What is a pathogen? This exploration delves into the fascinating world of disease-causing organisms, from the microscopic to the complex. We’ll unravel the mysteries behind these tiny invaders, examining their structures, functions, and the intricate ways they interact with their hosts. Understanding pathogens is crucial for comprehending human health and developing effective strategies to combat infection.
From bacteria and viruses to fungi and parasites, we’ll examine the different types of pathogens, their unique characteristics, and the diseases they cause. We’ll also look at how pathogens spread, evade the immune system, and impact human health. This comprehensive overview will equip you with a deeper understanding of these microscopic adversaries.
Defining Pathogens

Pathogens are biological agents capable of causing disease. Understanding these microscopic invaders is crucial for developing effective preventative measures and treatments. They encompass a wide range of organisms, each with unique characteristics and methods of infection. From the smallest viruses to complex parasites, pathogens pose a constant threat to human health.Pathogens differ fundamentally from beneficial microorganisms, such as the bacteria in our gut that aid digestion, or harmless viruses that exist in the environment without causing harm.
Key characteristics of pathogens include their ability to invade and replicate within a host organism, causing damage and disease. This contrasts with beneficial microorganisms that coexist peacefully or harmless viruses that have no detrimental impact.
Types of Pathogens
Pathogens are categorized into various groups based on their structure and mode of action. This classification system is essential for understanding the diverse strategies employed by pathogens to infect and cause disease. Knowing these different types helps us target specific treatments and develop appropriate prevention strategies.
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can reproduce rapidly. They can cause various infections, from mild skin irritations to life-threatening illnesses. Examples include
- Streptococcus*, causing strep throat, and
- Staphylococcus*, a common cause of skin infections. The diversity of bacterial pathogens highlights the importance of identifying the specific type of bacteria to determine appropriate treatments.
Viruses
Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and require a host cell to replicate. They can cause a wide range of diseases, from the common cold to severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Examples include the influenza virus, causing seasonal flu, and HIV, leading to AIDS. Viruses are known for their ability to mutate rapidly, making them difficult to combat with vaccines.
Fungi
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that can cause infections in humans, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Examples include
- Candida*, causing yeast infections, and
- Aspergillus*, which can lead to lung infections. Fungal infections can manifest in various forms, from superficial skin conditions to life-threatening systemic diseases.
Parasites
Parasites are organisms that live on or within another organism, deriving nourishment from it. Examples include
- Plasmodium*, causing malaria, and
- Schistosoma*, leading to parasitic infections in the bloodstream. Parasites can cause significant health problems, impacting various organ systems.
Prions
Prions are misfolded proteins that can cause neurodegenerative diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). They are unusual pathogens because they lack genetic material. Prion diseases are characterized by progressive deterioration of the nervous system.
Table of Pathogen Types
| Pathogen Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Single-celled organisms that reproduce rapidly. | *Streptococcus*, – Staphylococcus* |
| Viruses | Much smaller than bacteria, needing a host cell to replicate. | Influenza virus, HIV |
| Fungi | Eukaryotic organisms causing infections, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems. | *Candida*, – Aspergillus* |
| Parasites | Organisms living on or within another organism, deriving nourishment. | *Plasmodium*, – Schistosoma* |
| Prions | Misfolded proteins causing neurodegenerative diseases. | Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) |
Pathogen Structure and Function
Pathogens, the microscopic invaders responsible for a wide array of diseases, exhibit a remarkable diversity in their structural features. Understanding these structures and how they function is crucial to comprehending their virulence and developing effective treatments and diagnostic tools. This section delves into the intricate world of pathogen anatomy, exploring how specific structural components contribute to their ability to cause disease and the role of these features in diagnostic testing.Pathogen structures are intimately linked to their survival and ability to cause disease.
The specific components of a pathogen dictate how it interacts with the host, its ability to evade the immune system, and the type of disease it produces. From the intricate protein coats of viruses to the cell walls of bacteria, each structural element plays a critical role in the pathogen’s overall strategy.
Bacterial Structural Features
Bacterial cells, while relatively simple in structure, possess several crucial components that contribute to their pathogenicity. A rigid cell wall composed of peptidoglycans provides structural support and protection against osmotic pressure. The cell wall’s composition can be further categorized into gram-positive and gram-negative types, each with unique structural features affecting their susceptibility to antibiotics. Flagella, pili, and fimbriae are appendages that enable motility, attachment to host cells, and the transfer of genetic material.
Capsules surrounding some bacteria provide additional protection against the host immune system.
Viral Structural Features
Viruses, unlike bacteria, are acellular entities consisting primarily of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed within a protein coat called a capsid. The capsid’s shape and structure are crucial for viral recognition and entry into host cells. Some viruses also have an outer envelope derived from the host cell membrane, which may contain additional proteins crucial for viral attachment and entry.
The structural components of the virus directly impact its ability to infect and replicate within the host cell.
Fungal Structural Features
Fungi exhibit a diverse range of structural features, reflecting their unique life cycle and ecological roles. Fungal cells possess a cell wall composed of chitin, a polysaccharide that provides structural support. Their filamentous structure, often referred to as hyphae, enables them to invade and colonize host tissues. Dimorphism, the ability to exist in both yeast and hyphal forms, is a characteristic feature of some pathogenic fungi.
Diagnostic Applications of Pathogen Structures
Pathogen structures are valuable targets for diagnostic tests. Microscopic examination of bacterial cell walls can differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative species. Immunological assays, such as ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), can detect specific viral proteins or fungal antigens in patient samples. These tests rely on the unique structural features of the pathogens.
Replication Mechanisms
The replication strategies of pathogens vary significantly. Bacteria replicate by binary fission, a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Viruses hijack the host cell’s machinery to replicate their genetic material and assemble new viral particles. Fungi reproduce through a variety of mechanisms, including budding and spore formation. These differences in replication are critical for understanding the lifecycle of the pathogen and the development of effective therapeutic strategies.
Comparison of Key Structural Components
| Component | Bacterium | Virus | Fungus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Peptidoglycan | Absent | Chitin |
| Genetic Material | DNA | DNA or RNA | DNA |
| Motility | Flagella, pili | None | Hyphae |
| Replication | Binary fission | Host cell machinery | Budding, spore formation |
Pathogen Transmission and Entry
Pathogens, those microscopic invaders, need a way to reach their host to cause disease. This involves a complex interplay of mechanisms, and understanding these pathways is crucial for developing effective preventative strategies. From the moment a pathogen leaves its reservoir to the moment it enters a new host, numerous factors influence its success. This section delves into the various methods of transmission and the intricate processes by which pathogens gain entry into their hosts.The journey of a pathogen from one organism to another is a dynamic process influenced by environmental conditions, the pathogen’s characteristics, and the susceptibility of the host.
This intricate process, from the initial release to the final invasion, is essential to understand. Pathogens utilize diverse strategies to achieve transmission, each with unique implications for public health.
Modes of Pathogen Transmission
Understanding how pathogens spread is critical for implementing effective prevention strategies. Pathogens can be transmitted through various mechanisms, each with specific characteristics and implications.
- Direct Contact Transmission:
- Indirect Contact Transmission:
- Airborne Transmission:
- Vector-borne Transmission:
Direct contact transmission occurs when pathogens are transferred directly from an infected individual to a susceptible host. This can happen through physical touch, sexual contact, or droplet spread (short-range transmission of respiratory droplets). Examples include the transmission of influenza or sexually transmitted infections like HIV.
Pathogens can also spread through indirect contact, where an intermediate object or surface acts as a vehicle for transmission. This includes fomites, which are inanimate objects contaminated with pathogens. Examples include contaminated doorknobs or shared utensils.
Airborne transmission involves the spread of pathogens through tiny particles suspended in the air. These particles can be inhaled by a susceptible host, causing infection. Examples include the spread of measles or tuberculosis.
Pathogens are essentially anything that can cause disease, from bacteria to viruses. Understanding how these microscopic invaders work is crucial, and that knowledge is even more important when looking at specific cancers, like nodular melanoma, a type of skin cancer. Learning about nodular melanoma overview and more helps us appreciate the complexity of these diseases, and how crucial early detection is for successful treatment.
Ultimately, a deeper understanding of pathogens is key to preventing and treating illnesses.
Vectors, such as insects or animals, play a vital role in transmitting pathogens from one host to another. They act as intermediaries, carrying the pathogen from an infected individual to a healthy one. This method is prevalent in diseases like malaria or Lyme disease.
Pathogen Entry Mechanisms
Different pathogens utilize diverse mechanisms to breach the host’s defenses and gain entry.
- Ingestion:
- Inhalation:
- Injection:
- Absorption through skin or mucous membranes:
Some pathogens enter the host through ingestion, typically by contaminating food or water. The pathogen then travels to the digestive system, where it can multiply and cause infection. Examples include food poisoning from bacteria like Salmonella or Cholera.
Inhaling airborne pathogens is a common entry route. These pathogens often target the respiratory system, leading to infections like pneumonia or influenza.
Pathogens can be injected directly into the host through bites or stings of insects or animals. This is a primary method of transmission for diseases like rabies and West Nile virus.
Some pathogens can penetrate the skin or mucous membranes. This is frequently associated with skin infections, like ringworm, or sexually transmitted infections.
Factors Influencing Pathogen Transmission
Numerous factors influence the success of pathogen transmission.
- Environmental Factors:
- Host Susceptibility:
- Pathogen Virulence:
- Population Density:
Temperature, humidity, and the presence of vectors can all affect pathogen survival and transmission rates. For example, warm, humid environments can favor the multiplication and transmission of some mosquito-borne diseases.
So, what exactly is a pathogen? Basically, it’s a microorganism that can cause disease. Understanding these tiny invaders is crucial, especially when it comes to conditions like high blood pressure. Learning more about how to diagnose hypertension can help in the fight against these pathogens, and the related health complications. For a deep dive into all about hypertension diagnosis, check out this informative resource: all about hypertension diagnosis.
Ultimately, recognizing pathogens and their impact on our bodies is key to maintaining good health.
The host’s immune system, overall health, and genetic makeup influence their susceptibility to infection. Individuals with weakened immune systems are often more vulnerable.
The pathogen’s virulence, or its ability to cause disease, significantly impacts its transmission success. Highly virulent pathogens can rapidly spread.
Crowded populations can increase the chances of pathogen transmission due to close contact between individuals. This is particularly true for respiratory infections.
Role of Vectors in Pathogen Transmission
Vectors are crucial in the transmission of numerous diseases. They serve as intermediaries, carrying pathogens from one host to another.
- Examples of Vectors:
Mosquitoes (malaria, West Nile virus), ticks (Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever), and fleas (plague) are examples of vectors that transmit pathogens.
Transmission Flow Chart (Example: Influenza), What is a pathogen
This flow chart illustrates the steps in the transmission of influenza, a common airborne pathogen.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Infected individual coughs or sneezes, releasing respiratory droplets containing influenza virus. |
| 2 | Droplets containing the virus remain suspended in the air. |
| 3 | A susceptible individual inhales the contaminated droplets. |
| 4 | The virus infects the respiratory tract of the susceptible individual. |
| 5 | The virus multiplies, causing symptoms of influenza. |
Pathogen-Host Interactions: What Is A Pathogen
The battle between pathogens and their hosts is a constant, complex interplay. Pathogens, driven by their survival instinct, employ various strategies to overcome the host’s defenses. Conversely, the host’s immune system mounts a robust response, attempting to neutralize and eliminate the invaders. This dynamic interaction shapes the course of infection, ranging from asymptomatic carriage to severe disease. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing effective preventative and therapeutic strategies.
Pathogen Strategies for Immune Evasion
Pathogens employ a diverse arsenal of tactics to evade the host’s immune system. These strategies aim to disrupt or suppress the immune response, enabling the pathogen to replicate and cause disease. Some pathogens directly interfere with immune cell function, while others manipulate the host’s environment to create a more favorable niche for their survival.
- Immune System Suppression: Some pathogens produce proteins or enzymes that directly inhibit the activity of immune cells. These substances can interfere with the signaling pathways crucial for immune responses, effectively silencing the host’s defense mechanisms. For example, certain bacteria release proteins that prevent the activation of T cells, a critical component of the adaptive immune system.
- Antigenic Variation: Some pathogens, like certain viruses and parasites, have the remarkable ability to alter their surface antigens. This continuous evolution of surface proteins makes it challenging for the host’s immune system to recognize and effectively target the pathogen. This is particularly common in parasites like Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agent of African sleeping sickness. The parasite changes its surface proteins, thus evading antibodies and other immune defenses.
- Camouflage and Mimicry: Some pathogens employ clever camouflage strategies, using host proteins or molecules to disguise themselves. This allows them to evade detection by the immune system, much like a chameleon blending into its environment. Other pathogens mimic host proteins, confusing the immune system and preventing the recognition of foreign invaders.
Specific Pathogen-Host Cell Interactions
The interaction between pathogens and host cells often involves intricate molecular mechanisms. Pathogens employ various strategies to enter, replicate within, and exit host cells. These interactions can significantly impact the host cell’s function and contribute to the development of disease.
- Viral Entry: Viruses utilize specific receptors on the surface of host cells to gain entry. Once inside, the virus hijacks the host cell’s machinery to produce more viral particles, leading to cell lysis and potentially causing tissue damage. For example, influenza viruses use sialic acid receptors on respiratory epithelial cells for entry.
- Bacterial Interactions: Bacteria can interact with host cells in various ways. Some bacteria form biofilms, communities of bacteria encased in a protective matrix, enabling them to evade the immune system and persist in the host. Other bacteria directly invade host cells, causing intracellular infections, where they replicate inside cells, escaping immune surveillance.
Immune Responses to Pathogens
The host’s immune system mounts a multifaceted response to the presence of pathogens. These responses are crucial for containing the infection and preventing disease.
- Innate Immunity: The initial line of defense against pathogens is the innate immune system. This rapid, non-specific response involves physical barriers like skin and mucous membranes, as well as phagocytic cells like macrophages and neutrophils that engulf and destroy pathogens. Inflammation is a critical component of this response, attracting immune cells to the site of infection.
- Adaptive Immunity: Following the innate response, the adaptive immune system, characterized by its specificity and memory, takes over. This system produces antibodies that neutralize pathogens and cytotoxic T cells that directly kill infected cells. The adaptive response is slower but provides long-lasting immunity against specific pathogens.
Impact of Immune Response on Pathogen
The host’s immune response significantly influences the pathogen’s ability to cause disease. A robust immune response can limit pathogen replication, prevent the spread of infection, and even eliminate the pathogen entirely.
Table: Pathogen Manipulation of Host Immune System
| Pathogen | Mechanism of Immune Evasion | Effect on Host |
|---|---|---|
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Inhibition of macrophage activation and recruitment | Chronic infection, granuloma formation |
| Influenza virus | Antigenic drift and shift | Repeated infections, seasonal outbreaks |
| Helicobacter pylori | Suppression of inflammation | Chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease |
Pathogen Impact on Human Health
Pathogens, ranging from microscopic viruses to macroscopic parasites, exert a profound impact on human health. Their ability to invade and replicate within the human body triggers a cascade of responses, often resulting in debilitating diseases. Understanding the diverse ways pathogens affect us is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.The impact of pathogens on human health is multifaceted, encompassing a wide spectrum of diseases, from common colds to life-threatening infections.
This section will delve into the symptoms, consequences, and diagnostic methods associated with various pathogens, highlighting the intricate relationship between the invading microorganism and the human host.
Impact of Different Pathogens on Human Health
Pathogens cause a wide array of diseases, impacting various organ systems and leading to varying degrees of severity. The symptoms and consequences of infections depend on several factors, including the type of pathogen, the individual’s immune response, and the specific site of infection.
Examples of Diseases Caused by Different Pathogens
A variety of pathogens cause numerous diseases in humans. These diseases manifest in different ways, and their severity can range from mild to severe, potentially even fatal.
Methods Used to Diagnose Infections
Diagnosing infections caused by various pathogens relies on a combination of methods. These methods aim to identify the presence and type of pathogen, enabling appropriate treatment and management. A key aspect is the prompt identification of the pathogen for the most effective treatment. The specific methods employed depend on the suspected pathogen and the available resources.
Table of Pathogens, Diseases, Symptoms, and Treatments
| Pathogen | Disease | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) | Staphylococcal infections (e.g., skin infections, pneumonia) | Redness, swelling, pain, pus-filled lesions; fever, chills, difficulty breathing in pneumonia cases. | Antibiotics (e.g., methicillin, vancomycin) are typically prescribed. Appropriate wound care for skin infections. |
| Streptococcus pyogenes (bacteria) | Strep throat, scarlet fever | Sore throat, fever, headache, body aches; scarlet fever also includes a characteristic rash. | Antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) are effective. Rest and hydration are also important. |
| Influenza virus | Influenza (flu) | Fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, fatigue. | Rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms. Antiviral medications may be considered in some cases, especially for high-risk individuals. |
| Plasmodium (parasite) | Malaria | Recurring fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, anemia. | Anti-malarial drugs (e.g., chloroquine, artemisinin-based combinations) are crucial for treatment. Prevention measures are also vital, such as using mosquito nets. |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis (bacteria) | Tuberculosis (TB) | Persistent cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigue. | Multi-drug therapy (MDT) with antibiotics (e.g., isoniazid, rifampin) is typically required. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent transmission. |
Pathogen Control and Prevention
Controlling the spread of pathogens is crucial for public health. Effective strategies involve a multifaceted approach encompassing various methods of prevention and control. Understanding the life cycle of pathogens and their modes of transmission is essential for implementing targeted interventions.
Methods of Pathogen Control
Controlling the spread of pathogens necessitates a comprehensive approach. This includes both direct methods aimed at eliminating the pathogen and indirect strategies to limit exposure. Disinfection, sterilization, and sanitation are key direct methods, while isolation, quarantine, and vaccination programs are important indirect approaches.
Preventative Measures Against Infection
Effective preventative measures are crucial in reducing the risk of infection. These measures include avoiding contact with infected individuals, practicing good hygiene, and maintaining a healthy immune system. Proper handwashing techniques, covering coughs and sneezes, and avoiding close contact with individuals displaying symptoms of illness are all essential preventive steps. The importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep in bolstering the immune response cannot be overstated.
Importance of Sanitation and Hygiene
Maintaining proper sanitation and hygiene practices is paramount in preventing pathogen transmission. Sanitation involves maintaining clean and safe environments, while hygiene focuses on personal cleanliness and practices. Safe water sources, proper waste disposal, and regular handwashing are vital components of a comprehensive sanitation and hygiene program. These practices significantly reduce the risk of pathogen transmission through contaminated surfaces and water sources.
Pathogens are microscopic organisms that can cause disease, like bacteria or viruses. While I’m not a doctor, I’m curious about how certain habits might affect our health. For instance, the question of whether vaping can impact weight loss is an interesting one. This article investigates the relationship between vaping and weight loss, providing a comprehensive overview of the subject: does vaping make you lose weight.
Ultimately, understanding pathogens is crucial for preventing illness and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
For example, handwashing with soap and water removes pathogens from the skin, significantly reducing the risk of spreading infections.
Role of Vaccines in Preventing Pathogen-Related Diseases
Vaccines play a pivotal role in preventing pathogen-related diseases. They stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies against specific pathogens, conferring immunity without the need for contracting the illness. This protection not only benefits the individual but also protects the wider community by reducing the circulation of the pathogen. The success of vaccination programs is evident in the dramatic reduction of diseases like polio and measles globally.
Emerging Pathogens and their Impact on Global Health
Emerging pathogens pose a significant threat to global health. These novel pathogens often exhibit unique characteristics and modes of transmission, making them challenging to control. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, the re-emergence of diseases thought to be eradicated, and the constant threat of new zoonotic diseases highlight the dynamic nature of infectious diseases. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of global populations to emerging infectious diseases.
Summary Table of Preventative Measures
| Pathogen | Vaccination Status | Hygiene Practices | Vector Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza | Annual flu vaccination recommended | Regular handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes | Vaccination of susceptible animals, controlling vector populations (e.g., birds) |
| Salmonella | No vaccine available | Thorough handwashing after handling raw foods, proper food storage | No specific vector control measures |
| Plasmodium (Malaria) | Vaccines in development | Mosquito repellent use, protection from bites | Elimination of mosquito breeding grounds, insecticide use |
Pathogen Evolution and Adaptation
Pathogens, the microscopic villains that cause disease, are not static entities. They constantly evolve and adapt to their hosts, a dynamic process driven by natural selection. This adaptation allows pathogens to better exploit their hosts, survive in changing environments, and evade the host’s defenses. Understanding these evolutionary mechanisms is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.Pathogens, like all living organisms, undergo genetic mutations.
These mutations can lead to changes in their traits, some of which might provide advantages in their interaction with the host. Those advantageous mutations are more likely to be passed on to future generations, thus driving the evolution of the pathogen.
Mechanisms of Pathogen Evolution
Pathogens evolve through a combination of mechanisms. Mutations, a random process, introduce variations into the pathogen’s genetic material. Natural selection favors those mutations that improve the pathogen’s ability to survive and replicate within the host. Horizontal gene transfer, where genetic material is exchanged between different organisms, can also contribute to rapid evolutionary changes in pathogens.
Factors Driving Pathogen Evolution
Several factors influence the rate and direction of pathogen evolution. The pathogen’s environment, including the presence of antibiotics or other treatments, can select for resistant strains. The host’s immune response, and its ability to recognize and eliminate the pathogen, is another significant selective pressure. The availability of suitable hosts and the pathogen’s ability to transmit between them also plays a crucial role in its evolution.
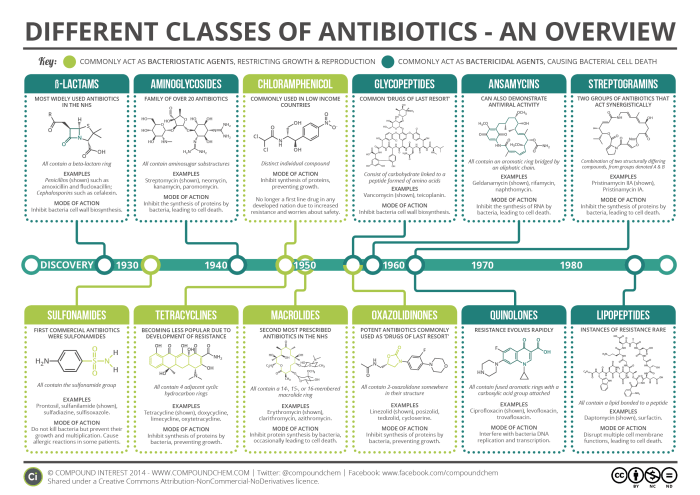
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance arises when bacteria develop mechanisms to counter the effects of antibiotics. This is often driven by mutations in genes that encode proteins involved in antibiotic targets, or by acquiring genes from other bacteria that confer resistance. The widespread and often inappropriate use of antibiotics accelerates the evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Pathogen Adaptation to Changing Environmental Conditions
Pathogens are capable of adapting to changes in their environment. For example, a pathogen might evolve to tolerate higher temperatures if the environment changes, or to utilize different nutrients if the source of nutrients changes. This adaptability is crucial for their survival and spread.
Illustrative Example: Influenza Evolution
Influenza viruses are a prime example of pathogen adaptation. They constantly evolve through mutations in their genes, particularly in the genes that code for proteins on their surface, like hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). These mutations allow the virus to evade the host’s immune response, leading to the emergence of new influenza strains and the need for annual flu vaccines.
The evolution of influenza is a dynamic process, driven by the selective pressure of the host immune response and the constant changes in the genetic makeup of the virus.
Graphic Representation of Pathogen Evolution
(Please note that I cannot create a visual graphic here. A graphic would illustrate a hypothetical pathogen, like a bacterium, evolving over multiple generations. It would show a change in the pathogen’s characteristics, such as its ability to resist antibiotics, over time. Different branches on the “evolutionary tree” would represent different strains of the pathogen, with each strain potentially having unique adaptations.)
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, pathogens are a vital part of the biological world, shaping ecosystems and impacting human health. Their complex interactions with hosts, from transmission to immune responses, highlight the intricacies of life. Understanding pathogens is key to developing effective treatments and preventative measures, ultimately safeguarding human health and well-being.