What to eat on your period? This isn’t just about cravings; it’s about understanding your body’s unique needs during menstruation. From boosting energy levels to easing discomfort, the right foods can make a real difference. This guide dives deep into the nutritional needs of your cycle, offering practical advice and delicious meal ideas. We’ll explore…
Tag: healthy eating
Foods for Kidney Health A Guide
Foods for kidney health play a crucial role in maintaining optimal kidney function. This comprehensive guide explores various dietary approaches, from beneficial foods to those to limit, highlighting the importance of a balanced diet for kidney well-being. We’ll delve into plant-based and animal-based protein sources, hydration strategies, and even the role of supplements. Understanding the…
Candida Diet Foods to Avoid A Comprehensive Guide
Candida diet foods to avoid are crucial for managing or preventing Candida overgrowth. This guide delves into a comprehensive list of problematic foods, categorized by food group. We’ll explore the science behind why certain foods fuel Candida yeast and offer practical tips for identifying and avoiding them, even when eating out. Discover hidden sources of…
Top Fish Choices for Protein Boost
Top fish choices to boost your protein intake are a fantastic way to nourish your body with essential nutrients. From the delicate flavors of salmon to the firm texture of tuna, a variety of fish offer an excellent source of high-quality protein, alongside vital vitamins and minerals. This guide explores the best fish options, delves…
Losing Weight Gluten-Free Your Guide
Losing weight gluten free can be a rewarding journey, but it’s crucial to approach it with the right knowledge and strategies. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, exploring the potential benefits and common pitfalls of a gluten-free diet for weight management. We’ll delve into meal planning, practical strategies, and important considerations to ensure a sustainable…
List of Starchy Vegetables A Deep Dive
Kicking off with a list of starchy vegetables, this post delves into the fascinating world of these nutrient-rich foods. From potatoes and sweet potatoes to corn and cassava, we’ll explore their nutritional value, culinary uses, and even their environmental impact. Get ready to discover the diverse ways these staples contribute to a healthy and balanced…
Olive Oil and Lemon Juice A Flavorful Fusion
Olive oil and lemon juice: a flavorful fusion that elevates countless dishes. From zesty marinades to bright dressings, this dynamic duo transforms simple meals into culinary masterpieces. This exploration dives into the world of olive oil and lemon juice, revealing their incredible versatility, surprising health benefits, and fascinating cultural significance. We’ll delve into the diverse…
Are Smoothies Good for You? A Deep Dive
Are smoothies good for you? This exploration delves into the nutritional value, health benefits, potential drawbacks, and more. We’ll examine the ingredients, preparation methods, and how smoothies fit into a balanced lifestyle. From the vitamins and minerals packed into various fruits and vegetables, to the potential pitfalls of excessive consumption, this guide will equip you…
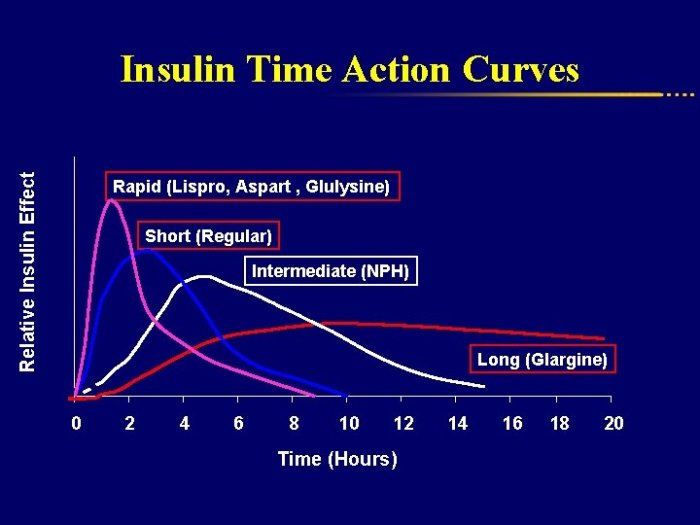
Type 2 Diabetes Diet Your Guide to Healthy Eating
Type 2 diabetes diet is crucial for managing this condition effectively. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the dietary principles and strategies necessary for a healthy lifestyle. It explores the fundamental aspects of a balanced diet, emphasizing portion control and the importance of specific food choices. We’ll delve into macronutrient balance, food recommendations, practical…
Type 2 Diabetes Meal Planning Your Guide
Type 2 diabetes meal planning is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and overall health. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential principles, practical strategies, and resources to create a personalized meal plan that fits your needs and lifestyle. We’ll explore everything from macronutrient distribution to carbohydrate counting, healthy food choices, and even meal planning…