Should you buy supplemental health insurance? This question is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of healthcare costs. A standard health insurance plan often falls short, leaving gaps in coverage for significant medical expenses. Understanding these gaps, your personal health needs, and alternative options is key to making an informed decision.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of supplemental insurance, helping you assess if it’s a necessary addition to your current coverage. We’ll delve into the details of various plans, compare costs, and examine alternative solutions like HSAs and HRAs.
Understanding Health Insurance Coverage
Navigating the world of health insurance can feel like deciphering a complex code. Different plans have varying benefits and costs, and understanding the nuances is crucial for making informed decisions about your health and financial well-being. This section will delve into the key components of health insurance plans, outlining the common terms and comparing different types to help you decipher the complexities.Health insurance plans are designed to share the financial burden of medical expenses.
They do this by establishing a framework of costs that you and the insurance company will each cover. Understanding these components—deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums—is essential for effectively managing your healthcare costs.
Key Components of a Health Insurance Plan
Understanding the financial aspects of a health insurance plan is critical. These components determine the level of your personal responsibility and the degree of financial protection offered by the plan.
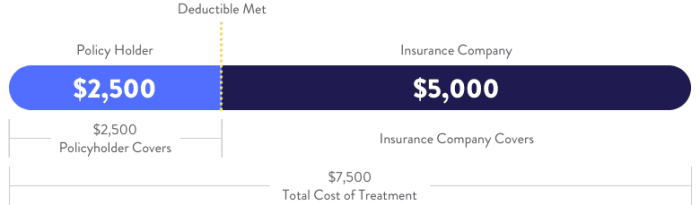
- Deductible: This is the amount you pay out-of-pocket for covered medical services before your insurance begins to pay. For example, if your deductible is $2,000, you will need to pay the first $2,000 of covered medical expenses before your insurance kicks in. This amount varies significantly between plans, and understanding your deductible is paramount.
- Co-pay: A co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for a specific medical service, such as a doctor’s visit or a prescription. For example, a co-pay for a doctor’s visit might be $25. Co-pays help manage costs for routine care and are typically set at a low amount to encourage utilization of preventive care.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: This is the maximum amount you will pay for covered medical expenses in a plan year. Once you reach this limit, your insurance company will pay 100% of covered expenses for the remainder of the year. For instance, an out-of-pocket maximum of $6,000 means you won’t pay more than $6,000 in a year, regardless of how much care you require.
Different Types of Health Insurance Plans
Understanding the various types of health insurance plans available is crucial for selecting a plan that aligns with your healthcare needs and budget.
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): HMO plans typically require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within their network. You generally need a referral from your PCP to see specialists. HMO plans often have lower premiums but may have limited network options, potentially requiring more travel time to see specialists. This is a good example of a plan with more controlled costs.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): PPO plans allow you to see any doctor or specialist in their network without needing a referral from a PCP. While PPO plans generally have larger networks, premiums tend to be higher than HMO plans. There is more flexibility in choosing providers.
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): EPO plans are similar to PPOs in that they allow you to see any doctor or specialist in their network without a referral. However, EPO plans typically have a more limited network than PPOs. EPO plans often have lower premiums than PPO plans, but accessing out-of-network care is generally more expensive.
Common Coverage Limitations and Exclusions
Health insurance plans often have limitations on what they cover. Understanding these exclusions is crucial for avoiding unexpected costs.
- Pre-existing conditions: Some plans may exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions, or limit coverage for a period of time after you enroll. It’s essential to review the specifics of a plan to understand the coverage limitations, especially when purchasing health insurance for the first time.
- Mental health services: Coverage for mental health services can vary greatly between plans, and there can be limitations on the frequency or type of therapy covered. In some plans, this coverage might be more limited compared to physical health care.
- Out-of-network care: Out-of-network care is generally more expensive than in-network care. Plans often have higher costs and reduced coverage for services received from providers outside their network.
Comparison of Plan Types
The following table provides a simplified comparison of the costs and benefits of different health insurance plan types. Note that specific details may vary based on individual plans and providers.
| Plan Type | Premiums | Network Size | Out-of-Network Costs | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | Lower | Smaller | High | Limited |
| PPO | Higher | Larger | Moderate | High |
| EPO | Moderate | Smaller than PPO | High | Moderate |
Assessing Your Personal Health Needs
Figuring out if supplemental health insurance is right for you involves a thorough self-assessment. Understanding your current health status, potential future needs, and the limitations of your primary insurance is crucial. This assessment goes beyond just identifying existing conditions; it considers lifestyle factors, family history, and preventive care habits. This in-depth look helps you make an informed decision about whether supplemental coverage is a valuable addition to your existing health insurance.
Factors to Consider in Evaluating Health Risks
Evaluating your health risks requires a comprehensive approach. Consider your age, family history of chronic diseases, and any existing health conditions. Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and smoking habits, also play a significant role. Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or occupational hazards, are also worth noting. For instance, someone with a family history of heart disease and a sedentary lifestyle would likely have a higher risk profile compared to a younger, active individual with no such family history.
Understanding these factors is essential for a realistic assessment of your personal health needs.
Common Conditions Requiring Supplemental Coverage
Many health conditions can strain your financial resources and necessitate supplemental insurance. Chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and cancer often require extensive treatment and ongoing management. Mental health conditions, including depression and anxiety, also place a substantial burden on individuals and their families, and often necessitate ongoing therapy and medication. Moreover, the cost of specialized treatments for conditions like multiple sclerosis or certain types of arthritis can be exorbitant, further highlighting the need for supplemental coverage.
It’s important to note that the specific conditions and their associated costs can vary greatly depending on the individual and the severity of the condition.
Thinking about supplemental health insurance? It really depends on your current coverage. For example, if you’re taking metronidazole for a bacterial infection, understanding how long the effects last is crucial for managing your health and knowing when to adjust your insurance needs. How long do the effects of metronidazole last is a key factor to consider when weighing the pros and cons of extra coverage.
Ultimately, a careful assessment of your individual needs and current insurance plan is essential for deciding whether supplemental coverage is the right choice for you.
Impact of Pre-Existing Conditions on Insurance Options
Pre-existing conditions can significantly affect your supplemental insurance options. While some policies may exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions entirely, others may offer coverage but with limitations or increased premiums. Thorough research and comparison of different plans are essential to understand the implications of pre-existing conditions. You should also be aware that some policies may impose waiting periods before coverage begins for pre-existing conditions.
Understanding these limitations is vital for a realistic assessment of your insurance needs.
Importance of Preventive Care in Managing Costs
Preventive care plays a vital role in managing overall health costs. Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can help detect potential health issues early, potentially reducing the severity and cost of treatment. By adopting a proactive approach to health, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic conditions and manage existing ones more effectively. For instance, regular blood pressure monitoring and cholesterol checks can help prevent heart disease.
Adopting a proactive approach to health maintenance is a key strategy for reducing overall healthcare costs.
Checklist for Evaluating Individual Health Needs
This checklist can guide you through a comprehensive assessment of your individual health needs:
- List any existing health conditions, including chronic diseases or injuries.
- Document your family history of chronic diseases.
- Assess your lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and smoking habits.
- Evaluate potential environmental risks or occupational hazards.
- Note any specific treatments or medications you may need.
- Review your current health insurance coverage to understand its limitations.
- Compare different supplemental insurance plans to identify the best fit for your needs.
Evaluating Supplemental Insurance Options
Supplemental health insurance plans offer a crucial layer of protection beyond your standard health insurance. These plans can help fill gaps in coverage, cover out-of-pocket expenses, and provide access to specialized care not always included in basic plans. Understanding the different types and their specific benefits is key to making an informed decision.
Types of Supplemental Health Insurance Plans
Supplemental health insurance plans come in various forms, each designed to address specific needs. These plans often focus on specific aspects of healthcare, like vision, dental, or critical illness coverage. A comprehensive understanding of these options is important when evaluating your needs.
- Accident Insurance: This type of plan covers expenses related to accidents, including medical bills, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs. It often provides a significant financial cushion in the event of an unexpected injury or accident.
- Critical Illness Insurance: These plans provide a lump-sum payment if you’re diagnosed with a critical illness, such as cancer or a heart attack. This can help offset the financial burden of treatment and other related costs.
- Hospital Indemnity Insurance: These policies pay a predetermined amount for each day you’re hospitalized. They’re often designed to help cover daily expenses while in the hospital.
- Vision and Dental Insurance: These plans cover routine eye exams, glasses, dental checkups, cleanings, and procedures. They often complement existing coverage by offering specific benefits in these areas.
- Medicare Supplement Plans: These plans fill gaps in Original Medicare coverage, helping to pay for co-pays, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket costs. Understanding the various options and their coverage details is crucial.
Coverage Options for Various Medical Expenses
Different supplemental plans offer various coverage options tailored to specific medical needs. A crucial aspect is recognizing how these plans can supplement your existing insurance.
- Prescription Drugs: Some supplemental plans offer coverage for prescription medications, helping to reduce the financial burden of prescription costs. This coverage can vary widely by plan.
- Mental Health Services: These plans may include coverage for mental health services, which are often not fully covered by standard health insurance. This can help ensure access to necessary care.
- Out-of-Pocket Expenses: Many supplemental plans address out-of-pocket expenses like co-pays, deductibles, and coinsurance. They can provide a significant buffer against financial strain during medical treatments.
- Rehabilitation Services: Some supplemental plans cover rehabilitation services, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. This can significantly aid recovery from injury or illness.
Gaps in Standard Coverage
Supplemental insurance can effectively bridge gaps in standard health insurance coverage. A thorough understanding of these gaps is essential for evaluating the value of supplemental plans.
- Co-pays and Deductibles: Standard plans often require significant out-of-pocket expenses for co-pays and deductibles. Supplemental insurance can help offset these costs, easing the financial burden.
- Specialized Care: Standard plans may not fully cover certain types of specialized care, such as advanced diagnostics or treatments. Supplemental insurance can address these gaps.
- Long-Term Care: Standard plans often do not cover long-term care expenses. Supplemental policies can help pay for long-term care services, including assisted living or nursing home care.
Supplemental Insurance Providers
Evaluating different providers is crucial for selecting the best supplemental insurance plan. A comparison of various providers and their services is essential.
- Reputation and Financial Stability: Choose providers with a strong reputation for customer service and financial stability. Research their track record and claims handling procedures.
- Customer Reviews: Read online reviews to gauge the experiences of other policyholders. This provides valuable insight into the provider’s service quality and responsiveness.
- Coverage Details: Compare the coverage details, including the types of benefits, exclusions, and limitations, across different providers.
Comparing Supplemental Plans
A detailed comparison of various supplemental plans helps in making an informed decision. This comparison should focus on key features and costs.
| Plan Name | Coverage Details | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Plan A | Comprehensive accident and critical illness coverage | $150/month |
| Plan B | Focus on hospital indemnity and vision/dental | $100/month |
| Plan C | Medicare supplement coverage with extended benefits | $200/month |
Analyzing Costs and Affordability

Figuring out the true cost of supplemental health insurance involves more than just the premium. Understanding the potential savings and added financial responsibilities is crucial before making a decision. This section delves into the financial implications, comparing standard plans with supplemental options, and explores ways to budget effectively.The cost of healthcare is a significant concern for many individuals and families.
Supplemental insurance can offer peace of mind by covering gaps in standard plans, but it’s vital to assess whether the added expense is justifiable given your personal needs and financial situation. Analyzing costs and affordability requires a careful examination of both short-term and long-term financial impacts.
Comparing Standard and Supplemental Insurance Costs
Standard health insurance plans typically cover a range of essential services. However, these plans often have limitations, particularly in areas like out-of-pocket expenses and coverage for specific procedures or treatments. Supplemental insurance can address these gaps, providing additional benefits and potentially reducing out-of-pocket costs. Comparing the total costs of a standard plan versus a plan with supplemental coverage involves considering both premiums and potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Financial Implications of Purchasing Supplemental Insurance
Purchasing supplemental insurance carries financial implications. Premiums need to be factored into monthly budgets. While the coverage may reduce future medical expenses, the initial cost should be weighed against the potential long-term savings. Consider the added cost of supplemental insurance against the current level of coverage provided by your standard health insurance. Analyze the potential savings against the cost of supplemental insurance.
Deciding if you need supplemental health insurance often comes down to your individual needs and coverage. For example, consider the nasal flu vaccine, Flumist, a good preventative measure, but knowing what it is and how it works can be crucial for informed decisions about your health. what is the nasal flu vaccine flumist. Ultimately, weighing your current insurance plan and potential costs alongside your health goals is key to figuring out if extra coverage is right for you.
Payment Options and Financial Assistance Programs
Many options exist for paying supplemental insurance premiums. These include flexible payment plans offered by insurance companies, or the possibility of splitting payments. Furthermore, various financial assistance programs may be available to help offset the costs. Some companies offer payment plans with interest-free installments or discounts. Also, consider government programs like subsidies or assistance for low-income individuals.
Research programs like Medicaid, CHIP, or tax credits for health insurance to see if they can reduce the financial burden.
Thinking about supplemental health insurance? Understanding your specific health needs is key. For example, if you’re concerned about conditions like osteopenia, it’s crucial to learn more about what that means for your health and potential treatment options. Check out this helpful resource on osteopenia what you need to know to get a better understanding.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to buy supplemental insurance comes down to weighing your current coverage and personal health risks.
Budgeting for Supplemental Insurance Premiums, Should you buy supplemental health insurance
Effective budgeting is key to incorporating supplemental insurance premiums. Create a detailed budget outlining all income and expenses. Allocate a specific amount for insurance premiums, treating it as a necessary expense. For example, if your budget allows, you could include supplemental insurance premiums as part of your monthly spending plan. Prioritize saving and allocate a portion of your income for premiums.
Calculating Healthcare Costs with and Without Supplemental Insurance
A crucial step is calculating the total cost of healthcare expenses with and without supplemental insurance. This calculation involves determining the out-of-pocket costs for various medical services, procedures, and potential emergencies. A useful method is to estimate annual medical expenses using historical records and projected needs. An example would be considering the costs of a possible dental procedure.
Consider a hypothetical scenario involving a family needing coverage for a complex medical issue. Estimating the cost of healthcare without supplemental insurance would highlight the potential gaps in coverage. Contrast this with the estimated costs with supplemental insurance to assess the potential savings. Using a spreadsheet or a dedicated healthcare cost calculator can help with these calculations.
By comparing the cost with and without supplemental insurance, a clearer picture of its financial impact emerges.
Exploring Alternative Options
Beyond supplemental insurance, several alternative financial strategies can help manage healthcare costs. These options, such as Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs), offer unique advantages and drawbacks that should be carefully considered alongside your health insurance plan. Understanding these alternatives can significantly impact your overall healthcare financial strategy.
Healthcare Savings Accounts (HSAs)
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) are tax-advantaged savings accounts designed specifically for qualified medical expenses. They’re particularly beneficial for individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs). Funds contributed to an HSA are tax-deductible, and the growth of the account is tax-free. Crucially, distributions for qualified medical expenses are also tax-free.
Key features of HSAs include:
- Tax-deductible contributions: The contributions you make to your HSA are deducted from your taxable income, lowering your tax burden.
- Tax-free growth: Earnings on your HSA investments grow tax-free.
- Tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses: This is a significant benefit, as it allows you to access the funds without incurring taxes or penalties.
- Portability: If you change jobs, your HSA funds are yours to take with you.
Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs)
Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) are employer-sponsored accounts that reimburse employees for qualified medical expenses. They’re often used in conjunction with other health insurance plans. Unlike HSAs, contributions to HRAs aren’t typically tax-deductible for the employee, although employers may have tax advantages. HRAs can be a useful tool to supplement existing insurance, but the specific benefits and restrictions depend heavily on the employer’s plan.
Key features of HRAs include:
- Employer-funded: HRAs are typically funded by the employer.
- Potential for employer tax deductions: Employer contributions to HRAs may be tax-deductible.
- Reimbursement for qualified medical expenses: Similar to HSAs, HRAs reimburse employees for eligible expenses.
- Often tied to employment: Eligibility and the ability to access funds are often tied to employment status.
Comparison of HSAs and HRAs
| Feature | HSA | HRA |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Individual contributions | Employer contributions |
| Tax Deductibility (Employee) | Yes (contributions) | Generally no (contributions) |
| Tax-Free Growth | Yes | Yes (on employer contributions) |
| Tax-Free Withdrawals | Yes (for qualified medical expenses) | Yes (for qualified medical expenses) |
| Portability | Yes | Generally no |
| Eligibility | Linked to high-deductible health plans | Linked to employer-sponsored plans |
How These Options Affect Supplemental Insurance Needs
HSAs and HRAs can significantly reduce the need for supplemental insurance, especially for individuals with high-deductible health plans. If you have a substantial HSA or HRA, you’ll likely need less supplemental coverage to cover out-of-pocket expenses. Consider your individual financial situation and health needs when deciding how these accounts fit into your overall health insurance strategy. For instance, an individual with a robust HRA may need less supplemental insurance than someone with an HSA, even if they both have high-deductible plans.
Making an Informed Decision: Should You Buy Supplemental Health Insurance
Deciding whether or not to purchase supplemental health insurance requires careful consideration of your individual circumstances and needs. This involves weighing the potential benefits against the costs and exploring alternatives. Understanding the nuances of your existing health coverage is crucial in making a well-informed choice.Evaluating supplemental insurance is not a one-size-fits-all process. The optimal approach depends heavily on factors such as your current health status, anticipated healthcare expenses, and financial situation.
A thorough assessment of these factors can help you determine if supplemental insurance is the right choice for you.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Supplemental health insurance can offer valuable protection against unexpected medical expenses that your primary insurance might not fully cover. It can also provide additional benefits like coverage for specific procedures or services. However, supplemental plans often come with premiums and deductibles that can add to your overall healthcare costs. A careful evaluation of these factors is essential to making an informed decision.
Key Questions to Ask Yourself
What are my current healthcare needs and expenses? Consider past medical bills, anticipated future procedures, and potential health concerns. How comprehensive is my current health insurance? Determine the gaps in your existing coverage that supplemental insurance could address. What is my budget for additional healthcare expenses?
Understanding your financial limitations is crucial for selecting a plan that fits within your budget. What are my long-term healthcare goals? Supplemental insurance can provide peace of mind regarding future healthcare costs.
Comparing and Selecting the Best Option
A systematic approach to comparing different supplemental insurance plans is crucial. Begin by gathering information from various providers. Consider factors such as coverage details, network availability, and claim processing procedures. Analyze the costs of different plans, factoring in premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses. Carefully review the plan’s exclusions and limitations to ensure it aligns with your specific healthcare needs.
Evaluating Plans Based on Needs and Budget
Use a spreadsheet or comparison tool to systematically list the features of different plans. Categorize features based on their relevance to your individual needs. Compare the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses for each plan. Evaluate the network of providers associated with each plan, considering the accessibility of doctors and hospitals. Compare the overall value proposition of each plan, balancing cost and coverage.
Resources for Additional Information
Numerous resources are available to help you research and understand supplemental health insurance. Your state insurance department website provides details on the plans available in your area. Reputable online comparison websites allow you to compare plans side-by-side. Consult with a qualified insurance agent or financial advisor for personalized guidance and recommendations. Online consumer reviews can provide insights into the experiences of other policyholders.
Understanding the Role of Insurance Brokers

Navigating the complexities of supplemental health insurance can feel overwhelming. Insurance brokers act as valuable intermediaries, helping individuals and families find the right coverage at the best possible price. They possess specialized knowledge and resources to streamline the search process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your specific needs and budget.Insurance brokers are experts in the insurance industry, possessing comprehensive knowledge of various supplemental health insurance plans.
They act as your personal advocates, helping you understand the nuances of different policies and compare options tailored to your unique circumstances. They can guide you through the entire process, from initial consultation to policy selection and ongoing support.
Insurance Broker Services
Insurance brokers offer a wide range of services to help you find the right supplemental insurance. They conduct thorough research, analyze your health needs and budget, and present a range of suitable options. This involves understanding your health history, pre-existing conditions, and desired coverage levels.
How Brokers Guide Clients
Brokers facilitate the selection process by explaining policy details, outlining coverage benefits, and highlighting potential exclusions. They help you compare different plans from various providers, emphasizing the pros and cons of each. For example, a broker might point out that a plan with higher premiums might include more comprehensive coverage for specific procedures or treatments. This personalized guidance ensures you’re choosing a plan that aligns with your individual needs.
They also provide ongoing support and assistance throughout the policy term.
Comparing Broker Services
Different brokers offer varying levels of service and may charge different fees. This section provides a general comparison.
| Broker Service | Description | Typical Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Consultation | Initial consultation to understand needs and provide basic plan recommendations. | Often free or low |
| Comprehensive Analysis | Detailed assessment of health needs, budget, and various plans, including in-depth comparisons and recommendations. | Potential for a commission or consultation fee |
| Policy Negotiation | Negotiating with insurers to secure the best possible policy terms and pricing. | Often a commission based on the policy’s value |
| Ongoing Support | Continued support and guidance during the policy term. | Generally not charged, but may be an added service for a fee |
Note: Fees can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the services rendered and the broker’s experience.
Evaluating Insurance Options Based on Needs
Brokers leverage their expertise to evaluate insurance options based on individual health needs. They consider factors like age, pre-existing conditions, and desired coverage levels when recommending plans. For example, a broker might suggest a plan with higher out-of-pocket maximums for a healthy individual who prefers greater flexibility and control over their healthcare spending. This personalized approach ensures the chosen plan is not just financially viable but also adequately addresses individual health requirements.
Researching and Selecting Qualified Brokers
Choosing a qualified insurance broker is crucial for a successful experience. Look for brokers with industry certifications, experience in supplemental health insurance, and positive client testimonials. Verify their licensing and insurance credentials. Check for complaints or regulatory actions against the broker. Seek recommendations from trusted sources or online review platforms.
In summary, thoroughly research and select a qualified broker to maximize your chances of finding suitable supplemental health insurance.
Outcome Summary
Ultimately, deciding whether to purchase supplemental health insurance is a personal choice. Weighing the potential benefits against the costs, and considering your specific health needs and financial situation, is paramount. This guide provides the information needed to make an informed decision, allowing you to confidently navigate the world of health insurance and protect yourself and your loved ones.