Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues offer a range of potential solutions, from dietary changes to herbal remedies. Understanding how these approaches work and their potential benefits, along with potential risks, is key to making informed choices. This exploration delves into various natural strategies for gallbladder support, emphasizing the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen.
Gallbladder function and common issues will be Artikeld, along with the general principles behind using natural remedies. A brief history of natural approaches to gallbladder problems will be shared, emphasizing the importance of professional consultation before starting any new treatment. A table comparing conventional and natural approaches will also be presented.
Introduction to Natural Remedies and Supplements for Gallbladder Issues
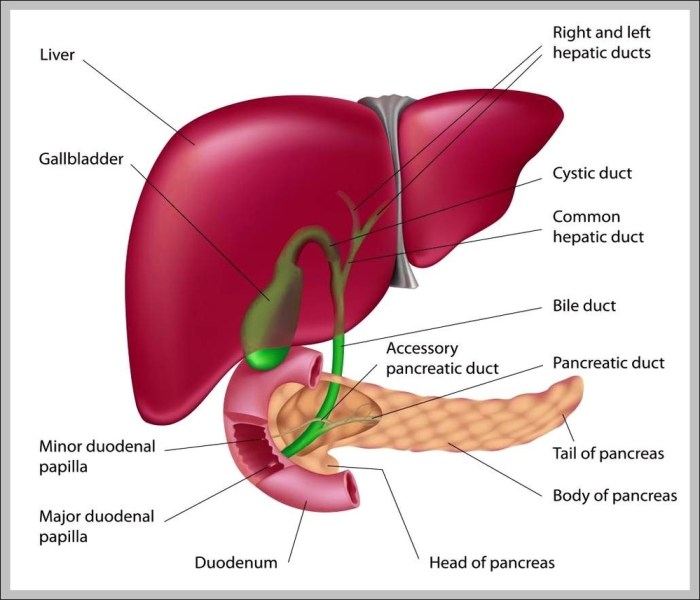
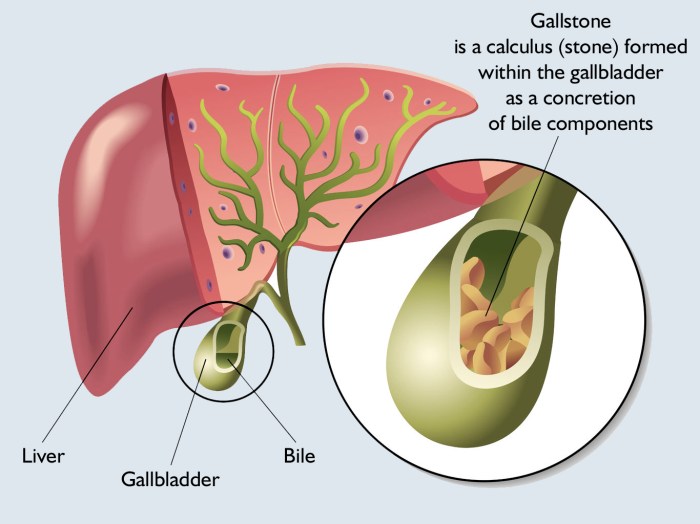
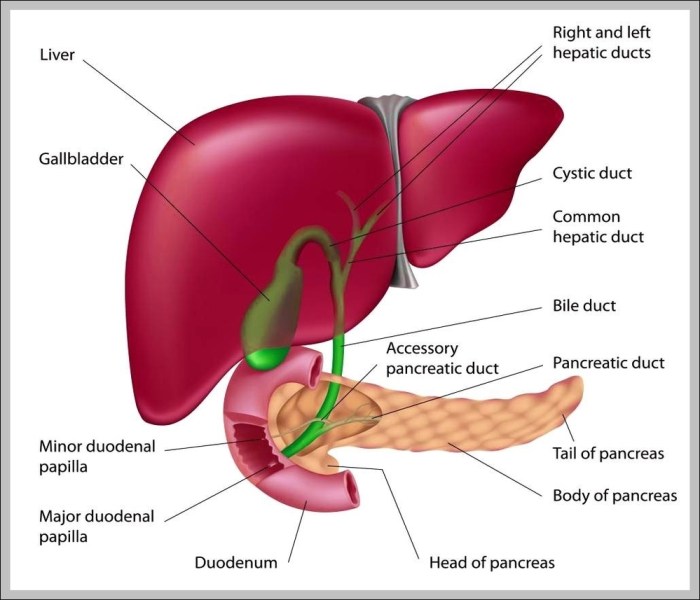
The gallbladder, a small pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver, plays a crucial role in the digestive process. It stores bile produced by the liver, a fluid essential for breaking down fats in the small intestine. Gallbladder problems, ranging from minor discomfort to serious conditions like gallstones, affect a significant portion of the population. Understanding the function of the gallbladder and its associated issues is vital for exploring natural approaches to maintaining its health.Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues often focus on supporting liver function, promoting bile flow, and potentially dissolving or preventing gallstones.
These approaches often incorporate dietary changes, herbal extracts, and lifestyle modifications, all aiming to address the root causes of gallbladder problems. A historical understanding of these methods can provide valuable context for evaluating their effectiveness and safety.
Gallbladder Function and Common Issues
The gallbladder concentrates bile, which is crucial for fat digestion. Blockages, inflammation (cholecystitis), and the formation of gallstones (cholelithiasis) are common issues. Gallstones can cause severe pain, inflammation, and potentially lead to complications if left untreated. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. The severity and frequency of symptoms vary depending on the individual and the specific condition.
General Principles Behind Natural Remedies
Natural approaches to gallbladder health often involve supporting liver function, promoting bile flow, and potentially dissolving or preventing gallstones. These methods often incorporate dietary changes, herbal extracts, and lifestyle modifications. A balanced diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and refined sugars is often recommended. Certain herbs, like milk thistle and dandelion, are believed to support liver health and bile production.
Regular exercise and stress management are also important components of a holistic approach.
Historical Approaches to Gallbladder Problems
Historically, various cultures have employed natural remedies to address digestive issues, including gallbladder problems. Traditional Chinese medicine, for example, often incorporated herbs and dietary practices to promote liver and gallbladder health. Ancient Greek and Roman physicians also recognized the importance of diet and lifestyle in managing digestive ailments. However, the scientific understanding of the gallbladder and its associated issues has advanced considerably over time.
It’s crucial to remember that historical practices should be evaluated within the context of modern medical knowledge.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before embarking on any new treatment, including natural remedies and supplements, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. Natural remedies may not be suitable for everyone, and interactions with medications or underlying health conditions can occur. Proper diagnosis and monitoring by a qualified healthcare professional are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficacy of any treatment plan.
Comparison of Conventional and Natural Approaches
| Feature | Conventional Approach | Natural Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Diagnostic imaging (ultrasound, CT scan) and blood tests | Assessment of symptoms and lifestyle factors |
| Treatment | Surgical intervention (cholecystectomy) for severe cases; medication for pain and symptom management | Dietary changes, herbal remedies, lifestyle modifications |
| Safety | Generally considered safe when performed by qualified professionals | Safety may vary depending on the specific remedy and individual factors; potential interactions with medications |
| Speed of Action | Rapid, especially for surgical interventions | Gradual, potentially requiring longer periods to show effects |
| Long-Term Management | May involve ongoing monitoring and follow-up | Emphasis on lifestyle changes for long-term support |
Common Natural Remedies
Many individuals explore natural remedies alongside conventional treatments for gallbladder issues. These remedies often focus on supporting liver function and promoting healthy digestion, which can indirectly alleviate some gallbladder symptoms. It’s crucial to remember that these remedies are not a substitute for professional medical advice and should be used in conjunction with your doctor’s recommendations.
Natural Remedies for Gallbladder Support
Natural remedies, while promising, may not always offer the same level of effectiveness or safety as prescribed medications. Individual responses to these remedies can vary significantly, and their purported mechanisms of action often need further scientific investigation. Always consult with your doctor before incorporating any new remedies into your treatment plan.
Milk Thistle
Milk thistle is a popular herbal remedy often used for its potential liver-protective properties. It’s believed to support liver function, which can be beneficial for gallbladder health. Studies suggest that milk thistle may help improve liver function and reduce inflammation. However, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to confirm its effectiveness for gallbladder-related issues.
Dandelion Root
Dandelion root is another herb often used for its potential liver support and diuretic properties. It is thought to stimulate bile flow, which could help with gallbladder function. Some studies indicate dandelion root may improve liver function and aid in detoxification. However, further research is necessary to establish a clear link between dandelion root consumption and gallbladder health.
Turmeric
Turmeric, known for its vibrant yellow color and potent anti-inflammatory properties, is often included in many cultures’ diets. Its active compound, curcumin, is believed to support liver health and reduce inflammation. Some research indicates that curcumin may improve liver function and reduce oxidative stress, which could indirectly support gallbladder health. Further studies are required to explore the specific effects on gallbladder issues.
Ginger
Ginger is a well-known spice with potential anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits. It is thought to aid in digestion and may reduce nausea and bloating. Research indicates ginger can help with nausea, a common symptom associated with gallbladder problems. The mechanisms by which ginger aids digestion and supports gallbladder health remain an area of further investigation.
Boldo Leaf
Boldo leaf is a South American herb traditionally used to support liver function and bile flow. It is believed to promote bile production and flow, potentially easing gallbladder symptoms. Limited scientific evidence supports its use for gallbladder-related issues. However, more research is needed to validate these claims.
Potential Benefits, Risks, and Sources of Natural Remedies for Gallbladder Support
| Remedy | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk Thistle | Potential liver support, reduction of inflammation | Possible allergic reactions, interactions with medications | Various scientific publications, herbal databases |
| Dandelion Root | Potential liver support, diuretic properties | Potential for gastrointestinal upset, interactions with medications | Various scientific publications, herbal databases |
| Turmeric | Potential anti-inflammatory effects, liver support | Possible digestive upset, interactions with certain medications | Various scientific publications, herbal databases |
| Ginger | Potential digestive support, reduction of nausea | Possible allergic reactions, interactions with anticoagulants | Various scientific publications, herbal databases |
| Boldo Leaf | Potential support for bile flow | Possible interactions with medications, not well-studied | Various scientific publications, herbal databases |
Dietary Recommendations for Gallbladder Health
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in supporting gallbladder function and preventing issues. Understanding which foods to include and avoid can significantly impact your overall gallbladder health. This section provides a comprehensive guide to dietary strategies for promoting a healthy gallbladder.Maintaining a balanced diet, rich in specific nutrients and low in others, can help prevent gallbladder inflammation and support its optimal function.
This includes focusing on foods that promote healthy digestion, reduce inflammation, and provide essential nutrients for the body’s overall well-being.
Foods to Include for Gallbladder Support
A diet rich in fiber, healthy fats, and certain vitamins and minerals can promote gallbladder health and function. These nutrients contribute to proper digestion and may help prevent gallstones. Include foods that are naturally low in saturated fat and high in soluble fiber, as these can contribute to overall gallbladder health.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They are low in calories and high in water content, which aids in digestion. Examples include berries, apples, leafy greens, and broccoli.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa are excellent sources of fiber. Fiber helps regulate digestion and may reduce the risk of gallstones by promoting healthy cholesterol levels.
- Healthy Fats: Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are crucial for gallbladder health. These healthy fats are found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. They can aid in digestion and reduce inflammation.
- Lean Protein Sources: Lean proteins, such as chicken breast, fish, and beans, provide essential amino acids for building and repairing tissues. They are generally low in saturated fat, supporting gallbladder function.
- Probiotics: Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kefir can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, which may positively impact gallbladder health by supporting digestion.
Foods to Reduce Gallbladder Strain
Certain foods can exacerbate gallbladder issues by increasing the risk of gallstone formation or increasing gallbladder contractions. Limiting these foods can lessen the strain on the gallbladder.
- High-Fat Foods: Foods high in saturated and trans fats can trigger gallbladder contractions and potentially lead to gallstone formation. Limit intake of fried foods, processed meats, and foods with high levels of unhealthy fats.
- Sugary Foods and Drinks: Excessive sugar intake can contribute to insulin resistance, which may impact gallbladder function. Limit intake of sugary sodas, candies, and desserts.
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption can negatively impact liver function, potentially leading to issues with gallbladder health. Limit alcohol intake or avoid it completely.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain high amounts of unhealthy fats and sugars, potentially increasing the risk of gallbladder problems. Minimize consumption of processed meats, packaged snacks, and fast foods.
Recommended Foods for Gallbladder Health
This table highlights foods that promote gallbladder health, emphasizing their impact.
| Food | Impact on Gallbladder Health |
|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables (berries, leafy greens) | Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, aiding digestion and reducing inflammation. |
| Whole Grains (oats, brown rice) | Excellent source of fiber, regulating digestion and potentially reducing gallstone risk. |
| Healthy Fats (avocado, nuts, seeds) | Essential for gallbladder function, aiding digestion and reducing inflammation. |
| Lean Protein (chicken breast, fish) | Provides essential amino acids without high saturated fat content, supporting gallbladder function. |
| Probiotic-rich foods (yogurt, kefir) | Maintains a healthy gut microbiome, potentially impacting gallbladder health positively. |
Herbal Supplements for Gallbladder Support
Many people explore natural remedies to support their gallbladder health. While herbal supplements can be part of a holistic approach, it’s crucial to remember that they are not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Consult with your doctor before incorporating any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications. Always prioritize evidence-based information and responsible use.Herbal supplements purportedly supporting gallbladder health work in various ways, often targeting inflammation, bile flow, and overall digestive function.
The underlying mechanisms of action are often complex and not fully understood. While some research suggests potential benefits, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to confirm these claims. Furthermore, individual responses to herbal supplements can vary significantly.
Exploring natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues is a fascinating area, but it’s important to remember that some seemingly healthy choices might have unexpected consequences. For instance, while researching alternative approaches to gallbladder health, it’s worth considering if the cooking methods you’re using might pose a health risk. Are air fryers truly safe? The potential health concerns surrounding certain cooking appliances, like can air fryers cause cancer , deserve careful consideration.
Ultimately, diligent research into natural remedies and supplements, combined with a balanced approach to nutrition and lifestyle, is key to managing gallbladder health effectively.
Specific Herbal Supplements
Several herbal supplements are traditionally used to support gallbladder health. Their purported benefits and potential risks should be carefully considered.
- Milk Thistle: Milk thistle is a popular herbal remedy for liver health. It’s believed to protect liver cells and improve bile flow. Possible benefits include supporting liver function, aiding bile production, and potentially reducing inflammation. Potential risks include allergic reactions in some individuals, and interactions with certain medications. Dosage typically ranges from 100 to 200mg, taken 1-3 times daily.
- Artichoke Leaf Extract: Artichoke leaf extract is often used for digestive support. It’s believed to stimulate bile flow and aid digestion. Possible benefits include improving bile secretion and promoting healthy digestion. Potential risks include allergic reactions, and interactions with certain medications. Dosage typically ranges from 100-250mg, taken 1-3 times daily, depending on the product and instructions.
- Dandelion Root: Dandelion root is known for its potential liver-supporting properties. It may help with bile flow and liver function. Possible benefits include supporting liver function, aiding in digestion, and possibly increasing bile production. Potential risks include allergic reactions, and interactions with certain medications. Dosage typically ranges from 250 to 500mg, taken 1-3 times daily.
Herbal Combinations
Some practitioners suggest combining specific herbs for enhanced gallbladder support. Examples include milk thistle paired with artichoke leaf extract, or dandelion root with turmeric, a spice known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
| Herbal Supplement | Potential Benefits | Potential Risks | Dosage Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk Thistle | Support liver function, aid bile production, potentially reduce inflammation. | Allergic reactions, interactions with certain medications. | 100-200mg, 1-3 times daily. |
| Artichoke Leaf Extract | Improve bile secretion, promote healthy digestion. | Allergic reactions, interactions with certain medications. | 100-250mg, 1-3 times daily. |
| Dandelion Root | Support liver function, aid digestion, potentially increase bile production. | Allergic reactions, interactions with certain medications. | 250-500mg, 1-3 times daily. |
Important Note: This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with your doctor before using any herbal supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Gallbladder Health

Beyond dietary choices and herbal supplements, lifestyle plays a crucial role in gallbladder health. Stress, exercise, and sleep quality all impact the function of this vital organ. Understanding these connections can empower individuals to make proactive choices for gallbladder well-being.Maintaining a healthy gallbladder involves more than just diet. Stress levels, exercise routines, and sleep patterns all contribute to the overall health of this organ.
Implementing positive lifestyle changes can significantly improve gallbladder function and reduce the risk of issues.
Stress and Gallbladder Issues
Chronic stress can negatively impact the entire digestive system, including the gallbladder. Elevated cortisol levels, a common response to stress, can lead to gallbladder spasms and potential inflammation. These spasms may manifest as pain or discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. Individuals experiencing persistent stress might find that managing their stress levels is an important step towards mitigating gallbladder issues.
Exploring natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues can be a fascinating journey. While many focus on dietary changes and herbal teas, it’s important to consider how certain practices, like extended fasting, can sometimes trigger headaches. For instance, understanding how fasting can cause a headache is crucial for managing potential side effects how fasting can cause a headache , and this knowledge can be helpful in determining the best natural approach to gallbladder health.
Ultimately, a holistic approach combining natural remedies and supplements, mindful fasting practices, and a balanced diet is key for managing gallbladder issues effectively.
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and yoga, can help to regulate cortisol levels and support gallbladder health.
Exercise and Gallbladder Health
Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall health, and this extends to gallbladder function. Exercise promotes healthy digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for gallbladder health, as excess weight can contribute to the formation of gallstones. Physical activity also improves blood flow and supports the efficient functioning of the digestive system, including the gallbladder.
Sleep Quality and Gallbladder Function
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health, and its impact extends to gallbladder function. Insufficient sleep can disrupt the body’s natural processes, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances that affect digestion. Poor sleep may also contribute to an increased risk of developing gallstones. Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal gallbladder function and overall health.
Stress Management Strategies
Various strategies can help manage stress and support gallbladder health. Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help calm the nervous system. Yoga and tai chi incorporate physical postures and controlled breathing, fostering relaxation and reducing stress. Time spent in nature, engaging in hobbies, and spending time with loved ones can also help to reduce stress levels.
These activities promote a sense of calm and well-being, which can positively impact gallbladder function.
Lifestyle Factors and Gallbladder Health
A healthy lifestyle encompassing these factors contributes to gallbladder well-being.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can lead to gallbladder spasms and inflammation. Effective stress management techniques can help alleviate these issues.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes healthy digestion and maintains a healthy weight, reducing the risk of gallstones and supporting gallbladder function.
- Quality Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and gallbladder function. Insufficient sleep can disrupt natural processes and potentially increase the risk of gallstones.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and processed foods can support gallbladder health. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables is also beneficial.
- Hydration: Staying properly hydrated is essential for overall health and the proper functioning of the digestive system, including the gallbladder.
Potential Risks and Precautions

While natural remedies can be beneficial for gallbladder issues, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and precautions involved. Many natural approaches lack rigorous scientific backing, and individual responses to these remedies can vary. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.Using natural remedies for gallbladder issues, while potentially helpful, doesn’t eliminate the need for professional medical guidance.
A healthcare provider can assess your specific situation, determine the appropriate course of action, and monitor your progress. Self-treating with natural remedies without professional oversight can lead to delays in receiving necessary medical care, potentially exacerbating existing conditions.
Potential Risks Associated with Natural Remedies
Natural remedies, despite their perceived safety, can pose potential risks. Some remedies may interact with prescription medications, leading to adverse effects. Additionally, individual sensitivities or allergies to specific ingredients in natural remedies can trigger allergic reactions or other health issues. The lack of rigorous testing and regulation for many natural products can also contribute to inconsistent quality and potential contamination.
It’s vital to source products from reputable suppliers.
Exploring natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues can be a rewarding journey. While focusing on these remedies, it’s important to consider how diet plays a role in overall health. For instance, certain foods can significantly impact weight gain, and incorporating foods to help gain weight into your daily routine could be beneficial alongside natural remedies.
Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines natural remedies and a balanced diet is often the most effective strategy for managing gallbladder issues.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Certain natural remedies can interact with medications, either enhancing or diminishing their effects. For example, some herbal supplements can interfere with blood-thinning medications, increasing the risk of bleeding. Others may alter the absorption of certain drugs, impacting their effectiveness. Thorough research and consultation with a doctor or pharmacist are crucial to avoid adverse interactions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Even when using natural remedies, prompt medical attention is essential for certain symptoms. Persistent or worsening gallbladder pain, fever, chills, jaundice, or nausea should always prompt a visit to a healthcare professional. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring immediate medical intervention. Delaying medical care in such cases could have detrimental consequences.
Comparison of Risks and Benefits of Various Natural Approaches
Different natural remedies offer varying levels of support for gallbladder health. For instance, dandelion root tea may help with bile flow, but it could also cause digestive upset in some individuals. Similarly, milk thistle, often touted for liver support, might not be suitable for everyone. Understanding the potential benefits and risks associated with each natural remedy is crucial for making informed decisions.
This involves careful consideration of individual health conditions and potential interactions.
Summary Table of Potential Risks and Precautions
| Natural Remedy | Potential Risks | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Dandelion Root Tea | Digestive upset, potential interactions with medications | Consult a doctor before use, especially if taking blood thinners or other medications. |
| Milk Thistle | Potential interactions with medications, liver issues in susceptible individuals | Consult a doctor before use, especially if taking other medications or have pre-existing liver conditions. |
| Turmeric | Potential interactions with blood thinners, stomach upset in some individuals | Consult a doctor before use, especially if taking blood thinners or other medications. |
| Chamomile | Potential allergic reactions, interactions with certain medications | Perform a patch test before using chamomile, consult a doctor if you have known allergies or are taking other medications. |
Illustrative Examples of Gallbladder Health Improvement Stories
Embarking on a journey to better gallbladder health often involves a blend of lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, and potentially natural remedies. Seeing firsthand how others have navigated these changes and experienced positive outcomes can be incredibly motivating. These stories, while individual, offer valuable insights into the potential benefits of a holistic approach to gallbladder health.These success stories highlight the importance of individual responses to natural remedies.
What works for one person may not work for another, and consistent monitoring and adaptation are crucial. The journey toward optimal gallbladder health is often a personalized one, demanding patience and understanding.
Personal Accounts of Success
Many individuals have reported positive changes in their gallbladder health through a combination of dietary modifications and natural remedies. These changes can be subtle or dramatic, depending on the individual’s starting point and commitment to the process. Consistent, sustained efforts often yield the most significant results.
“I was experiencing severe gallbladder pain for years. After incorporating a low-fat diet, increasing my intake of fiber-rich foods, and starting a daily herbal tea regimen, I noticed a significant reduction in my symptoms. I’m now able to enjoy meals without the debilitating pain, and I feel much more energetic.”
Sarah M.
Factors Influencing Individual Responses
Individual responses to natural remedies vary significantly. Several factors play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of these approaches. These include the severity of the gallbladder issue, the individual’s overall health, adherence to the treatment plan, and potential interactions with other medications. Consistency and patience are key components in achieving positive outcomes.
Table of Successful Experiences, Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues
| Individual | Initial Symptoms | Natural Remedies Implemented | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarah M. | Severe gallbladder pain, digestive discomfort | Low-fat diet, fiber-rich foods, daily herbal tea | Significant reduction in symptoms, improved energy levels |
| David L. | Occasional bloating, indigestion | Increased water intake, mindful eating, ginger tea | Improved digestion, reduced bloating frequency |
| Emily R. | Frequent episodes of nausea after meals | Dietary changes emphasizing whole foods, lemon water, and dandelion root tea | Reduced nausea frequency, improved overall digestive health |
| John S. | Severe pain after consuming fatty foods | Low-fat diet, regular exercise, and dandelion root tea | Reduced pain intensity and frequency, improved overall health |
Last Word: Natural Remedies And Supplements For Gallbladder Issues
This exploration of natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues highlights a diverse range of potential approaches. While these remedies may offer potential benefits, it’s crucial to remember that individual responses vary. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for determining the most appropriate course of action, especially when considering natural remedies alongside conventional treatments. A balanced approach incorporating lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and potentially herbal supplements, when used with proper medical guidance, can potentially support gallbladder health.