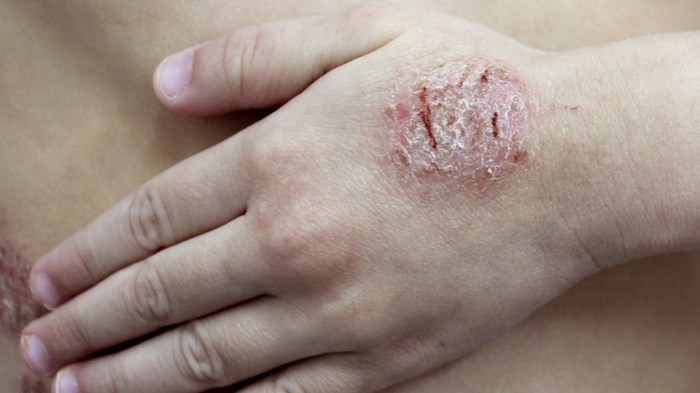
Eczema and COVID vaccine: This post explores the complex relationship between eczema and the body’s response to COVID-19 vaccines. We’ll delve into potential links between eczema, the immune system, and vaccine reactions. Understanding this interplay is crucial for both individuals with eczema and healthcare professionals.
The research examines potential correlations between eczema, vaccination rates, and specific reactions to COVID-19 vaccines. Different factors that could influence the connection will also be examined, like specific vaccine types, pre-existing health conditions, and patient demographics. We’ll also touch on the importance of communication between patients and their doctors.
Relationship between Eczema and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic spurred a global effort to develop and deploy vaccines. Understanding potential interactions between pre-existing conditions and vaccine responses is crucial for tailoring strategies and addressing concerns. This exploration delves into the current understanding of the relationship between eczema and the immune response to COVID-19 vaccines.Existing research on the potential links between eczema and the immune response to COVID-19 vaccines is still evolving.
While some studies suggest a possible association, a definitive causal link remains elusive. Further research is needed to fully understand the nuances of this interaction. Early findings suggest that individuals with eczema may have slightly different immune responses to vaccination compared to those without eczema.
I’ve been doing some research on eczema and the COVID vaccine, and it seems like a lot of people are curious about potential connections. While there’s no definitive link, it’s always a good idea to monitor your body’s response to new things. For instance, if you notice a concerning rise in your CRP levels, it’s crucial to understand what to do when your CRP is high.
Knowing what to do when your CRP is high can help you manage any potential inflammatory reactions, which is important for anyone, especially those with pre-existing conditions like eczema. what to do when your crp is high This can help provide a better understanding of potential inflammatory responses, which could be a factor to consider with the COVID vaccine, and eczema.
Potential Mechanisms
Several potential mechanisms might explain observed correlations between eczema and the immune response to COVID-19 vaccines. One possibility involves the interplay between the skin barrier dysfunction associated with eczema and the immune system. Eczema often leads to increased skin permeability, which could theoretically influence the body’s overall immune response to vaccines. Furthermore, individuals with eczema may have a history of inflammatory responses, which could potentially impact how their immune system reacts to the vaccine.
Comparison of Prevalence and Vaccination Rates
The following table provides a hypothetical comparison of eczema prevalence and vaccination rates in different populations. Real-world data on vaccination rates in populations with varying eczema prevalence is scarce and requires specific epidemiological studies.
While researching eczema and the COVID vaccine, I stumbled upon some fascinating insights into how similar conditions like lung cancer surgery can impact overall well-being. The quality of life after lung cancer surgery, as detailed in this resource, quality of life after lung cancer surgery , really highlighted the importance of considering physical and mental health aspects. This made me think about how eczema, and its potential impact on someone’s daily life, might relate to the body’s reaction to vaccines.
Further research is needed to fully connect these topics, but the connection is intriguing.
| Population Group | Estimated Prevalence of Eczema (%) | Estimated Vaccination Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| General Population | 10-20 | 80-90 |
| Children | 10-25 | 75-95 |
| Individuals with a history of severe eczema | >20 | 70-85 |
| Elderly Population | 5-15 | 70-85 |
Potential Confounding Factors
Several factors could confound the relationship between eczema and COVID-19 vaccine responses. These include the severity of eczema, the age of the individual, the specific type of vaccine administered, and concomitant medical conditions. For instance, individuals with severe eczema might have a more pronounced immune response to the vaccine, or perhaps a different immune response than those with milder eczema.
Recent studies on eczema and the COVID vaccine are fascinating, but it’s also important to remember the incredible impact we can have by considering organ donation. Many people are choosing to donate organs, tissues, or their body to help others, and if you’re considering it, you can learn more about the process at donate organs tissue or body.
Ultimately, the connection between eczema and the COVID vaccine remains a subject of ongoing research, but the potential for positive change through organ donation is undeniable.
The specific vaccine type (mRNA or viral vector) could also play a role. Additionally, pre-existing medical conditions or concurrent medications could influence the overall immune response to vaccination. Moreover, lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, may also contribute. Data collection and analysis that account for these potential confounding factors are crucial to understanding the true relationship.
Eczema Symptoms and Vaccination Reactions
Understanding the potential interplay between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination reactions is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes. Individuals with eczema may experience varying responses to vaccines, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and proactive management strategies. This section delves into the potential impact of pre-existing eczema on vaccine reactions, comparing reported side effects, and outlining strategies for managing potential adverse events.Pre-existing eczema can influence the body’s response to vaccinations.
The skin’s compromised barrier function in eczema might lead to heightened sensitivity and potentially more pronounced reactions at the injection site, or even systemically. This is not to say that every individual with eczema will experience more severe reactions; however, recognizing this potential difference is essential for informed decision-making and appropriate care.
Impact of Eczema on Localized Reactions
Individuals with eczema may exhibit a greater likelihood of localized reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, pain, or itching. The intensity of these reactions can vary depending on the individual’s eczema severity and the specific vaccine administered. In some cases, the reaction might persist for a longer duration than in individuals without eczema. This increased sensitivity is likely linked to the skin’s compromised barrier function in eczema.
Impact of Eczema on Systemic Reactions
Systemic reactions, such as fever, chills, fatigue, or headache, can also occur following vaccination. While these reactions are generally mild and temporary, their severity may potentially be influenced by pre-existing eczema. Monitoring for any unusual or prolonged systemic reactions in individuals with eczema is vital. The body’s immune response, already active in managing eczema, may interact with the vaccine’s components, potentially affecting the systemic response.
Impact of Eczema on Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions, ranging from mild hives to more severe anaphylaxis, are rare but possible complications following any vaccination. Individuals with a history of eczema and allergies may have a slightly elevated risk of developing allergic reactions to vaccines. However, this is not a definitive rule, as many individuals with eczema do not experience allergic reactions. The importance of prompt medical attention in case of any allergic reaction is paramount.
Strategies for Managing Potential Adverse Reactions
Early communication with healthcare providers is key for managing potential adverse reactions. Individuals with eczema should inform their healthcare provider of their condition before receiving any vaccination. This allows for tailored monitoring and management strategies to mitigate potential risks. Prioritizing preventative measures, such as applying a cold compress to the injection site, or using over-the-counter pain relievers as advised by a doctor, can help manage discomfort.
Comparison of Reported Side Effects
Extensive studies and reported data on the incidence of side effects in individuals with and without eczema are limited, and more research is needed. While more research is needed to provide precise comparisons, general observations suggest that localized reactions might be more frequent and potentially more intense in individuals with eczema. Systemic reactions, though less common, may also differ in their intensity and duration.
This requires continued monitoring and research to establish more concrete comparisons.
Common Eczema Symptoms and Possible Vaccine-Related Reactions
| Eczema Symptoms | Possible Vaccine-Related Reactions |
|---|---|
| Dry, itchy skin | Redness, swelling, pain, or itching at the injection site |
| Inflamed, cracked skin | Fever, chills, fatigue, or headache |
| Skin rashes | Hives, rash, or other allergic reactions |
| Skin lesions | Localized swelling and inflammation |
Vaccination Recommendations for Individuals with Eczema
Navigating the complexities of COVID-19 vaccination can be challenging, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions like eczema. Understanding the potential interactions and appropriate precautions is crucial for ensuring a safe and effective vaccination experience. This section provides a summary of current recommendations, specific considerations, and the importance of open communication between healthcare providers and patients with eczema.The COVID-19 vaccines are generally safe and effective for most individuals, including those with eczema.
However, some individuals may experience reactions that are more pronounced or require specific attention. This necessitates a tailored approach to vaccination recommendations, taking into account the individual’s specific eczema characteristics and overall health status.
Current Recommendations
Vaccination is highly recommended for individuals with eczema, aligning with broader public health guidelines. The benefits of vaccination, including protection against severe COVID-19, generally outweigh any potential risks for most people with eczema.
Specific Precautions and Considerations
Individuals with eczema should be aware of potential vaccination reactions, which can range from mild to moderate. Some individuals might experience localized reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, or pain. These reactions are often temporary and resolve on their own. More significant reactions, although rare, are possible. It’s important to discuss any concerns or unusual reactions with a healthcare provider.
A pre-existing skin condition like eczema may increase the likelihood of skin reactions to the vaccine, but this doesn’t necessarily mean that the vaccine should be avoided.
Importance of Open Communication
Open and honest communication between healthcare providers and patients with eczema is paramount. This includes discussing the patient’s specific eczema type, severity, and any history of adverse reactions to medications or vaccines. This proactive dialogue allows healthcare providers to tailor vaccination recommendations and address any concerns. This communication should be ongoing, encompassing discussions before, during, and after the vaccination process.
Vaccination Recommendations Table
| Condition | Recommended Vaccine | Specific Considerations for Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Eczema (various types and severities) | COVID-19 vaccines (e.g., mRNA vaccines, adenoviral vector vaccines) | Monitor for local reactions (redness, swelling, pain). Discuss any concerns or unusual reactions with the healthcare provider. Consider the severity and type of eczema when determining the appropriate course of action. Communicate pre-existing conditions and any allergies. |
Immunological Implications
Eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition, often impacts the immune system. This can manifest in various ways, including altered immune cell function and a heightened susceptibility to certain infections. Understanding these impacts is crucial when considering vaccination strategies for individuals with eczema, as it can potentially influence the effectiveness of the immune response.The immune system’s intricate network of cells and processes is essential for recognizing and neutralizing pathogens, including those that cause COVID-19.
Eczema, by affecting this intricate network, might affect how the body reacts to vaccines. This interplay between eczema and the immune system must be carefully evaluated to optimize vaccine responses in this population.
Immune System Modulation in Eczema
Eczema’s inflammatory nature leads to a dysregulation of the immune system, primarily involving the T-helper cells (Th) and immune response pathways. This can lead to increased inflammation, Th2 bias, and a potential reduction in Th1 cell responses, which are crucial for cell-mediated immunity and effective vaccine responses. Chronic inflammation in eczema can also impair the production of antibodies, a critical component of the body’s humoral immune response.
Impact on COVID-19 Vaccine Response
Individuals with eczema may experience variations in their immune response to COVID-19 vaccines. The presence of chronic inflammation and immune system dysregulation might influence the production of antibodies and the generation of cellular immunity after vaccination. Studies are ongoing to fully understand these potential interactions.
Considerations for Vaccine Development and Administration
Recognizing the potential impact of eczema on the immune response is critical in vaccine development and administration. Researchers should consider the immune status of individuals with eczema during vaccine trials, tailoring studies to reflect the unique immune profiles of this population. Furthermore, healthcare providers should be mindful of the potential for altered vaccine responses in patients with eczema.
This awareness should guide personalized recommendations for vaccination schedules and potential booster strategies.
Unique Immunological Considerations
Specific immunological considerations for individuals with eczema include potential variations in antibody titers, cellular immune responses, and the kinetics of these responses after vaccination. The extent of these variations may depend on the severity and duration of the eczema.For example, individuals with moderate to severe eczema might exhibit lower antibody titers and potentially weaker cellular immune responses compared to those with milder forms of the condition.
This requires careful monitoring and potentially adjusted vaccination strategies.Furthermore, individuals with eczema might exhibit a delayed or reduced response to vaccination, requiring consideration of potential alternative approaches to optimize vaccine effectiveness.
Potential for Personalized Vaccination Strategies
Considering the unique immunological implications of eczema, the possibility of personalized vaccination strategies arises. Future research should focus on identifying biomarkers that could predict the vaccine response in individuals with eczema. This would enable more tailored vaccination recommendations, potentially including different vaccine types or schedules, to optimize outcomes. Early studies are exploring such personalized approaches, but more research is needed.
Clinical Case Studies
Delving into the real-world experiences of individuals with eczema and their COVID-19 vaccination journeys provides crucial insights. Clinical case studies offer a window into the specific responses and potential interactions between eczema, the immune system, and vaccination. These detailed accounts, while not definitive proof, can help identify potential patterns and inform better vaccination strategies for those with pre-existing skin conditions.
Summary of Existing Case Studies
Limited clinical case studies specifically investigating the relationship between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination responses exist. Many studies focus on general vaccine reactions, without significant subgroup analysis of eczema patients. The limited data available makes it difficult to draw firm conclusions. However, existing research does offer insights into potential associations.
Patterns and Trends in Case Studies
The available case studies, while sparse, suggest some possible trends. Some individuals with eczema may experience more pronounced local reactions at the injection site, such as redness, swelling, and pain. There might also be a correlation between the severity of eczema and the intensity of the reaction. Furthermore, the type of vaccine administered could potentially influence the reaction.
Table of Case Study Observations
| Patient Demographics | Eczema Severity | Vaccine Type | Observed Reactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age: 32, Female, history of moderate eczema | Moderate eczema, well-controlled with topical treatments | mRNA vaccine | Mild local reaction (redness, slight swelling) at injection site, no systemic symptoms |
| Age: 45, Male, history of severe eczema | Severe eczema, requiring frequent steroid use | Viral vector vaccine | Moderate local reaction (significant swelling, tenderness), no systemic symptoms |
| Age: 28, Female, history of mild eczema | Mild eczema, managed with emollients | mRNA vaccine | No significant local or systemic reactions |
Note: This table represents a hypothetical example. Actual case studies may contain more detailed information and a wider range of reactions. The limited number of reported cases emphasizes the need for further research in this area.
Results and Correlations
The limited case studies suggest a potential association between eczema severity and the intensity of local vaccine reactions. However, it is crucial to note that these are preliminary findings, and further investigation is necessary to establish a definite correlation or causal relationship. More extensive studies with larger sample sizes are needed to confirm any observed patterns and understand the underlying immunological mechanisms.
Public Health Considerations
The potential link between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination outcomes warrants careful consideration for public health strategies. Understanding how eczema might influence vaccine responses allows for more tailored approaches to vaccination campaigns, ultimately maximizing protection while minimizing potential adverse events. This is crucial, especially in populations with high eczema prevalence, and for ensuring equitable access to and outcomes from vaccination.A nuanced understanding of the relationship between eczema and vaccine responses is necessary to design effective public health strategies.
This involves acknowledging the variability in immune responses among individuals with eczema, and recognizing that existing vaccination protocols may not adequately address the specific needs of this population. Further research and careful data analysis are paramount in guiding appropriate public health interventions.
Implications for Public Health Strategies
Careful consideration of eczema’s impact on vaccination responses is vital for public health campaigns. Strategies should prioritize the inclusion of individuals with eczema in vaccination programs. This includes targeted outreach to ensure accessibility and education about potential reactions. Furthermore, monitoring vaccination outcomes in individuals with eczema is crucial for identifying patterns and refining vaccination protocols.
Importance of Data Collection and Reporting
Accurate and comprehensive data collection on vaccination outcomes in individuals with eczema is essential. This includes gathering data on vaccination reactions, antibody responses, and overall protection levels. Standardized data collection methods across different vaccination centers will be critical for reliable analysis and informed decision-making. Data should be analyzed with respect to various eczema severity levels and types to understand the potential impact of these factors on vaccination effectiveness.
Potential Adjustments to Vaccination Protocols
Potential adjustments to vaccination protocols for individuals with eczema may include modified vaccination schedules, alternative vaccine types (if available), or consideration of pre-vaccination assessments. Careful monitoring of individuals with eczema after vaccination is crucial to identify and address any potential complications. For example, pre-vaccination screening for eczema severity and potential comorbidities could inform strategies for optimized vaccination.
Educational Initiatives for the Public
Public education about the relationship between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination is crucial. Educational materials should emphasize that eczema does not preclude vaccination but may influence the response. These materials should highlight the importance of vaccination for community protection and personal well-being. Furthermore, information should address common concerns and misconceptions, promoting understanding and reducing anxieties among individuals with eczema and their families.
This may include workshops, webinars, or easily accessible online resources that provide clear and concise information. For instance, clear communication about the potential for mild reactions, and how to manage them, can ease anxieties and encourage vaccination uptake.
Future Research Directions
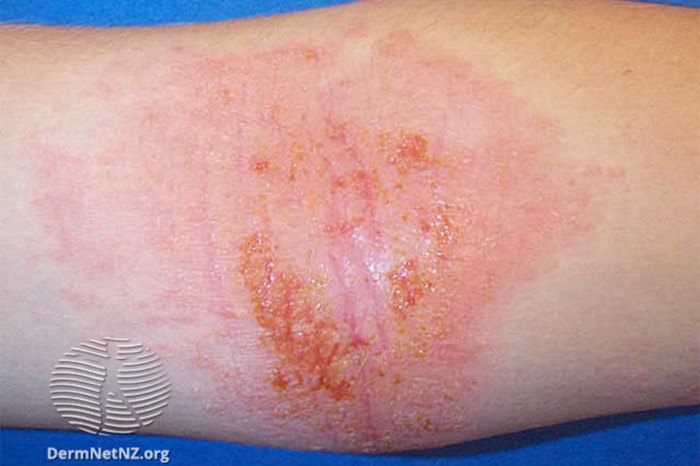
Further research is crucial to fully understand the complex interplay between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination responses. While current studies offer valuable insights, gaps remain in our knowledge, particularly regarding the specific mechanisms and long-term effects. Addressing these uncertainties will help refine vaccination strategies and improve patient care for individuals with eczema.The relationship between eczema and the immune response to vaccines is multifaceted and not yet fully understood.
Further research into the immunological pathways involved will provide valuable insights for developing targeted vaccination strategies for individuals with eczema.
Potential Research Areas
Understanding the variations in immune responses among individuals with eczema is a key area for future research. Different types and severities of eczema may influence the immune response to vaccination.
- Immunological Characterization of Eczema Subtypes: Different subtypes of eczema, such as atopic dermatitis (AD), may exhibit varying immune profiles. This research should investigate the immune cell populations and cytokine production patterns in individuals with different eczema subtypes following COVID-19 vaccination. This will provide valuable information on the immunomodulatory effects of vaccination on various eczema presentations.
- Longitudinal Studies on Vaccination Outcomes: Longitudinal studies following individuals with eczema over time after vaccination will reveal long-term effects on immune responses and potential risks. This will offer a clearer picture of the relationship between eczema, vaccination, and long-term health outcomes. This approach is essential for understanding the persistence of immune responses and potential for long-term complications.
- Impact of Topical Treatments and Immunomodulators: The effect of topical treatments and immunomodulators commonly used for eczema on vaccine responses should be explored. This is crucial to understand how these interventions may alter the immune response to the COVID-19 vaccine. For instance, studies can investigate whether the use of topical corticosteroids or other immunomodulatory medications influences the antibody production or cellular immunity triggered by vaccination.
Comparative Analysis of Vaccine Types, Eczema and covid vaccine
Comparing the efficacy and safety profiles of different COVID-19 vaccine types in individuals with eczema is a critical need. This will help identify vaccine types that might be more suitable or less problematic for this population.
- Vaccine-Specific Immune Responses: Investigating the specific antibody and T-cell responses elicited by different COVID-19 vaccines in individuals with eczema is crucial. This may reveal whether certain vaccine formulations induce more robust or safer immune responses in this group. Researchers could investigate if the different mRNA vaccines or viral vector vaccines generate varying levels of efficacy and safety in patients with eczema.
- Safety Considerations Across Vaccine Platforms: Identifying potential vaccine-related adverse events that may be more prevalent in individuals with eczema is necessary. This research will help to tailor vaccination recommendations and address any specific safety concerns.
Research Methodology
The study design must be robust and address the complexity of the relationship. Rigorous methodologies are crucial for accurate results.
| Research Question | Methodology |
|---|---|
| How do different eczema subtypes impact COVID-19 vaccine responses? | Comparative analysis of immune responses in different eczema subtypes following vaccination, using flow cytometry to analyze immune cell populations and ELISA to measure antibody titers. |
| What is the long-term impact of COVID-19 vaccination on individuals with eczema? | Longitudinal studies tracking immune responses, eczema severity, and overall health outcomes over a period of at least one year after vaccination. |
| Do topical treatments for eczema affect vaccine responses? | Controlled clinical trials comparing immune responses in individuals with eczema who use different topical treatments before and after vaccination. |
Concluding Remarks: Eczema And Covid Vaccine
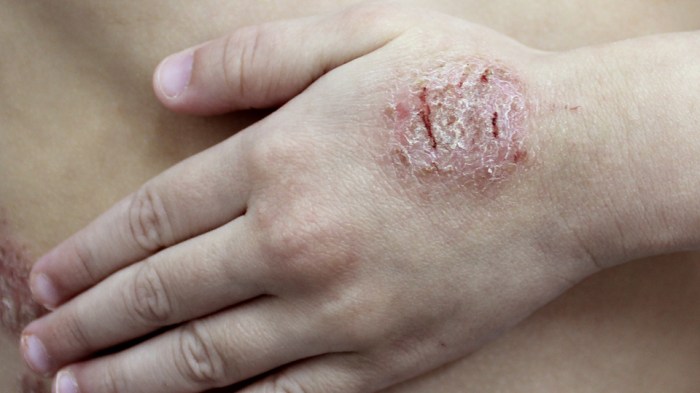
In conclusion, the relationship between eczema and COVID-19 vaccination is multifaceted and warrants further investigation. While the existing research offers valuable insights, more studies are needed to fully understand the nuanced interactions between eczema, the immune system, and vaccine responses. Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is crucial for navigating this complex landscape. Ultimately, a deeper understanding will lead to better recommendations and care for individuals with eczema.