Two dates a day for health benefits: This post explores the potential advantages of incorporating two dates daily into your diet. From understanding the nutritional powerhouse that dates are, to learning how to incorporate them into various meals and snacks, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll examine different date types, preparation methods, potential…
Tag: healthy eating
Weight Loss Reverses Type 2 Diabetes
Weight loss reverse type 2 diabetes is a powerful concept, showing how shedding pounds can dramatically improve health. This journey involves understanding the mechanisms linking obesity to diabetes, learning about effective weight loss strategies, and the vital role of lifestyle modifications. From dietary approaches to exercise and stress management, this exploration will guide you through…
Watercress Benefits A Nutrition Profile
Watercress benefits and nutrition profile sets the stage for an exploration of this vibrant leafy green. From its historical uses to its modern-day health advantages, we’ll delve into the nutritional value, potential health benefits, and various ways to enjoy this versatile ingredient. Discover the surprising wealth of nutrients packed within each bite. This comprehensive guide…
Avocados Amazing Health Benefits
Health benefits of avocado are plentiful and impressive. This delicious fruit packs a powerful nutritional punch, offering a wide array of advantages for your overall well-being. From supporting heart health and healthy digestion to managing blood sugar and even promoting healthy skin, avocados are a versatile and valuable addition to any healthy diet. Let’s dive…
How to Eat Healthy A Comprehensive Guide
How to eat healthy is a journey, not a destination. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of healthy eating, exploring everything from fundamental nutritional principles to practical strategies for incorporating healthy choices into your daily life. We’ll cover a wide range of topics, including understanding balanced nutrition, practical dietary guidelines, and addressing specific dietary…
Foods and Drinks to Avoid for Weight Loss
Foods and drinks to avoid for weight loss are crucial for successful weight management. This guide dives deep into the world of nutrition, exploring the detrimental effects of certain foods and beverages on your weight loss journey. From sugary drinks to processed meals, we’ll uncover hidden pitfalls and provide practical alternatives for a healthier lifestyle….
What to Eat Before a Workout Fuel Your Fitness
What to eat before a workout is crucial for peak performance. This guide dives deep into the science behind pre-workout nutrition, exploring the ideal foods, timing, and macronutrient ratios to maximize your energy and minimize discomfort. From carbohydrate-rich powerhouses to protein-packed muscle builders, and healthy fats for sustained energy, we’ll cover it all. Learn how…
Foods to Help Gain Weight A Comprehensive Guide
Foods to help gain weight are more than just calorie-dense options; they’re the building blocks for a healthy, positive transformation. This guide delves into the nutritional value of various foods, highlighting the importance of macronutrients like protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats for muscle growth and overall well-being. We’ll explore calorie-dense foods, safe strategies for weight…
Best Way to Boost Fiber Without Bloating
Best way to boost fiber without bloating is a crucial concern for many. This guide delves into a variety of high-fiber foods, strategies to ease your way into increased fiber, and how to manage any potential bloating. We’ll explore different types of fiber, their impact on digestion, and ways to incorporate them into your diet…
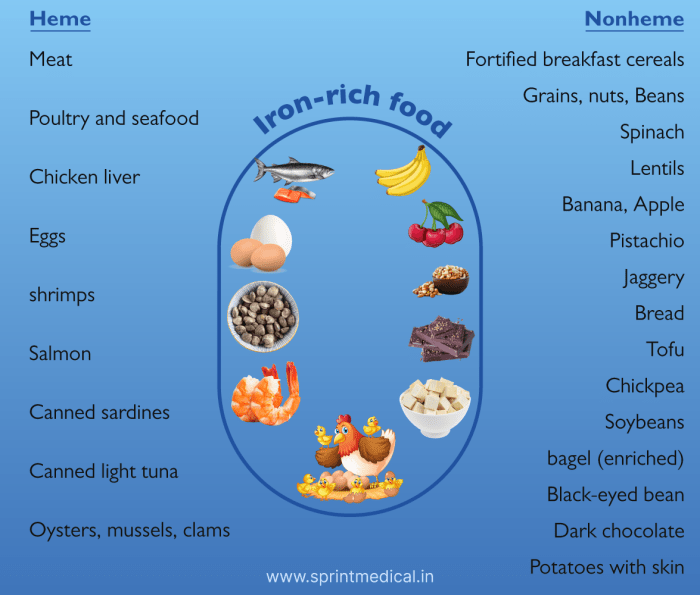
Foods with More Protein Than Chicken
Foods with more protein than chicken are a great way to boost your daily intake. Beyond the familiar chicken breast, a wealth of other protein powerhouses exist, offering diverse nutritional benefits. This exploration delves into various protein-rich foods, comparing their protein content to chicken and highlighting their overall nutritional profiles. From lean meats to plant-based…