Understanding the purpose of lymph nodes sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the intricate network of these vital structures within the human body. This exploration delves into the anatomical structure of lymph nodes, revealing their role in maintaining a healthy immune system. We’ll examine how these tiny filters work to defend us against disease, and how they can be involved in various health conditions.
This deep dive will unravel the mechanisms behind lymph node function, highlighting their crucial role in immune responses and disease diagnosis.
From their microscopic structure to their role in disease detection, we’ll explore the multifaceted nature of lymph nodes. We’ll also uncover the intricate processes involved in lymph node assessment, diagnosis, and imaging. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide a thorough understanding of lymph nodes, making complex information accessible and engaging.
Lymph Node Structure and Function
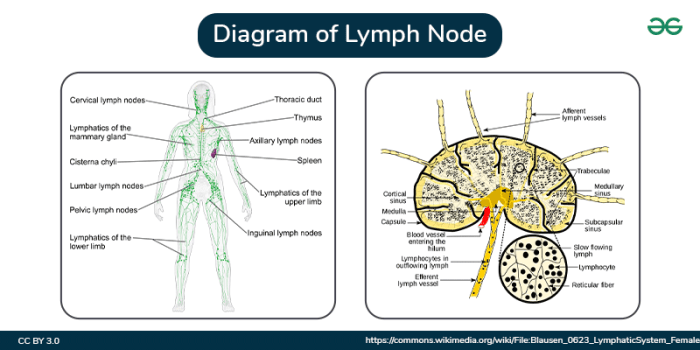
Understanding the intricate structure and function of lymph nodes is crucial for grasping their vital role in the immune system. These small, bean-shaped structures act as filters for lymph, a fluid containing immune cells and waste products. They are strategically positioned throughout the body, connecting lymphatic vessels to help maintain fluid balance and identify and neutralize pathogens.
Anatomical Structure of a Lymph Node
Lymph nodes possess a characteristic bean-shaped structure, encased in a fibrous capsule. This capsule extends inward, creating partitions that divide the node into distinct regions. The outer region, known as the cortex, is densely populated with lymphocytes, primarily B cells, and dendritic cells. These cells are crucial for initiating immune responses. The inner region, the medulla, contains aggregates of lymphocytes and plasma cells, which are responsible for antibody production.
Specialized networks of sinuses, spaces filled with lymph, permeate the cortex and medulla, facilitating the flow of lymph and the interaction of immune cells.
Cellular Components of Lymph Nodes
A diverse array of immune cells populate lymph nodes. Lymphocytes, specifically B cells and T cells, are paramount. B cells mature into plasma cells, producing antibodies that neutralize pathogens. T cells play a critical role in cell-mediated immunity, directly attacking infected cells. Macrophages and dendritic cells, antigen-presenting cells, capture and process foreign substances, presenting them to T cells for activation.
Natural killer (NK) cells are also present, providing a rapid response to infected or cancerous cells. These various cell types interact within the lymph node environment, orchestrating an effective immune response.
Lymphatic Vessels and Lymph Flow
Lymphatic vessels form a network throughout the body, collecting lymph from tissues. These vessels converge, leading to larger vessels that eventually drain into the bloodstream. Afferent lymphatic vessels carry lymph into the lymph node, while efferent lymphatic vessels transport filtered lymph out. The one-way valves within these vessels ensure unidirectional lymph flow, preventing backflow. Lymph nodes act as checkpoints, allowing immune cells to encounter and respond to pathogens or foreign substances within the lymph.
Comparison of Lymph Node Regions
| Region | Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Cortex | Outer layer, densely packed with lymphocytes (especially B cells), dendritic cells. Contains germinal centers, where B cells proliferate and differentiate. | Initial encounter of antigens with lymphocytes, initiation of immune responses, B cell maturation. |
| Medulla | Inner layer, contains medullary cords (aggregates of lymphocytes and plasma cells) and medullary sinuses. | Antibody production by plasma cells, further filtering of lymph, interaction of immune cells. |
| Sinuses | Networks of spaces filled with lymph, located throughout the cortex and medulla. | Passageway for lymph, allowing interaction between lymphocytes and antigens, facilitating immune cell migration. |
Lymph Node Function in Immunity: Understanding The Purpose Of Lymph Nodes
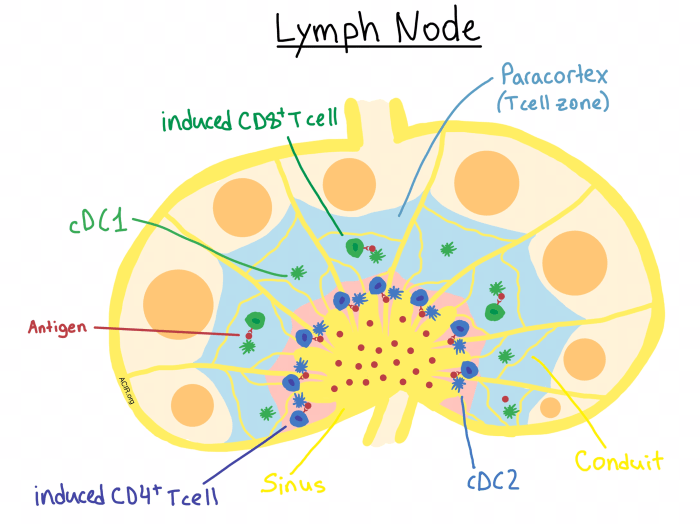
Lymph nodes, small bean-shaped structures strategically positioned throughout the lymphatic system, are crucial components of the immune system. They act as filters for lymph, a fluid containing immune cells and debris, playing a pivotal role in identifying and eliminating pathogens. Understanding their function in immunity provides insight into how our bodies defend against infections and maintain overall health.Lymph nodes are not just passive filters; they are dynamic hubs where immune cells interact and orchestrate responses to invading pathogens.
This intricate process involves a complex interplay of cell-to-cell communication, antigen presentation, and activation, ultimately leading to the elimination of threats and the development of immunological memory.
Filtering Lymph
Lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, waste products, and cellular debris, circulates throughout the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes act as checkpoints along this network, filtering the lymph as it passes through. Specialized cells within the lymph nodes, including macrophages and dendritic cells, actively scan the lymph for foreign particles, cellular debris, and pathogens. This filtering process ensures that harmful substances are removed from the lymphatic system, preventing them from spreading throughout the body.
The effectiveness of this filtering process is crucial for maintaining the body’s overall health.
Antigen Presentation and Immune Cell Activation
The process of antigen presentation is central to the activation of immune cells within lymph nodes. Macrophages and dendritic cells, acting as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), engulf and process foreign antigens. They then present these processed antigens on their surface, combined with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. This presentation allows T lymphocytes (specifically helper T cells) to recognize the specific antigen.
Upon recognition, T cells become activated, initiating a cascade of events leading to the activation of other immune cells, such as B cells, to eliminate the pathogen.
Initiating and Regulating Immune Responses
Lymph nodes play a vital role in initiating and regulating immune responses. The presence of specific antigens within the lymph node triggers a focused immune response. The organized structure of lymph nodes, with distinct zones for different immune cell types, ensures that the immune response is appropriately targeted and regulated. The interaction between various immune cells, such as T cells, B cells, and macrophages, within the lymph node is carefully orchestrated to maximize the effectiveness of the immune response.
Different Immune Cell Interactions
Various immune cells interact within lymph nodes to effectively combat pathogens. B cells, responsible for antibody production, encounter activated T cells presenting the same antigen. This interaction, mediated by specific surface receptors and cytokines, leads to the activation and proliferation of B cells, resulting in the production of antibodies tailored to neutralize the pathogen. T cells, another critical component of the adaptive immune response, play a crucial role in coordinating the entire process.
Their interaction with other immune cells fine-tunes the immune response and prevents excessive inflammation.
Understanding the purpose of lymph nodes is crucial for overall health. They’re part of our immune system, filtering out harmful substances and helping our bodies fight off infection. This intricate network plays a vital role in our well-being, much like the complexities surrounding a diagnosis like diabetes. For more information on whether diabetes is considered a disability, check out this resource: is diabetes a disability.
Ultimately, a strong understanding of the body’s systems, like the lymphatic system, is essential for informed decisions about health and well-being.
Activation of B and T Lymphocytes in Lymph Nodes
| Step | B Lymphocyte Activation | T Lymphocyte Activation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antigen encounter and uptake by B cells | Antigen presentation by APC (e.g., dendritic cell) to T cell receptor (TCR) |
| 2 | Processing and presentation of antigen on MHC class II molecules | Recognition of antigen-MHC complex by T cell receptor (TCR) |
| 3 | Interaction with helper T cell (Th) that recognizes the same antigen | Activation of the T cell |
| 4 | Activation and proliferation of B cells, leading to antibody production | Release of cytokines that activate other immune cells |
This table Artikels the key steps in B and T lymphocyte activation within lymph nodes, highlighting the coordinated nature of these processes.
Lymph Node Involvement in Disease
Lymph nodes, tiny filters throughout the body’s lymphatic system, play a crucial role in immune responses. They are strategically positioned to encounter and trap pathogens and abnormal cells. When these nodes become involved in disease processes, they often show characteristic changes that provide valuable diagnostic clues for healthcare professionals. This involvement can arise from infections, cancerous growths, or other pathological conditions.
Understanding these changes is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.Pathological changes in lymph nodes are frequently observed in a wide range of diseases, providing critical information about the underlying cause and severity of the condition. The appearance and consistency of these nodes, along with other clinical findings, contribute to the diagnostic process.
Lymph Node Involvement in Infections, Understanding the purpose of lymph nodes
Infections trigger an immune response, often leading to alterations in lymph node structure and function. Lymph nodes swell and become tender, a visible sign of increased activity within. This swelling is often accompanied by inflammation, characterized by redness and warmth in the surrounding tissues. Inflammatory cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, accumulate within the lymph node, attempting to eliminate the invading pathogens.
Understanding the purpose of lymph nodes is crucial for overall health. They’re essentially the body’s filtration system, helping to fight off infection. Factors like blood pressure and heart rate can indirectly affect lymph node function, influencing how effectively they clear out waste products. Monitoring these vital signs, like blood pressure heart rate , can offer insights into the body’s overall health and how well the lymphatic system is functioning.
Ultimately, understanding lymph node function is key to a healthier immune response.
Pathological Changes in Lymph Nodes During Infections
Lymph nodes, when challenged by pathogens, exhibit specific changes. These include an increase in the number of lymphocytes and other immune cells, resulting in enlargement. The nodes become more cellular and less organized. Macrophages, responsible for engulfing pathogens, may accumulate in significant numbers. Suppurative (pus-forming) infections can lead to the formation of pus within the node, causing localized abscesses.
The presence of these changes can be indicative of the type and severity of the infection.
Lymph Node Involvement in Cancer Development
Cancer cells, like pathogens, can spread throughout the body, including the lymphatic system. Metastasis, the spread of cancer from its primary site to distant locations, frequently involves the lymphatic system. Cancer cells can enter the lymphatic vessels, traveling to regional lymph nodes. These nodes can become involved through the process of metastasis, leading to the formation of secondary tumor growths.
Metastasis Through the Lymphatic System
Cancer cells detach from the primary tumor and enter the lymphatic capillaries. The cells travel through the lymphatic vessels, arriving at regional lymph nodes. If the cancer cells evade the immune defenses within the nodes, they can continue to proliferate and form new tumors in these nodes. This process, metastasis, is a critical aspect of cancer progression. The extent of lymph node involvement is a key prognostic factor for the patient’s survival and guides treatment decisions.
Diagnostic Use of Lymph Node Involvement
Examination of lymph nodes is a critical diagnostic tool. The size, consistency, and appearance of lymph nodes can provide valuable clues about the underlying disease. Biopsies of involved lymph nodes allow pathologists to analyze the cellular composition and identify the specific type of cells present. This analysis is instrumental in diagnosing infections, malignancies, and other diseases. The presence and extent of lymph node involvement are often included in staging systems, which help determine the extent of the disease and guide treatment strategies.
Summary Table of Diseases Affecting Lymph Nodes
| Disease Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Infectious Mononucleosis | Characterized by enlarged, tender lymph nodes, often in the neck and armpits. Fever and fatigue are common. |
| Lymphoma | Cancers of the lymphatic system, resulting in the formation of malignant tumors in lymph nodes. Various subtypes exist, each with distinct characteristics. |
| Metastatic Cancer | Cancer cells spread from a primary tumor site to regional lymph nodes, forming secondary tumors. The extent of metastasis significantly influences treatment strategies. |
| Tuberculosis | Infectious disease affecting the lungs and other organs. Can lead to granulomatous inflammation in lymph nodes. |
Lymph Node Assessment and Diagnosis
Understanding the status of lymph nodes is crucial in diagnosing various diseases, particularly those affecting the immune system. Proper assessment methods, including physical examination and imaging techniques, are vital for identifying potential abnormalities and guiding further investigations. Accurate diagnosis hinges on a thorough evaluation of lymph node characteristics and their correlation with clinical symptoms.
Methods of Lymph Node Assessment
Assessment of lymph nodes involves a multifaceted approach, combining physical examination with sophisticated imaging techniques. Physical examination, often the first step, relies on palpation to detect abnormalities in size, consistency, and mobility. Imaging modalities, such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, provide detailed visualization of lymph nodes, allowing for more precise evaluation of their morphology and extent of involvement.
Understanding the purpose of lymph nodes is crucial for overall health. They’re like tiny filtering stations in your body, helping your immune system fight off infections. But sometimes, issues like allergies can lead to fatigue, which can be mistaken for other things. For instance, are you experiencing unusual tiredness? If so, exploring potential links between your allergies and overall health, like the impact on your lymph nodes, might be worthwhile.
Knowing more about the role of your lymph nodes in your immune system can be key to understanding how your body works in dealing with allergies. Check out this informative article on can allergies make you tired to learn more.
Lymph Node Biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is a crucial procedure for obtaining tissue samples for microscopic examination, aiding in the definitive diagnosis of suspected pathologies. This invasive technique allows pathologists to examine the cellular composition and architecture of the lymph node, offering critical insights into the nature of any observed abnormalities.
Lymph Node Biopsy Procedure
The procedure for a lymph node biopsy typically involves the following steps:
- Patient Preparation: The patient is prepped and draped, and the area around the lymph node to be biopsied is cleansed. Local anesthesia is often administered to minimize discomfort during the procedure.
- Incision: A small incision is made over the targeted lymph node. The incision size is carefully determined based on the anticipated size of the sample needed.
- Excision: The lymph node, or a portion of it, is carefully excised, maintaining tissue integrity as much as possible. Techniques like fine-needle aspiration (FNA) may be used for smaller or more superficial nodes.
- Closure: The incision site is meticulously closed with sutures, and a dressing is applied.
- Pathology Review: The excised tissue is sent to a pathologist for microscopic examination and subsequent interpretation.
Comparison of Imaging Techniques
| Imaging Technique | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Real-time imaging, portable, relatively inexpensive | Limited depth penetration, operator-dependent, not ideal for deep-seated nodes |
| Computed Tomography (CT) Scan | Excellent spatial resolution, multiplanar imaging, can evaluate adjacent structures | Exposure to ionizing radiation, potential for contrast reactions |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Excellent soft-tissue contrast, allows for detailed visualization of nodal architecture | Longer scan times, can be more expensive than CT |
Significance of Lymph Node Characteristics
The size, consistency, and location of lymph nodes can offer valuable clues in the diagnostic process. Enlarged lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy) often signal an underlying inflammatory or neoplastic process. Hard or firm consistency might suggest malignancy, whereas soft consistency may point to an inflammatory condition. The location of the enlarged nodes can also provide clues about the possible source of the disease.
Lymph Node Pathologies and Imaging Appearances
| Pathology | Typical Imaging Appearance |
|---|---|
| Reactive Lymphadenitis | Enlarged, sometimes tender, nodes; often with homogeneous appearance on imaging. |
| Metastatic Cancer | Enlarged, firm, or hard nodes, often with irregular margins on imaging; may show calcification or necrosis. |
| Lymphoma | Enlarged, sometimes matted nodes; may have heterogeneous appearance, and potentially show a mass effect on surrounding structures on imaging. |
Lymph Node Imaging and Biopsy
Understanding lymph nodes is crucial for diagnosing various medical conditions. Imaging techniques and biopsies play vital roles in evaluating lymph nodes, helping clinicians determine the presence and nature of abnormalities. This section delves into the specifics of these procedures, their preparation, and potential findings.
Common Imaging Techniques for Visualizing Lymph Nodes
Various imaging modalities aid in visualizing lymph nodes, providing crucial information about their size, shape, and internal structure. These techniques are often employed to detect abnormalities before biopsy is necessary.
- Ultrasound (US): Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal structures. It is a non-invasive, relatively inexpensive, and readily available technique, particularly useful for superficial lymph nodes. Real-time imaging allows for dynamic assessment of the nodes during the procedure. It’s particularly helpful in evaluating the presence of fluid collections (cysts) or masses within the nodes.
- Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans utilize X-rays and sophisticated computer processing to generate cross-sectional images of the body. CT provides detailed anatomical information, including the size, location, and relationship of lymph nodes to surrounding structures. It’s frequently used to assess deeper lymph nodes and evaluate the extent of disease involvement. Contrast agents may be administered to enhance the visibility of lymph nodes and surrounding tissues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI utilizes strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. MRI excels at distinguishing between different soft tissues, providing valuable information about the characteristics of lymph nodes. It’s often employed to evaluate the presence of inflammation, edema, or specific types of tumors within the nodes. The use of contrast agents further enhances the visualization of subtle abnormalities.
Types of Lymph Node Biopsies
A biopsy is a procedure to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination. Different types of biopsies are performed depending on the location and size of the lymph node, as well as the suspected pathology.
- Excisional Biopsy: This involves the complete removal of the lymph node. It is often chosen for smaller, superficial nodes where the complete removal is feasible and does not compromise important structures. This approach is typically preferred for suspected benign conditions.
- Incisional Biopsy: This procedure involves removing a portion of the lymph node. It is a less invasive alternative to an excisional biopsy, particularly useful for larger nodes or those located in areas with complex anatomy. An incisional biopsy provides a representative sample for pathologic evaluation.
Preparation for Lymph Node Imaging Techniques
Preparation for imaging procedures varies depending on the specific technique. For ultrasound, no special preparation is usually needed. CT and MRI scans may require fasting or the administration of contrast agents.
- Ultrasound: No special preparation is generally required, except for removing any loose clothing or jewelry that may interfere with the procedure. The patient may be asked to drink water or other liquids to help with distention of the targeted area.
- CT: Patients are typically required to fast for a certain period before the scan, depending on the type of contrast agent used. Patients should inform the technician about any allergies or previous reactions to contrast agents. If contrast is required, intravenous access is typically established.
- MRI: Preparation for MRI is similar to that of CT. Fasting may be required, and patients should inform the technician about any implanted medical devices or metal in the body.
Preparation for a Lymph Node Biopsy
Preparation for a lymph node biopsy is dependent on the type of biopsy and the patient’s overall health. The physician will provide specific instructions.
- General Instructions: Patients are often asked to fast for a few hours before the procedure. Inform the medical team about any medications, allergies, or medical conditions. Any relevant medical history and current medications should be disclosed to the physician.
Typical Findings on Lymph Node Imaging
Lymph node imaging findings can vary depending on the underlying pathology.
| Pathology | Typical Imaging Findings |
|---|---|
| Benign Lymphadenopathy | Enlarged lymph nodes, typically symmetrical, with smooth margins, and no internal calcifications. |
| Malignant Lymphoma | Enlarged lymph nodes, often asymmetrical, with irregular margins and possible internal calcifications or necrosis. |
| Metastatic Disease | Enlarged lymph nodes, often multiple, with varying sizes and shapes, and possible internal calcifications or masses. |
Interpreting Lymph Node Biopsy Results
Pathologists meticulously examine the biopsy specimens under a microscope. Microscopic examination helps determine the nature of the cells and tissues within the lymph node.
- Microscopic Evaluation: The pathologist analyzes the cellular architecture, the presence of atypical cells, and any signs of inflammation or infection. The results of this analysis are crucial in determining the diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Lymph Node Location and Drainage
Understanding the intricate network of lymphatic drainage is crucial for comprehending the body’s immune responses and disease processes. This system, a vital component of the circulatory system, plays a critical role in transporting lymph, a fluid containing immune cells, throughout the body. Knowledge of lymphatic drainage patterns is indispensable in diagnosing and staging various illnesses, particularly cancers.
Major Lymph Node Groups
The lymphatic system comprises a vast network of vessels and nodes. Major lymph node groups are strategically positioned throughout the body, acting as filters for lymph. These groups are interconnected, ensuring efficient drainage and immune surveillance. Their locations and drainage patterns are essential for interpreting diagnostic findings.
Drainage Patterns of Different Body Regions
The lymphatic drainage follows specific pathways, conveying lymph from different body regions to particular lymph node groups. The upper extremities, for instance, drain into axillary lymph nodes, while the lower extremities drain into inguinal lymph nodes. Head and neck regions drain into cervical lymph nodes. This directional flow facilitates the identification of the origin of infections or malignancies.
Clinical Significance of Lymphatic Drainage Patterns
Understanding the lymphatic drainage patterns is of paramount importance in clinical settings. Knowing the drainage pathways allows healthcare professionals to accurately identify the region of origin of an infection or tumor. For instance, if swelling or abnormalities are detected in the axillary lymph nodes, it might suggest a problem originating in the upper limb or breast region. This crucial information aids in determining the appropriate diagnostic procedures and treatment strategies.
Lymph Node Drainage in Cancer Diagnosis and Staging
In cancer diagnosis and staging, the lymphatic drainage patterns are invaluable. Cancer cells can spread through the lymphatic system, metastasizing to distant lymph nodes. Assessing the presence and extent of metastasis in regional lymph nodes provides critical information for determining the stage of the disease. This knowledge is crucial for planning appropriate treatment strategies and predicting patient outcomes.
The higher the number of lymph nodes involved, the more advanced the stage of the cancer is often considered.
Lymphatic Drainage of the Upper Limb
The lymphatic drainage of the upper limb follows a predictable pattern, originating at the fingertips and progressing upwards.
| Body Region | Drainage to | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Fingers, Palm | Anterior axillary lymph nodes | Lymphatic vessels ascend along the veins of the hand and arm, converging at the axillary lymph nodes. |
| Lateral forearm | Lateral axillary lymph nodes | The lateral aspect of the forearm drains to the lateral axillary nodes. |
| Medial forearm | Anterior axillary lymph nodes | The medial forearm drains to the anterior axillary lymph nodes. |
| Upper arm | Apical and central axillary lymph nodes | The lymph from the upper arm ultimately flows to the apical and central axillary lymph nodes. |
This detailed drainage system allows for precise identification of the location and extent of potential spread of cancer from the upper limb. This understanding is crucial for staging and treatment planning.
Last Point
In conclusion, understanding the purpose of lymph nodes is crucial for comprehending the intricate workings of the immune system. Their function in filtering lymph, initiating immune responses, and involvement in disease processes is undeniable. We’ve explored the structure, function, and clinical implications of lymph nodes, emphasizing their significance in disease diagnosis and treatment. This comprehensive overview should equip readers with a deeper understanding of these essential components of the human body.



![Jiaogulan: The Next Big Thing? [Latest Research] - urbol.com The lowdown on jiaogulan](https://healthytipp.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/jiaogulan1-1.jpg)