How to stop overeating is a crucial question for many, and this guide dives deep into the various factors contributing to this issue. From understanding the psychological and physiological triggers to developing healthy eating habits and implementing effective strategies for control, we’ll explore the entire spectrum of solutions. Get ready to uncover the secrets to breaking free from overeating and embarking on a journey toward a healthier relationship with food.
We’ll cover everything from identifying your unique eating patterns to crafting a personalized action plan that works for you. This isn’t just about weight loss; it’s about cultivating a mindful and sustainable approach to nourishment, empowering you to take control of your relationship with food and achieve lasting well-being.
Understanding Overeating Triggers

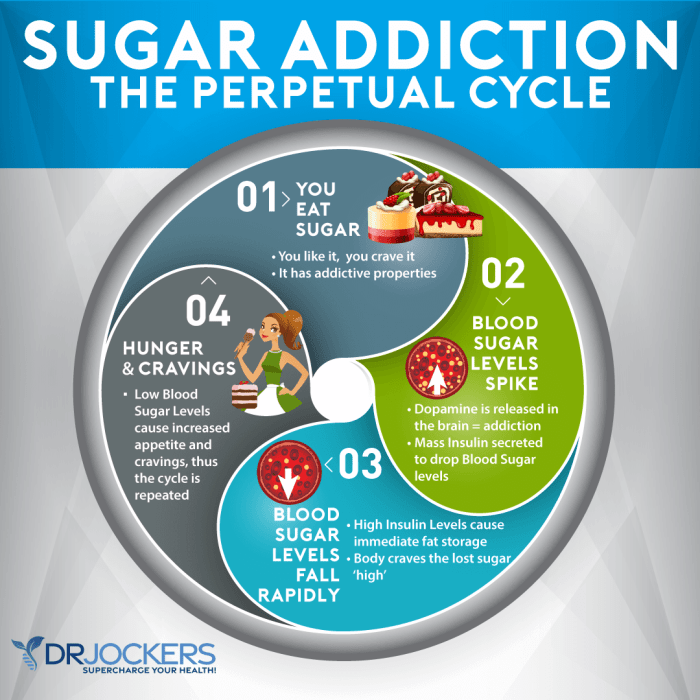
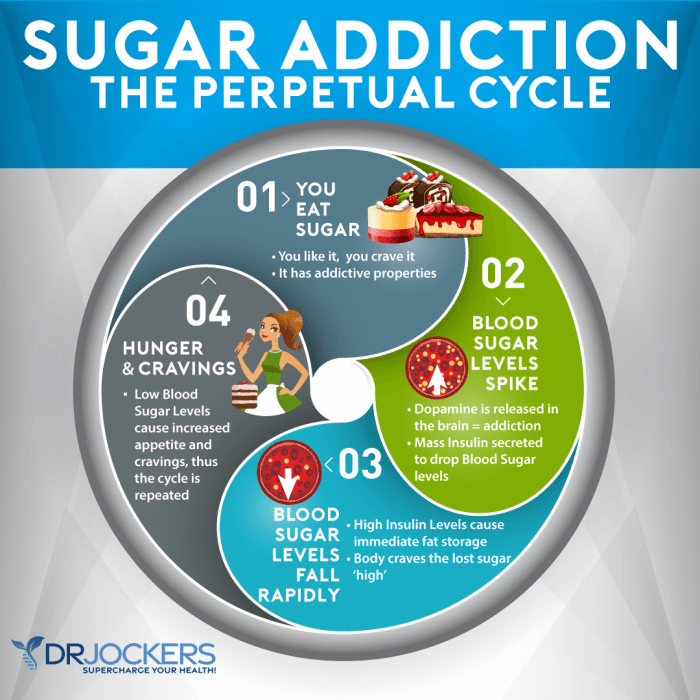
Overeating is a complex issue often stemming from a combination of psychological, physiological, and environmental factors. Recognizing these triggers is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and overcome overeating habits. This understanding provides a framework for identifying the root causes and tailoring interventions to individual needs.Understanding the various triggers behind overeating can help us develop personalized strategies for change.
We can better address the specific challenges individuals face by identifying the underlying reasons for their behaviors. This knowledge empowers us to create more effective and sustainable solutions.
Psychological Triggers
Psychological factors play a significant role in driving overeating. Stress, boredom, and emotional distress are common triggers that can lead to impulsive eating. Negative emotions often prompt individuals to seek comfort and distraction in food. Addressing these emotional triggers is key to breaking the cycle of overeating.
- Stress: Chronic stress activates the body’s stress response, which can lead to increased cortisol levels. Elevated cortisol levels can increase appetite and cravings for high-calorie foods. Individuals under stress might turn to food as a coping mechanism, leading to overeating. For example, a person facing a deadline at work might resort to eating comfort foods to alleviate stress.
- Boredom: Boredom can also trigger overeating. When people are bored, they might turn to food as a way to fill the void and pass the time. A lack of engaging activities or fulfilling hobbies can contribute to this pattern. For example, someone with limited social interactions might turn to excessive snacking as a way to fill the time.
- Emotional Distress: Emotional distress, including sadness, anxiety, and anger, can trigger overeating. Food can be used as a way to regulate emotions, creating a cycle of emotional eating. For example, a person experiencing grief might turn to food as a means of self-soothing.
Physiological Triggers
Hormonal imbalances and metabolic issues can significantly influence eating habits. These factors can impact appetite regulation, leading to increased hunger and cravings.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones like insulin, leptin, and ghrelin can affect appetite and metabolism. Imbalances can lead to increased hunger and difficulty in regulating food intake. For example, fluctuations in menstrual cycles can cause changes in appetite in women.
- Metabolic Issues: Conditions such as hypothyroidism or insulin resistance can affect metabolism and lead to increased cravings for food. These conditions may result in a higher tendency to overeat. For example, a person with undiagnosed hypothyroidism may experience a significant increase in hunger and overeating.
Social and Environmental Triggers
Social and environmental factors also play a crucial role in promoting overeating habits. Cultural norms, food marketing, and the availability of highly processed foods all contribute to the problem.
- Cultural Norms: Cultural norms surrounding food and eating can influence eating habits. Certain cultures may encourage or accept larger portions of food or certain types of food. For example, a culture that values large portions of food at social gatherings might contribute to overeating.
- Food Marketing: Aggressive food marketing, particularly for processed and high-calorie foods, can stimulate cravings and encourage overconsumption. For example, advertisements for unhealthy foods targeted at children often contribute to developing unhealthy eating habits.
- Availability of Highly Processed Foods: The widespread availability of highly processed and convenient foods makes it easier to overeat. These foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients, contributing to poor dietary choices. For example, easy access to fast food restaurants encourages overeating in many communities.
Summary Table
| Trigger type | Description | Examples | Potential coping mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Psychological | Stress, boredom, and emotional distress trigger impulsive eating | Stress eating, emotional eating, boredom snacking | Stress management techniques, mindfulness, emotional regulation |
| Physiological | Hormonal imbalances and metabolic issues affect appetite regulation | Hormonal fluctuations, metabolic disorders | Medical interventions, dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications |
| Social and Environmental | Cultural norms, food marketing, and food availability influence eating habits | Cultural food traditions, food advertising, readily available unhealthy foods | Cultural awareness, mindful consumption, healthier food choices |
Identifying Eating Patterns
Understanding your eating patterns is crucial for identifying the root causes of overeating. It’s not just about the
- what* you eat, but also the
- why* and
- how*. Different eating patterns manifest with distinct characteristics, and recognizing these patterns is the first step toward developing sustainable strategies for change. By understanding your individual eating patterns, you can tailor your approach to address the underlying issues driving your overeating behaviors.
Types of Eating Patterns
Various eating patterns contribute to overeating. Recognizing these patterns allows for targeted interventions.
- Emotional Eating: This pattern involves using food to cope with emotions like stress, sadness, anxiety, or boredom. Individuals may turn to food for comfort or distraction, leading to overconsumption when emotional triggers are present. This often results in feelings of guilt and shame afterward, perpetuating the cycle. For example, a person experiencing stress might find themselves reaching for high-calorie comfort foods, regardless of hunger, simply to alleviate the emotional distress.
This can lead to weight gain and other health complications.
- Binge Eating: Characterized by episodes of consuming large quantities of food in a short period, binge eating is often accompanied by feelings of loss of control. Individuals experiencing this pattern might eat rapidly, until uncomfortably full, and feel disgusted or ashamed afterward. Binge eating episodes can be triggered by various factors, including stress, emotional distress, or even boredom.
Figuring out how to stop overeating can be tricky, especially when you’re feeling sluggish. Sometimes, those cravings are linked to something else entirely, like a lingering illness. If you’re wondering if you have a cold or COVID, checking out this resource on do i have a cold or covid might help clarify the situation. Once you know the root cause, you can focus on the right strategies to manage your appetite and stop overeating.
Crucially, these episodes are not associated with other compensatory behaviors, like purging, seen in bulimia nervosa. A person experiencing binge eating may consume an entire pizza in one sitting, or several boxes of cookies, feeling completely out of control during the episode, and afterward experiencing significant guilt and regret.
- Compulsive Eating: Similar to binge eating, compulsive eating involves a loss of control over eating behaviors. However, compulsive eating is driven by an intense urge to eat, often irrespective of hunger cues. This pattern frequently manifests as a repetitive cycle of eating large quantities of food, often the same types of food, and experiencing significant distress or guilt afterwards.
The compulsion to eat overrides rational judgment, and individuals may struggle to stop once they’ve started. For instance, someone might repeatedly eat excessive amounts of ice cream, even when they are not physically hungry, driven by an overwhelming urge to consume it.
Characteristics of Each Pattern
Understanding the distinguishing characteristics of each pattern is essential for accurate self-assessment.
| Eating Pattern | Characteristics | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional Eating | Using food to cope with emotions; eating when not physically hungry; experiencing guilt or shame afterward. | Weight gain, potential for developing unhealthy relationships with food, emotional distress. |
| Binge Eating | Consuming large quantities of food in a short period; feeling a loss of control; experiencing feelings of disgust or shame after the episode; lack of compensatory behaviors. | Weight gain, potential for developing unhealthy relationships with food, digestive issues, anxiety. |
| Compulsive Eating | An intense urge to eat, irrespective of hunger; eating large quantities of food repeatedly; experiencing distress or guilt after the episode. | Weight gain, potential for developing unhealthy relationships with food, difficulty controlling impulses. |
Identifying Your Eating Patterns: A Checklist
This checklist can help you identify your own eating patterns.
Controlling portions and mindful eating are key to stopping overeating. However, understanding health conditions like macular degenerations vs glaucoma can significantly impact your overall well-being. This often leads to changes in lifestyle, including dietary choices. Ultimately, finding a balanced approach to both your physical and mental health is essential for long-term success in managing overeating.
- Do you find yourself reaching for food to cope with stress, sadness, or other emotions?
- Do you experience episodes of eating large quantities of food in a short period of time?
- Do you feel a loss of control over your eating behaviors?
- Do you eat large amounts of food regardless of your physical hunger?
- Do you experience guilt or shame after eating?
- Do you feel a strong compulsion to eat specific foods or types of food?
Developing Healthy Eating Habits
Cultivating healthy eating habits is a cornerstone of managing overeating and achieving long-term well-being. It’s not about rigid restrictions but rather about adopting sustainable practices that nourish your body and mind. This involves understanding portion sizes, mindful consumption, and a balanced approach to nutrition. By incorporating these principles, you can establish a positive relationship with food and create a foundation for a healthier lifestyle.A key aspect of developing healthy eating habits is understanding the crucial role of balanced nutrition.
This isn’t about deprivation but rather about incorporating a variety of foods that provide the essential nutrients your body needs. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, fuels your body effectively and contributes to overall well-being.
Portion Control
Effective portion control is a vital strategy in managing overeating. Understanding appropriate serving sizes helps prevent excessive calorie intake and promotes a healthier relationship with food. Using smaller plates and mindful eating techniques can help you better regulate your food intake. Pay attention to the signals your body sends regarding fullness. Learning to recognize the difference between hunger and emotional eating is crucial in establishing healthy eating habits.
Mindful Eating
Mindful eating encourages paying attention to the sensory experience of eating. This involves savoring each bite, noticing the taste, texture, and aroma of the food. By eating slowly and without distractions, you can better recognize when you’re full and avoid overeating. This practice fosters a deeper connection with your body’s needs and helps you develop a healthier relationship with food.
Balanced Nutrition
A balanced diet encompasses a variety of food groups, each contributing specific nutrients to your overall health. Fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, and beans, are crucial for building and repairing tissues. Whole grains offer complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy. Dairy products (or alternatives) and healthy fats are also essential components of a balanced diet.
The optimal intake of these groups will differ based on individual needs and activity levels.
Importance of Different Food Groups
- Fruits and vegetables provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber, essential for bodily functions and digestive health.
- Lean proteins support muscle growth, repair, and overall bodily functions.
- Whole grains offer complex carbohydrates, providing sustained energy for physical activity and mental clarity.
- Dairy (or alternatives) contributes to strong bones and teeth, and provides essential nutrients.
- Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production, brain function, and cell health.
Realistic Meal Plans
A sample meal plan showcasing balanced nutrition includes:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and nuts, a glass of milk.
- Lunch: Salad with grilled chicken or chickpeas, whole-grain bread.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice.
- Snacks: Fruits, vegetables with hummus, or a handful of almonds.
These are examples, and you should adjust them based on your specific needs and preferences.
Healthy Food Swaps
| Unhealthy Choice | Healthy Swap | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| White bread | Whole-grain bread | Provides more fiber and nutrients. |
| Sugary drinks | Water, unsweetened tea, or milk | Reduces added sugar intake. |
| Fried foods | Baked, grilled, or steamed foods | Reduces unhealthy fats. |
| Processed snacks | Fruits, vegetables, or nuts | Provides essential nutrients and avoids added preservatives. |
| Fast food | Homemade meals using fresh ingredients | More control over ingredients and portion sizes. |
Implementing Effective Strategies for Control
Taking control of your eating habits is a journey, not a destination. It involves understanding your triggers, recognizing patterns, and developing healthy strategies to manage cravings and portions. This section dives into practical methods for building self-control, managing emotional eating, and leveraging physical activity for improved appetite regulation.Effective strategies for managing overeating extend beyond simply restricting food. They focus on cultivating mindful awareness, understanding emotional triggers, and integrating healthy lifestyle choices into daily routines.
This holistic approach is crucial for lasting change and achieving sustainable weight management goals.
Mindful Eating Techniques
Mindful eating involves paying close attention to the sensations associated with eating. This includes noticing the taste, texture, and aroma of food, as well as your body’s hunger and fullness cues. By practicing mindful eating, you can develop a deeper understanding of your eating patterns and learn to eat more intuitively.
- Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues: Instead of eating until you feel stuffed, practice recognizing the subtle signs of hunger and fullness. Notice the physical sensations in your stomach and how your body feels as you eat. This can help you stop eating before you become overly full.
- Eating slowly and savoring each bite: Take your time to chew your food thoroughly. Savor the flavors and textures of each bite. This allows your body to register the fullness signals more effectively, preventing overeating.
- Eating in a distraction-free environment: Avoid distractions like television, work, or social media while eating. Focus solely on the food in front of you and the sensations associated with eating.
- Using smaller plates and utensils: Visual cues can significantly impact portion control. Using smaller plates and utensils can make portions appear larger, encouraging you to eat less.
Portion Control Strategies
Portion control is essential for managing calorie intake. It involves consciously regulating the amount of food you consume.
- Using measuring cups and spoons: Measuring your food portions using accurate measuring tools can help you maintain consistent portions and monitor your calorie intake more effectively.
- Utilizing smaller plates and bowls: Serving food on smaller plates and bowls can make portions appear larger than they actually are, helping you eat less without feeling deprived.
- Practicing mindful eating: As discussed earlier, mindful eating involves paying close attention to your hunger and fullness cues. This awareness helps you eat until you’re satisfied, rather than until you’re stuffed.
- Visualizing portion sizes: Before eating, imagine the appropriate portion size for a meal. This can help you regulate your intake more effectively.
The Role of Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a crucial role in weight management and appetite regulation. Regular exercise helps boost metabolism, burn calories, and potentially reduce cravings.
- Regular exercise improves metabolism: Physical activity increases your metabolism, allowing your body to burn more calories throughout the day. Even moderate-intensity exercise can contribute to improved metabolic rate.
- Exercise helps regulate appetite: Regular physical activity can help regulate your appetite by affecting hormones and neurotransmitters that control hunger and fullness cues.
- Examples of physical activity: Examples include brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, or any other form of exercise you enjoy and can consistently integrate into your routine.
Building Self-Control Over Eating Habits
Building self-control over eating habits requires consistent effort and a commitment to making sustainable lifestyle changes.
- Setting realistic goals: Establish achievable goals for portion control and mindful eating. Gradually making changes rather than drastic alterations is more sustainable.
- Rewarding progress: Celebrate milestones to maintain motivation and reinforce positive habits.
- Seeking support: Consider joining support groups or working with a registered dietitian or therapist to provide encouragement and guidance.
Managing Emotional Eating
Emotional eating involves using food to cope with difficult emotions or stressful situations. Recognizing these triggers and developing healthier coping mechanisms is essential for managing emotional eating.
- Identifying emotional triggers: Keep a food journal to track your eating patterns and identify situations or emotions that lead to overeating.
- Developing healthy coping mechanisms: Engage in activities that help manage stress and difficult emotions, such as exercise, meditation, spending time in nature, or pursuing hobbies.
Mindfulness and Emotional Regulation
Taking control of your eating habits involves more than just understanding your triggers and patterns. A crucial element is learning to manage your emotions and cultivate a mindful relationship with food. Mindfulness practices can help you become more aware of your internal cues, allowing you to respond to hunger and fullness signals rather than reacting to emotional distress.
By understanding the connection between emotions and eating, you can develop healthier coping mechanisms.Emotional eating is a common response to stress, anxiety, or sadness. It’s a learned behavior, and with practice, you can break the cycle. By incorporating mindfulness techniques into your daily life, you can develop greater self-awareness, leading to more conscious food choices and a healthier relationship with food.
Mindfulness During Meals
Mindfulness during meals enhances your awareness of the sensations associated with eating. This involves paying attention to the taste, texture, and smell of food without judgment. Instead of mindlessly consuming food while distracted, you become fully present in the moment. This heightened awareness helps you recognize the physical signs of hunger and fullness.
- Savor each bite: Pause between bites and fully experience the flavor and texture of the food. Notice the different sensations in your mouth, the aroma, and the temperature. Avoid rushing through meals, allowing yourself to truly experience the meal.
- Engage all your senses: Take time to observe the appearance, aroma, and texture of your food. Use your senses to connect with your meal. This increased sensory awareness helps create a more conscious eating experience.
- Notice your body’s signals: Pay attention to the physical sensations in your stomach and your body as you eat. Do you feel satisfied, full, or still hungry? Acknowledge these sensations without judgment.
Identifying and Managing Emotional Triggers
Understanding the underlying emotions driving your overeating is crucial for developing healthier coping mechanisms. Common emotional triggers include stress, boredom, loneliness, anxiety, and sadness. Identifying these triggers is the first step toward managing them effectively.
- Keep a food journal: Record what you eat, when you eat it, and how you feel before, during, and after each meal. This can help you identify patterns and connections between your emotions and your eating habits.
- Recognize your emotional state: Before eating, take a moment to identify how you’re feeling. Are you stressed, anxious, or simply bored? Acknowledging your emotions is the first step toward managing them.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Explore alternative ways to manage difficult emotions. Engage in activities like exercise, spending time in nature, listening to music, or talking to a trusted friend or therapist. These healthy coping mechanisms can help you manage stress and avoid turning to food as a way to cope.
Stress Reduction and Emotional Regulation Techniques
Stress reduction and emotional regulation are vital components of controlling overeating. Stress often leads to emotional eating, and developing healthy stress management techniques can significantly impact your eating habits. Consider these strategies:
- Deep breathing exercises: Incorporate deep breathing exercises into your daily routine to calm your nervous system and reduce stress. Deep breaths can help regulate your emotions and reduce feelings of anxiety.
- Mindfulness meditation: Regular mindfulness meditation can help you become more aware of your thoughts and emotions without judgment. This increased self-awareness can help you recognize emotional triggers and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: This technique involves tensing and releasing different muscle groups in your body. Progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce physical tension and promote relaxation.
Mindfulness Exercises for Meals
| Exercise | Before Meal | During Meal | After Meal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mindful Breathing | Take 5 deep breaths, focusing on the sensation of each breath. | Pause between bites, focusing on the taste and texture of the food. | Take 5 deep breaths, reflecting on the meal. |
| Body Scan Meditation | Notice any tension in your body and release it. | Pay attention to the physical sensations in your stomach and your body. | Notice any physical sensations related to digestion. |
| Sensory Awareness | Engage your senses by smelling and looking at your food. | Observe the appearance, aroma, and texture of the food. | Reflect on the sensations from the meal, without judgment. |
Support Systems and Professional Help
Overcoming overeating often requires more than just individual effort. Building a strong support network and seeking professional guidance can significantly increase your chances of success. This support can provide accountability, emotional support, and expert strategies tailored to your specific needs. The journey to healthier eating is often smoother with the right kind of help.The importance of support extends beyond personal relationships to include structured programs and professional guidance.
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of overeating can provide encouragement and a sense of community. Professionals offer specialized knowledge and tools to help navigate emotional triggers and develop lasting healthy habits.
Seeking Support from Friends, Family, and Support Groups
A strong support system is crucial for maintaining motivation and coping with setbacks. Sharing your struggles with trusted friends and family members can provide emotional support and encouragement. These individuals can offer practical help and act as accountability partners, reminding you of your goals and helping you stay on track. Support groups offer a unique environment where individuals can connect with others facing similar challenges.
The shared experiences and mutual encouragement within these groups can significantly impact the journey to overcoming overeating. This shared experience can reduce feelings of isolation and foster a sense of community.
Sometimes, dealing with persistent cravings and overeating can feel overwhelming. It’s crucial to address any underlying health issues that might be contributing to these patterns. For example, oral health problems like those sometimes seen in HIV patients, such as hiv mouth sores pictures , can significantly impact appetite and lead to overeating. So, focus on healthy eating habits, portion control, and stress management techniques to effectively curb overeating.
The Role of Registered Dietitians, Therapists, and Healthcare Professionals
Registered dietitians (RDs) play a critical role in addressing overeating issues. RDs possess specialized knowledge in nutrition and can help you develop personalized meal plans and strategies for healthy eating. They can help you understand the relationship between food and emotions and can offer guidance on creating a balanced and sustainable eating pattern. Therapists, such as licensed clinical social workers (LCSWs) or psychologists, can address the emotional and psychological factors contributing to overeating.
They can help you identify and manage underlying emotional issues, develop coping mechanisms, and improve your overall well-being. Other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, can provide medical assessments and ensure there are no underlying medical conditions contributing to the overeating behavior. Their involvement is crucial for a comprehensive approach to tackling the issue.
Types of Professional Help Available
Various types of professional help are available for individuals struggling with overeating. Individual therapy offers one-on-one guidance and support to address the root causes of overeating and develop healthy coping mechanisms. Group therapy provides a platform for shared experiences and support from others facing similar challenges. Nutritional counseling offers personalized dietary plans and strategies to promote healthy eating habits.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) helps identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to food and eating. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) focuses on emotional regulation and coping skills to manage impulsive eating behaviors.
Resources for Support Groups and Professionals
| Type of Resource | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Online Support Groups | Overeaters Anonymous (OA), National Eating Disorders Association (NEDA) online forums | Online communities provide support and connection with others facing similar challenges. |
| Local Support Groups | Local chapters of Overeaters Anonymous, support groups facilitated by therapists or RDs | Face-to-face support groups offer a sense of community and accountability. |
| Registered Dietitians | Find RDs in your area through online directories like the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics website | RDs can provide personalized nutritional guidance and meal planning. |
| Therapists | Use online directories or contact your insurance provider to locate licensed therapists | Therapists can address emotional and psychological factors contributing to overeating. |
| Eating Disorder Specialists | Search for therapists or doctors specializing in eating disorders through professional organizations | Specialists offer specialized knowledge and experience to address complex eating disorder issues. |
Finding the right support and professional help is a crucial step in your journey towards healthier eating. Explore the various resources available to connect with support groups and professionals who can offer tailored guidance.
Maintaining Long-Term Habits

Sustaining healthy eating habits requires a long-term commitment and a proactive approach. Simply adopting a new plan for a few weeks won’t guarantee lasting change. Building lasting habits involves understanding the nuances of your lifestyle and making adjustments that fit seamlessly into your daily routine. This requires patience, flexibility, and a willingness to adapt as your needs evolve.Maintaining healthy eating habits is a journey, not a destination.
It’s about consistently making positive choices that support your well-being. This involves understanding your triggers, recognizing your eating patterns, and developing strategies for managing those patterns. Remember, setbacks are inevitable; the key is to learn from them and keep moving forward.
Strategies for Long-Term Success
Successfully integrating healthy eating habits into your life requires strategies that go beyond simply making changes. It involves creating a supportive environment, understanding your unique needs, and being prepared for challenges. This proactive approach ensures that healthy eating becomes an ingrained part of your lifestyle, rather than a temporary trend.
- Consistency is Key: Regularity in your dietary choices is crucial for establishing long-term habits. Eating at consistent times each day and sticking to your meal plan, as much as possible, creates a predictable pattern. This predictability reduces impulsive eating and reinforces positive behaviors.
- Gradual Changes: Significant shifts in dietary habits can be overwhelming and lead to setbacks. Making gradual changes allows your body and mind to adjust without feeling deprived or restricted. Start with one or two manageable modifications, such as replacing sugary drinks with water or increasing your vegetable intake. As these become routine, gradually incorporate more changes.
- Celebrate Small Victories: Acknowledge and celebrate your progress, no matter how small. Recognizing your achievements reinforces positive behaviors and motivates you to continue. This could be anything from successfully sticking to your meal plan for a week to incorporating a new healthy recipe into your routine. Acknowledging your accomplishments is crucial for building momentum and confidence.
- Adaptability is Essential: Life throws curveballs. Be prepared for unexpected events, social gatherings, or changes in your schedule. Having backup plans and adaptable strategies ensures that your healthy eating habits don’t falter in the face of challenges. For example, having healthy snacks readily available can prevent overeating when you’re caught off guard.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Maintaining long-term healthy eating habits involves proactively addressing potential setbacks. Understanding common pitfalls allows you to anticipate and mitigate potential challenges. By acknowledging these issues, you can develop strategies to prevent them from derailing your progress.
- Emotional Eating: Recognize the emotional triggers that contribute to overeating. Developing healthy coping mechanisms for stress, sadness, or boredom can help prevent emotional eating. Engage in activities that provide emotional support, such as exercise, spending time with loved ones, or pursuing hobbies.
- Social Situations: Plan ahead for social gatherings and restaurant outings. Choose restaurants that offer healthier options or have menus available online. Share your intentions with friends and family so they can support your choices. Communicate your dietary needs to restaurant staff.
- Stress and Fatigue: Stress and fatigue can often lead to unhealthy choices. Prioritize self-care activities, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and adequate sleep. These can help mitigate the negative impact of stress on your eating habits.
- Lack of Planning: Without a plan, you’re more likely to make impulsive and unhealthy choices. Planning your meals and snacks in advance reduces the likelihood of resorting to less nutritious options when hunger strikes.
Adapting to Different Lifestyles
Healthy eating habits should be adaptable to fit your individual lifestyle and circumstances. By tailoring your approach to various situations, you can ensure long-term success. Adapting your habits to different situations is crucial for sustaining healthy eating patterns.
- Busy Schedules: Prepare meals in advance or utilize quick and healthy recipes to make it easier to stick to your plan during busy periods. Pre-portion snacks and meals to avoid overeating when time is limited.
- Travel: Pack healthy snacks and meals for trips, and research restaurants that cater to your dietary needs. Choose meals that can be easily prepared and consumed on the go.
- Holidays and Celebrations: Enjoy the occasion while maintaining balance. Choose healthier options at celebrations or prepare your own dishes with healthier alternatives to traditional recipes.
- Social Events: Be mindful of social pressure and choose your meals wisely. Select meals with nutritious ingredients and portion your food accordingly.
Addressing Specific Dietary Needs: How To Stop Overeating
Successfully managing your eating habits requires careful consideration of individual needs and circumstances. This includes allergies, intolerances, specific health conditions, and even the demands of an active lifestyle. Understanding these factors allows for the development of personalized dietary plans that are not only effective but also sustainable and enjoyable.
Dietary Modifications for Allergies and Intolerances
Allergies and intolerances necessitate significant dietary adjustments. For example, a person with a dairy allergy must eliminate all dairy products from their diet. This often requires careful reading of food labels and substitutions with suitable alternatives. Similarly, those with gluten intolerance need to avoid wheat, barley, and rye, focusing on gluten-free options.
Adjusting Eating Habits for Athletes and Active Individuals, How to stop overeating
Active individuals require higher calorie and nutrient intake to support their training and recovery. This might include increasing protein intake for muscle repair and carbohydrates for energy. Proper hydration is crucial for optimal performance and should be a priority for athletes. The amount of calories needed depends on the intensity and duration of workouts.
Dietary Needs for Specific Health Conditions
Individuals with conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease need specialized dietary plans. For instance, those with diabetes need to manage their carbohydrate intake carefully to maintain stable blood sugar levels. High blood pressure often requires a low-sodium diet, and heart disease patients often benefit from a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Dietary Plans Comparison
| Dietary Need | Key Adjustments | Example Foods to Include | Example Foods to Exclude |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Allergy | Replace dairy products with alternatives like almond milk, soy milk, or oat milk. | Fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, gluten-free grains | Milk, cheese, yogurt, ice cream |
| Gluten Intolerance | Avoid wheat, barley, and rye. Opt for gluten-free alternatives. | Rice, quinoa, corn, potatoes, meat, fruits, vegetables | Bread, pasta, cereals, beer |
| Athlete | Increase calorie intake, focus on protein and complex carbohydrates. | Lean meats, fish, eggs, fruits, vegetables, whole grains | Processed foods, sugary drinks |
| Diabetes | Manage carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood sugar. | Non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats | Sugary drinks, processed foods, refined grains |
Creating a Personalized Action Plan
Overcoming overeating is a journey, not a sprint. A personalized action plan is crucial for tailoring strategies to your unique needs and circumstances. This plan acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the process with specific steps, measurable goals, and adjustments as you progress. It’s not a static document; it evolves with you, reflecting your changing needs and responses.This plan will be more effective than generic approaches, as it incorporates your individual preferences, strengths, and weaknesses.
By acknowledging your unique context, you create a more sustainable and personally relevant strategy for managing your relationship with food.
Action Plan Template
A well-structured action plan incorporates various aspects of your life to ensure comprehensive change. This template provides a framework to customize your plan:
- Identifying Triggers: List specific situations, emotions, or external factors that trigger overeating. Examples include stress, boredom, social events, or specific types of foods.
- Recognizing Patterns: Describe your typical eating patterns, including meal times, portion sizes, and types of foods consumed. This helps pinpoint any recurring habits that contribute to overeating.
- Setting Realistic Goals: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Instead of “eat healthier,” aim for “reduce portion sizes at dinner by 25% for three consecutive days.” This clarity is key to tracking progress.
- Developing Coping Mechanisms: Artikel strategies for dealing with triggers and emotional responses that lead to overeating. For instance, practice deep breathing exercises, engage in a hobby, or call a friend during stressful situations.
- Dietary Adjustments: Include details on dietary changes, such as incorporating more fruits and vegetables, reducing processed foods, or choosing healthier alternatives. Be specific about what foods to increase or decrease.
- Physical Activity: Schedule regular exercise or physical activity. Specify the type, duration, and frequency. Include ways to make it a sustainable part of your routine, such as walking with a friend or joining a fitness class.
- Mindfulness Practices: Artikel mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or mindful eating, to enhance awareness of hunger and fullness cues. Include examples of specific exercises or apps you can use.
- Support System: Identify individuals or groups who can offer support and accountability. This might include family members, friends, or support groups.
Progress Evaluation Checklist
Regular assessment is crucial for adapting the plan as needed. This checklist helps monitor progress and identify areas requiring adjustments:
| Criteria | Rating (1-5, 5 being excellent) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Trigger Awareness | How well are you recognizing triggers? | |
| Eating Pattern Identification | How accurately do you recognize your patterns? | |
| Goal Achievement | Have you met your set goals? | |
| Coping Mechanism Effectiveness | How helpful are your coping mechanisms? | |
| Dietary Changes | Are you sticking to your dietary adjustments? | |
| Physical Activity | How consistent is your physical activity? | |
| Mindfulness Practice | How frequently do you practice mindfulness? | |
| Support System Engagement | How effective is your support system? |
Adjusting the Plan
The plan should be flexible and adaptable to individual responses. Regular reviews are essential to fine-tune strategies. If a particular coping mechanism isn’t working, try a different approach. If a goal is proving too challenging, adjust the timeframe or the goal itself.
Examples of Successful Action Plans
- Sarah, a student: Sarah identified stress as a trigger and incorporated mindfulness exercises and deep breathing into her routine. She also adjusted her meal schedule to include smaller, more frequent meals. Her plan focused on maintaining healthy eating habits while managing academic pressure.
- Mark, a professional: Mark recognized that boredom led to overeating. He joined a cooking class, which provided healthy alternatives and a fulfilling activity. His plan prioritized finding new hobbies to replace unproductive behaviors.
Illustrative Examples
Overcoming overeating is a journey, not a destination. Real-life stories of individuals who have successfully navigated these challenges offer invaluable insights and inspiration. These examples highlight the diverse strategies that can be employed and the persistent dedication required for lasting change. They also demonstrate the common threads of struggle and triumph that unite those facing similar issues.
Case Studies of Success
These case studies showcase the diversity of experiences and the varied approaches to conquering overeating. They illustrate that there is no one-size-fits-all solution, and that personalized strategies are key to long-term success. The individuals in these accounts share a common thread: a commitment to self-discovery and a willingness to adapt their approach based on their unique circumstances.
- Sarah, a 30-year-old professional: Sarah initially struggled with emotional eating, using food to cope with stress and anxiety. Through therapy and mindfulness practices, she learned to identify her triggers and develop healthier coping mechanisms. She incorporated regular exercise and a balanced diet, gradually replacing emotional eating with more constructive outlets. Her success was not immediate, but the consistent application of mindfulness and support from a therapist helped her achieve long-term stability.
She recognized that her journey wasn’t a linear progression; there were setbacks, but each setback became an opportunity for reflection and adjustment.
- David, a 45-year-old stay-at-home father: David’s overeating stemmed from a combination of stress, boredom, and a lack of healthy alternatives. He found himself relying on comfort food to deal with his daily routine. He initially attempted restrictive diets, which only led to frustration and feelings of deprivation. Instead, he focused on slowly introducing healthier food options into his daily meals. He started meal prepping and planned for outings to ensure he always had healthy options available.
He also joined a local sports club, finding camaraderie and support to stay active and motivated. David’s key to success was gradual, sustainable change, not radical transformation.
Challenges and Successes
The challenges faced in overcoming overeating are often intertwined with personal circumstances, lifestyle factors, and underlying emotional issues. Successes arise from tailored strategies that acknowledge these factors. Consistency, patience, and the development of coping mechanisms are essential components of a successful journey.
| Case Study | Challenges | Strategies | Successes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sarah | Emotional eating, lack of coping mechanisms, inconsistent habits | Therapy, mindfulness, healthy coping mechanisms, consistent support | Reduced emotional eating, improved self-awareness, healthier lifestyle |
| David | Stress, boredom, lack of healthy alternatives, restrictive dieting | Gradual introduction of healthy foods, meal prepping, joining a sports club | Sustainable healthy eating habits, improved physical health, emotional well-being |
Key Takeaways
The table above summarizes the common threads from the case studies. These takeaways highlight the importance of tailored strategies, consistent effort, and a holistic approach to tackling overeating. Understanding the root causes of overeating and implementing strategies to address those causes are crucial to long-term success.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, stopping overeating is a multifaceted process that requires understanding the root causes, developing healthy habits, and implementing effective strategies. This guide provides a comprehensive framework for achieving lasting change. By combining knowledge of triggers, eating patterns, and practical strategies, you can create a personalized plan for managing overeating and cultivate a healthier relationship with food. Remember, consistency and support are key to long-term success.