Signs of liver disease can be subtle, often overlooked, but early detection is crucial. This guide delves into the various indicators, from common symptoms to risk factors, empowering you to understand your liver health better. We’ll explore different types of liver disease, their causes, and how to recognize the early warning signs.
From digestive issues to skin changes, we’ll categorize these potential symptoms to help you understand their connection to liver health. Understanding these signs can lead to timely diagnosis and effective treatment, ensuring the best possible outcome.
Introduction to Liver Disease
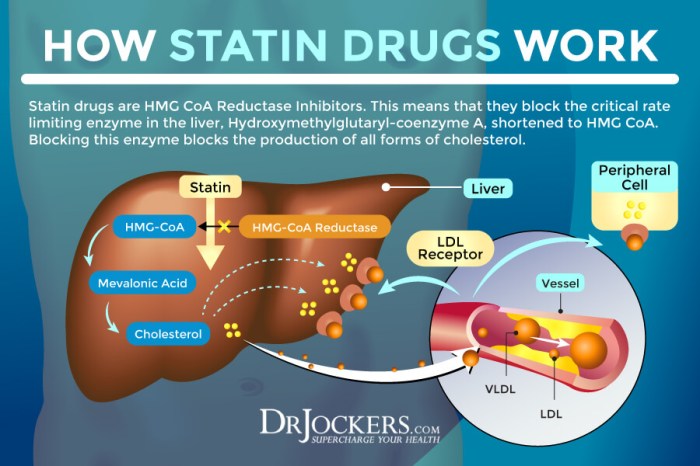
Liver disease encompasses a wide range of conditions affecting the liver, a vital organ responsible for numerous bodily functions. These functions include filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile for digestion, and synthesizing essential proteins. When the liver is damaged, its ability to perform these tasks is compromised, leading to a cascade of potential health complications. Understanding the different types of liver disease, their causes, and the stages of progression is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Types of Liver Disease
Liver disease can be broadly categorized into various types, each with its own set of underlying causes. These include viral infections, alcohol abuse, autoimmune disorders, and genetic factors. Understanding these distinct types helps in developing targeted interventions and treatment strategies.
Causes of Liver Disease
A multitude of factors can contribute to liver disease. Viral infections, such as hepatitis A, B, and C, are significant causes, often leading to chronic inflammation and damage. Alcohol abuse is another common culprit, causing alcoholic liver disease, which can progress to cirrhosis. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly prevalent, linked to obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Autoimmune disorders, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the liver, can also result in liver damage. Finally, genetic factors can predispose individuals to certain types of liver disease.
Ever noticed some unusual symptoms? They could be subtle signs of liver disease, like fatigue or jaundice. Understanding how long it takes your body to process food, for instance, can be really helpful in the bigger picture. Factors like the type of food and your overall health can significantly affect digestion time. You can find more on this by checking out this article on how long does it take to digest food.
Ultimately, if you’re concerned about any persistent symptoms, it’s always best to see a doctor to get a proper diagnosis and rule out any underlying issues.
Stages of Liver Disease Progression
Liver disease often progresses through several stages, each characterized by increasing severity of liver damage. Early stages may be asymptomatic, but as the disease advances, symptoms become more pronounced. The progression may involve inflammation, fibrosis (scarring), cirrhosis, and ultimately, liver failure. It’s crucial to note that early intervention can often slow or halt the progression of the disease.
Key Differences Between Types of Liver Disease
| Disease Type | Cause | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Viral Hepatitis (e.g., Hepatitis C) | Viral infection (Hepatitis viruses) | Fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, loss of appetite | Antiviral medications, supportive care |
| Alcoholic Liver Disease | Chronic alcohol abuse | Fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, jaundice, enlarged liver | Alcohol cessation, nutritional support, medications |
| Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) | Obesity, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome | Often asymptomatic in early stages; fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice in later stages | Weight loss, dietary modifications, medications to manage underlying conditions |
| Autoimmune Hepatitis | Immune system attacks the liver | Fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, joint pain, skin rashes | Immunosuppressive medications |
Early Warning Signs

Spotting the early signs of liver disease is crucial for timely intervention and better outcomes. Many early indicators are subtle and easily missed, often mistaken for other common ailments. Recognizing these subtle clues can significantly impact a person’s health journey. This understanding empowers individuals to take proactive steps and consult with healthcare professionals.
Common Manifestations of Early Signs
Early liver disease symptoms often mimic other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. The specific symptoms can vary widely depending on the individual and the type of liver disease. Factors like age, overall health, and the specific underlying condition influence how symptoms present. For example, fatigue might be a subtle initial sign in one person, while digestive issues might be more pronounced in another.
Digestive System Clues
Digestive symptoms are frequently the first indicators of liver problems. These can range from mild discomfort to more severe issues. Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting are common early indicators. Changes in appetite, such as loss of appetite or a sudden increase in cravings, are also potential signs. Constipation or diarrhea can also be indicative.
Furthermore, persistent indigestion or heartburn can be linked to liver dysfunction.
Skin and Eyes: Visual Indicators
Changes in skin and eyes can provide important clues to liver health. Jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, is a classic sign of liver disease. This happens when the liver struggles to process bilirubin, a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. Other skin manifestations include itchy skin (pruritus), which is often associated with bile duct issues.
Spider angiomas, small, dilated blood vessels visible on the skin, can also be a sign of liver damage. Dark urine and pale stools are also potential warning signs.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological symptoms, while less common as early indicators, can still occur. These can include confusion, difficulty concentrating, and even personality changes. Changes in sleep patterns, such as insomnia or excessive sleepiness, can also be related to liver disease. In severe cases, hepatic encephalopathy, a neurological disorder, can manifest. It’s important to note that neurological symptoms are often associated with more advanced stages of liver disease.
A Table of Common Early Warning Signs
| Symptom Type | Potential Early Warning Signs |
|---|---|
| Digestive | Abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, changes in appetite, constipation/diarrhea, indigestion, heartburn |
| Skin | Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes), itchy skin (pruritus), spider angiomas, dark urine, pale stools |
| Neurological | Confusion, difficulty concentrating, personality changes, changes in sleep patterns, hepatic encephalopathy (in advanced stages) |
Common Symptoms
Understanding the common symptoms of liver disease is crucial for early detection and appropriate management. Liver disease often presents with subtle signs, making it challenging to identify early. Many of these symptoms can be attributed to other conditions, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any persistent discomfort or changes in your well-being.Symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific type and stage of liver disease.
Sometimes, subtle signs of liver disease can be tricky to spot. One unusual symptom might be a pustular rash, which could indicate underlying liver issues. Understanding the different types of pustular rashes and their potential treatments is important for proper diagnosis. For a comprehensive guide on pustular rash types treatment, check out this resource: pustular rash types treatment.
While a rash could be a sign, it’s crucial to remember that other symptoms like jaundice or abdominal pain could also point to liver problems. Consulting a doctor is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment plans.
Mild symptoms may be easily dismissed, while advanced disease can lead to severe and debilitating conditions. This section will delve into the most prevalent symptoms, their potential severity, and how they relate to the different stages of liver disease.
Symptoms by Category
Recognizing patterns in symptoms can help you understand the potential presence of liver disease. Symptoms are categorized here for easier comprehension. This structured approach allows for a more thorough evaluation of the condition.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: These often include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal discomfort. In early stages, these symptoms may be intermittent and mild, potentially mistaken for other ailments. As the disease progresses, these symptoms can become more persistent and severe, leading to significant disruptions in daily life. Examples include chronic nausea and vomiting that interfere with eating and hydration, causing malnutrition and dehydration.
- Metabolic Symptoms: Liver disease can impact the body’s metabolism, leading to a range of symptoms. These can include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, and weight loss. Jaundice, for example, may appear as a subtle yellowing initially, but can become more pronounced as the disease progresses. Fatigue can vary in severity, ranging from mild tiredness to profound exhaustion, impacting daily activities.
- Vascular Symptoms: Certain liver conditions can affect blood circulation. This may manifest as easy bruising, spider angiomas (small, red, spider-like blood vessels), or ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen). Spider angiomas, for instance, are often an early indicator of liver disease and can be seen on the skin. Ascites, however, typically occurs in more advanced stages and can cause significant discomfort and swelling.
- Neurological Symptoms: As liver disease progresses, it can affect the nervous system. These symptoms may include confusion, difficulty concentrating, and in severe cases, hepatic encephalopathy (a severe neurological complication). Hepatic encephalopathy is characterized by a range of neurological symptoms that can progress to coma.
Symptom Severity and Organ Systems Affected, Signs of liver disease
The severity of symptoms can vary greatly depending on the stage of liver disease. Early-stage symptoms may be mild and intermittent, while advanced stages can lead to more pronounced and frequent symptoms.
| Symptom | Potential Severity | Organ Systems Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea/Vomiting | Mild (occasional), Moderate (frequent), Severe (persistent) | Gastrointestinal |
| Jaundice | Mild (subtle yellowing), Moderate (noticeable yellowing), Severe (intense yellowing) | Hepatic (liver), Integumentary (skin) |
| Fatigue | Mild (tiredness), Moderate (significant exhaustion), Severe (inability to perform daily tasks) | Neurological, Musculoskeletal |
| Ascites | Mild (slight swelling), Moderate (significant swelling), Severe (severe abdominal distention) | Gastrointestinal, Cardiovascular |
| Confusion/Cognitive Impairment | Mild (difficulty concentrating), Moderate (disorientation), Severe (coma) | Neurological |
Diagnostic Methods
Unveiling the secrets of liver health requires a battery of diagnostic tools. These methods range from simple blood tests to more complex imaging scans and biopsies. Understanding these procedures and their potential results is crucial for early detection and effective management of liver disease.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are often the initial step in evaluating liver health. They measure the levels of various substances in the blood that can indicate liver function and damage. These substances include liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins. Abnormal levels of these markers can signal a problem.
- Liver Enzymes: These enzymes are released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged or inflamed. Elevated levels of enzymes like aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) often suggest liver injury. For example, a person experiencing significant alcohol abuse may exhibit elevated AST and ALT levels, indicating potential liver inflammation.
- Bilirubin: Bilirubin is a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. The liver processes bilirubin and excretes it in bile. High levels of bilirubin can cause jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes. This could indicate conditions like hepatitis or biliary obstruction.
- Proteins: The liver produces several crucial proteins. Low levels of albumin or clotting factors can suggest liver dysfunction. This could be due to chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis.
Imaging Scans
Imaging scans, such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, provide detailed visual representations of the liver. They can help identify structural abnormalities, such as tumors, cysts, or blockages.
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive technique uses sound waves to create images of the liver. It’s valuable for assessing the size and shape of the liver, detecting gallstones, and identifying fluid buildup around the liver. Ultrasound is frequently used as a first-line imaging tool due to its affordability and lack of radiation exposure.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): CT scans use X-rays and computer processing to produce cross-sectional images of the liver. This method can provide more detailed information than ultrasound, especially when evaluating the extent of liver damage or identifying tumors.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the liver. It is particularly useful for distinguishing between different tissues and identifying subtle abnormalities, often providing superior contrast resolution compared to CT scans.
Biopsies
A liver biopsy involves removing a small tissue sample from the liver for microscopic examination. This procedure is often performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure accurate placement of the needle. It allows pathologists to assess the extent of liver damage, identify specific diseases, and determine the stage of the disease.
- Procedure: A small needle is inserted into the liver guided by imaging. The collected tissue sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The analysis involves examining the tissue under a microscope to determine if there’s inflammation, scarring, or abnormal cell growth.
- Potential Complications: Although generally safe, complications like bleeding, infection, or pain can occur, and proper patient selection and post-procedure care are essential.
Diagnostic Tests Summary
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose | Potential Results | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Tests | Assess liver function and identify abnormalities in liver enzymes, bilirubin, and proteins. | Elevated liver enzymes, abnormal bilirubin levels, low protein levels. | May not always pinpoint the specific cause of liver issues. |
| Imaging Scans (Ultrasound, CT, MRI) | Visualize liver structure, identify abnormalities, and assess extent of damage. | Liver enlargement, tumors, cysts, fluid buildup, or blockages. | May not detect subtle abnormalities or early-stage diseases. Radiation exposure for CT scans. |
| Liver Biopsy | Obtain tissue sample for microscopic examination to assess the severity of liver damage. | Inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, or specific disease identification. | Invasive procedure with potential complications, not always necessary. |
Limitations of Diagnostic Methods
No single diagnostic method is perfect. Blood tests may not always pinpoint the specific cause of liver issues. Imaging scans may not detect subtle abnormalities or early-stage diseases. A liver biopsy, while providing detailed information, is an invasive procedure with potential complications. A combination of these methods is often used to obtain a comprehensive evaluation of liver health.
Risk Factors
Understanding the factors that increase your likelihood of developing liver disease is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Knowing your risk profile empowers you to make informed choices about lifestyle and healthcare. Identifying these risk factors allows for proactive measures to minimize the potential for liver damage.A multitude of factors can contribute to liver disease, ranging from genetic predispositions to environmental exposures.
Some risk factors are modifiable, meaning you can take steps to mitigate their impact, while others are non-modifiable, requiring a different approach to managing the associated risks. Recognizing these distinctions is essential in tailoring preventative strategies to individual circumstances.
Major Risk Factors
Various factors significantly increase the risk of developing liver disease. These factors can be categorized based on lifestyle choices, genetics, and environmental exposures. Understanding the interplay between these categories is vital in comprehending the complex nature of liver disease.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices play a substantial role in liver health. Poor dietary habits, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can all contribute to the development of liver disease. These choices often interact with each other, compounding the risk.
- Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in saturated fats, processed foods, and excessive sugar can lead to fatty liver disease (FLD), a common precursor to more serious liver conditions. Regular consumption of sugary drinks, especially sodas, has also been linked to a higher risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Chronic alcohol abuse is a significant risk factor for alcoholic liver disease (ALD). Even moderate to heavy drinking over time can cause liver damage.
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to weight gain and obesity, both of which are associated with a heightened risk of NAFLD.
Genetics
Genetic predispositions can also significantly influence a person’s risk of developing liver disease. Certain genetic variations can make individuals more susceptible to certain liver conditions.
- Family History: A family history of liver disease, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, can indicate a genetic predisposition. This information is crucial for individuals to discuss with their healthcare providers to understand their personal risk and potential need for more frequent monitoring.
- Specific Genetic Variations: Specific genetic variations can increase the risk of certain liver diseases. For example, some genetic markers are associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also contribute to liver disease. Exposure to certain toxins and infections can increase the risk of liver damage.
- Infections: Certain viral infections, such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C, can cause chronic liver inflammation and potentially lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Vaccination against these viruses is a crucial preventative measure.
- Toxins and Chemicals: Exposure to certain environmental toxins and chemicals can damage the liver. Examples include exposure to certain industrial solvents and pesticides.
Risk Factor Categorization
| Category | Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Choices | Unhealthy Diet | High in saturated fats, processed foods, and excessive sugar |
| Lifestyle Choices | Excessive Alcohol Consumption | Chronic alcohol abuse |
| Lifestyle Choices | Lack of Physical Activity | Sedentary lifestyle, contributing to weight gain |
| Genetics | Family History | Presence of liver disease in family members |
| Genetics | Specific Genetic Variations | Certain genetic markers increasing susceptibility |
| Environmental Factors | Infections | Viral infections (e.g., hepatitis B, C) |
| Environmental Factors | Toxins and Chemicals | Exposure to certain industrial solvents, pesticides |
Prevention Strategies
Protecting your liver health is a proactive approach that can significantly reduce your risk of developing liver disease and its complications. Taking steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle and making informed choices can make a substantial difference in preserving liver function. Early intervention and prevention are crucial for managing existing liver conditions and mitigating future damage.Implementing preventative measures is not just about avoiding specific triggers; it’s about cultivating a holistic approach to well-being.
This involves understanding the interplay between lifestyle choices, environmental factors, and genetic predispositions. By making conscious decisions, individuals can empower themselves to significantly reduce their risk of developing or worsening liver conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Risk
Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise are cornerstone strategies in liver health management. These lifestyle choices impact liver function and reduce the risk of developing liver diseases. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, coupled with regular physical activity, can contribute to overall health and liver well-being. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol intake is equally important.
Preventative Measures for Existing Conditions
Addressing existing liver conditions requires a multifaceted approach. Early detection and consistent management are key to slowing the progression of liver damage and improving quality of life. This includes adhering to prescribed medications, attending regular check-ups, and making lifestyle adjustments as advised by healthcare professionals. Regular monitoring allows for early intervention and prevents further complications.
Actionable Steps to Lower Risk
Implementing practical steps can significantly reduce the risk of liver disease. A proactive approach involves understanding the factors that contribute to liver damage and taking appropriate steps to minimize these risks. These steps can be tailored to individual needs and circumstances, ensuring a personalized and effective prevention plan.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients that support liver health.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. Exercise improves overall health, including liver function.
- Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limit alcohol intake to recommended levels. Excessive alcohol consumption is a major risk factor for liver damage. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial. Obesity significantly increases the risk of liver disease. Consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for guidance on healthy weight management strategies.
- Avoiding Harmful Substances: Avoid illicit drug use and exposure to environmental toxins. These substances can contribute to liver damage.
- Vaccination: Vaccination against Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B is recommended. These vaccines provide protection against viral infections that can cause liver disease.
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor, especially if you have risk factors for liver disease. Early detection and management of potential issues can prevent serious complications.
Comparing Preventive Strategies
Different preventive strategies offer varying levels of impact on liver health. For instance, adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise is a cornerstone of preventing and managing liver disease, contributing to overall well-being. While abstaining from alcohol is crucial for reducing the risk of alcohol-related liver damage, lifestyle changes, like weight management, can help prevent and address non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Spotting signs of liver disease can be tricky, but jaundice is a common one. While researching ways to soothe irritated skin, I stumbled upon some interesting uses of aloe vera for eczema relief. Learning how to use aloe vera for eczema could potentially help with some skin issues that might be a symptom of liver problems. how to use aloe vera for eczema This, however, doesn’t replace professional medical advice, and it’s crucial to remember that a proper diagnosis for liver disease needs to be done by a doctor.
Regular check-ups are essential for early detection and intervention. Each strategy, when combined, creates a comprehensive approach to protecting liver health.
Treatment Approaches
Liver disease, unfortunately, doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all treatment. The most effective approach hinges on the specific type of liver disease, its severity, and the patient’s overall health. Different treatment strategies aim to address the underlying cause, slow disease progression, and alleviate symptoms. These approaches often involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and in severe cases, surgical interventions.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for liver disease focus on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and addressing the underlying cause. This can involve medications to control inflammation, support liver function, and manage complications like cirrhosis or portal hypertension. Dietary changes, such as reducing alcohol intake, are also crucial in many cases.
- Antivirals: For viral hepatitis, antiviral medications are crucial. These medications aim to eliminate the virus, reducing inflammation and preventing further liver damage. The effectiveness of antivirals varies depending on the specific virus (e.g., Hepatitis C treatments have seen significant advancements, leading to high cure rates). Potential side effects include mild gastrointestinal issues, fatigue, or skin rashes.
Examples of successful antiviral treatment include those used for Hepatitis C, where in many cases, the virus can be eradicated, significantly improving the long-term prognosis.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases of autoimmune hepatitis, where the immune system attacks the liver, immunosuppressants are used to modulate the immune response. These medications can effectively control inflammation and prevent further liver damage. Side effects can include increased susceptibility to infections and other immune-related complications. The use of these medications must be carefully monitored to balance the benefits and risks.
- Medications for specific symptoms: Various medications can manage symptoms like ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen) or hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction). These medications can significantly improve quality of life for patients with advanced liver disease.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing and preventing liver disease. Changes in diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption can significantly impact liver health.
- Dietary Changes: A balanced diet low in fat and processed foods is often recommended. Avoiding excessive alcohol intake is critical for individuals with alcoholic liver disease or those at risk. A well-planned diet can significantly reduce the burden on the liver.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and help manage weight, which is often a factor in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Alcohol Cessation: Abstaining from alcohol is essential for those with alcoholic liver disease. Even moderate alcohol consumption can exacerbate the condition in vulnerable individuals.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are reserved for advanced cases of liver disease or complications. These procedures can improve liver function and alleviate symptoms.
- Liver Transplantation: This is a life-saving procedure for end-stage liver disease. Transplants are often the only option for patients with irreversible liver failure. Success rates vary based on patient health and the availability of donor organs.
- Other Procedures: Procedures like TIPS (transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt) may be used to manage complications of portal hypertension. The specific surgical approach is tailored to the individual patient’s needs and the nature of their liver condition.
Treatment Effectiveness Table
| Treatment Option | Target Area | Potential Success Rate (General Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Antivirals (Hepatitis C) | Viral eradication, inflammation reduction | High (often >90%) |
| Immunosuppressants (Autoimmune Hepatitis) | Immune modulation, inflammation control | Moderate to High (depends on disease severity and response) |
| Dietary Changes | Reducing liver burden, weight management | High (when part of a comprehensive approach) |
| Liver Transplantation | End-stage liver failure | High (long-term survival rates are significant) |
Note: Success rates are estimates and can vary significantly based on individual factors.
Lifestyle Considerations
Taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle is crucial for preventing and managing liver disease. A balanced approach that incorporates proper nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management significantly impacts liver health. These lifestyle choices are not just preventative measures; they are integral to the overall well-being of individuals with liver conditions, contributing to improved quality of life and disease management.Liver health is closely intertwined with our daily habits.
The choices we make regarding food, activity, and stress response directly influence the health and function of this vital organ. Understanding and implementing positive lifestyle changes can make a substantial difference in preventing further damage and supporting the liver’s natural restorative processes.
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition is paramount for liver health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support liver function. Hydration is equally important, as water helps flush out toxins and supports various bodily functions, including liver detoxification.
- A diet rich in fruits and vegetables offers a wealth of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, crucial for protecting the liver from oxidative stress and damage.
- Limiting processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugar intake is vital. These can contribute to fatty liver disease and worsen existing liver conditions.
- Prioritize lean proteins for building and repairing tissues, while avoiding excessive intake of processed meats.
- Sufficient hydration is essential for liver function, supporting detoxification processes. Water helps to flush out toxins and promotes overall bodily functions.
Exercise and Stress Management
Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also play a significant role in liver health. Chronic stress can negatively impact liver function.
- Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming, helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
- Moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week is generally recommended.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help reduce the negative impact of chronic stress on liver function.
- Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances and inflammation, which can indirectly affect liver health.
Dietary Guidelines for Liver Health
Adhering to specific dietary guidelines can greatly improve liver health. These guidelines emphasize the importance of nutrient-dense foods and the avoidance of harmful substances.
- Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Limit consumption of processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive sugar intake.
- Consume lean proteins to support tissue repair and maintenance.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Choose healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, in moderation.
Sample Healthy Meal Plans
These sample meal plans provide examples of how to incorporate the dietary guidelines into daily meals, tailored to promote liver health.
| Meal | Description |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or a smoothie with spinach, banana, and protein powder. |
| Lunch | A salad with grilled chicken or fish, mixed greens, and a light vinaigrette dressing. |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables or lentil soup with whole-wheat bread. |
Illustrations of Liver Damage
The liver, a vital organ, plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions. When liver disease progresses, its structure and function change dramatically. Understanding these alterations is essential for recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate medical care. This section will detail the visible and functional changes in the liver as it deteriorates, and the impact on other bodily systems.The liver’s intricate structure is gradually compromised by disease processes.
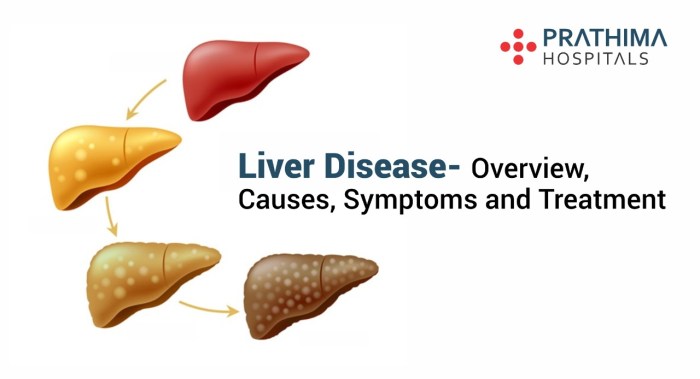
Fibrosis, an initial stage, involves the accumulation of scar tissue within the liver, disrupting its normal architecture. This scarring process progressively hinders the liver’s ability to perform its functions. Further progression leads to cirrhosis, a more advanced stage where the liver’s healthy tissue is extensively replaced by scar tissue. This severe scarring distorts the liver’s shape and structure, making it nodular and shrunken.
Liver Structure Alterations
Liver disease progressively changes the organ’s structure. Initially, fibrosis forms as scar tissue accumulates between the liver cells. This process gradually disrupts the liver’s normal architecture and functionality. As the disease advances, this scar tissue continues to build up, eventually leading to cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is characterized by a distorted liver structure with a nodular appearance, where healthy liver tissue is replaced by extensive scar tissue.
This structural change leads to a significant reduction in the liver’s functional capacity.
Changes in Liver Function and Size
As liver disease progresses, its functional capacity decreases significantly. Initially, the liver may still perform its tasks, but gradually, these functions are compromised. The liver’s ability to filter blood, produce essential proteins, and metabolize nutrients diminishes. This deterioration often manifests as an increase in liver enzymes, indicative of impaired function. The liver’s size may also change, shrinking in advanced stages due to the replacement of healthy tissue with scar tissue.
This reduction in size is a consequence of the progressive damage.
Impact on Other Organ Systems
Liver disease significantly impacts other organ systems due to the liver’s vital role in numerous bodily processes. As liver function declines, toxins build up in the blood, affecting various systems. For example, jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes, occurs due to the accumulation of bilirubin, a byproduct of hemoglobin breakdown. The liver’s role in protein synthesis is also affected, leading to edema (swelling) in the extremities and ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen).
Further complications include portal hypertension (high blood pressure in the portal vein), leading to esophageal varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus) and potentially life-threatening bleeding. Liver damage can also impact the brain, resulting in encephalopathy (brain dysfunction), characterized by confusion, altered mental status, and even coma.
Impact on Overall Well-being and Quality of Life
Liver disease’s impact extends far beyond the liver itself, affecting a person’s overall well-being and quality of life. The symptoms and complications associated with liver disease can significantly reduce a person’s ability to engage in daily activities, causing fatigue, nausea, and discomfort. The emotional toll of the diagnosis and ongoing treatment is also substantial. Loss of appetite, weight loss, and other symptoms can lead to nutritional deficiencies and further compromise the body’s ability to heal.
The impact on relationships and social life can also be significant. The chronic nature of some liver conditions and the need for ongoing medical care can significantly reduce the patient’s ability to participate in their normal routines.
Complications of Liver Disease: Signs Of Liver Disease
Advanced liver disease can lead to a cascade of serious complications, significantly impacting a patient’s health and quality of life. These complications arise from the liver’s diminished ability to perform its vital functions, such as filtering toxins, producing essential proteins, and regulating metabolism. Understanding these complications is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers to develop effective management strategies.
Portal Hypertension
Portal hypertension is a common complication of cirrhosis, characterized by elevated pressure within the portal vein, the blood vessel that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. This elevated pressure forces blood to seek alternative routes, leading to the development of collateral vessels. These abnormal vessels can cause esophageal varices (enlarged veins in the esophagus), which are prone to bleeding, potentially life-threatening.
Patients with portal hypertension may also experience ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen), splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), and hemorrhoids. The severity of portal hypertension is often measured by the presence and severity of complications like variceal bleeding and ascites.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy is a neuropsychiatric disorder caused by the liver’s inability to remove toxins from the blood. As toxins accumulate, they can impair brain function, leading to a range of symptoms, from subtle changes in personality and behavior to confusion, disorientation, and coma. The severity of hepatic encephalopathy can fluctuate, depending on factors like the underlying liver disease, the presence of infections, and the patient’s overall health.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent further deterioration and complications.
Hepatorenal Syndrome
Hepatorenal syndrome is a severe kidney dysfunction that develops in patients with advanced liver disease. The exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, but it’s believed to be related to the liver’s inability to regulate blood flow and the body’s fluid balance. This leads to a decline in kidney function, resulting in decreased urine output and fluid retention. Hepatorenal syndrome is a serious complication with a poor prognosis.
Jaundice
Jaundice, a yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes, is a common sign of liver dysfunction. It occurs when the liver struggles to process bilirubin, a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown. The severity of jaundice can vary significantly, ranging from a mild, barely noticeable discoloration to a severe, life-threatening condition. This complication can be a manifestation of various liver conditions, ranging from mild to severe.
Ascites
Ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. This fluid buildup puts pressure on the organs and can cause significant discomfort and pain. It’s often a symptom of advanced liver disease, particularly portal hypertension. The presence of ascites often indicates the need for careful management of fluid balance and potential interventions. Its severity can impact a patient’s ability to perform daily tasks.
Table of Complications
| Complication | Causes | Potential Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Portal Hypertension | Cirrhosis, increased pressure in portal vein | Lifestyle modifications, medications to reduce pressure, endoscopic procedures for varices, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) |
| Hepatic Encephalopathy | Liver’s inability to remove toxins from the blood | Dietary restrictions, medications to improve liver function, lactulose to reduce ammonia levels, liver transplant |
| Hepatorenal Syndrome | Complex interaction of liver and kidney dysfunction | Treatment of underlying liver disease, supportive care, medications to support kidney function, liver transplant |
| Jaundice | Impaired bilirubin processing by the liver | Treatment of underlying liver disease, supportive care, medications to reduce bilirubin levels |
| Ascites | Fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity, often due to portal hypertension | Dietary restrictions, diuretics, paracentesis (removal of fluid), liver transplant |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of liver disease is vital for proactive health management. By understanding the early warning signs, common symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, you can take control of your liver health. Remember, early intervention is key to preventing the progression of liver disease and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.