Early stage toenail fungus is a common condition that often goes unnoticed in its initial stages. This guide dives into the specifics, from recognizing the early symptoms and causes to understanding preventative measures, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, including home remedies. We’ll explore everything from visual comparisons of healthy and infected nails to detailed tables outlining different infection stages.
Knowing the early signs of toenail fungus is crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed understanding of the condition, empowering you with the knowledge to address it promptly and effectively.
Introduction to Early Stage Toenail Fungus
Early-stage toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection affecting the toenails. It typically begins subtly and progresses over time if left untreated. Understanding the early signs and causes can help in early detection and prompt treatment, potentially preventing more severe complications. Recognizing the differences between healthy nails and those showing early signs of infection is crucial for prompt action.Early-stage toenail fungus often presents with subtle changes that can be easily overlooked.
Dealing with early stage toenail fungus can be a real drag, but it’s not the only health concern that can pop up. Sometimes, issues like fatty liver disease can be a factor, and understanding its connection to overall health is crucial. For a detailed look at overview of fatty liver disease , remember that even seemingly unrelated health problems can intertwine, so keeping a watchful eye on your body’s signals is key.
This all highlights the importance of addressing early stage toenail fungus effectively and promptly.
These early signs can be mistaken for other conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. This makes understanding the initial symptoms and the progression of the infection critical for effective management.
Early Symptoms of Toenail Fungus
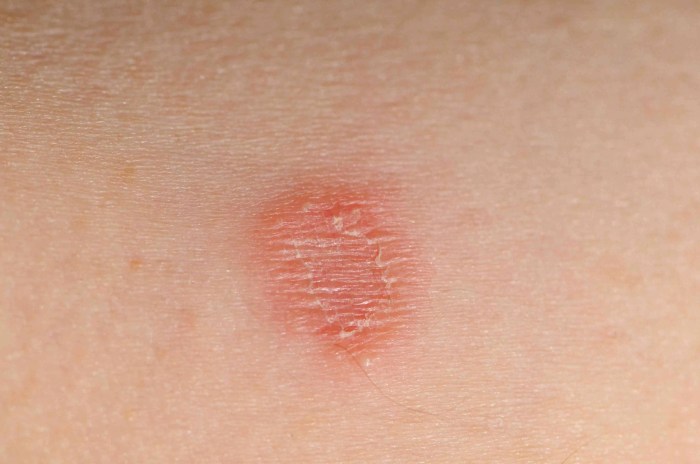
The initial symptoms of toenail fungus are often subtle and can easily be missed. Common early symptoms include discoloration, changes in texture, and mild thickening of the nail plate. These early symptoms may be mistaken for other nail conditions, or simply ignored. It’s important to be aware of these subtle changes to seek medical attention promptly.
Causes of Early Toenail Fungus
Several factors can contribute to the development of early-stage toenail fungus. These include exposure to fungi in damp, humid environments, such as public pools, locker rooms, or poorly ventilated showers. Sharing personal items, such as nail clippers or towels, with others who have the infection can also increase the risk. Underlying health conditions that weaken the immune system may also play a role.
It is crucial to maintain good hygiene to prevent fungal infections.
Healthy vs. Infected Toenail Appearance
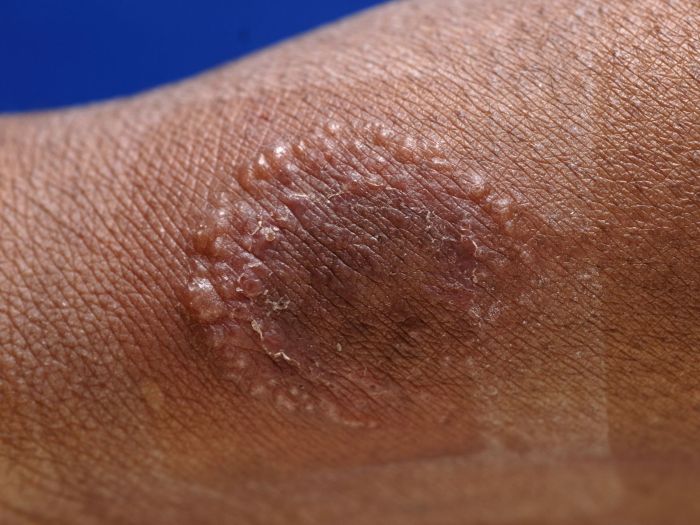
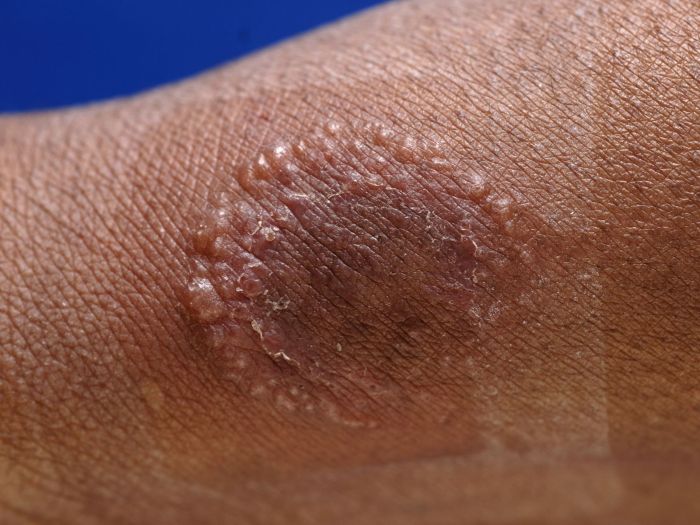
Healthy toenails typically exhibit a smooth, consistent surface and a natural, translucent or pinkish-white appearance. The nail plate is firm and well-formed. In contrast, early-stage toenail fungus can manifest with visible changes in the nail’s appearance. These include discoloration, ranging from yellowish-brown to dark brown or even black, along with a rough or uneven surface. The infected nail plate may become brittle or thick, and may separate from the nail bed.
The infection may start in one or two toenails.
Comparison of Mild, Moderate, and Severe Toenail Fungus
| Stage | Symptoms | Nail Appearance | Potential Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild | Slight discoloration (e.g., yellowish or brownish spots), slight thickening, or minor changes in the nail’s surface texture. May be asymptomatic. | Discoloration in a small area, mild thickening, and slight changes in the nail surface. The infected nail may not show significant separation from the nail bed. | Discomfort or pain may be minimal or absent. The infection may spread to other toenails or fingernails if not treated. |
| Moderate | Increased discoloration (e.g., significant discoloration spreading across the nail), substantial thickening, and crumbling or splitting of the nail. Some discomfort may be present. | Significant discoloration covering a larger portion of the nail, noticeable thickening, and more significant separation from the nail bed. The nail may show crumbling or splitting. | Increased discomfort or pain, potential spreading to other toenails or fingernails, and potential complications with mobility or hygiene if left untreated. |
| Severe | Extensive discoloration (e.g., complete discoloration of the nail plate), significant thickening and distortion of the nail, severe pain and discomfort, and possible separation from the nail bed. The nail may become extremely brittle and deformed. | Complete discoloration, significant thickening and distortion of the nail plate, complete separation from the nail bed, and potential complete destruction of the nail plate. | Severe pain and discomfort, difficulty with mobility and hygiene, increased risk of spreading to other parts of the body, and potential long-term effects on the nail’s structure and appearance. |
Risk Factors and Prevention

Toenail fungus, while often appearing in early stages as subtle discoloration, can quickly progress if left untreated. Understanding the risk factors and implementing preventative measures are crucial in halting the spread and maintaining healthy toenails. This section will explore potential causes, Artikel effective preventive strategies, and detail essential foot hygiene practices.Proper foot hygiene and awareness of potential risk factors are key to preventing toenail fungus.
By understanding what increases your likelihood of infection and implementing preventative steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this common condition.
Potential Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of contracting toenail fungus. These include compromised immune systems, which may not effectively fight off infections. Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, which can affect circulation and wound healing, are also contributing factors. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems or compromised circulation are more susceptible to infection.
Preventative Measures
Implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of toenail fungus. Maintaining good foot hygiene is paramount. This includes regular washing and drying of feet, particularly between the toes. Wearing appropriate footwear is also critical, ensuring that shoes provide adequate ventilation and are made of breathable materials.
Practical Tips for Healthy Toenails
Maintaining healthy toenails is crucial in preventing fungus. Regularly trimming toenails straight across and avoiding excessively tight or poorly fitting shoes are vital. Inspecting your toenails regularly for any signs of discoloration or changes in texture is important. Additionally, consider using antifungal foot powders or sprays to create a protective barrier. Avoid sharing personal items like towels and shoes, as this can spread fungal infections.
Proper Foot Hygiene Practices
Thorough foot hygiene is a cornerstone of preventing toenail fungus. Washing your feet daily with warm, soapy water is essential. Pay particular attention to cleaning between the toes, a common area for fungal growth. After washing, dry your feet thoroughly, especially between the toes, to eliminate moisture, a breeding ground for fungi.
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wearing breathable footwear | Choosing shoes made of breathable materials like leather or mesh allows for proper air circulation, reducing moisture buildup. | High | May require a larger investment in shoes. |
| Regular nail trimming | Trimming toenails straight across, avoiding ingrown nails, and maintaining a short length. | Moderate | Potential for ingrown nails if not done correctly. |
| Avoiding walking barefoot in public areas | Public spaces often have high concentrations of fungal spores. Protecting your feet minimizes exposure. | High | May require extra effort when outdoors. |
| Using antifungal powders | Applying antifungal powders between toes and on feet can help prevent fungal growth. | Moderate | May cause mild skin irritation in some individuals. |
Diagnosis and Assessment

Early detection of toenail fungus is crucial for effective treatment and preventing its spread. Proper diagnosis ensures the right course of action, avoiding unnecessary or ineffective therapies. A misdiagnosis can delay treatment, potentially leading to more severe fungal infections and complications. This section will delve into the methods used to diagnose early-stage toenail fungus, emphasizing the role of healthcare professionals in accurate assessment.
Methods for Diagnosing Early-Stage Toenail Fungus
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment of early-stage toenail fungus. Various methods help determine the presence and extent of the infection. Visual inspection and physical examination play a significant role in identifying the early signs.
Dealing with early stage toenail fungus can be a real drag, but it’s totally manageable. One thing that often gets overlooked is how to increase stamina, which can be surprisingly helpful. If you’re finding yourself constantly tired, and that’s affecting your ability to keep up with your daily routine, check out this guide on how to increase stamina.
Building your stamina can indirectly help with the early stages of toenail fungus by improving your overall well-being and enabling you to take better care of your feet. Keeping your feet clean and dry is crucial in preventing and treating early stage toenail fungus.
Importance of Proper Diagnosis
A precise diagnosis is critical in managing early-stage toenail fungus. It ensures the appropriate treatment is initiated, minimizing the risk of the infection worsening and spreading to other nails or skin areas. Misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, delaying the healing process and potentially increasing the risk of complications. Early intervention with the correct treatment plan greatly increases the likelihood of successful resolution.
Role of a Healthcare Professional in Diagnosis
A healthcare professional, typically a dermatologist or podiatrist, plays a vital role in diagnosing toenail fungus. Their expertise allows for a comprehensive evaluation, including visual inspection, physical examination, and potentially, additional diagnostic tests. They can differentiate between toenail fungus and other conditions that might mimic its symptoms. Their knowledge and experience are crucial in ensuring an accurate diagnosis and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Common Diagnostic Tests for Toenail Fungus
Careful evaluation and consideration of various diagnostic tests are essential to properly assess and treat toenail fungus.
| Test Type | Procedure | Accuracy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | The healthcare professional visually examines the affected toenail, looking for characteristic signs such as discoloration, thickening, crumbling, or separation from the nail bed. | Generally good for initial screening, especially for obvious cases. | May not be sufficient to definitively diagnose early-stage infections; requires additional testing for confirmation. |
| Microscopic Examination | A small sample of the affected toenail is scraped and examined under a microscope. This allows for the identification of fungal hyphae, which are characteristic of fungal infections. | Highly accurate for confirming the presence of fungi. | Requires a skilled technician and may not detect all types of fungi. The sample may not be representative of the entire nail surface. |
| Culture | A sample of the affected toenail is placed in a growth medium to allow fungi to grow. The type of fungus can then be identified. | Highly accurate for identifying the specific fungal species causing the infection. | Can take several weeks to produce results; not always readily available. |
| Wood’s Lamp Examination | The affected toenail is examined under a Wood’s lamp, which emits ultraviolet light. Certain types of fungi fluoresce under this light, making them visible. | Helpful for detecting some types of fungal infections. | Not suitable for all types of fungal infections; may not detect early-stage infections; not always conclusive. |
Examining a Toenail for Early Signs of Fungus
Regular self-examination can help identify early signs of toenail fungus. Pay close attention to any changes in the appearance of your toenails, such as discoloration (yellowing, browning, or darkening), thickening, crumbling, or separation from the nail bed. If you notice any of these signs, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection is key to successful management of toenail fungus.
Treatment Options
Dealing with toenail fungus can be frustrating, but early intervention significantly improves treatment success. Effective treatment often involves a multifaceted approach tailored to the individual’s specific situation and the severity of the infection. Different treatment options have varying degrees of effectiveness, especially in the early stages.Early-stage toenail fungus is often treatable with topical antifungal medications. Systemic treatments, like oral medications, might be necessary for more advanced cases, but topical options are a primary line of defense for mild infections.
Choosing the right treatment depends on factors such as the extent of the infection, individual health conditions, and personal preferences.
Over-the-Counter Treatments
Over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal creams and lacquers are frequently the first line of defense for early-stage toenail fungus. These products contain antifungal agents that work to inhibit the growth of the fungus. While effective for mild infections, OTC treatments often require consistent and prolonged use for significant improvement.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Type | Description | Effectiveness (early stage) | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Antifungal Creams/Lacquer | Applied directly to the affected toenail. Creams penetrate the nail plate, while lacquers provide a protective layer. | Generally effective for early-stage infections if used diligently. Results may take several weeks or months. | Possible skin irritation, allergic reactions, or discomfort at the application site. May not be effective in all cases. |
| Oral Antifungal Medications | Taken orally, these medications target the fungus throughout the body. | Highly effective but typically reserved for more severe or widespread infections. | Potential for side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or liver problems. Requires close monitoring by a physician. |
| Laser Therapy | Uses focused light energy to target and destroy the fungus. | Effectiveness in early stages is still being researched, but it has shown promise in treating some cases. | Potential for mild discomfort or skin reactions. Usually more expensive than other treatments. |
Proper Application of Topical Antifungal Medications, Early stage toenail fungus
Proper application is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of topical antifungal treatments. Cleanliness is key. First, thoroughly clean the affected toenail and surrounding skin with soap and water. Then, carefully dry the area. Apply the medication to the affected toenail, ensuring complete coverage, following the product instructions.
Use a cotton swab or applicator to spread the medication evenly. It is essential to repeat the application daily or as directed by the product instructions for optimal results. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the treatment plan might be needed depending on the progress of the infection.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Dealing with toenail fungus can be frustrating, and the urge to find quick, home-based solutions is understandable. While some remedies might offer temporary relief or minor improvements, it’s crucial to understand their limitations. Many home remedies haven’t been rigorously studied and aren’t guaranteed to eliminate the fungus completely. Always consult a dermatologist or podiatrist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, especially for persistent or worsening symptoms.While some home remedies might seem promising, it’s important to remember that they are often not scientifically proven to effectively treat toenail fungus.
Their use should be approached with caution and should not replace professional medical advice. A holistic approach that combines home remedies with professional guidance can be more effective.
Potential Home Remedies
Many people turn to natural remedies to address early-stage toenail fungus. However, the effectiveness of these remedies varies widely, and they should be considered as complementary, not as a primary treatment. It’s essential to approach these remedies with realistic expectations.
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil is often touted for its antiseptic properties. It may help reduce inflammation and inhibit the growth of some fungi. However, it can also cause irritation and skin reactions in some individuals. Application should be done carefully, diluted with a carrier oil like coconut oil, and monitored for any adverse effects.
- Vinegar (Apple Cider or White): Vinegar, particularly apple cider vinegar, is another popular home remedy. Its acidic nature may help to create an environment less favorable for fungal growth. However, vinegar can be quite irritating to the skin and may not be suitable for everyone.
- Garlic: Garlic has been used traditionally for its antibacterial properties. It may help to combat fungal infections. However, the effectiveness of garlic as a topical treatment for toenail fungus is limited, and it may cause skin irritation.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has antimicrobial properties. Applying coconut oil topically might help to soothe the affected area. However, it may not directly eliminate the fungus itself.
Applying Essential Oils or Other Home Remedies
Proper application is crucial to maximize any potential benefits of home remedies and minimize discomfort. Always dilute essential oils with a carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil) before applying them to the affected toenail. This dilution prevents potential skin irritation.
- Clean the Affected Area: Clean the affected toenail and surrounding skin thoroughly with mild soap and water to remove dirt and debris. This helps create a clean surface for the application.
- Apply the Remedy: Apply a small amount of the diluted essential oil or home remedy directly to the affected toenail. Avoid applying it to healthy skin.
- Cover the Area: If desired, you can cover the affected toenail with a bandage or a breathable material to help the remedy stay in place and provide moisture.
- Monitor for Reactions: Pay close attention to any reactions, such as redness, irritation, or pain. If you experience any discomfort, stop using the remedy and consult a healthcare professional.
Managing Discomfort and Preventing Spread
It’s essential to take steps to manage discomfort associated with toenail fungus and to prevent its spread. Keeping the affected area clean and dry is critical.
- Keep Nails Dry: Avoid moisture buildup by ensuring the affected foot and nails are dry. Avoid wearing tight shoes that trap moisture.
- Proper Hygiene: Practice good foot hygiene by washing your feet regularly with mild soap and water, and ensuring they are completely dry after washing.
- Separate Shoes and Socks: Use separate shoes and socks for the affected foot to prevent the spread of fungus to other areas.
- Use Separate Tools: Use separate nail clippers, files, and other tools for the affected foot to avoid spreading the infection to other nails or areas.
Common Ingredients in Home Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- White Vinegar
- Garlic
- Coconut Oil
- Olive Oil
Long-Term Management and Prevention
Preventing toenail fungus recurrence requires a proactive and sustained approach. While treatment can effectively address the infection, preventing future outbreaks hinges on understanding the factors that contribute to its development and consistently implementing preventative measures. This phase of care is crucial for long-term well-being and avoiding the potential for the infection to return and potentially affect other nails.Long-term management isn’t just about stopping the current infection; it’s about fostering a healthy environment for your toenails to thrive and resist future fungal incursions.
This proactive approach includes regular monitoring, appropriate lifestyle adjustments, and diligent foot hygiene practices. Consistent attention to these details significantly reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Strategies for Preventing Toenail Fungus Recurrence
To effectively prevent recurrence, a multi-faceted approach is essential. This involves addressing both the immediate environment and the underlying factors that contribute to the infection.
Early stage toenail fungus can be tricky to spot, often starting with subtle discoloration. It can sometimes mimic other skin conditions, making diagnosis a bit of a puzzle. Similar to the way a Covid rash in adults might appear , early signs can be easily overlooked. Fortunately, early intervention for toenail fungus is key to preventing further spread and discomfort.
- Maintaining Good Foot Hygiene: Regular foot hygiene is paramount. This includes washing your feet daily with mild soap and warm water, paying special attention to the spaces between toes. Drying thoroughly, particularly between the toes, is crucial to prevent moisture buildup, a prime breeding ground for fungus. Use clean, dry towels and avoid sharing towels with others.
- Choosing Appropriate Footwear: Opt for well-ventilated shoes and socks made of breathable materials like cotton. Avoid tight-fitting or poorly ventilated shoes, as they can trap moisture and create an ideal environment for fungal growth. Change socks daily, and consider using antifungal foot powders or sprays.
- Regular Nail Trimming and Care: Keeping toenails trimmed short and straight helps to prevent ingrown nails and allows for better airflow around the nail. Use clean, sharp clippers and avoid sharing tools. Consider using a nail file to smooth any rough edges, which can reduce the risk of injury and subsequent infection.
- Monitoring for Recurrence: It’s essential to consistently monitor your toenails for any signs of infection, even after successful treatment. Look for changes in color, texture, or thickness. Prompt identification of recurrence allows for early intervention and treatment, potentially preventing the spread to other nails.
Importance of Long-Term Management
Ignoring long-term management strategies can lead to a higher risk of the infection returning. By understanding the contributing factors and implementing preventative measures, individuals can actively participate in maintaining healthy toenails and avoiding a recurring fungal infection. A proactive approach is more cost-effective and less stressful in the long run.
- Preventing Recurrence: Consistent preventative measures significantly reduce the likelihood of the infection returning. This includes maintaining proper foot hygiene, choosing appropriate footwear, and monitoring for any signs of reinfection.
- Minimizing Impact on Quality of Life: The discomfort and potential embarrassment associated with toenail fungus can negatively impact daily life. Long-term management helps to prevent recurrence, thus minimizing the potential impact on quality of life.
- Avoiding Secondary Infections: If left untreated, toenail fungus can sometimes spread to other parts of the body or cause secondary infections. Long-term management strategies, including appropriate foot hygiene, can help prevent these complications.
Lifestyle Changes for Healthy Toenails
Adopting specific lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to the long-term health of your toenails and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health, including nail health. Include foods rich in zinc, biotin, and vitamin B, as these nutrients are vital for healthy nail growth and structure.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of toenail fungus. Managing underlying conditions effectively is crucial in maintaining overall health and minimizing the risk of recurrence.
- Avoiding Overuse and Trauma: Overuse of your feet or trauma to the nails can create an opening for infection. Protecting your feet and minimizing stress on your toenails through appropriate footwear and supportive practices is key.
Significance of Maintaining Good Foot Hygiene
Good foot hygiene is a fundamental aspect of long-term toenail fungus prevention. It plays a crucial role in reducing moisture and preventing the ideal environment for fungal growth. Proper hygiene extends beyond just washing and drying; it includes consistent attention to the areas between toes and the use of clean, dry towels.
- Preventing Moisture Buildup: Moisture trapped between toes provides an ideal environment for fungal growth. Regular washing and drying thoroughly are essential to maintain dry, clean feet.
- Reducing Fungal Growth: By keeping feet clean and dry, individuals significantly reduce the likelihood of fungal growth, a key factor in preventing toenail fungus.
- Promoting Overall Foot Health: Consistent good foot hygiene practices contribute to the overall health and well-being of your feet, reducing the risk of various foot-related problems, including toenail fungus.
When to Seek Professional Help
Dealing with toenail fungus can be frustrating, but it’s important to know when to seek professional help. Ignoring early symptoms can lead to more serious complications, potentially requiring more extensive and complex treatment. This section Artikels the warning signs and situations where immediate medical intervention is crucial for effective management and preventing long-term damage.
Signs of Toenail Fungus Complications
Ignoring toenail fungus can sometimes lead to serious complications. These complications may require more aggressive treatment approaches and, in some cases, might lead to permanent damage to the nail. Understanding the symptoms associated with complications is crucial for timely intervention and minimizing potential damage.
Symptoms Requiring Medical Intervention
Certain symptoms indicate a need for professional evaluation and treatment. These symptoms may suggest the infection has progressed beyond the early stages or has developed complications. If you notice any of these, it’s important to schedule a consultation with a podiatrist or dermatologist.
| Symptom | Severity | Duration | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe pain or throbbing | Moderate to severe | More than a few days | Consult a doctor immediately. Severe pain may indicate an infection spreading to the surrounding tissues. |
| Increased redness and swelling around the affected toenail | Moderate to severe | More than a few days | Seek medical attention. Increased inflammation could signal a systemic infection or a more aggressive fungal growth. |
| Thickening and crumbling of the toenail | Moderate to severe | More than a few months | Schedule an appointment with a medical professional. This could indicate a more advanced stage of infection. |
| Pus or drainage from the affected area | Severe | Any duration | Seek immediate medical attention. Pus indicates a possible bacterial infection, which often requires antibiotics. |
| Difficulty walking or wearing shoes due to severe pain or discomfort | Severe | More than a few days | Urgent medical evaluation. Significant discomfort may indicate complications or the need for pain management. |
| Visible discoloration or discoloration spreading to other nails | Moderate to severe | More than a few weeks | Consult a medical professional. Spread to other nails indicates a potential systemic issue or an advanced stage of the infection. |
| Fever or chills | High | Any duration | Immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a systemic infection, potentially requiring systemic antifungal medication. |
Final Summary
In conclusion, early stage toenail fungus, while often treatable, requires proactive measures. By understanding the early symptoms, risk factors, and various treatment options, you can effectively manage this condition. Remember that proper foot hygiene, preventative measures, and timely consultation with a healthcare professional are essential in preventing further complications and achieving long-term management. This guide provides a solid foundation for navigating the challenges of early stage toenail fungus.