Tresiba vs lantus what s the difference – Delving into tresiba vs lantus what’s the difference, this exploration uncovers the nuances between these two long-acting insulin analogs. Understanding their distinct pharmacokinetic profiles, potential side effects, and optimal use cases is crucial for effective diabetes management. This comprehensive guide will dissect the specifics of each medication,…
Tag: Diabetes
Levemir Discontinued? How to Switch Insulin
Levemir discontinued how to switch insulin? This comprehensive guide dives into the process of transitioning from Levemir to a different insulin regimen. We’ll explore why your doctor might choose to discontinue Levemir, the steps involved in the switch, and important considerations for specific patient groups. Understanding the nuances of insulin management is crucial, and this…
Tirzepatide Zepbound Lowers Blood Pressure
Tirzepatide Zepbound reduces blood pressure, a promising development in managing hypertension. This innovative medication, a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, offers a novel approach to blood pressure regulation, potentially impacting not just blood pressure but also metabolic health and weight management. Early clinical trials are exploring its efficacy and safety profile, comparing it to…
Diabetes Nutrition and Weight Loss Your Guide
Diabetes nutrition and weight loss is a crucial aspect of managing this condition effectively. Understanding the connection between food choices, portion sizes, and activity levels is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight while controlling blood sugar. This guide delves into balanced nutrition plans, effective weight loss strategies, and considerations for diverse populations, all…
Tirzepatide Heart Failure Data A Deep Dive
Tirzepatide heart failure data is generating considerable interest, raising important questions about the drug’s potential cardiovascular risks. This comprehensive analysis explores the evidence, examining key studies, potential mechanisms, and the clinical implications for patients and healthcare professionals. Understanding the complexities of this emerging data is crucial for informed decision-making. This overview delves into the mechanism…
Blood Glucose Test Strips Levels and Process Explained
Blood glucose test strips levels and process are crucial for managing blood sugar. This exploration dives into the world of these strips, from their function and various types to understanding the results and managing fluctuations. We’ll cover the process, typical levels, and factors influencing blood sugar, ultimately providing a comprehensive guide for effective monitoring. This…
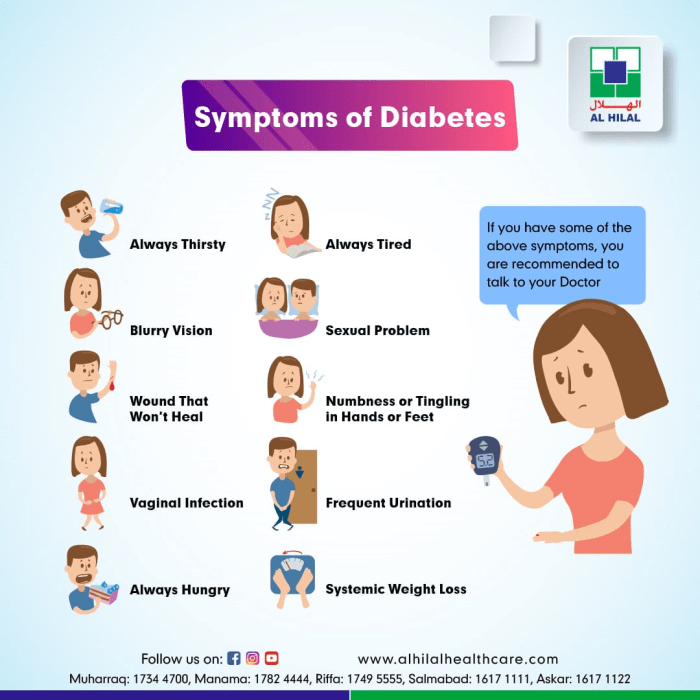
Causes of Numbness and Tingling A Deep Dive
Causes of numbness and tingling can range from seemingly minor issues to more serious underlying conditions. This exploration delves into the various factors that can lead to these sensations, from common vitamin deficiencies to more complex neurological problems. Understanding these causes is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. We’ll examine everything from peripheral neuropathy, a…
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome A Deep Dive
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) is a serious complication of diabetes, characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels without the presence of ketones. This often occurs in individuals with type 2 diabetes, particularly those who aren’t managing their blood sugar well. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for anyone at risk….
Zepbound Tirzepatide Diabetes Risk A Deep Dive
Zepbound tirzepatide diabetes risk is a critical area of concern for those managing diabetes. This in-depth look examines the potential risks associated with tirzepatide, a medication increasingly used to control blood sugar. We’ll explore its mechanism of action, potential side effects, risk factors, and the latest research. Understanding these risks is crucial for informed decision-making…
Diabetes and Intermittent Fasting A Deep Dive
Diabetes and intermittent fasting are two significant health concepts that are increasingly interconnected. This exploration delves into the potential benefits and risks of integrating intermittent fasting (IF) into diabetes management. We’ll examine various IF methods, their impact on blood glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, and overall health, along with crucial considerations for safe implementation. Understanding the…