Overview of strep throat dives deep into the world of this common ailment, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. From understanding the initial stages to recognizing potential complications, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to navigate this health concern effectively.
This comprehensive overview will cover everything from the initial symptoms to the necessary treatments and potential complications. We’ll explore the different ways strep throat can manifest, and the crucial importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, we’ll discuss the various preventive measures you can take to safeguard yourself and others.
Introduction to Strep Throat
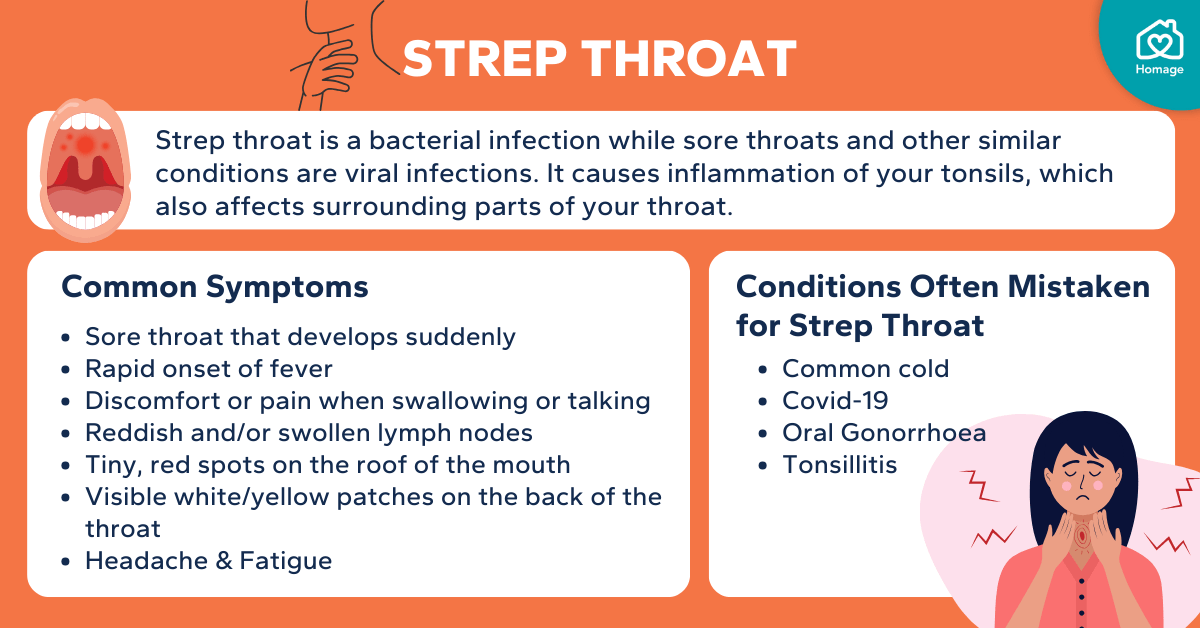
Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a common bacterial infection of the throat and tonsils. It’s typically caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria, and while it can affect people of all ages, it’s more prevalent in children and young adults. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and progression of strep throat is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Early intervention is key to preventing potential complications.This condition is characterized by a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity. Identifying these symptoms early can significantly impact the course of treatment and recovery. The infection typically progresses through distinct phases, each marked by specific characteristics. Prompt recognition of these phases is essential for initiating timely treatment and minimizing the risk of complications.
Recognizing the patterns of symptoms, including their severity and duration, can be instrumental in aiding medical professionals in making accurate diagnoses.
Defining Strep Throat
Strep throat is a contagious bacterial infection of the throat and tonsils. The infection is caused by the Streptococcus pyogenes bacterium. It’s characterized by inflammation and soreness in the throat, often accompanied by other symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Strep Throat
The symptoms of strep throat often develop suddenly and can include:
- Sore throat, often described as scratchy or painful, especially when swallowing.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Fever, sometimes reaching high temperatures.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
- Headache.
- Body aches.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting (more common in children).
- Red and swollen tonsils, possibly with white patches or streaks of pus.
These symptoms, while common, can vary in severity and presentation depending on the individual and the stage of the illness.
Typical Progression of Strep Throat, Overview of strep throat
Strep throat typically begins with a sudden onset of symptoms. The initial phase is characterized by the rapid development of throat pain and inflammation. The symptoms often peak within a few days and then gradually subside with proper treatment. If left untreated, strep throat can lead to potential complications, including rheumatic fever and kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis). This is why prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications and promoting a faster recovery. Untreated strep throat can lead to serious complications, such as rheumatic fever, a potentially life-threatening inflammatory disease that can affect the heart, joints, and brain. Prompt medical attention allows for appropriate antibiotic treatment, which can significantly reduce the duration of illness and prevent these complications.
Overview of Strep Throat Types (if any exist)
While strep throat is primarily caused by group A Streptococcus, different strains can exhibit varying degrees of severity. However, there are no distinct “types” of strep throat categorized based on different bacterial strains in a clinically significant way. The focus is on the symptoms and prompt treatment rather than variations in bacterial types.
Stages of Strep Throat
| Symptom |
Severity |
Duration |
| Sore throat, slight fever |
Mild |
1-3 days |
| Severe sore throat, high fever, swollen tonsils |
Moderate |
3-5 days |
| Persistent sore throat, lingering fever, possible complications |
Severe |
5+ days (requires medical intervention) |
This table provides a general guideline for the typical progression of strep throat symptoms. Severity and duration can vary considerably depending on individual factors and response to treatment.
Causes and Transmission
Strep throat, a common ailment, is caused by a specific type of bacteria, making it a contagious infection. Understanding the causative agents and transmission methods is crucial for prevention and treatment. This section will delve into the factors contributing to strep throat transmission, including the role of bacteria, transmission routes, and associated risk factors.The primary culprit behind strep throat isStreptococcus pyogenes*, a bacterium belonging to the group A streptococci (GAS).
These bacteria produce toxins that irritate the throat and cause the characteristic symptoms. This specific type of bacteria is responsible for the infection, distinguishing it from other throat irritations.
Causative Agents
The primary causative agent of strep throat isStreptococcus pyogenes*. This bacterium, known as group A streptococcus (GAS), is a common inhabitant of the throat and nasal passages. Its presence does not always lead to infection; however, under certain conditions, it can multiply rapidly and cause the symptoms associated with strep throat.
Transmission Methods
Strep throat is highly contagious, spreading through close contact with an infected person. The bacteria are transmitted through respiratory droplets expelled when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or talks. Direct contact with contaminated objects, such as shared utensils or toys, can also facilitate transmission. The virus spreads rapidly in enclosed spaces like schools and dormitories.
So, I’ve been researching strep throat lately, and it’s surprisingly complex. Understanding the different types and how to treat them is key. This leads me to consider other health challenges, like the progression of time to castration resistant prostate cancer , and the various strategies for managing it. Ultimately, it all boils down to the importance of proactive health care and staying informed.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the susceptibility to strep throat.
Age
Children in school-age and preschool years are at higher risk due to close contact and frequent exposure to respiratory droplets. Younger children often have less developed immune systems and are more likely to contract strep throat when exposed. Adults can also be susceptible, but their immune systems generally provide a better defense.
Environment
Crowded environments, such as classrooms, daycare centers, and dormitories, significantly increase the risk of strep throat transmission. The close proximity and frequent contact among individuals in these settings facilitate the spread of respiratory droplets containing the bacteria.
Personal Hygiene
Poor hygiene practices, such as inadequate handwashing, can contribute to the spread of strep throat. Failure to wash hands after coughing or sneezing can spread the infection to others. Sharing personal items like utensils and drinking glasses can also transmit the bacteria. The importance of frequent handwashing and maintaining hygiene cannot be overstated in preventing the spread of the infection.
Comparison of Transmission Routes
| Infectious Agent |
Transmission Route |
| *Streptococcus pyogenes* (Strep Throat) |
Respiratory droplets, direct contact with contaminated objects |
| Influenza Virus |
Respiratory droplets |
| Common Cold Virus |
Respiratory droplets, direct contact with contaminated surfaces |
This table highlights the common transmission routes for various infectious agents. Note the overlap in transmission methods, emphasizing the importance of general hygiene practices in preventing the spread of different infections.
Prevention Through Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in preventing the spread of strep throat. Frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after coughing or sneezing, is essential. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals, particularly in enclosed spaces, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Disinfecting frequently touched surfaces and objects can also help prevent the spread of the infection.
Diagnosis and Testing
Figuring out if you have strep throat often involves a combination of physical examination and specific tests. Doctors use these methods to identify the bacteria responsible for the infection and determine the best course of treatment. A prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for preventing complications and ensuring a faster recovery.Doctors typically begin with a physical examination, looking for signs like redness and swelling in the throat, white patches or spots on the tonsils, and swollen lymph nodes.
This initial assessment helps guide the decision on which tests to perform.
Rapid Antigen Tests
Rapid antigen tests are a quick and convenient way to detect the presence of strep bacteria. These tests use a sample of fluid from the back of the throat to identify specific proteins produced by the bacteria. Results are usually available within minutes, allowing for a prompt diagnosis and immediate treatment initiation.
Throat Culture
A throat culture is a more definitive diagnostic method, although it typically takes longer to produce results compared to rapid antigen tests. For a throat culture, a cotton swab is used to collect a sample from the back of the throat. This sample is then sent to a laboratory where it’s examined under a microscope to identify the presence of streptococcal bacteria.
Diagnostic Test Comparison
The accuracy of these tests varies slightly. A table below summarizes the key characteristics and accuracy rates of the diagnostic methods:
| Test Type |
Accuracy |
Time to Results |
Cost |
| Rapid Antigen Test |
Typically 80-95% accurate |
Minutes |
Relatively low |
| Throat Culture |
Very high accuracy (95-98%) |
24-48 hours |
Slightly higher |
Note: Accuracy rates can vary depending on the specific test used and the experience of the healthcare provider.
Interpreting Rapid Strep Test Results
Understanding the results of a rapid strep test is crucial for appropriate action. A positive result indicates the presence of strep bacteria, while a negative result suggests the absence of strep. However, a negative result does not always rule out strep throat. If the result is negative, a throat culture might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis, especially if clinical symptoms strongly suggest strep throat.
Importance of Follow-Up Testing
If a rapid strep test is negative, but symptoms persist or worsen, a follow-up throat culture may be necessary to confirm or rule out the presence of strep throat. This ensures that the most accurate diagnosis is made and the appropriate treatment is given. Additionally, it helps prevent the spread of the infection, especially in close contacts, by providing a clear diagnosis.
For example, if a child shows symptoms but a rapid strep test is negative, a follow-up throat culture may be necessary to confirm or rule out the infection.
Treatment and Management
Strep throat, while often uncomfortable, is typically treatable and manageable. Prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery. The cornerstone of treatment is the use of antibiotics, which effectively target the bacterial infection. Understanding the treatment protocols, including the importance of completing the entire course, is vital for successful management.Effective management of strep throat involves a combination of medical interventions and home remedies to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
A comprehensive approach ensures a swift and comfortable return to health.
Standard Treatment Protocols
Treatment for strep throat typically involves a course of antibiotics. These medications, specifically designed to combat bacteria, are essential in eradicating the infection. The selection and duration of antibiotics are determined by the patient’s medical history and the severity of the infection.
Role of Antibiotics in Treating Strep Throat
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for strep throat. They work by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria, the causative agent of strep throat. This disruption of bacterial activity allows the body’s immune system to effectively clear the infection. By targeting the bacteria directly, antibiotics help to reduce the duration and severity of symptoms.
Importance of Completing the Entire Course of Antibiotics
It’s crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms subside. Stopping the medication prematurely can lead to the resurgence of the infection. This incomplete treatment allows some bacteria to survive and potentially develop antibiotic resistance. This resistance can make future strep throat infections more challenging to treat. Following the prescribed dosage schedule is essential to achieve the desired therapeutic effect and prevent the development of resistant strains.
Potential Side Effects of Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment, while effective, can sometimes have side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. In rare cases, more serious allergic reactions can occur. It’s essential to discuss any concerns about potential side effects with your healthcare provider. They can advise on how to manage any discomfort and monitor for any adverse reactions.
Comparison and Contrast of Different Antibiotic Regimens
Various antibiotics are effective against strep throat. Penicillin is often a first-line treatment due to its generally good safety profile and effectiveness. Amoxicillin, a penicillin derivative, is also commonly used. Other antibiotics, like cephalosporins, are considered if penicillin allergies exist. The choice of antibiotic depends on several factors, including individual patient sensitivities and potential allergic reactions.
Consult your physician to determine the most suitable antibiotic regimen for your specific needs.
Home Remedies for Symptom Relief
While antibiotics address the bacterial infection, several home remedies can provide symptom relief. Rest, hydration, and a soft diet can help alleviate discomfort. Warm salt water gargles can soothe sore throats. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage fever and pain. Applying a cool compress to the neck can also provide temporary relief.
These remedies can enhance comfort and well-being during the recovery period.
So, you’re looking for a quick overview of strep throat? It’s a common bacterial infection, often causing sore throats, fever, and sometimes a rash. Interestingly, recent studies, like the sauerkraut gut health study , are exploring the potential link between gut health and immune function, which might play a role in how our bodies fight off infections like strep throat.
Hopefully, this overview gives you a good starting point!
Antibiotic Regimens
| Antibiotic |
Dosage |
Potential Side Effects |
| Penicillin V |
250-500 mg orally every 6-8 hours for 10 days |
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions (rare) |
| Amoxicillin |
250-500 mg orally every 8 hours for 10 days |
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions (rare) |
| Cephalexin |
250-500 mg orally every 6-8 hours for 10 days |
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, allergic reactions (rare) |
Complications and Prevention: Overview Of Strep Throat
Strep throat, while often treatable with antibiotics, can lead to serious complications if left untreated or inadequately addressed. Understanding these potential issues and the measures to prevent them is crucial for maintaining overall health. This section will delve into the complications of strep throat, highlighting both immediate and long-term consequences. It also emphasizes the importance of preventative measures, including vaccination and hygiene practices.Untreated or improperly treated strep throat can lead to a cascade of problems, some of which can significantly impact a person’s well-being.
Prompt and appropriate medical intervention minimizes these risks. Prevention, therefore, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the health and well-being of individuals and communities.
Potential Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
Untreated strep throat can lead to a variety of complications, ranging from mild to severe. These complications arise from the infection spreading to other parts of the body. Acute rheumatic fever is a significant concern, potentially causing long-term heart damage. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, an inflammatory condition affecting the kidneys, is another potential complication. These complications underscore the importance of seeking prompt medical attention for strep throat.
Long-Term Consequences of Strep Throat
While most cases of strep throat resolve without long-term issues, the potential for long-term consequences necessitates careful consideration. Untreated strep throat can result in severe conditions such as rheumatic heart disease. This condition, a consequence of rheumatic fever, can lead to permanent heart valve damage, impacting cardiac function over a lifetime. Another consequence is post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, an inflammatory kidney condition that can cause kidney damage and require long-term medical monitoring.
Understanding these potential long-term consequences is critical for promoting preventative measures.
Preventive Measures to Reduce Strep Throat Risk
Preventing strep throat involves a multifaceted approach focusing on hygiene and reducing exposure to the bacteria. Maintaining good hand hygiene, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals are crucial steps. Avoiding sharing personal items like utensils and cups can also help prevent transmission.
Preventive Strategies Comparison
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Effectiveness | Considerations ||—|—|—|—|| Hand Hygiene | Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching shared surfaces. | High | Ensuring adequate handwashing duration and proper technique. || Cough and Sneeze Etiquette | Covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or the crook of the elbow to prevent the spread of droplets.
| Moderate | Consistent practice and reminding others of the importance. || Avoiding Close Contact | Minimizing close contact with individuals showing symptoms of strep throat. | High | Difficult to completely avoid all close contact in social settings. || Vaccination (if applicable) | Vaccination is not currently available for strep throat, but preventative measures such as avoiding contact with infected individuals can reduce risk.
| Limited | Focusing on personal hygiene practices and avoiding close contact with symptomatic individuals. || Proper Hygiene | Maintaining cleanliness in personal spaces, including regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces. | Moderate | Effectiveness varies based on the environment and frequency of cleaning. |
Preventing the Spread of Strep Throat
Preventing the spread of strep throat is vital in limiting the impact of this infection. Practicing good hygiene, particularly frequent handwashing, is paramount. Individuals should cover coughs and sneezes to minimize the transmission of droplets containing the bacteria. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals and promptly treating cases of strep throat are also crucial steps. Community-wide awareness and educational initiatives can further promote preventative measures and minimize the spread of strep throat.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Strep throat, while often treatable with antibiotics, can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial for preventing these issues. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment significantly reduce the risk of long-term health problems.Understanding the potential complications and recognizing the warning signs allows for timely intervention, ultimately safeguarding your well-being.
Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Recognizing the symptoms that necessitate immediate medical attention is vital for preventing potential complications. These symptoms often indicate a more severe condition that warrants prompt medical evaluation.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing: Severe difficulty in breathing or swallowing can signal a life-threatening airway obstruction. This is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. A person struggling to breathe or swallow might exhibit signs of distress, such as rapid or shallow breathing, wheezing, or bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis). Examples include severe swelling in the throat or difficulty opening the mouth, potentially due to inflammation or an abscess.
- Severe or persistent headache, neck stiffness, or body aches: These symptoms, particularly if accompanied by fever or difficulty swallowing, could indicate a more serious infection spreading to surrounding areas. For instance, a severe headache combined with neck stiffness could suggest meningitis, a serious infection of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. The urgency arises from the potential for the infection to rapidly spread and cause further complications.
- High fever (101°F or higher) lasting more than 24-48 hours: A persistent high fever, especially if it doesn’t respond to over-the-counter medications, may indicate a more severe infection or potential complications. The fever is a crucial indicator, as prolonged high temperatures can put undue stress on the body and potentially lead to dehydration. It’s important to consult a medical professional if the fever persists.
- Drooling or inability to swallow saliva: Inability to swallow saliva, especially if accompanied by other concerning symptoms, suggests a serious blockage or infection in the throat or mouth. This could be a sign of an abscess or a significant swelling that is causing difficulty swallowing and could lead to aspiration if left untreated. Prompt medical attention is needed to evaluate the situation and determine the best course of action.
Understanding strep throat involves recognizing its symptoms, like a sore throat and fever. While not directly related, knowing how to perform the ac joint compression test can help in differentiating strep throat from other potential causes of upper body pain. This test, the ac joint compression test , can help rule out specific shoulder issues, ultimately leading to a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan for strep throat or other ailments.
It’s important to seek professional medical advice for any health concerns.
- Significant swelling of the neck or face: Rapid swelling of the neck or face, especially if accompanied by difficulty breathing or swallowing, is a serious concern that warrants immediate medical attention. This is a possible sign of an infection spreading rapidly and potentially causing airway obstruction. The urgency stems from the risk of severe complications and potential breathing difficulties.
Severity of Potential Complications
Untreated strep throat can lead to a range of serious complications. The severity of these complications varies, depending on the individual’s immune response and the timeliness of treatment. These potential complications can include rheumatic fever, kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis), and severe complications affecting the heart and kidneys.
- Rheumatic fever: This serious inflammatory condition can affect the heart valves, potentially causing permanent damage. Untreated strep throat can increase the risk of rheumatic fever, leading to severe heart problems later in life. This is a significant concern as it can impact the cardiovascular system.
- Glomerulonephritis: This condition involves inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units. Untreated strep throat can increase the risk of kidney damage, leading to long-term kidney problems or even kidney failure. This underlines the importance of prompt treatment for preventing this complication.
Urgency Associated with Certain Symptoms
The urgency of seeking medical attention is directly related to the severity and nature of the symptoms. Symptoms like difficulty breathing or swallowing demand immediate action, whereas persistent fever or severe pain might necessitate a quicker consultation.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing: This necessitates immediate action due to the potential for airway obstruction or serious complications. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to prevent life-threatening situations.
- Persistent high fever: Prolonged high fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter medications requires prompt medical evaluation to rule out more serious infections.
- Severe pain or swelling: Significant throat pain or swelling, especially if accompanied by other concerning symptoms, demands attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of complications.
Actions to Take When Symptoms Worsen
If symptoms worsen, it is critical to contact a healthcare professional promptly. This could involve seeking emergency care or scheduling an appointment. The worsening of symptoms could be an indication of complications.
- Contact your doctor or seek emergency medical attention if your symptoms worsen, or if you experience any new or concerning symptoms.
- Provide your doctor with a complete medical history and details about your current symptoms.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions for monitoring your symptoms and any prescribed medications.
Decision-Making Flowchart for Seeking Medical Care
This flowchart Artikels the decision-making process for seeking medical care based on the severity of strep throat symptoms.
| Symptom |
Action |
| Mild symptoms (sore throat, slight fever) |
Schedule an appointment with your doctor within 24-48 hours. |
| Moderate symptoms (severe sore throat, high fever, difficulty swallowing) |
Contact your doctor immediately or seek urgent care. |
| Severe symptoms (difficulty breathing, drooling, significant swelling) |
Seek emergency medical attention immediately. |
Warning Signs in Order of Increasing Urgency
Recognizing warning signs in increasing order of urgency can help determine the appropriate course of action.
- Mild sore throat, low-grade fever
- Severe sore throat, high fever, difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing, drooling, significant swelling
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Strep throat, while often treatable, can be confusing due to its similarities with other sore throat conditions. This FAQ section addresses common questions about strep throat, differentiating it from other infections, and clarifying potential misconceptions. Understanding the answers to these questions can empower you to seek appropriate care and manage your health effectively.
Understanding Strep Throat Symptoms
Strep throat is characterized by specific symptoms that distinguish it from other common viral infections. A key aspect of identifying strep throat involves recognizing the unique set of symptoms it presents. A significant indicator is the presence of a sudden onset of sore throat, often accompanied by pain when swallowing. Other frequent symptoms include fever, headache, and body aches.
A noticeable feature is the development of a white or yellowish coating on the tonsils, which can sometimes appear inflamed and swollen.
Treatment and Management Strategies
The appropriate management of strep throat is crucial for ensuring swift recovery and preventing potential complications. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to effectively eliminate the Streptococcus bacteria responsible for strep throat. Adherence to the prescribed antibiotic regimen is vital to prevent the recurrence of strep throat and minimize the risk of complications. Over-the-counter pain relievers and throat lozenges can help alleviate discomfort and facilitate swallowing.
Rest and hydration are equally important components of the treatment plan, promoting the body’s natural healing processes.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Preventing strep throat involves adopting proactive measures to minimize exposure to the bacteria. Frequent handwashing, particularly after touching surfaces in public areas, is a crucial preventative step. Avoiding close contact with individuals exhibiting symptoms of strep throat is another vital preventative strategy. Maintaining a healthy immune system through a balanced diet and sufficient rest can also help strengthen the body’s defense against infection.
Distinguishing Strep Throat from Other Throat Infections
Differentiating strep throat from other throat infections can be challenging, as many share overlapping symptoms. While viral infections often cause sore throats, the presence of specific symptoms, such as a white or yellowish coating on the tonsils, along with a sudden onset of fever and pain when swallowing, may suggest strep throat. A rapid strep test or throat culture can definitively diagnose strep throat, enabling the appropriate medical intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions and Concise Answers
| Question |
Answer |
| What are the key symptoms of strep throat? |
Sudden onset sore throat, pain when swallowing, fever, headache, body aches, and sometimes a white or yellowish coating on the tonsils. |
| How is strep throat treated? |
Typically treated with antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria. |
| How can I prevent strep throat? |
Frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and maintaining a healthy immune system. |
| How is strep throat different from other throat infections? |
While both can cause sore throats, strep throat is caused by bacteria and often features a distinctive coating on the tonsils, along with specific symptoms. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, understanding strep throat is key to managing your health and well-being. By grasping the information presented in this overview, you’ll be better equipped to identify the signs, seek prompt medical attention when needed, and take proactive steps to prevent its spread. Remember, early intervention is critical for a swift recovery. This detailed overview provides the essential knowledge for navigating this health issue effectively.