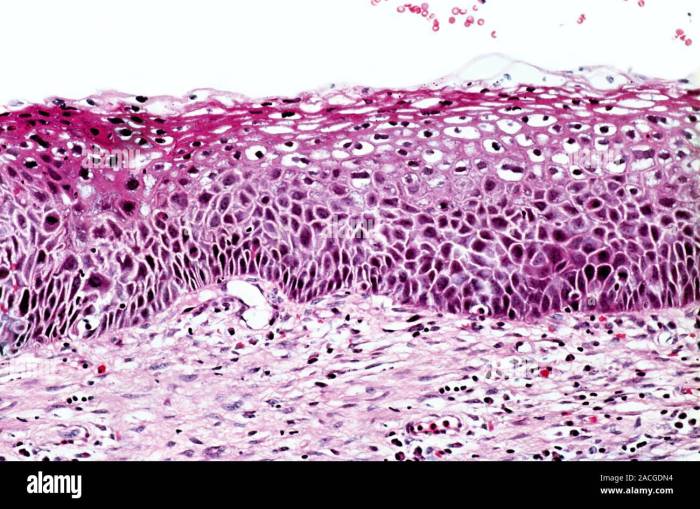
What is cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)? This condition, often linked to HPV, represents abnormal cell growth on the cervix. Understanding its various grades, from CIN 1 to CIN 3, is crucial for early detection and effective management. This blog post delves into the specifics of CIN, exploring its causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventative strategies. We’ll also examine potential complications and long-term implications.
CIN, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, is a condition where abnormal cells grow within the lining of the cervix. It’s important to note that CIN isn’t cancer itself, but it can progress to cervical cancer if left untreated. Different grades of CIN reflect varying degrees of abnormality, with CIN 1 being the least severe and CIN 3 the most concerning.
Early detection is key, so understanding the symptoms and risk factors is paramount.
Definition and Overview
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a precancerous condition affecting the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. It involves abnormal cell growth within the lining of the cervix. Understanding CIN is crucial because early detection and treatment can prevent progression to cervical cancer. CIN is a spectrum of changes, ranging from mild to severe, and is often detected through routine Pap smears.
Grades of CIN
CIN is categorized into three grades: CIN 1, CIN 2, and CIN 3, reflecting the severity of the abnormal cell growth. These grades represent increasing degrees of dysplasia, a term for abnormal cell development. Progression from one grade to another can occur, but not always.
CIN 1
CIN 1, the least severe form, typically shows mild abnormalities in the cervical cells. These changes are often reversible and do not necessarily indicate a high risk of progressing to cancer. The cells may show some unusual features but are still largely normal. CIN 1 is usually managed with close monitoring and follow-up.
CIN 2
CIN 2 indicates more significant cellular abnormalities. The abnormal cells are more widespread and display more severe dysplasia. While still considered precancerous, the risk of progression to cancer is higher than with CIN 1. Treatment options for CIN 2 often include cryotherapy or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP).
CIN 3
CIN 3 represents the most severe form of CIN. It involves extensive abnormal cell growth and significant dysplasia. The cells exhibit marked abnormalities, increasing the risk of developing cervical cancer. Treatment options for CIN 3 are often more aggressive, potentially including a cone biopsy or LEEP. In some cases, the severity might necessitate more extensive procedures.
Typical Presentation of CIN
Typically, CIN presents with no noticeable symptoms. This is why routine Pap smears are essential for early detection. In some cases, patients might experience abnormal vaginal bleeding, particularly after sexual intercourse, or unusual vaginal discharge. However, these symptoms are not specific to CIN and can be caused by other conditions.
Stages of CIN
| Stage | Symptoms | Risk Factors | Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIN 1 | Usually asymptomatic; occasionally, abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. | Early sexual activity, multiple sexual partners, history of HPV infection. | Close monitoring, repeat Pap smears, possibly cryotherapy or LEEP. |
| CIN 2 | Usually asymptomatic; occasionally, abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. | Same as CIN 1, plus smoking, weakened immune system. | Cryotherapy, LEEP, or other ablative procedures. |
| CIN 3 | Usually asymptomatic; occasionally, abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. | Same as CIN 1 and 2, plus higher viral load of HPV, long-term HPV infection. | Cone biopsy, LEEP, or other ablative procedures, potentially followed by further monitoring. |
Symptoms and risk factors are not always present in all cases. A healthcare professional should always be consulted for diagnosis and treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) isn’t a single event but a spectrum of abnormal cell changes in the cervix. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors is crucial for prevention and early detection. These factors influence the likelihood of developing CIN, and recognizing them can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce their risk.The primary driver behind CIN development is often linked to a viral infection, and in particular, the human papillomavirus (HPV).
While other factors also play a role, HPV infection is a significant contributor to the progression of these abnormal cellular changes. Different types of HPV are associated with varying degrees of risk. Understanding these relationships is essential for preventative measures.
Role of HPV Infection in CIN
HPV, a common sexually transmitted infection, is the leading cause of CIN. Certain types of HPV, known as high-risk types, are particularly linked to the development of precancerous lesions. These high-risk types can integrate their DNA into the host cell’s DNA, leading to cellular changes and ultimately, the potential for cancerous transformation. The presence of HPV alone doesn’t always guarantee CIN development, but it significantly increases the risk.
Comparison of Risk Factors Across CIN Grades
The risk factors associated with different grades of CIN can vary. Lower-grade CIN often involves a milder form of cellular abnormality and may have different contributing factors than higher-grade CIN. Higher-grade CIN carries a greater risk of progression to cervical cancer, and the underlying risk factors may be more pronounced.
Other Risk Factors
Beyond HPV infection, other factors can increase the risk of developing CIN. Sexual history plays a significant role. Multiple sexual partners, a history of sexually transmitted infections, and early sexual debut are all associated with a higher risk. Lifestyle choices can also influence the risk. Smoking, for instance, has been strongly linked to a greater likelihood of CIN progression.
Poor diet and a lack of regular exercise can also be contributing factors.
Table: Comparison of Risk Factors Across CIN Grades
| Risk Factor | Low-Grade CIN | High-Grade CIN |
|---|---|---|
| HPV Infection (High-Risk Types) | Present, but potentially less frequent or less aggressive strain | Present, often with a more aggressive strain or persistent infection |
| Multiple Sexual Partners | May be a factor, but potentially less significant | Stronger association with multiple partners |
| Early Sexual Debut | Potentially a factor | Potentially a more significant factor |
| Smoking | May contribute to the risk | Stronger association and can accelerate progression |
| Weakened Immune System | May increase vulnerability | May significantly increase vulnerability |
Diagnosis and Testing
Discovering cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) relies on a series of diagnostic tests, each playing a crucial role in identifying the extent and severity of the condition. These tests are essential for accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment planning. Early detection is paramount, as it allows for interventions that can prevent the progression to more serious conditions.A comprehensive approach to diagnosis involves a stepwise process, progressing from initial screening to more invasive procedures when necessary.
This methodical approach ensures that the most appropriate diagnostic tools are utilized to determine the nature and extent of the abnormal cells, providing clinicians with the information required for effective treatment strategies.
Pap Smears, What is cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Pap smears are a cornerstone of cervical cancer screening. They are a simple and relatively painless procedure that involves collecting cells from the cervix for microscopic examination. The procedure typically involves using a speculum to open the vaginal canal, allowing the healthcare provider to visualize the cervix. A small brush or spatula is then used to gently collect cells from the surface of the cervix.
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a condition where abnormal cells develop on the cervix. While researching the potential health impacts of food additives, I stumbled upon the question of whether MSG is truly harmful. Digging deeper into the science behind CIN, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a precursor to cervical cancer and needs proper medical attention. Learning about the safety of additives like MSG is interesting, but it shouldn’t distract from the importance of cervical health screenings and early detection of CIN.
is msg bad for you. Ultimately, prioritizing women’s health is paramount.
These cells are then placed on a slide and sent to a laboratory for analysis. A pathologist then examines the cells under a microscope to identify any abnormal characteristics.
Colposcopy
Colposcopy is a procedure that allows for a detailed visual examination of the cervix and surrounding tissues. A colposcope, a specialized microscope with a light source, is used to magnify the area. Solutions are often applied to the cervix to highlight any abnormal areas, which are then further evaluated. This allows for a more thorough assessment of the cervix, enabling the identification of subtle changes that might not be visible during a regular Pap smear.
The procedure involves placing a speculum inside the vagina to allow visualization of the cervix. The colposcope is then positioned to allow a magnified view of the cervix.
Biopsies
A biopsy is a procedure that involves removing a small tissue sample from the cervix for microscopic examination. If abnormal cells are detected during a colposcopy, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the abnormality. The procedure typically involves using a small instrument to collect a tissue sample from the affected area.
This sample is then sent to a pathologist for analysis. The type of biopsy used depends on the location and extent of the abnormal tissue, with options including punch biopsies, cone biopsies, and endocervical curettage.
Diagnostic Tests for CIN
| Test | Description | Accuracy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pap Smear | Screening test for cervical abnormalities | High sensitivity for detecting precancerous changes | Can miss some precancerous lesions, especially if they are small or hidden |
| Colposcopy | Visual examination of the cervix under magnification | Highly effective in identifying suspicious areas | Requires specialized equipment and expertise |
| Biopsy | Removal of tissue sample for microscopic analysis | Gold standard for confirming diagnosis and determining extent | Invasive procedure, carries a small risk of complications |
These diagnostic methods, when used in conjunction, provide a comprehensive approach to diagnosing CIN. Each method plays a unique role, from initial screening to definitive diagnosis, ensuring that appropriate and timely interventions can be implemented.
Treatment Options
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) treatment varies significantly depending on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. The goal of treatment is to remove or destroy abnormal cells, preventing them from progressing to cancer. Early intervention is crucial for the best possible outcomes. Choosing the right treatment strategy is a collaborative process between the patient and their healthcare provider, weighing the benefits and potential risks of each approach.
Conservative Management Strategies
Conservative management is often the first approach for early-stage CIN, particularly in cases of mild dysplasia. These strategies aim to monitor the condition closely without immediate intervention, allowing time for the body to resolve the abnormal cells naturally. This approach is usually suitable for patients with a low risk of progression. These methods often include regular follow-up appointments for Pap smears and colposcopies to monitor the changes over time.
In some cases, cryotherapy or laser therapy may be used as an additional intervention for targeted removal of abnormal tissue, whilst still falling under the umbrella of conservative management.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions are generally reserved for moderate to severe CIN, where conservative approaches may not be sufficient or where the risk of progression is higher. These procedures aim to remove the affected tissue and prevent the development of cervical cancer. Common surgical procedures include loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), cone biopsy, and, in more severe cases, hysterectomy. The choice of surgical procedure depends on the extent of the lesion and the patient’s desire for future fertility.
For example, a LEEP may be sufficient for localized CIN, while a cone biopsy might be required for larger or deeper lesions. A hysterectomy, a more extensive procedure, is considered when other options are inadequate or the patient chooses to prioritize the prevention of cervical cancer over future fertility.
Criteria for Choosing a Treatment Approach
The decision to choose a specific treatment approach for CIN is multifaceted. Factors influencing the selection process include the grade of CIN (CIN 1, CIN 2, or CIN 3), the extent of the lesion, the patient’s age and overall health, and her desire for future fertility. A thorough evaluation of these factors allows the healthcare team to tailor the treatment plan to the individual patient’s needs.
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is basically abnormal cell growth in the cervix. While it’s often a precursor to cervical cancer, it’s crucial to remember that many cases resolve on their own. Finding healthy ways to manage stress can be really helpful, and incorporating breathing exercises to lower blood pressure into your routine might just be the key to overall well-being, which can, in turn, contribute to a healthier cervix.
Ultimately, staying informed about CIN and getting regular checkups are key for maintaining good reproductive health.
For instance, a younger woman who desires future pregnancies might opt for less invasive procedures than a woman who has already completed her family. The clinician will also consider the potential risks and benefits of each treatment option, including the chance of recurrence, complications, and potential long-term effects.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative Management (Monitoring) | Effective for early-stage CIN, often successful in resolving the condition naturally. | Potential for recurrence; close monitoring required; may not be suitable for all cases. |
| Cryotherapy | Effective in destroying abnormal cells; relatively quick procedure. | Potential for mild cramping, spotting, or bleeding after the procedure; possible scarring. |
| Laser Therapy | Effective in removing abnormal tissue; precise targeting. | Potential for mild cramping, spotting, or bleeding after the procedure; risk of scarring. |
| LEEP (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure) | Highly effective in removing abnormal tissue; generally less invasive than other surgical procedures. | Potential for cramping, bleeding, or infection; rare but possible complications include cervical stenosis (narrowing) or injury to surrounding tissues. |
| Cone Biopsy | Effective in removing a wider area of abnormal tissue. | Potential for increased bleeding, infection, or scarring; may impact fertility if performed repeatedly. |
| Hysterectomy | Definitive treatment for CIN, preventing any further risk of cervical cancer; effective in cases where other options are not suitable. | Major surgical procedure with potential for complications including infection, blood clots, and scarring; significantly impacts fertility. |
Prevention and Management
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a condition that can lead to cervical cancer if left untreated. Thankfully, proactive prevention and early management strategies can significantly reduce the risk of progression and improve outcomes. Understanding these strategies empowers individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
Preventative Measures to Reduce CIN Risk
Effective prevention plays a crucial role in reducing the likelihood of developing CIN. A multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle choices and preventive measures can significantly lower the risk. These measures include maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and engaging in regular physical activity. Smoking cessation is paramount, as smoking significantly increases the risk of developing CIN.
Avoiding risky sexual behaviors, such as multiple partners and unprotected sex, can also help to reduce the risk of contracting HPV, a major causative factor in CIN.
Importance of Regular Screenings and Follow-up Care
Regular screenings are essential for early detection and management of CIN. Pap smears and HPV testing are vital tools in identifying abnormal cells in the cervix. These screenings allow for early intervention, potentially preventing the progression of CIN to cancer. Follow-up care, including colposcopy and biopsies, ensures comprehensive evaluation of any suspicious findings. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical in managing CIN effectively and preventing complications.
Role of Vaccination in Preventing CIN
HPV vaccination is a highly effective preventative measure against CIN. The vaccine protects against the types of HPV most commonly associated with cervical cancer and precancerous lesions. Vaccination is recommended for adolescents and young adults to provide long-term protection against HPV infection. Vaccination significantly lowers the risk of CIN development and can have a positive impact on public health.
Guidance on Managing CIN to Prevent Progression
Managing CIN involves a range of strategies tailored to the individual’s specific situation. Treatment options for CIN vary depending on the severity of the condition. These options include cryotherapy, laser therapy, and surgical removal of abnormal tissue. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and detect any signs of recurrence. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and adhering to prescribed follow-up care are vital for successful management and prevention of progression.
Strategies for Prevention and Management of CIN
| Category | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Prevention |
|
| Management |
|
Complications and Prognosis: What Is Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is a significant concern, not just for the immediate health implications, but also for the potential long-term consequences. Understanding the complications that can arise, the factors affecting prognosis, and the likelihood of progression to cancer is crucial for effective patient management and informed decision-making. This section delves into these aspects, offering a clearer picture of the potential outcomes associated with CIN.
Potential Complications of CIN
CIN, if left untreated, can progress to cervical cancer, a serious and potentially life-threatening disease. Beyond cancer, other complications may arise, though less frequently. These can include difficulties in conception and pregnancy, as well as complications during childbirth. The likelihood and severity of these complications vary depending on the grade of CIN and the individual’s overall health.
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is basically abnormal cell growth in the cervix. Understanding the role of nitric oxide in overall health is crucial, as it’s linked to various bodily functions. For a deeper dive into the world of nitric oxide, check out this comprehensive guide on nitric oxide everything you need to know. While CIN isn’t directly about nitric oxide, understanding its role in the body can be helpful when considering overall health.
Ultimately, recognizing and managing CIN is key for maintaining reproductive health.
Factors Influencing CIN Prognosis
Several factors influence the prognosis of CIN, impacting the likelihood of progression and the effectiveness of treatment. These factors include the grade of CIN, the patient’s age, overall health, and lifestyle choices. Smoking, for example, is a significant risk factor, increasing the risk of progression. Additionally, a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can play a role.
Early detection and prompt treatment are essential in improving outcomes.
Likelihood of CIN Progressing to Cancer
The likelihood of CIN progressing to cervical cancer depends on several factors, including the grade of CIN. Lower-grade CIN, such as CIN 1, is less likely to progress to cancer compared to higher-grade CIN, such as CIN 3. However, even lower-grade CIN can progress, highlighting the importance of regular screening and follow-up. It’s crucial to understand that this is not a definitive prediction for every individual case.
Long-Term Health Implications of CIN
Long-term health implications of CIN extend beyond the initial diagnosis. Treatment options, such as cryotherapy or cone biopsy, may have short-term side effects like bleeding or discomfort. The impact on future fertility, sexual health, and psychological well-being should be carefully considered. Proper counseling and support are essential for patients undergoing treatment for CIN.
Survival Rates for Different Grades of CIN
Survival rates for CIN are generally excellent when detected early and treated promptly. However, the specific survival rates vary depending on the grade of CIN. Data suggests that survival rates are significantly higher for patients diagnosed with lower-grade CIN compared to those with higher-grade CIN. Furthermore, the presence of other risk factors can affect these rates. Detailed information on survival rates can be found in reputable medical publications and databases.
Importantly, survival rates are not absolute guarantees, and individual experiences can vary.
Illustrative Case Studies
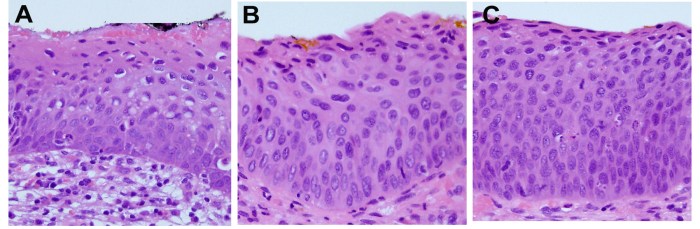
Understanding cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) involves exploring real-world scenarios. These case studies offer a practical look at how CIN presents, progresses, and is managed, providing a deeper insight into the disease.These illustrative cases, while fictionalized to protect patient privacy, are based on common clinical observations and highlight the spectrum of CIN presentations. They demonstrate the importance of early detection, appropriate diagnosis, and tailored treatment plans.
Case Study 1: CIN 1
This case involves a 25-year-old woman who presented with abnormal Pap smear results. Colposcopy revealed mild dysplasia in a few areas, consistent with CIN 1. The patient had no significant risk factors for CIN. The colposcopic findings showed a few areas of mild abnormal squamous epithelium, but the majority of the tissue appeared normal. No other symptoms were reported.
Given the low-grade nature of the abnormality, the patient was managed with close follow-up and repeat Pap smears every six months for two years. The patient’s repeat Pap smears returned to normal, indicating the lesions resolved spontaneously.
Case Study 2: CIN 2
A 32-year-old woman, with a history of smoking and multiple sexual partners, presented with abnormal Pap smear results. Colposcopy revealed moderate dysplasia in a significant portion of the transformation zone, consistent with CIN 2. The patient underwent a loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) to remove the abnormal tissue. Histological analysis confirmed CIN 2. The patient’s treatment was successful, and she was followed up with regular Pap smears to monitor for recurrence.
This case highlights the importance of addressing CIN 2 early to prevent progression to more advanced stages.
Case Study 3: CIN 3
A 45-year-old woman, with a history of HPV infection and a long period of untreated CIN 1, presented with severe dysplasia in the transformation zone, indicating CIN 3. Colposcopy revealed marked abnormal squamous epithelium. She underwent a cone biopsy to remove a larger portion of the abnormal tissue for a more thorough evaluation. The biopsy confirmed CIN 3 and showed evidence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL).
Management involved a more aggressive approach, with a hysterectomy to remove the affected tissue. This case underscores the critical role of timely intervention and management in CIN 3 to prevent potential progression to invasive cervical cancer.
Case Study 4: CIN Progression
A 28-year-old woman initially diagnosed with CIN 1 was monitored closely with regular Pap smears. Over a three-year period, her Pap smears showed a progression to CIN 2, and subsequently, CIN 3. The case highlights the importance of diligent follow-up for patients with CIN 1, as the disease can progress over time. The progression was managed through various procedures as Artikeld in the previous cases, including colposcopy, LEEP, and ultimately, a hysterectomy.
This scenario emphasizes the need for regular screening and appropriate interventions to prevent potential cervical cancer development.
Summary Table of Illustrative Cases
| Case Study | CIN Grade | Risk Factors | Diagnosis | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIN 1 | CIN 1 | None Significant | Abnormal Pap smear, colposcopy | Close follow-up, repeat Pap smears | Resolved spontaneously |
| CIN 2 | CIN 2 | Smoking, multiple sexual partners | Abnormal Pap smear, colposcopy | LEEP | Successful treatment, follow-up |
| CIN 3 | CIN 3 | HPV infection, untreated CIN 1 | Abnormal Pap smear, colposcopy, cone biopsy | Hysterectomy | Successful treatment, prevention of cancer |
| CIN Progression | CIN 1 to CIN 3 | None initially, then unknown | Regular Pap smears, colposcopy, biopsy | Progressive management, LEEP, cone biopsy, hysterectomy | Progression halted, prevented cancer |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) requires a multifaceted approach involving early detection, understanding the different grades, and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention, and potential complications, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. Regular screenings and open communication with healthcare providers are vital for managing and preventing the progression of CIN.