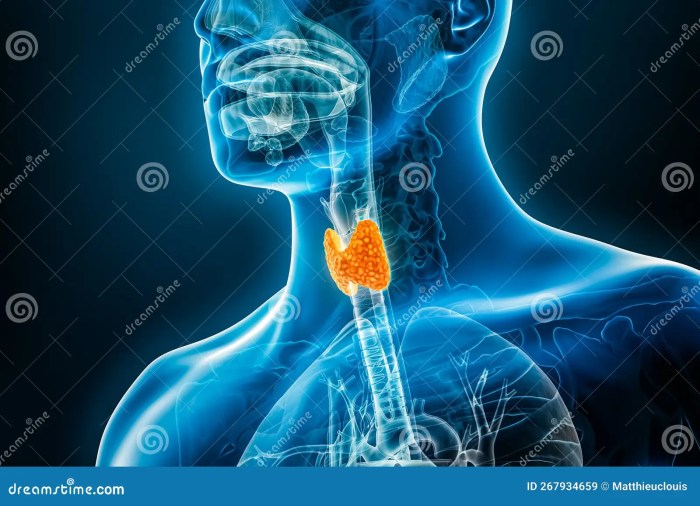
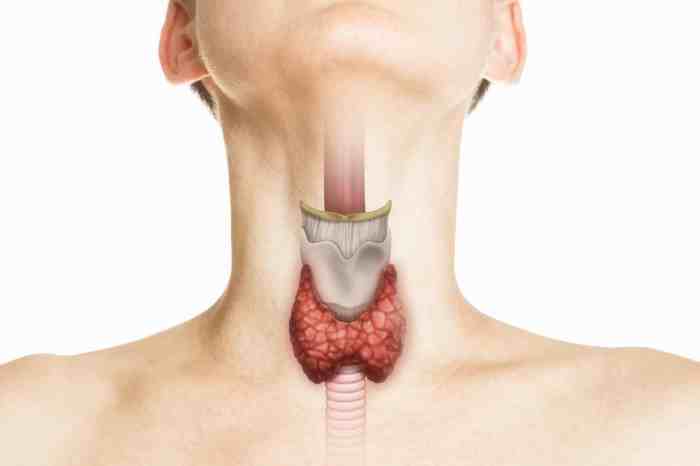
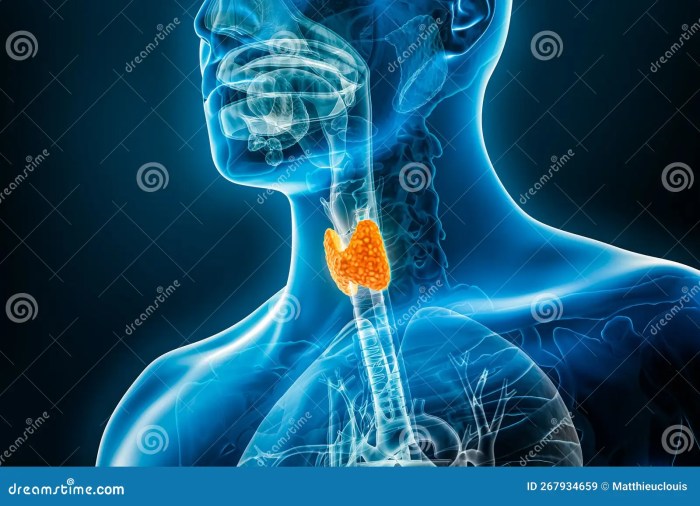
Paxlovid mouth what to do? This guide explores the potential oral side effects of Paxlovid, offering practical strategies for managing discomfort, and highlighting the crucial role of professional interventions and patient self-care.
Many users experience oral issues while taking Paxlovid, ranging from dry mouth and sores to more severe complications. Understanding the potential problems, along with proactive strategies for managing them, can make a significant difference in your experience. We’ll cover everything from common complaints and potential causes to effective home remedies and when to seek professional help.
Understanding Paxlovid-Related Oral Issues
Paxlovid, a highly effective antiviral medication, is often prescribed for COVID-19 treatment. While generally well-tolerated, some individuals experience oral side effects. Understanding these potential issues can help patients and healthcare providers manage any discomfort effectively.Oral side effects associated with Paxlovid use are a significant consideration. The medication’s mechanism of action, and its potential interaction with oral tissues, can lead to a range of symptoms.
These symptoms vary in severity and duration, and careful monitoring is crucial.
Potential Oral Side Effects of Paxlovid
Paxlovid’s active components can interact with the oral mucosa, potentially causing discomfort. This includes the lining of the mouth, gums, and tongue. Common complaints range from mild dryness and irritation to more pronounced issues. These effects are generally temporary and resolve with the discontinuation of the medication.
Common Paxlovid-Related Oral Complaints
A variety of oral complaints are frequently reported by Paxlovid users. These include: xerostomia (dry mouth), altered taste perception, oral pain, and difficulty swallowing. Other complaints include the development of oral sores, and, in some cases, bleeding gums. The severity and frequency of these complaints can differ between individuals.
Mechanisms of Paxlovid-Induced Oral Discomfort
The exact mechanisms underlying Paxlovid-related oral issues are still under investigation. However, some potential factors include the medication’s effect on saliva production, its impact on oral tissue inflammation, and its interaction with existing oral health conditions. For instance, individuals with pre-existing dry mouth conditions may experience exacerbated symptoms.
“Possible mechanisms may involve altered saliva flow, inflammatory responses, or interactions with existing oral health conditions.”
Timeframe of Oral Effects
The onset of oral side effects associated with Paxlovid use typically occurs within the first few days of treatment. The duration of these effects varies, but generally resolves within a few days or weeks after discontinuation of the medication.
Comparison of Reported Oral Symptoms
| Symptom | Description | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xerostomia (Dry Mouth) | A persistent feeling of dryness in the mouth, often leading to difficulty swallowing and discomfort. | High | Mild to Moderate |
| Altered Taste Perception | Changes in the perception of taste, including a metallic, bitter, or otherwise unusual taste. | Moderate | Mild to Moderate |
| Oral Pain | Localized pain or discomfort in the mouth, potentially affecting chewing or speaking. | Low | Mild to Severe |
| Oral Sores | The development of painful ulcers or sores in the mouth. | Low | Moderate to Severe |
| Bleeding Gums | Gums that bleed easily or exhibit increased bleeding upon brushing or other oral activities. | Low | Mild to Moderate |
Paxlovid Dosage and Oral Reactions
While a direct causal link between Paxlovid dosage and specific oral reactions is not fully established, some anecdotal reports suggest potential correlations. Larger dosages may be associated with increased instances of certain side effects, although further research is required. However, individual responses to the medication can vary significantly.
Dealing with a dry or sore mouth from Paxlovid? It’s a common side effect. While you’re looking for ways to soothe that discomfort, have you considered natural remedies like incorporating fenugreek into your daily routine? Fenugreek for hair growth is also known for its potential to moisturize, which might help with oral dryness. Ultimately, though, remember to always prioritize your doctor’s recommendations when managing any Paxlovid side effects.
| Paxlovid Dosage | Potential Oral Reaction Correlation |
|---|---|
| Higher Dosage | Potentially increased frequency or severity of xerostomia and altered taste perception. |
| Standard Dosage | Generally associated with a lower incidence of severe oral reactions. |
Managing Paxlovid-Induced Oral Discomfort: Paxlovid Mouth What To Do
Paxlovid, while effective in treating COVID-19, can sometimes lead to unpleasant oral side effects. Understanding these potential issues and implementing proactive oral care strategies can significantly improve the patient experience and ensure optimal treatment outcomes. Taking proactive steps to manage oral discomfort can help patients stay comfortable and compliant with their medication regimen.Oral side effects, such as dryness and sores, are common side effects of Paxlovid.
Addressing these issues early can prevent more severe complications and ensure a smoother treatment journey. This includes not just immediate relief but also preventing long-term oral health issues.
Oral Care Regimens for Paxlovid Users
Different oral care regimens can effectively mitigate Paxlovid-related oral discomfort. The key is to find a routine that works best for you and to be consistent. Some individuals may find that certain products or techniques are more effective than others.
A regimen focusing on frequent, gentle cleaning and moisturizing is crucial. A consistent approach, rather than sporadic bursts of care, is more beneficial in the long run. This helps maintain a healthy oral environment.
Recommended Oral Hygiene Practices
Consistent oral hygiene is paramount in managing Paxlovid-related oral discomfort. These practices, when followed diligently, can help prevent or alleviate dryness, sores, and other potential side effects.
- Regular Brushing: Brush your teeth gently twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Avoid harsh scrubbing, which can irritate already sensitive oral tissues.
- Gentle Flossing: Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth, preventing buildup that can contribute to discomfort and infection.
- Mouth Rinsing: Rinse your mouth with a fluoride mouthwash or a saline solution after meals and before bed. This helps to remove food particles and neutralize acids that can contribute to oral irritation.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Saliva production is directly related to hydration levels, and staying well-hydrated helps maintain a healthy oral environment.
The Role of Saliva in Oral Health, Paxlovid mouth what to do
Saliva plays a critical role in maintaining oral health. It helps wash away food particles, neutralizes acids, and provides lubrication. Decreased saliva production, a common side effect of Paxlovid, can lead to increased oral discomfort and an elevated risk of oral health problems.
Understanding the importance of saliva highlights the need for proactive hydration and oral care practices. Maintaining adequate hydration is a crucial part of managing Paxlovid’s potential oral side effects.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups are essential for all individuals, but especially for Paxlovid users. These appointments allow dentists to monitor oral health, detect any early signs of problems, and provide personalized recommendations for managing potential issues.
Early detection and intervention are crucial for preventing more serious oral health problems. Dental checkups provide an opportunity to address concerns before they escalate.
Addressing Persistent Oral Discomfort
If oral discomfort persists despite implementing home remedies, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can evaluate the situation, rule out other potential causes, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional help if home remedies aren’t providing relief. A healthcare provider can determine the underlying cause and suggest tailored solutions.
Home Remedies for Oral Dryness
| Remedy | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sipping Water Frequently | Drink small sips of water throughout the day to maintain hydration. | High | None |
| Chewing Sugar-Free Gum | Stimulates saliva production. | Moderate | Potential for gum irritation if not sugar-free. |
| Using a Humidifier | Increases moisture in the air. | Low to Moderate | Requires careful maintenance to prevent mold growth. |
| Applying a Petroleum Jelly or Lip Balm | Moisturizes the oral mucosa. | Low to Moderate | May not be suitable for all individuals. |
Professional Interventions for Oral Issues
Navigating Paxlovid-related oral discomfort requires a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare professionals. Understanding the potential side effects and seeking prompt intervention is crucial for managing these issues effectively and minimizing long-term complications. Early detection and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the patient experience and prevent any adverse effects.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in identifying, diagnosing, and managing Paxlovid-related oral issues. Their expertise in evaluating symptoms, recommending appropriate treatments, and monitoring patient response is essential for optimal care. A thorough understanding of the medication’s potential side effects, coupled with a patient’s detailed history, allows for accurate assessment and tailored interventions.
Types of Professionals Involved
Several healthcare professionals can contribute to the management of Paxlovid-related oral issues. Primary care physicians, dentists, and oral medicine specialists are often involved in the initial assessment and subsequent treatment planning. Dentists are particularly well-equipped to diagnose and address oral conditions, while oral medicine specialists provide expertise in complex oral diseases. Pharmacists can also play a role by advising patients on proper medication use and potential interactions.
Communication and Patient History
Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is paramount. Patients should promptly report any oral discomfort, including pain, sores, or changes in taste or mouth dryness. Detailed descriptions of the symptoms, including their onset, duration, and severity, are essential for accurate diagnosis. The patient’s medical history, including any pre-existing oral conditions or other medications, is also critical information.
So, you’re taking Paxlovid and experiencing some mouth discomfort? It’s a common side effect, and while it’s generally temporary, knowing what to do can make a big difference. For instance, some studies suggest that certain compounds in Japanese knotweed might offer potential benefits in certain contexts, although more research is needed. To learn more about the uses, safety, and other considerations related to Japanese knotweed compounds, check out this helpful resource: japanese knotweed compounds uses safety and more.
Regardless, staying hydrated and gently rinsing your mouth with warm water might help soothe the feeling. Ultimately, always consult with your doctor about any specific concerns regarding Paxlovid side effects.
Diagnostic Procedures
A thorough oral examination is the cornerstone of diagnosis. This includes visual inspection of the oral mucosa, tongue, and palate for signs of inflammation, lesions, or ulcers. In some cases, biopsies may be necessary to rule out more serious conditions. Additional tests, such as blood tests or imaging, might be required depending on the specific symptoms and the healthcare professional’s assessment.
Treatment Options
A variety of treatment options are available for managing Paxlovid-induced oral discomfort. These options range from over-the-counter remedies to prescription medications and, in some cases, surgical interventions. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and nature of the oral issue. Proper communication and shared decision-making between the patient and the healthcare provider are crucial to selecting the most suitable approach.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Oral Symptom | Potential Treatment | Efficacy | Precautions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Mouth | Sugar-free lozenges, increased water intake, saliva substitutes | Generally effective for mild cases | May not be sufficient for severe cases; monitor for worsening symptoms. |
| Oral Ulcers | Topical anesthetic gels, mouthwashes, oral corticosteroids | Variable; efficacy depends on ulcer size and severity | Potential side effects of corticosteroids; follow professional guidance. |
| Swelling or inflammation | Cold compresses, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids | Can reduce inflammation and swelling | NSAIDs may cause stomach upset; consult healthcare provider. |
| Changes in taste | Nutritional counseling, dietary adjustments, supportive care | Effectiveness depends on underlying cause | Monitor for nutrient deficiencies; follow a balanced diet. |
Patient Self-Care Strategies
Taking proactive steps to manage potential oral side effects of Paxlovid is crucial for patient comfort and well-being. This section details practical strategies that Paxlovid users can employ to minimize discomfort and maintain good oral health during treatment. Understanding how to adjust your oral care routine and dietary choices can significantly impact your experience.
Proactive Oral Care
Addressing potential oral issues proactively is key to a comfortable Paxlovid experience. Simple adjustments to your daily oral hygiene routine can make a world of difference. Consistency and mindful choices are vital.
- Adjusting Oral Care Routines: Frequent rinsing with lukewarm water, or a mild saline solution, can help to gently cleanse the mouth and remove any potential irritants. This is especially important after taking Paxlovid, as the medication can sometimes linger in the mouth. Consider using a soft-bristled toothbrush and a fluoride-containing toothpaste. Gentle brushing techniques and avoiding harsh scrubbing are essential.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is paramount for overall health and can help to dilute the medication and wash away any residue that might contribute to oral discomfort. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day. Water’s crucial role in maintaining oral health should not be overlooked.
Over-the-Counter Relief
Several over-the-counter products can provide relief from Paxlovid-related oral discomfort. Choosing the right product can be tailored to your specific needs.
- Mouthwashes: A variety of mouthwashes, including those with soothing ingredients like aloe vera or chamomile, can help to reduce inflammation and dryness. Look for formulations specifically designed for oral discomfort. Choose a mouthwash that complements your oral hygiene routine and that you find comfortable to use.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage any pain or discomfort associated with oral side effects. Consult your physician if you have any concerns about dosage or interactions with other medications.
- Dry Mouth Remedies: If dryness is a concern, consider using a sugar-free lozenge or chewing gum to stimulate saliva production. These can be useful in conjunction with other strategies to alleviate discomfort.
Dietary Considerations
Food and drink choices can significantly influence oral health. Understanding which choices exacerbate or alleviate side effects can greatly improve comfort.
So, you’re taking Paxlovid and experiencing some mouth discomfort? It’s a common side effect, and thankfully, there are usually simple solutions. Similar to managing other medications, paying attention to your diet can play a crucial role. For instance, certain foods can interact with metformin, a diabetes medication, and knowing what to avoid can significantly impact your overall well-being.
Check out this helpful guide on foods to avoid while taking metformin to see what you should steer clear of. Keeping your diet in check alongside the Paxlovid will help you navigate this phase more comfortably.
- Foods to Avoid: Foods high in acidity, such as citrus fruits and acidic juices, can exacerbate dryness and potential irritation. Similarly, extremely hot or cold foods and drinks should be consumed cautiously, as these can cause discomfort. Avoid overly sugary or sticky foods, as they can increase the risk of oral issues. Examples of foods that could exacerbate issues include hard candies, spicy foods, and overly acidic beverages.
- Foods to Consider: Choose soft, bland foods that are easy to eat and won’t further irritate the mouth. Water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables can help maintain hydration and keep the mouth moist. Examples of helpful foods include applesauce, mashed potatoes, and yogurt.
- Beverages to Consider: Warm or lukewarm beverages, rather than extremely hot or cold ones, are preferable. Plain water is the best option for hydration and overall health.
Choosing the Right Oral Care Products
Selecting the right oral care products is essential for maintaining good oral health. Personal preferences and specific needs should guide your choices.
- Toothpaste: Opt for a fluoride-containing toothpaste with a gentle formula to avoid further irritation. Avoid highly abrasive or whitening toothpastes.
- Toothbrush: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid injury to the gums or mouth tissues. Consider a toothbrush with a smaller head for better access to hard-to-reach areas.
- Mouthwash: Select a mouthwash that is specifically designed for oral health and discomfort management. If needed, consult with your dentist or pharmacist to determine the most appropriate choice.
Illustrative Case Studies (Descriptive)
Paxlovid, while highly effective in treating COVID-19, can sometimes lead to oral side effects. Understanding how these manifest and how best to manage them is crucial for patient well-being. These case studies offer real-world examples of observed issues and successful interventions.
Case of Oral Irritation
A 62-year-old patient, experiencing mild COVID-19 symptoms, was prescribed Paxlovid. Within the first few days, the patient reported a persistent burning sensation in their mouth, particularly on the tongue and inner cheeks. The sensation was described as a mild, yet consistent, discomfort. The patient also noted some dryness and slight swelling. This case highlights the potential for localized irritation as a side effect of Paxlovid.
Effective Management Strategies
The patient in the previous case experienced relief after implementing several self-care strategies. These included frequent rinsing with lukewarm salt water (1/2 teaspoon of salt in 8 ounces of water), avoiding acidic and spicy foods, and using a soft-bristled toothbrush. Additionally, the patient found that applying a thin layer of lip balm throughout the day helped alleviate dryness.
Professional Intervention Required
Another patient, a 45-year-old with a history of oral ulcers, experienced severe oral pain after commencing Paxlovid. The pain was accompanied by the development of multiple painful sores on the inside of their mouth. This case demonstrates the importance of seeking professional medical attention when oral discomfort intensifies or doesn’t improve with self-care measures. A consultation with a dentist or oral physician proved necessary to rule out secondary infections and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as topical anesthetics or anti-inflammatory medications.
Successful Patient Self-Care
A 38-year-old patient, experiencing mild oral dryness after taking Paxlovid, successfully managed the issue using a few simple techniques. The patient found that drinking plenty of water throughout the day and avoiding sugary drinks significantly reduced the dryness. Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on ice chips also helped. This case illustrates that simple, readily available self-care measures can often be effective in mitigating minor oral discomfort associated with Paxlovid.
Comprehensive Evaluation of Patient Response
A 50-year-old patient, experiencing a combination of oral dryness, altered taste, and mild oral sores, provided a detailed record of their Paxlovid experience and oral care practices. The patient diligently documented the severity of symptoms, the timing of their onset relative to Paxlovid intake, and their response to different self-care strategies. A review of this patient’s case history, including their medical background, and the documentation of their responses to various treatments, allows for a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s overall response to Paxlovid and oral care.
This detailed approach helps in understanding the individual variability in the patient’s reaction to the medication.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, navigating Paxlovid-related oral issues requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the potential side effects, implementing proactive self-care strategies, and knowing when to seek professional help, you can effectively manage these challenges and maintain your oral health. Remember, consistent oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and open communication with your healthcare provider are key to a positive experience.