Ella vs Plan B: This in-depth comparison explores the key differences between EllaOne and Plan B, two emergency contraceptive options. We’ll delve into their active ingredients, potential side effects, effectiveness, cost, and accessibility. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
From active ingredients and dosages to potential side effects and user experiences, we’ll cover everything you need to know to compare these two options. We’ll also discuss the situations where one might be a better choice than the other, along with the legal and regulatory aspects surrounding their use.
Comparing Contraceptive Options

Understanding the nuances between emergency contraceptive options like EllaOne and Plan B is crucial for informed decision-making. Both medications aim to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex, but they differ in their mechanisms of action and potential side effects. This comparison will delve into the specifics of each, helping you determine which might be the most appropriate choice for your situation.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Action
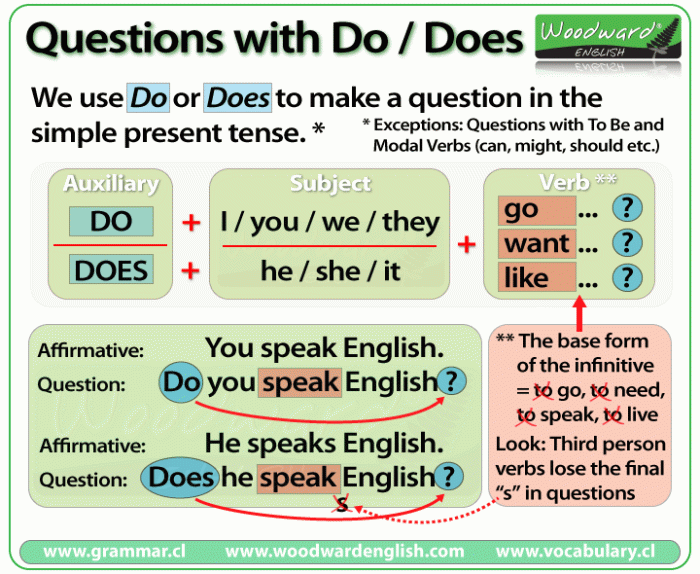
EllaOne and Plan B utilize different active ingredients, leading to distinct mechanisms of action. EllaOne contains ulipristal acetate, a selective progesterone receptor modulator. Plan B, on the other hand, typically contains levonorgestrel, a progestin. Ulipristal acetate works by delaying or inhibiting ovulation, while levonorgestrel primarily inhibits or delays ovulation and may also affect fertilization. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating how each option works within the body’s reproductive cycle.
Potential Side Effects
Both EllaOne and Plan B can cause various side effects, although the frequency and severity often differ. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, headache, and abdominal pain. These symptoms typically subside within a few days. Less common but potentially more severe side effects, such as changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, are possible with both options.
Dosage and Considerations
The dosage for EllaOne and Plan B is crucial. EllaOne is typically a single dose, while Plan B is available in various dosages depending on the specific formulation. Important considerations include the timing of administration after unprotected sex. Taking these medications as soon as possible after unprotected intercourse generally maximizes their effectiveness.
Suitability for Different Situations
The suitability of each option depends on individual circumstances. EllaOne may be a more suitable choice in situations where Plan B might not be as effective, such as for women with higher body weight. Plan B is often preferred for its ease of access and affordability. Consider individual factors such as medical history, body weight, and personal preferences when deciding which option is most appropriate.
Comparison Table
| Feature | EllaOne | Plan B |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Ulipristal acetate | Levonorgestrel |
| Dosage | Single dose of 30 mg | Varying dosages depending on formulation |
| Potential Side Effects | Nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, changes in menstrual bleeding | Nausea, vomiting, headache, fatigue, changes in menstrual bleeding |
| Suitability | Potentially more effective for higher body weight individuals; may have a longer duration of effectiveness. | Often preferred for ease of access and affordability. |
Effectiveness and Reliability: Ella Vs Plan B
Understanding the effectiveness of emergency contraception is crucial for informed decision-making. Both EllaOne and Plan B are highly effective when used correctly, but their effectiveness varies depending on factors like timing and individual characteristics. This section delves into the typical effectiveness rates, potential influencing factors, and optimal usage windows for each medication.
Typical Effectiveness Rates
EllaOne and Plan B are both effective methods of emergency contraception. Their effectiveness is generally high, but not absolute. The typical effectiveness rates vary slightly between the two. Studies have shown that both medications are most effective when taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex.
Factors Influencing Effectiveness
Several factors can impact the effectiveness of both EllaOne and Plan B. One key factor is the time elapsed since unprotected intercourse. The sooner these medications are taken, the higher the likelihood of preventing pregnancy. Other factors include individual variations in metabolism and the specific characteristics of the menstrual cycle.
Time Frame for Optimal Effectiveness
The ideal time frame for taking EllaOne or Plan B to maximize effectiveness is crucial. The sooner the medication is taken after unprotected sex, the more likely it is to prevent ovulation or fertilization. Delaying administration can reduce the effectiveness. EllaOne is typically most effective when taken within 120 hours (5 days) of unprotected intercourse. Plan B is generally effective up to 72 hours (3 days) after unprotected sex.
Potential Impact of Weight on Effectiveness
Weight can influence the effectiveness of emergency contraception, though the effect is generally modest. Studies have shown that in some cases, individuals with higher body mass indices (BMI) might experience slightly reduced effectiveness compared to those with lower BMIs. This is due to variations in how the body metabolizes the medication. However, the impact is not significant enough to negate the effectiveness of these medications for most individuals.
Figuring out Ella vs. Plan B can be tricky, right? But incorporating a healthy habit like walking 30 minutes a day can actually impact your overall well-being, which can indirectly influence the best choice for you. Ultimately, understanding your needs and potential side effects of each option is key when making your decision about Ella vs Plan B.
For instance, if someone weighs 200 pounds, they may experience slightly lower effectiveness than someone who weighs 130 pounds. However, this difference isn’t a reason to avoid using these methods.
Effectiveness Comparison Table
| Medication | Typical Effectiveness (within 24 hours) | Influencing Factors | Optimal Time Frame | Weight Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EllaOne | >95% | Time since unprotected sex, individual metabolism | Within 120 hours (5 days) | Potentially slightly reduced effectiveness with higher BMI |
| Plan B | >89% | Time since unprotected sex, individual metabolism | Within 72 hours (3 days) | Potentially slightly reduced effectiveness with higher BMI |
Important Note: These effectiveness rates are averages. Individual results may vary. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Accessibility and Cost
Emergency contraception, like EllaOne and Plan B, plays a crucial role in preventing unintended pregnancies. Understanding the accessibility and cost of these options is vital for informed decision-making. Different factors, such as location and healthcare system, significantly impact the availability and pricing of these medications.The cost of emergency contraception can vary considerably, influenced by factors like local regulations, healthcare provider policies, and even the specific brand.
This difference in cost can create disparities in access to vital reproductive healthcare.
Pricing Variations
Understanding the price differences between EllaOne and Plan B is essential for making informed choices. The cost of these medications can fluctuate across various regions due to factors like import costs, local taxes, and even brand-specific pricing strategies. For instance, a single dose of Plan B One-Step might cost slightly less than a single dose of EllaOne in some regions, while in others the reverse may be true.
Direct comparisons are challenging without specific regional data, but the general principle holds.
Availability Across Locations
The availability of EllaOne and Plan B varies across different countries and even within specific regions. Factors such as local regulations, healthcare policies, and the presence of pharmacies stocking these medications impact their accessibility. For example, Plan B is more widely available in many countries than EllaOne. This difference in availability may be due to various factors, such as differing regulatory approvals or the presence of competing brands.
Prescription Requirements
The prescription requirements for EllaOne and Plan B also differ based on local regulations. In some areas, a prescription may be necessary for EllaOne, while Plan B might be available over-the-counter. This difference in prescription status affects the ease of access, particularly for individuals without a regular healthcare provider. For example, some countries may have policies that allow over-the-counter access to Plan B for all ages, while EllaOne may require a prescription even for adults.
Out-of-Pocket Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses associated with emergency contraception can vary significantly. This includes not only the cost of the medication itself but also potential costs related to consultations or appointments with healthcare providers if a prescription is needed. Factors like insurance coverage play a critical role in reducing or eliminating these out-of-pocket expenses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | EllaOne | Plan B |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing (Estimated) | $50-$70 (USD) | $40-$60 (USD) |
| Availability | May require prescription; varies by location | Often available over-the-counter; varies by location |
| Prescription Requirement | Often yes | Often no |
Note
* Pricing and availability are estimates and can vary significantly based on location and specific pharmacy. It is recommended to check with local pharmacies or healthcare providers for precise information.
Medical Considerations
Choosing between EllaOne and Plan B is a personal decision, but understanding potential medical implications is crucial. Both medications are effective emergency contraceptives, but individual health factors can influence suitability. This section delves into potential interactions, contraindications, and when a doctor’s consultation is essential.
Potential Medication Interactions
Understanding potential interactions between EllaOne and Plan B, and other medications, is vital for informed decision-making. Certain drugs can alter the effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects of these emergency contraceptives. For instance, medications that induce or inhibit certain enzymes in the liver can impact how the body processes these medications. This can lead to either reduced effectiveness or an increased risk of side effects.
Medical Conditions Excluding Use
Certain medical conditions can make either EllaOne or Plan B unsuitable for some individuals. Conditions like liver disease, specific hormonal imbalances, or a history of blood clots can increase the risk of complications. A healthcare professional can assess individual risk factors and determine the safest course of action.
Conditions Requiring Doctor Consultation
Several situations necessitate consultation with a healthcare provider before taking either EllaOne or Plan B. These include a history of severe migraines, certain heart conditions, or undiagnosed pelvic pain. It is also advisable to seek professional guidance if you are breastfeeding or using other medications, especially those affecting liver function. Consulting a doctor is always recommended before using emergency contraception, as it can help determine if it’s suitable for an individual’s specific circumstances.
Potential Long-Term Health Implications
While both EllaOne and Plan B are generally considered safe for short-term use, potential long-term health implications are minimal. However, there are no definitive long-term studies directly assessing these implications. Some individuals may experience side effects like nausea or headaches, but these are typically temporary. In rare cases, more serious complications could occur, but these are often associated with pre-existing medical conditions.
In summary, while uncommon, long-term implications are a low risk compared to the immediate benefit of preventing unintended pregnancy.
Medical Considerations Table
| Medical Consideration | Contraindications | Potential Interactions | Situations Requiring Consultation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver Disease | May require reduced dosage or alternative options | Certain medications can affect liver enzyme activity | Consult a doctor before using either medication. |
| History of Blood Clots | Use may be contraindicated | Increased risk of blood clots, especially with certain hormonal medications. | Essential to consult a doctor to assess the risks. |
| Hormonal Imbalances | May impact effectiveness | Interaction with other hormonal medications | Consult a doctor to evaluate the specific hormonal profile and suitability. |
| Breastfeeding | Potential impact on milk production | Limited research on impact on breastfeeding | Consult a doctor to discuss the potential effects on milk production. |
| Use of other medications | Potential interaction | Consult a doctor if using other medications, especially those affecting liver function. | Always consult a doctor to determine potential drug interactions. |
User Experiences and Reviews
Navigating the world of emergency contraception can be daunting. Real-world experiences with EllaOne and Plan B offer valuable insights beyond the clinical data. Understanding the potential benefits, drawbacks, and common concerns can empower individuals to make informed choices.
Figuring out Ella vs. Plan B can be tricky, right? It’s all about your individual needs and circumstances. While considering those options, have you ever wondered if you could use a CPAP machine if you mouth breathe? Learning more about that could help you make a more informed decision about your health and well-being.
Check out this helpful resource to explore the topic further: can i use cpap if i mouth breathe. Ultimately, the best choice for you regarding Ella or Plan B will depend on your unique situation. Consider all factors before making a final decision.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
User experiences with both EllaOne and Plan B highlight a range of potential benefits and drawbacks. Positive experiences often center on the effectiveness and ease of use, allowing individuals to address potential unintended pregnancies quickly and discreetly. However, the medications are not without their challenges, as side effects and individual responses can vary significantly.
Common User Experiences
User feedback on EllaOne and Plan B often centers around menstrual cycle changes. Some individuals report experiencing slight changes in their period timing or flow, while others experience no noticeable impact. The impact on menstrual cycles is a recurring concern and question among users, which underscores the importance of open communication with healthcare providers. It’s crucial to understand that individual responses can differ, making generalized statements about menstrual cycle effects challenging.
Potential Side Effects
Reported side effects of both medications include nausea, vomiting, headache, and abdominal pain. While these side effects are generally mild and temporary, they can be distressing for some individuals. The severity and duration of side effects can vary. For instance, some individuals may experience only mild nausea, while others may experience more severe symptoms.
Figuring out Ella vs. Plan B can be tricky, but understanding your body’s signals is key. Changes in vaginal discharge can be subtle indicators of hormonal shifts, which are often linked to birth control choices. For a comprehensive guide on interpreting different discharge colors, check out this helpful resource: vaginal discharge color guide. Ultimately, consulting with a healthcare professional is best for personalized advice on which emergency contraception method might be right for you.
Positive Experiences
Positive user experiences often emphasize the rapid action and accessibility of these medications. The ability to address potential unintended pregnancies quickly and discreetly is a significant positive aspect. The convenience of over-the-counter availability (for Plan B) also contributes to positive experiences for some. In situations where a woman has missed a pill or had unprotected sex, EllaOne and Plan B offer a readily available and potentially effective option.
Common Questions and Concerns
Common questions and concerns often revolve around the impact on future fertility, the duration of potential side effects, and the potential for long-term health consequences. Addressing these concerns through open communication with healthcare professionals is crucial for informed decision-making. The safety and efficacy of these medications are generally well-established, but individuals should be aware of the potential for side effects and discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider.
Impact on Menstrual Cycles
The impact of EllaOne and Plan B on menstrual cycles is a frequently discussed topic. Some individuals report changes in their period timing or flow, while others experience no noticeable impact. The timing of the administration relative to the anticipated period can also influence the extent of the effect. It’s essential to remember that menstrual cycle responses vary significantly between individuals, and it’s not possible to predict the specific impact on any given person.
Summary Table
| User Experience | Potential Side Effects | Positive Experiences | Common Questions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Changes in menstrual cycle (timing/flow) | Nausea, vomiting, headache, abdominal pain | Effectiveness, ease of use, quick access | Impact on future fertility, long-term health consequences, duration of side effects |
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
The availability and accessibility of emergency contraception like EllaOne and Plan B vary significantly across countries due to differing legal and regulatory frameworks. These factors influence pricing, marketing, and even the types of emergency contraception available in various regions. Understanding these regulations is crucial for anyone considering these options.
Legal Status of EllaOne and Plan B
The legal status of emergency contraception like EllaOne and Plan B is often determined by local laws and regulations. Some countries may have specific restrictions on the sale of these medications, requiring prescriptions or age limits. These laws are constantly evolving, with some jurisdictions updating their regulations in response to changing social attitudes and scientific advancements.
Regulations Surrounding Sale and Distribution
Regulations surrounding the sale and distribution of emergency contraception like EllaOne and Plan B differ substantially from country to country. These regulations often involve restrictions on marketing materials, age limits for purchase, and requirements for pharmacists or healthcare providers to provide information and counseling to consumers.
Specific Requirements and Restrictions, Ella vs plan b
Specific requirements and restrictions on purchasing emergency contraception, such as EllaOne and Plan B, can include prescription requirements, age restrictions, and mandatory counseling sessions. Some regions may permit over-the-counter sales without any limitations, while others may impose specific regulations. These factors can significantly impact access to these vital medications.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in the approval and oversight of emergency contraception products. These bodies evaluate the safety and efficacy of the medications, ensuring they meet established standards. The process often involves rigorous testing and clinical trials before a product is deemed safe and effective for use. Regulatory bodies also monitor the post-market use of these medications to identify any potential adverse events or safety concerns.
Table: Legal and Regulatory Landscape for EllaOne and Plan B
| Region | Legal Status | Regulations | Distribution Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally available over-the-counter for most ages, with some state-level variations. | Marketing restrictions may exist regarding age and product claims. | Some pharmacies may require ID verification for minors. |
| European Union | Generally available over-the-counter or with a prescription, depending on the country. | Varying regulations on marketing and labeling. | Age restrictions may apply in some countries. |
| Canada | Generally available over-the-counter. | Regulations regarding marketing and advertising may be present. | Pharmacists may be required to provide information. |
| Australia | Available over-the-counter for those 16 or older. | Marketing restrictions may exist regarding product claims. | Pharmacists may be required to provide information. |
| India | Prescription-based. | Regulations regarding product safety and efficacy are stringent. | Distribution limited to pharmacies and healthcare providers. |
Last Word

In conclusion, Ella and Plan B offer similar yet distinct approaches to emergency contraception. Ultimately, the best choice depends on individual circumstances, medical history, and personal preferences. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized advice and ensuring the safest and most effective course of action. We hope this comparison has provided clarity and empowered you to make the best decision for your needs.