate | Variable depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s compliance with the treatment plan. | Generally higher success rates in addressing severe tears and restoring full function, especially for athletes. |
“The ultimate decision rests with the patient, in consultation with their surgeon, weighing the potential benefits and risks of each approach.”
Potential Complications and Risks
Hip labrum surgery, while often effective, carries potential risks. Understanding these complications is crucial for informed decision-making, alongside a thorough discussion with your surgeon. Proper preparation and proactive risk mitigation strategies can significantly reduce the likelihood of encountering these issues.
Potential Complications
Post-operative complications can arise from various factors, including the surgical procedure itself, individual patient characteristics, and post-operative care. Careful monitoring and management are essential to address these issues promptly and effectively.
Infection
Surgical procedures, by their nature, introduce a risk of infection. This risk is not unique to hip labrum surgery but is a concern across various surgical interventions. The prevalence of infection following hip labrum surgery is relatively low, typically reported in the range of 0.5% to 1.5%. Severity can range from localized skin infections to more systemic infections requiring intravenous antibiotics.
Maintaining meticulous surgical technique, proper wound care, and vigilant monitoring for signs of infection are crucial strategies to minimize this risk.
Blood Clots (Deep Vein Thrombosis – DVT)
Blood clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are a possible complication following any surgical procedure that involves prolonged immobilization. DVTs can develop in the deep veins of the leg and, in rare cases, can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). While the exact prevalence varies, studies suggest that DVTs occur in a percentage of patients undergoing hip surgery.
Strategies to reduce the risk of DVT include early mobilization, compression stockings, and medication like anticoagulants.
Persistent Pain
Although hip labrum surgery aims to alleviate pain, some patients may experience persistent or even increased pain after the procedure. This can stem from various factors, including incomplete healing, scar tissue formation, or other underlying conditions. While not all cases result in persistent pain, the percentage of patients experiencing some level of persistent pain can range from a small percentage to a higher number depending on the individual factors.
Rehabilitation programs tailored to individual needs, and proactive management of pain are essential strategies.
Other Potential Complications
Other potential complications include, but are not limited to, nerve damage, numbness, or weakness in the affected leg, and, in rare instances, a reaction to anesthesia. These complications are less frequent but can still occur. Factors such as the surgeon’s experience and surgical technique can play a role in the likelihood of these complications.
Signs and Symptoms of Complications
| Potential Complication | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Infection | Redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus or drainage from the incision site, fever, chills. |
| DVT | Swelling, pain, redness, warmth in the affected leg, especially in the calf, difficulty moving the leg. |
| Persistent Pain | Continued or increased pain in the hip area, even after rehabilitation. |
| Nerve Damage | Numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of sensation in the affected leg or foot. |
Alternatives and Other Considerations
Hip labrum surgery is a significant procedure, and it’s crucial to explore all available options before making a decision. While often the most effective treatment for severe hip labrum tears, it’s not always the right choice for every patient. Factors like the severity of the tear, the patient’s overall health, and lifestyle play a critical role in determining the best course of action.
This section will delve into alternative treatments and essential considerations beyond surgery.Alternative approaches to treating hip labrum tears exist, offering potential benefits for specific cases. These range from conservative management to minimally invasive procedures, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these alternatives allows patients to make informed decisions in conjunction with their healthcare providers.
Alternative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment often forms the initial approach for hip labrum tears. This typically involves a combination of physical therapy, activity modification, and pain management strategies. Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles surrounding the hip joint, improving flexibility, and restoring proper biomechanics. Activity modification aims to reduce the impact on the injured area, while pain management can include over-the-counter pain relievers or, in more severe cases, prescription medications.
In some instances, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation. These conservative measures can be effective in managing mild to moderate hip labrum tears, allowing for a non-surgical solution.
Patient-Specific Factors
Patient-specific factors significantly influence the choice of treatment. Age is a crucial consideration. Younger patients, particularly athletes, may benefit from surgical intervention to maintain optimal joint function and prevent long-term complications. Older patients might find non-surgical options more suitable, given their potential for a slower recovery period. Overall health conditions, such as arthritis or other joint issues, also impact treatment choices.
Deciding if hip labrum surgery is the right choice can be tough. It’s important to consider all your options, and understanding your health insurance is key. For example, knowing the difference between an HSA and an FSA can significantly impact your out-of-pocket costs, especially when considering a procedure like this. hsa vs fsa whats the difference Ultimately, talking to your doctor about your specific situation and carefully weighing the pros and cons of surgery is crucial for making an informed decision.
Lifestyle factors, like the patient’s occupation and level of physical activity, play a role in determining the suitability of various treatments. For example, a professional athlete with a significant hip labrum tear will likely require surgical intervention to maintain their performance level, while a sedentary individual might be able to manage the condition with non-surgical therapies.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches
A comprehensive comparison of hip labrum surgery with other treatments is crucial for informed decision-making. Surgery is often reserved for severe cases, including those with significant instability or persistent pain not responding to conservative measures. In contrast, conservative management provides a less invasive approach, suitable for individuals with milder symptoms. Minimally invasive procedures, such as arthroscopy, represent a middle ground, offering a less extensive surgical intervention than traditional open surgery.
The success rate of each approach depends on factors such as the severity of the tear, the individual’s response to treatment, and the expertise of the medical team.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical approaches are valuable options for managing hip labrum tears, especially in the initial stages or for individuals not suitable for surgery. These methods often focus on reducing pain, improving function, and preventing further damage.
| Treatment Option | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Exercises to strengthen hip muscles, improve flexibility, and restore proper mechanics. | Improved joint stability, reduced pain, and enhanced function. | Requires commitment and adherence to a prescribed regimen. |
| Activity Modification | Adjusting activities to reduce stress on the hip joint. | Reduces pain and inflammation. | May require significant lifestyle adjustments. |
| Pain Management | Over-the-counter or prescription medications, or corticosteroid injections. | Reduces pain and inflammation. | May have side effects, and injections may not address the root cause. |
| Injections (e.g., Corticosteroids) | Administering corticosteroids directly into the hip joint. | Temporary pain relief and reduced inflammation. | Potential for side effects, and not a long-term solution. |
Patient Experiences and Success Stories (Illustrative)
Hip labrum surgery, while often a necessary procedure, can evoke a range of emotions and expectations in patients. Understanding real-life experiences can provide valuable insights into the recovery process and the potential outcomes. This section highlights illustrative cases to illustrate successful outcomes and emphasize the importance of realistic patient expectations.
Illustrative Patient Experiences
Many patients report significant improvements in their quality of life following hip labrum surgery. The recovery journey, however, varies greatly depending on individual factors such as age, pre-existing conditions, and the extent of the tear.
Successful Outcomes and Positive Aspects
A common theme in positive patient experiences is a noticeable reduction in pain and improved mobility. This improvement often translates to increased participation in daily activities and hobbies. For instance, a 35-year-old professional athlete who underwent hip labrum repair reported a return to competitive play within six months, albeit with a modified training regimen. This illustrates how surgery can enable a return to a fulfilling lifestyle, albeit with careful consideration of physical limitations during recovery.
Another patient, a 60-year-old retiree, regained the ability to walk comfortably and participate in social activities like gardening. These experiences demonstrate the positive impact of surgery on overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes and Benefits
Hip labrum surgery can lead to significant lifestyle changes, and these changes are often perceived positively by patients. Many patients report being able to engage in activities they previously found painful or impossible, like dancing, hiking, or simply enjoying a longer walk with their loved ones. The ability to resume everyday tasks without pain significantly enhances their quality of life.
Importance of Patient Expectations and Realistic Outcomes
It’s crucial for patients to understand that complete recovery and a full return to previous activity levels may not be immediate. While surgery can be a significant step toward improvement, realistic expectations about recovery time and potential limitations are essential for a positive experience. A thorough discussion with the surgeon about potential limitations and necessary physical therapy is critical to manage expectations and avoid disappointment.
The surgeon’s role in counseling patients about the potential range of outcomes is paramount. This includes discussing possible limitations, long-term care needs, and the need for ongoing physical therapy. Realistic expectations prevent disappointment and promote a more positive and sustainable recovery.
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not hip labrum surgery is the right treatment is a personal one. Weighing the potential benefits and risks, alongside your individual circumstances, is key. This detailed analysis should empower you to make an informed choice, working closely with your doctor to determine the best course of action for your specific needs.