DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis are a crucial part of managing this chronic autoimmune disease. These disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs work to slow or halt the progression of the disease, improving quality of life for those affected. This guide explores the various types of DMARDs, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and treatment strategies, empowering readers with a deeper understanding of this important area of rheumatology.
We’ll delve into the different categories of DMARDs, examining their individual mechanisms of action and how they impact disease progression. From methotrexate to biologics, we’ll cover a range of options and discuss factors influencing treatment selection. Furthermore, we’ll explore the crucial role of monitoring and managing side effects, ensuring patients receive the best possible care.
Overview of DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are a crucial component of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. They are designed not just to alleviate symptoms, but to slow or halt the progression of the disease itself. This is a significant difference from symptomatic treatments, which only address the current pain and inflammation. DMARDs work by targeting the underlying immune system mechanisms driving RA.DMARDs achieve their disease-modifying effects through various mechanisms, often by suppressing the overactive immune response that attacks the joints in RA.
This leads to reduced joint damage, improved function, and a better quality of life for those with the condition.
Different Categories of DMARDs
DMARDs are broadly categorized based on their mechanism of action. This categorization helps in selecting the most appropriate drug for a specific patient. Different categories have different strengths and weaknesses, and the choice is often personalized to the individual’s response and potential side effects.
Traditional DMARDs
Traditional DMARDs, also known as conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs), have been used for many years to treat RA. These drugs work by various means, often by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune response.
- Methotrexate is a cornerstone of RA treatment. It is often the first-line csDMARD due to its effectiveness and generally manageable side effects. It works by interfering with the synthesis of DNA and RNA, thereby slowing down immune cell activity.
- Sulfasalazine is another traditional DMARD, known for its ability to reduce inflammation. It inhibits certain enzymes involved in inflammatory processes.
- Hydroxychloroquine is an antimalarial drug with anti-inflammatory properties. It is often used in combination with other DMARDs, particularly in early RA, to manage the disease.
- Leflunomide is a newer csDMARD that works by suppressing the immune system. It is an effective treatment option for many patients.
Biological DMARDs
Biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) are a more recent class of DMARDs. They target specific proteins or cells involved in the inflammatory process, offering a more precise approach.
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) inhibitors, such as etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab, are a common type of bDMARD. These drugs block TNF, a key inflammatory cytokine in RA.
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6) inhibitors, such as tocilizumab, are another type of bDMARD. They target IL-6, a cytokine also involved in the inflammatory response in RA.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors, such as tofacitinib and baricitinib, are a newer class of bDMARDs. They inhibit the activity of certain enzymes in the immune system, reducing inflammation.
Comparison of DMARD Categories
| DMARD Category | Mechanism of Action | Efficacy | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional DMARDs (csDMARDs) | Interfere with immune system function, reduce inflammation, suppress immune cell activity. | Generally effective, but may require higher doses for optimal results in some patients. | Gastrointestinal upset, liver problems, and blood disorders are potential side effects. These are often manageable with monitoring and adjustments to treatment. |
| Biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) | Target specific proteins or cells involved in the inflammatory response, providing a more precise approach. | Often highly effective in reducing inflammation and disease activity. | Increased risk of infections, immune system suppression, and certain rare but serious side effects, such as heart failure, require careful monitoring. |
Effectiveness and Efficacy of DMARDs
Understanding how Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) impact rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is crucial for effective treatment strategies. DMARDs work on multiple levels, targeting the underlying causes of RA, and not just the symptoms. This approach can significantly slow or halt the progression of the disease and prevent long-term joint damage. Their effectiveness varies based on the specific DMARD and the individual patient’s response.DMARDs achieve their effects through a variety of mechanisms.
Some work by suppressing the immune system, while others aim to reduce inflammation. The varying success rates among individuals highlight the complexity of RA and the need for personalized treatment plans. A thorough understanding of the individual patient’s response to different DMARDs is paramount for optimizing outcomes.
Impact on RA Activity Markers
DMARDs demonstrate varying degrees of success in influencing key markers of RA activity. These markers, often measured through blood tests, provide insights into the disease’s inflammatory state and the effectiveness of treatment. The table below summarizes the observed impacts of various DMARDs on key RA activity markers.
| DMARD | Impact on RA Activity Markers (e.g., CRP, ESR, etc.) |
|---|---|
| Methotrexate | Generally effective in reducing inflammatory markers like CRP and ESR, often demonstrating significant improvement in patients. |
| Sulfasalazine | Can be effective in reducing inflammation markers, though typically to a lesser extent compared to methotrexate. Its impact varies depending on the individual patient. |
| Hydroxychloroquine | Generally well-tolerated and effective in reducing inflammation markers in some patients. It often exhibits a more gradual improvement compared to other DMARDs. |
| Leflunomide | Often demonstrates a substantial impact on inflammatory markers, comparable to methotrexate in many cases. It’s often considered a strong option for patients who do not respond well to methotrexate. |
| Biologics (e.g., TNF inhibitors) | Highly effective in reducing inflammatory markers, often leading to significant symptom relief and a reduction in disease activity. These medications are often reserved for more severe cases or when conventional DMARDs are not sufficient. |
Effect on Disease Progression
DMARDs significantly influence the progression of RA by targeting the underlying immune mechanisms driving the disease. By controlling inflammation and reducing immune cell activity, they can slow or halt the progression of joint damage. Early intervention with DMARDs is crucial, as it allows for a better chance of preventing or delaying irreversible joint damage and preserving long-term function.
Long-Term Efficacy
The long-term efficacy of DMARDs varies, and the best choice often depends on factors like individual patient response, the severity of the RA, and the presence of other health conditions. Some DMARDs, like methotrexate, have a well-established track record of long-term efficacy in controlling RA symptoms and slowing joint damage. However, the effectiveness can vary among individuals, highlighting the need for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan.
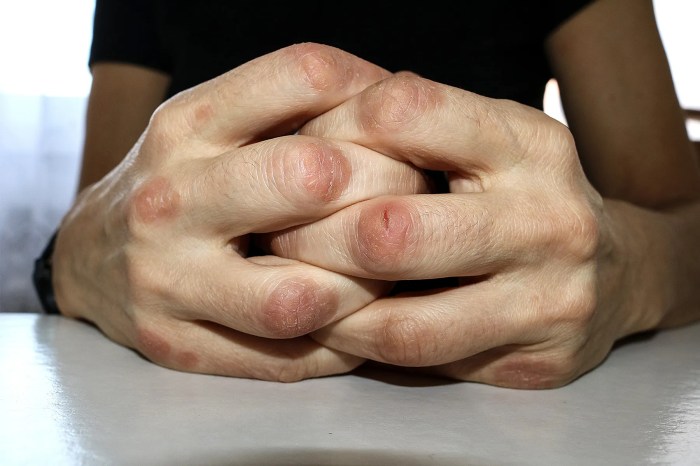
Impact on Joint Damage
DMARDs play a crucial role in mitigating joint damage associated with RA. Early and aggressive treatment with effective DMARDs can significantly slow down or even halt the progressive erosion of cartilage and bone that occurs in RA. This can help maintain joint function and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Patients who achieve early and sustained remission under DMARD treatment often have a significantly better long-term prognosis and quality of life.
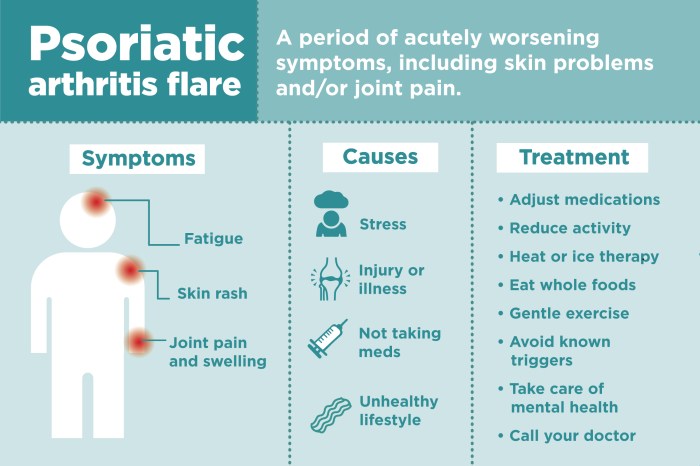
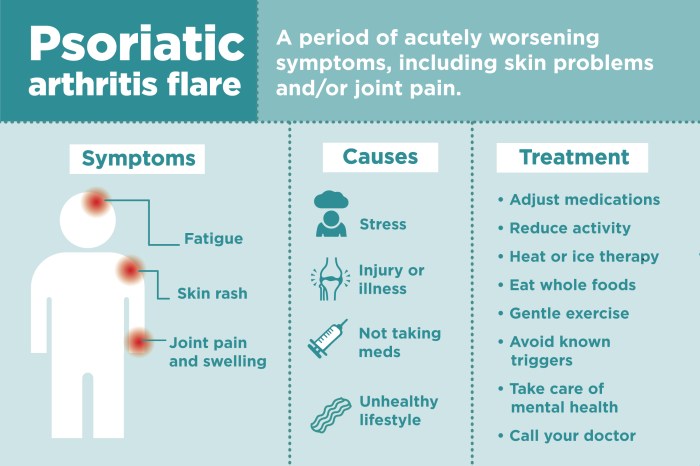
Side Effects and Potential Risks of DMARDs: Dmards For Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding the potential side effects of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) is crucial for effective rheumatoid arthritis management. While DMARDs are essential for controlling the disease and improving quality of life, they can sometimes lead to adverse reactions. A proactive approach to monitoring side effects and a thorough understanding of potential risks are paramount for both patients and healthcare providers.DMARDs, though beneficial in managing rheumatoid arthritis, can have a range of side effects, some mild and manageable, others potentially more serious.
Recognizing the possible reactions and knowing how to address them can greatly improve the treatment experience and overall well-being. Proper monitoring and open communication between patients and their healthcare teams are essential for navigating these potential challenges.
Potential Side Effects by DMARD Type
Different DMARDs have varying profiles of potential side effects. Understanding these distinctions is vital for personalized treatment strategies.
- Methotrexate: Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Liver damage is a potential concern, especially with higher doses or prolonged use. Lung problems, such as pneumonitis, can also occur. Monitoring liver function tests and complete blood counts is crucial for patients on methotrexate.
- Sulfasalazine: Gastrointestinal upset, including nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea, is relatively common. Some patients experience allergic reactions, such as skin rashes or itching. Hematologic effects, like anemia, are also possible.
- Leflunomide: Liver damage and gastrointestinal problems are potential side effects. Hair loss and skin rashes can also occur. Careful monitoring of liver function and complete blood counts is essential.
- Hydroxychloroquine: Eye problems, including retinopathy, are a significant concern, necessitating regular eye examinations. Gastrointestinal issues like nausea and diarrhea can also manifest. Skin reactions, like rashes, are possible, but less common.
- TNF Inhibitors (e.g., adalimumab, etanercept): Infections, both bacterial and viral, are a substantial risk. Increased risk of serious infections like tuberculosis or opportunistic infections needs to be considered. Also, allergic reactions, skin problems, and rarely, serious heart conditions can occur. Careful monitoring for infections and other side effects is crucial.
Importance of Monitoring for Side Effects
Regular monitoring is critical to detect and manage side effects promptly. This approach minimizes the severity of adverse reactions and allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans.
- Frequency of Checkups: The frequency of monitoring varies based on the specific DMARD, its dosage, and individual patient factors. Routine blood tests and physical examinations are necessary to assess for potential complications. Patients should closely follow their healthcare provider’s instructions for monitoring schedules.
- Early Detection: Early detection of side effects is key. Patients should report any unusual symptoms or changes in their health to their doctor promptly. Early intervention can significantly mitigate potential harm.
- Adapting Treatment: Monitoring allows for adjustments to treatment regimens, reducing the severity or frequency of adverse effects. This flexibility ensures optimal management of rheumatoid arthritis while minimizing the risks of DMARDs.
Long-Term Risks Associated with DMARD Use
While DMARDs are vital for managing rheumatoid arthritis, long-term use can pose certain risks. The risks are often related to the cumulative effects of medications over time.
- Cumulative Toxicity: Some DMARDs, like methotrexate, can accumulate in the body, potentially leading to long-term organ damage if not carefully monitored. Regular checkups and appropriate dosage adjustments are essential.
- Increased Risk of Infections: Certain DMARDs, particularly TNF inhibitors, can weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections. Patients should take precautions to minimize infection risks and promptly report any signs of infection to their healthcare providers.
Table of Common Side Effects, Severity, and Management Strategies
| DMARD | Common Side Effects | Severity | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methotrexate | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, liver damage, lung problems | Mild to severe | Regular liver function tests, blood counts, and dose adjustments as needed. Consider alternative medications if severe side effects persist. |
| Sulfasalazine | Gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, anemia | Mild to moderate | Symptom management, possible dose adjustments, allergy testing if necessary. |
| Leflunomide | Liver damage, gastrointestinal issues, hair loss, skin rashes | Mild to moderate | Regular liver function tests, blood counts, and dose adjustments. Alternative medications if necessary. |
| Hydroxychloroquine | Eye problems (retinopathy), gastrointestinal issues, skin reactions | Mild to moderate | Regular eye examinations, symptom management, and dose adjustments as needed. |
| TNF Inhibitors | Infections, allergic reactions, skin problems, heart conditions | Moderate to severe | Regular monitoring for infections, prompt treatment of infections, and careful monitoring for other side effects. |
Patient Selection and Treatment Strategies
Choosing the right Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug (DMARD) for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a critical aspect of effective treatment. Individual patient factors, including their overall health and specific characteristics, play a significant role in determining the most suitable DMARD. A personalized approach, considering potential risks and benefits, is paramount to achieving optimal outcomes.Understanding the nuances of patient selection and treatment protocols ensures that patients receive the most effective and tailored care possible.
This involves careful consideration of individual responses to different DMARDs, potential side effects, and the patient’s overall health profile. This approach maximizes the chances of achieving remission or significant symptom reduction.
Factors Influencing DMARD Selection
Several factors influence the selection of a specific DMARD for a patient with RA. These factors encompass the patient’s disease activity, previous responses to treatment, and potential comorbidities. Understanding these factors is crucial for tailoring treatment strategies to achieve the best possible outcomes.
DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis can be a game-changer for managing symptoms, but it’s important to understand the potential side effects. Sometimes, seemingly unrelated issues like drool rash, which can be confused with hand-foot-and-mouth disease, can pop up. Knowing the differences is crucial, and resources like drool rash vs hand foot mouth can help you understand the tell-tale signs.
Ultimately, open communication with your doctor about any new or unusual rashes is key when on DMARDs.
- Disease Activity:
- Previous Treatment Responses:
- Comorbidities:
The severity and duration of RA symptoms, as well as the presence of inflammatory markers (e.g., elevated ESR, CRP), directly impact DMARD selection. Early intervention with aggressive treatment strategies is crucial in managing active disease and preventing long-term joint damage.
Patients’ past experiences with different DMARDs provide valuable insights into their potential responses to future treatments. This historical data allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding subsequent treatment strategies. If a patient has had a positive response to a specific DMARD in the past, it’s more likely that they will respond positively to similar drugs.
DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis can be a game-changer, but sometimes underlying conditions like Hashimoto’s disease can complicate things. Understanding how to test for Hashimoto’s disease is crucial, as it can influence the best course of DMARD treatment. For instance, knowing the proper steps for diagnosing Hashimoto’s disease could help your doctor fine-tune your DMARD strategy to maximize effectiveness and minimize side effects.
How to test for Hashimoto’s disease is a great place to start if you’re curious about the process. Ultimately, a holistic approach to managing rheumatoid arthritis, including thorough testing for potential comorbidities, is key.
Patients with RA frequently have other health conditions (comorbidities). These conditions can influence DMARD selection due to potential drug interactions or contraindications. For instance, a patient with a history of liver disease might not be suitable for certain DMARDs that can further stress the liver.
Importance of Considering Patient Comorbidities
Comorbidities are significant factors in DMARD selection, as they can affect drug metabolism, increase the risk of side effects, or contraindicate certain medications. Carefully assessing these conditions is essential for a safe and effective treatment plan.
- Drug Interactions:
- Increased Risk of Side Effects:
- Contraindications:
Certain DMARDs can interact with medications used to treat other conditions, potentially leading to adverse effects. For example, some DMARDs can affect kidney function, so careful monitoring is needed in patients with pre-existing kidney issues. Drug interactions must be evaluated to avoid potential complications.
Patients with comorbidities may be more susceptible to the side effects of DMARDs. For instance, a patient with a history of heart failure might be at higher risk for heart-related complications if prescribed certain DMARDs.
Some DMARDs are contraindicated in patients with specific comorbidities. For example, certain DMARDs are not recommended for individuals with active infections or severe liver disease. It’s crucial to identify such contraindications to prevent adverse health outcomes.
Role of Early Intervention with DMARDs in RA
Early initiation of DMARD therapy is crucial in managing RA. The sooner treatment begins, the greater the chance of preventing joint damage and improving long-term outcomes. Early intervention is critical to mitigate the impact of RA on a patient’s quality of life.
- Preventing Joint Damage:
- Improving Long-Term Outcomes:
Early DMARD therapy aims to halt or slow the progression of joint damage, reducing the long-term disability associated with RA. Early intervention is crucial for reducing the impact of the disease on patients.
Studies consistently demonstrate that early aggressive DMARD therapy significantly improves long-term outcomes in RA. This includes reducing disease activity, improving functional capacity, and enhancing overall quality of life.
Typical Treatment Protocols Involving DMARDs for RA
Treatment protocols for RA typically involve a stepwise approach. This approach starts with a single DMARD and progressively incorporates additional medications or changes in dosage if the initial treatment is ineffective.
- Stepwise Approach:
- Combination Therapy:
- Monitoring and Adjustments:
Treatment usually begins with a single DMARD. If the response is inadequate, a second DMARD may be added, or the dosage of the initial DMARD may be increased. A stepwise approach is important to effectively manage RA.
In some cases, combining different DMARDs can be more effective than using a single DMARD alone. This strategy is frequently employed when a patient does not respond adequately to a single DMARD.
Throughout the treatment process, regular monitoring of disease activity and patient response is essential. This enables healthcare providers to adjust the treatment plan as needed to optimize outcomes and minimize side effects.
Decision-Making Flowchart for DMARD Selection
The following flowchart illustrates a simplified decision-making process for selecting a DMARD for a patient with RA. It emphasizes the importance of considering various factors, including disease activity, comorbidities, and patient preferences.[Flowchart Image Description: A simplified flowchart begins with “Patient with suspected RA.” Branches lead to assessments of disease activity, comorbidities, and previous treatment responses. Based on these factors, different DMARD options are presented, such as methotrexate, TNF inhibitors, or other biologics.
Further considerations include potential side effects, patient preferences, and cost. The flowchart culminates in a chosen DMARD treatment plan, with ongoing monitoring and adjustments as needed. ]
Combination Therapies and Emerging Treatments
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease requiring multifaceted approaches to effectively manage its progression. While single disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can be beneficial, combining therapies often leads to better outcomes and reduced disease activity. This approach is particularly valuable for individuals who do not respond adequately to a single DMARD or those with more aggressive forms of the disease.
Dealing with DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis can sometimes lead to digestive issues, like diarrhea. Finding effective relief is crucial. Fortunately, there are several over-the-counter and prescription options for diarrhea relief, including various medications. For a comprehensive guide on managing diarrhea symptoms, check out this helpful resource on diarrhea relief otc and prescription medications. Understanding these options can significantly improve your overall experience managing rheumatoid arthritis and its potential side effects.
Emerging therapies further enhance the arsenal available for RA treatment, promising new avenues for managing the condition.Combination DMARD strategies represent a key component in optimizing RA treatment. By targeting multiple pathways involved in the disease process, these approaches aim to achieve better disease control and minimize the risk of disease progression. This approach can also potentially reduce the need for high doses of individual DMARDs, minimizing the risk of side effects.
Furthermore, the combined effects of different medications can often lead to synergistic benefits, enhancing the overall therapeutic outcome.
Combination DMARD Regimens
Different combinations of DMARDs are employed, tailored to individual patient needs and disease characteristics. The choice of combination therapy is often based on the patient’s response to prior treatments, disease activity levels, and potential side effects. Commonly used combinations often include methotrexate (MTX) with other DMARDs such as hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), sulfasalazine (SSZ), or TNF inhibitors. The specific combination is carefully selected by the rheumatologist.
Rationale Behind Combining DMARDs
Combining DMARDs is based on the understanding that RA involves multiple inflammatory pathways. Targeting these pathways simultaneously with different mechanisms of action can lead to more effective disease suppression. For example, methotrexate inhibits cell proliferation, while TNF inhibitors block tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), a key inflammatory cytokine. By combining these agents, the overall inflammatory response is mitigated more comprehensively, resulting in a greater chance of achieving remission.
Examples of Combination DMARD Regimens
A common combination regimen involves methotrexate with hydroxychloroquine and sulfasalazine. This triad often provides effective disease control in early-stage RA. Another frequently used combination is methotrexate with a biologic DMARD, such as a TNF inhibitor. This approach is often employed in cases where the disease is more aggressive or not adequately controlled with MTX alone. Specific combinations are chosen based on individual patient characteristics and treatment history.
Emerging Therapies for RA
Emerging therapies for RA are continuously evolving, and new approaches are being explored. These therapies often target specific pathways involved in RA pathogenesis. For example, some therapies are focused on inhibiting B-cell activity or modulating the immune system’s response. These newer treatments hold significant promise for improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects. However, the long-term efficacy and safety of these emerging therapies need to be fully evaluated through extensive clinical trials.
Comparison of Combination DMARD Therapies
| Combination Therapy | Rationale | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Methotrexate + Hydroxychloroquine + Sulfasalazine | Targets multiple inflammatory pathways with diverse mechanisms of action. | Often effective in early-stage RA, leading to significant disease reduction. |
| Methotrexate + TNF Inhibitor | Synergistic effect of inhibiting cell proliferation and blocking TNF-α. | High efficacy in aggressive RA, often leading to remission. |
| Methotrexate + JAK inhibitor | Targets specific intracellular signaling pathways involved in inflammation. | Demonstrates promising results in patients who have not responded to other DMARDs. |
Monitoring and Management of DMARD Therapy
Staying on top of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment is crucial, and careful monitoring of DMARD therapy is essential for achieving optimal outcomes and minimizing side effects. Consistent monitoring allows for adjustments to the treatment plan, ensuring patients receive the most effective and safe dose of medication. This is a dynamic process, requiring collaboration between patients, healthcare providers, and potentially other specialists.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring during DMARD treatment is vital for assessing the effectiveness of the therapy and identifying any potential adverse reactions. This allows for timely interventions and adjustments to the treatment plan, preventing complications and improving patient outcomes. Monitoring also facilitates the early detection of side effects, enabling prompt management and minimizing their impact. Furthermore, regular assessments help track disease progression and adapt treatment strategies as needed.
Methods for Monitoring DMARD Efficacy and Side Effects
Monitoring DMARD efficacy and side effects involves a multifaceted approach. Clinical assessments, including physical examinations and patient questionnaires, play a significant role. These evaluations provide valuable insights into disease activity and the patient’s overall well-being. Laboratory tests, such as blood tests to measure inflammatory markers (e.g., ESR, CRP), are crucial for quantifying disease activity and response to treatment.
Imaging techniques, like X-rays or MRI scans, are used to evaluate joint damage and monitor structural changes over time.
Adjusting DMARD Dosages Based on Patient Response, Dmards for rheumatoid arthritis
Treatment adjustments are based on the patient’s response to the DMARD therapy. Regular monitoring helps healthcare professionals determine whether the current dose is effective in controlling symptoms and reducing inflammation. If the patient is not responding adequately, the dosage may need to be increased or a different DMARD might be considered. Conversely, if the patient experiences significant side effects, the dosage may need to be reduced or the treatment modified.
This process is iterative, with adjustments made based on ongoing assessment and feedback.
Strategies for Managing Adverse Effects of DMARDs
Managing adverse effects of DMARDs is critical to maintaining patient comfort and adherence to the treatment plan. Strategies include proactive monitoring, prompt intervention, and potentially modifying the treatment regimen. Close communication with the healthcare team is paramount, enabling the early identification and management of any adverse effects. Support from a rheumatologist, pharmacist, or other relevant healthcare professionals can be valuable.
DMARD Therapy Monitoring Checklist for RA Patients
This checklist helps track important aspects of DMARD therapy for patients with RA.
- Date of Assessment: Records the date of each monitoring session.
- Patient Demographics: Includes age, sex, and relevant medical history.
- Symptoms: Details any current symptoms, including pain, stiffness, swelling, and fatigue.
- Physical Examination: Includes joint assessments, range of motion, and overall physical status.
- Laboratory Results: Documents results for inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP), blood counts, and other relevant tests.
- Imaging Findings: Summarizes findings from X-rays, MRI scans, or other imaging studies.
- DMARD Medication: Records the specific DMARD, dose, and frequency.
- Adverse Effects: Notes any side effects experienced, including gastrointestinal issues, skin reactions, or other complications.
- Treatment Adjustments: Documents any changes made to the DMARD regimen, including dose adjustments or switching to a different medication.
- Patient Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs): Includes patient assessments of disease impact and quality of life, such as questionnaires or visual analog scales.
- Patient Compliance: Tracks the patient’s adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.
- Follow-up Appointments: Schedules and records follow-up appointments.
This comprehensive checklist ensures a structured and thorough approach to monitoring DMARD therapy, facilitating proactive management of RA.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, DMARDs play a vital role in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. By understanding the various DMARD types, their effectiveness, potential risks, and treatment strategies, patients and healthcare professionals can collaborate to achieve optimal outcomes. Early intervention, personalized treatment plans, and diligent monitoring are key to effectively managing this complex condition. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a valuable resource for navigating the intricacies of DMARD therapy.