Anthony wilson my journey with type 2 diabetes – Anthony Wilson’s journey with type 2 diabetes sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. He chronicles his experience from initial diagnosis to lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments, and the emotional and mental impact of managing the condition. His personal account highlights the challenges and triumphs of living with diabetes, providing valuable insights and inspiration for others.
This blog post delves into Anthony’s personal story, exploring his journey in detail, covering everything from the initial diagnosis and its impact on his life, to the lifestyle changes he implemented and the emotional toll he faced. He shares his coping mechanisms and the support systems that played a crucial role in his journey. The post also discusses the medical treatments and therapies he utilized, including alternative approaches.
Ultimately, the narrative explores the lessons learned, the impact on his life, and how it inspired others.
Introduction to Anthony Wilson’s Journey: Anthony Wilson My Journey With Type 2 Diabetes
Anthony Wilson, a dedicated family man and avid outdoorsman, found his life significantly altered by a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. His journey, filled with both challenges and triumphs, is a testament to the resilience of the human spirit and the importance of proactive health management. His experiences offer valuable insights into the day-to-day realities of living with this chronic condition.The initial diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, which arrived unexpectedly, caused a profound shift in Anthony’s life.
He had to re-evaluate his lifestyle, dietary habits, and daily routines. This change required adjustments to both his personal and professional life. He found himself grappling with the implications of the disease, learning about the necessary lifestyle modifications and treatment plans. The impact extended beyond the immediate physical symptoms, touching on emotional well-being and social dynamics.
Initial Diagnosis and Impact
Anthony’s diagnosis came after a routine physical examination, revealing elevated blood sugar levels. This unexpected result led to a series of tests and consultations with specialists, ultimately confirming the type 2 diabetes diagnosis. The news profoundly impacted Anthony’s life, causing anxiety and uncertainty about his future. He struggled with the initial shock, but was determined to learn about the condition and actively participate in managing it.
He felt a sense of responsibility to understand his condition thoroughly and to work towards maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Anthony Wilson’s journey with type 2 diabetes has been a fascinating one, filled with both challenges and triumphs. One crucial aspect of managing the condition is being vigilant about potential complications, like liver damage. It’s important to understand the signs of liver damage, as they can sometimes be subtle. Checking for these indicators is a vital part of ongoing health monitoring for anyone living with diabetes, like Anthony.
Learning about the signs of liver damage can help people like Anthony proactively manage their health. signs of liver damage Understanding these early warning signals can help in seeking timely medical attention and ensure better overall health outcomes. Anthony’s story reminds us of the importance of proactive health management.
Early Struggles and Challenges
The initial period of managing type 2 diabetes was fraught with challenges. Anthony struggled with understanding the complexities of dietary restrictions and the importance of regular exercise. He grappled with the adjustments to his eating habits, finding it difficult to adapt to the recommended low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet. He also faced the physical challenge of incorporating regular exercise into his busy schedule.
Furthermore, he felt isolated, initially, as he navigated the medical system and the changes in his daily life.
Motivations and Driving Forces
Anthony’s primary motivation for documenting his journey was to share his experiences and offer support to others facing similar challenges. He felt a strong desire to connect with a community of people with type 2 diabetes, to learn from their experiences, and to provide encouragement. He believed that sharing his story could help others feel less alone and more empowered to take control of their own health.
He wanted to provide a relatable account of the struggles and triumphs in managing the condition, and provide realistic advice and strategies.
Scope and Goals of the Journey
Anthony’s journey with type 2 diabetes aims to provide practical advice and support to others facing a similar diagnosis. His goal is to demonstrate that a positive outcome is achievable through a combination of medical guidance, lifestyle changes, and a strong support network. He intends to share his experiences, providing insights into the emotional, physical, and social aspects of living with the condition.
He plans to emphasize the importance of consistent medical monitoring, healthy eating habits, and regular exercise in achieving optimal health outcomes. He also seeks to foster a sense of community and shared experience among individuals affected by type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Changes and Adaptations

Embarking on a journey with type 2 diabetes necessitates significant lifestyle adjustments. Anthony Wilson’s experience highlights the crucial role of these changes in managing the condition effectively and improving overall well-being. The following sections detail the dietary modifications, exercise routines, meal planning strategies, and the impact these changes had on his blood sugar levels.Anthony’s approach to managing his type 2 diabetes focused on a holistic strategy encompassing dietary changes, exercise, and mindful meal planning.
He recognized that consistent adherence to these strategies was key to achieving and maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Dietary Changes
Anthony made significant dietary modifications to control his blood sugar levels. He prioritized whole, unprocessed foods over highly processed options. This involved incorporating more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains into his diet while minimizing refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats. He replaced sugary cereals with oatmeal, swapped white bread for whole-grain bread, and substituted sugary snacks with fruits and vegetables.
Exercise Routines
Anthony understood the importance of regular physical activity in managing type 2 diabetes. He implemented a consistent exercise routine that incorporated both aerobic and resistance training. His aerobic exercises included brisk walking, swimming, and cycling, while his resistance training involved weightlifting and bodyweight exercises. He aimed for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Anthony Wilson’s journey with Type 2 diabetes has been a real rollercoaster, full of ups and downs. He’s learned a lot about managing his blood sugar levels, but recently, he’s been focusing on ways to boost his immune system, specifically increasing white blood cells. Learning about the importance of increase white blood cells has been a crucial part of his ongoing research and understanding of his overall health.
This knowledge is helping him better navigate his diabetes management plan and stay healthier overall.
He recognized that consistent exercise improved insulin sensitivity and helped manage his weight.
Meal Planning Approaches
Anthony explored several meal planning approaches. He experimented with the Mediterranean diet, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, and the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which focuses on reducing sodium intake. He also used various online resources and apps to create meal plans that aligned with his dietary needs and preferences.
He found that meal prepping and portion control were crucial components of his successful approach. He learned to understand portion sizes and how different foods affected his blood sugar levels.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels
Implementing these lifestyle changes had a demonstrably positive impact on Anthony’s blood sugar levels. His blood glucose readings became more stable, and he experienced fewer instances of high or low blood sugar. He tracked his progress meticulously, monitoring his blood sugar levels before and after meals and exercise. Regular monitoring and adjustments to his plan based on the results were essential to maintaining optimal control.
Before and After Impact of Dietary Changes
| Aspect | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Glucose Levels (fasting) | 120-160 mg/dL (variable) | 80-110 mg/dL (consistent) |
| HbA1c | 8.5% | 6.5% |
| Weight | 210 lbs | 185 lbs |
| Energy Levels | Low and fluctuating | Stable and consistent |
| Overall Health | Increased fatigue, frequent headaches | Increased energy, reduced headaches |
Emotional and Mental Well-being
Living with type 2 diabetes can be emotionally challenging. The constant need for monitoring, medication management, dietary restrictions, and lifestyle adjustments can take a toll on one’s mental and emotional state. Navigating these changes requires resilience, self-compassion, and a strong support system. Anthony’s journey highlights the importance of prioritizing emotional well-being alongside physical health management.The emotional burden of managing a chronic condition like type 2 diabetes can manifest in various ways.
It can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even depression. The unpredictability of blood sugar levels, the fear of complications, and the need for constant vigilance can be overwhelming. Anthony’s experience demonstrates the critical role that coping mechanisms and support systems play in navigating these challenges.
Coping Mechanisms for Stress and Anxiety
Anthony employed a multifaceted approach to manage stress and anxiety. He recognized the importance of acknowledging and accepting the emotional impact of his condition. This involved journaling, reflecting on his feelings, and understanding the triggers that exacerbated his emotional responses. Crucially, he focused on building positive coping mechanisms.
Support Systems
Anthony’s journey underscores the significance of support systems. He actively sought and maintained relationships with family members, friends, and support groups. These connections provided a safe space to share experiences, receive encouragement, and gain perspective on his journey. He also benefited from professional support, including counseling sessions, which helped him process his emotions and develop healthy coping strategies.
The support systems were vital in providing emotional stability and reducing feelings of isolation.
Importance of Self-Care and Mindfulness
Anthony understood the importance of self-care and mindfulness in managing his emotional well-being. He incorporated regular exercise, meditation, and spending time in nature into his routine. These practices helped him manage stress, reduce anxiety, and promote a sense of calm and balance. He also focused on cultivating a positive mindset, emphasizing gratitude and self-compassion.
Effectiveness of Coping Mechanisms
| Coping Mechanism | Effectiveness (Scale: 1-5, 5 being most effective) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Journaling | 4 | Provided a structured outlet for emotional expression and reflection, helping to identify patterns and triggers. |
| Meditation | 3 | Reduced anxiety and promoted a sense of calm, aiding in managing stress related to blood sugar fluctuations. |
| Support Groups | 5 | Offered a platform for shared experiences, encouragement, and peer support, fostering a sense of community and belonging. |
| Professional Counseling | 4 | Provided a structured environment for processing emotions, developing coping strategies, and addressing underlying anxieties related to the condition. |
| Regular Exercise | 4 | Improved physical and mental well-being, providing a healthy outlet for stress and promoting a sense of accomplishment. |
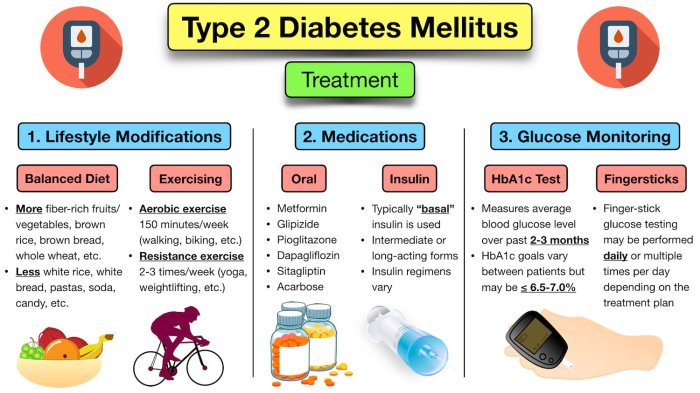
Medical Treatments and Therapies
Navigating Type 2 diabetes requires a multifaceted approach, and a crucial part of that journey involves understanding and implementing appropriate medical treatments and therapies. Anthony’s experience highlights the importance of personalized care, tailoring strategies to individual needs and responses. He diligently explored various options to manage his condition effectively.
Medication Regimen
Anthony’s initial treatment plan focused on oral medications to control blood glucose levels. This approach aimed to achieve optimal blood sugar control without resorting to injectable therapies initially. The effectiveness of these medications varied, and adjustments were made over time to maintain stable glucose levels. Medication adherence played a critical role in achieving and maintaining health goals.
Role of Insulin Therapy
As Anthony’s condition progressed and oral medications alone were insufficient to manage his blood glucose, he transitioned to insulin therapy. This decision was driven by the need for more aggressive glucose control to prevent long-term complications. Insulin therapy, while requiring careful management and potential adjustments, proved crucial in achieving target blood glucose levels.
Alternative Therapies
While conventional medicine formed the cornerstone of Anthony’s treatment, he also explored complementary and alternative therapies. These included dietary supplements, mindfulness practices, and regular exercise. The rationale behind these choices was to support overall well-being and potentially enhance the efficacy of his prescribed medications. These complementary therapies were integrated into his lifestyle, not as a replacement for medical care, but as a means of holistic support.
Impact on Overall Well-being
Medication adherence and management significantly impacted Anthony’s overall well-being. The consistency in taking prescribed medications, coupled with regular monitoring and adjustments as needed, proved crucial in controlling blood glucose levels and preventing potential complications. This allowed Anthony to participate more fully in activities he enjoyed, contributing to a positive outlook on his health journey.
Detailed Medication and Therapy Table
| Medication/Therapy | Rationale | Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Common first-line treatment for Type 2 diabetes, reducing glucose production in the liver. | Generally well-tolerated, effective in lowering blood glucose levels. | Gastrointestinal upset (e.g., diarrhea, nausea) in some patients. |
| Insulin (e.g., Humalog, Lantus) | Used when blood glucose control is not adequate with oral medications. Provides rapid or sustained insulin action. | Effective in achieving tight glucose control. | Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain, allergic reactions. |
| Dietary Supplements (e.g., chromium picolinate) | Potentially supports glucose metabolism. | Potential improvements in insulin sensitivity. | Limited scientific evidence supporting significant benefit. Potential interactions with other medications. |
| Mindfulness Practices (e.g., meditation) | To manage stress and improve emotional well-being. | May contribute to reduced stress levels, potentially impacting blood glucose regulation indirectly. | No direct negative side effects, but individual responses vary. |
Learning and Growth
Anthony’s journey with type 2 diabetes has been a profound learning experience, transforming his understanding of health and wellness. He’s embraced the challenges, and his journey showcases the power of adaptation, resilience, and continuous learning in managing a chronic condition. This section delves into the key lessons Anthony has learned, highlighting the role of education and support in his journey.
Key Lessons Learned
Anthony’s journey has yielded valuable lessons, shaping his perspective on health management and self-care. These lessons extend beyond the immediate challenges of diabetes management, impacting his overall approach to life. He’s discovered the importance of proactive engagement with his health and the profound impact of support networks.
- Understanding the Importance of Consistent Self-Monitoring: Anthony recognized that meticulous monitoring of blood sugar levels, diet, and activity levels is crucial. This allows him to identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to his treatment plan, leading to better control of his condition.
- Adapting Diet and Lifestyle for Optimal Management: Anthony discovered that adjusting his diet and lifestyle significantly impacted his blood sugar levels. This required careful consideration of portion sizes, carbohydrate intake, and regular physical activity. He learned to prioritize nutrient-dense foods and balanced meals.
- The Significance of a Supportive Network: Anthony realized that having a strong support system—including family, friends, and healthcare professionals—is vital. Sharing experiences and seeking guidance from others helped him navigate the challenges of managing diabetes effectively.
- Prioritizing Mental Well-being: Managing a chronic condition like type 2 diabetes can be emotionally taxing. Anthony discovered that prioritizing mental well-being through mindfulness, stress reduction techniques, and seeking emotional support is critical for overall health and adherence to his treatment plan.
- The Value of Continuous Learning: Anthony understands that diabetes management is an ongoing process. He appreciates the importance of staying updated on the latest research, treatments, and best practices in diabetes care.
Impact of Learning on Health and Wellness
Anthony’s experience with type 2 diabetes has profoundly impacted his understanding of health and wellness. He now views health as a holistic concept encompassing physical, mental, and emotional well-being. He appreciates the interconnectedness of these factors and understands that managing diabetes effectively requires a multi-faceted approach.
Anthony Wilson’s journey with Type 2 diabetes has been deeply personal, and understanding the potential genetic factors involved is key. Learning about what a DNA test can reveal about predispositions to certain conditions, like what is a dna test , is crucial for managing his health proactively. He’s exploring these options to potentially gain a better understanding of his own unique health profile and how it relates to his diabetes journey.
| Lesson Category | Key Lesson | Impact on Anthony’s Life |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Health | Understanding the importance of consistent self-monitoring and adapting diet and lifestyle | Improved blood sugar control, increased energy levels, and enhanced overall physical well-being. |
| Mental Well-being | Prioritizing mental well-being and recognizing the importance of emotional support | Reduced stress levels, improved mood, and enhanced coping mechanisms for managing the challenges of diabetes. |
| Social Well-being | Recognizing the significance of a supportive network | Strengthened relationships, gained valuable insights and support from others facing similar challenges, and fostered a sense of community. |
| Lifelong Learning | The value of continuous learning and staying updated on the latest advancements in diabetes care. | Improved understanding of diabetes management, enhanced decision-making, and confidence in adapting to future developments in the field. |
Impact and Inspiration
Anthony’s journey with type 2 diabetes has not only transformed his life but has also sparked a ripple effect of inspiration and awareness within his community and beyond. His willingness to share his experiences, challenges, and triumphs offers a powerful message of hope and resilience for others facing similar health conditions. He’s become a beacon of encouragement, demonstrating that managing diabetes is achievable with dedication and the right support system.Sharing personal narratives like Anthony’s can have a profound impact on individuals living with type 2 diabetes.
Hearing relatable stories of struggles and successes fosters a sense of community and understanding. It encourages open dialogue, reducing the isolation often associated with chronic illness and promoting a greater sense of shared experience. This can lead to increased motivation and engagement in managing the condition, as individuals feel less alone in their journey.
Inspiring Others, Anthony wilson my journey with type 2 diabetes
Anthony’s story has resonated deeply with numerous individuals facing similar health challenges. His commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing his diabetes through consistent effort has been particularly impactful. He serves as a role model, demonstrating that even with the complexities of diabetes, a fulfilling and active life is achievable. This encouragement extends beyond immediate circles, fostering a wider understanding of the disease’s impact.
Impact on the Wider Community
Anthony’s journey holds significant value for the wider community. His willingness to share his story elevates the conversation around type 2 diabetes. By openly discussing the emotional, physical, and social aspects of the condition, Anthony helps to reduce stigma and promotes empathy. This is crucial in creating a supportive environment where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and support. The sharing of experiences, including challenges and triumphs, can empower others and break down barriers to effective management and treatment.
Public Awareness and Understanding
Anthony’s journey has undeniably contributed to raising public awareness and understanding of type 2 diabetes. His transparent approach to discussing his experiences fosters empathy and dispels myths surrounding the disease. By sharing personal anecdotes, he humanizes the condition, moving beyond statistics and scientific jargon to demonstrate the real-life consequences and the human impact of living with diabetes. This shift in perspective is crucial in fostering more compassionate and informed public discourse about the disease.
Shaping Future Goals and Aspirations
Anthony’s journey has profoundly shaped his future aspirations. His experience has underscored the importance of proactive health management and the significance of fostering a supportive community. This newfound perspective has inspired him to advocate for greater awareness and resources for individuals with type 2 diabetes. He envisions a future where individuals feel empowered and supported in managing their health conditions, free from stigma and with access to comprehensive care.
Illustrative Content
Anthony’s journey with type 2 diabetes is a testament to the power of adaptation and resilience. Visual representations of his daily life, support network, and medical choices can paint a more complete picture of his experience. These images showcase the significant changes he made and the profound impact these changes had on his overall well-being.
A Day in Anthony’s Life
Imagine a vibrant image, showcasing Anthony’s morning routine. He’s meticulously preparing a healthy breakfast, incorporating ingredients from his meal plan. Fresh fruit, lean protein, and whole grains are clearly visible, contrasted against a backdrop of natural light streaming into his kitchen. He’s calmly checking his blood sugar levels using a device that sits prominently on the countertop.
A water bottle, a reminder of his commitment to hydration, is placed beside it. His face reflects a quiet determination and peace, a clear indication of the positive changes he’s made in his daily routine. The emotional tone is one of calm acceptance and proactive management, reflecting the positive impact of these changes on his overall well-being.
The Strength of Community
A supportive image depicts a group of individuals, all engaged in a discussion at a community support group meeting. Anthony is smiling and nodding attentively, actively participating in the conversation. The faces around him convey empathy and understanding. A large whiteboard is visible, showing a variety of resources, tips, and success stories shared by the group members.
The image conveys a sense of unity and shared experience, illustrating the invaluable support that Anthony found in his community, which is crucial in managing type 2 diabetes. The emotional tone is warm, supportive, and empowering, highlighting the strength and encouragement found in shared experiences.
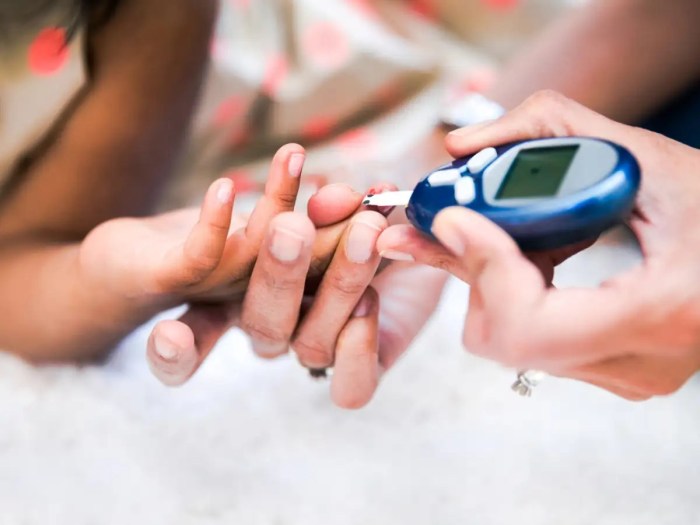
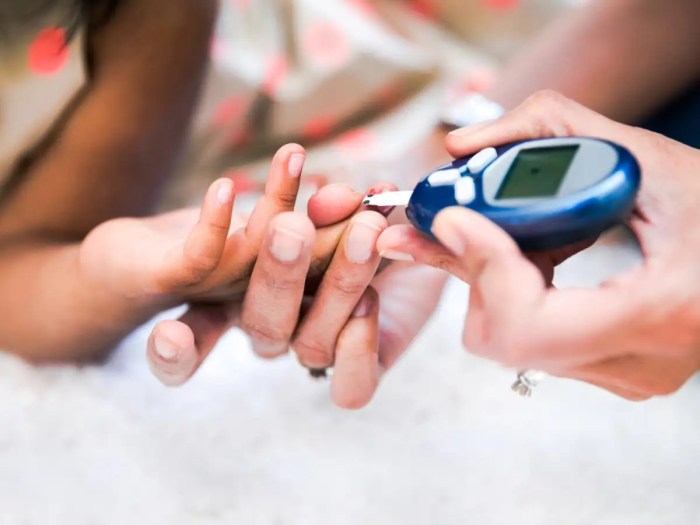
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
A close-up image of a blood sugar monitoring device is shown, displaying a recent reading. The clear digital display shows a healthy blood sugar level, signifying Anthony’s successful management of his condition. The device’s small size and simple design suggest ease of use and accessibility, highlighting the convenience and integration of this technology into his daily life. The image also shows the importance of regular monitoring and the reassurance that comes from knowing his blood sugar levels.
This provides the crucial data for effective management and adjustments to his lifestyle and treatment.
Adapting to a New Meal Plan
A colourful and visually appealing image of a meal plan is displayed, showcasing a variety of nutritious foods that are now a staple in Anthony’s diet. A colourful plate with grilled fish, mixed greens, and a side of steamed vegetables is prominent in the image. A detailed chart showing portion sizes and carbohydrate counts accompanies the plate. This image illustrates the positive changes Anthony made in his dietary choices.
The emphasis is on variety and balance, highlighting the enjoyable and satisfying aspect of adapting to a new meal plan, which positively impacts his overall health and well-being. The image conveys a sense of control and empowerment over his diet, illustrating the significant impact these dietary changes have had on his life.
Epilogue

Anthony Wilson’s journey with type 2 diabetes serves as a powerful testament to resilience and determination. His story showcases the multifaceted aspects of living with this condition, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle adjustments, emotional well-being, and the support of loved ones. By sharing his experiences, Anthony inspires hope and understanding for others facing similar challenges. Ultimately, his journey highlights the power of personal narratives in fostering empathy and promoting a more supportive community.