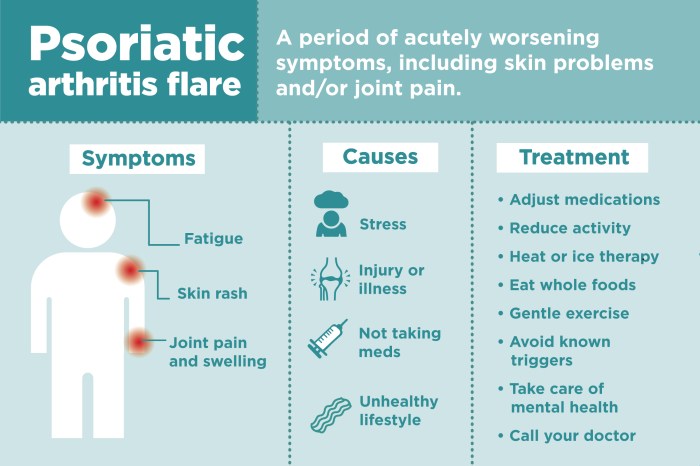
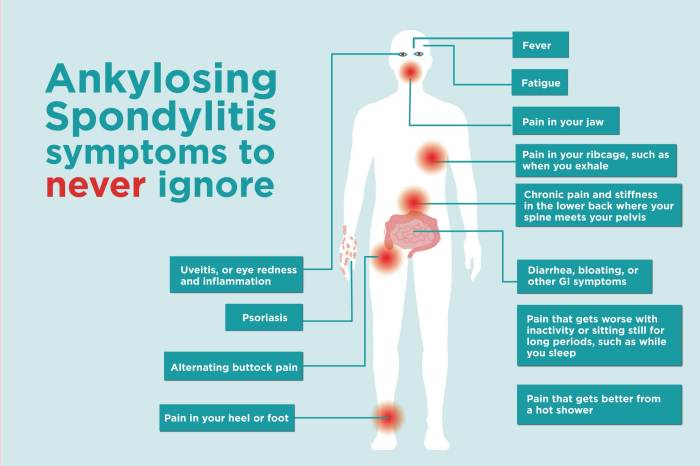
What medications treat psoriatic arthritis? This comprehensive guide delves into the various treatments available for this complex condition. Psoriatic arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disease, affects not only the joints but also the skin, causing pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Understanding the different medication options and their mechanisms of action is crucial for effective management. We’ll explore…
Tag: arthritis
Ankylosing Spondylitis and Teeth Problems A Deep Dive
Ankylosing spondylitis and teeth problems are intricately linked, creating a complex interplay between spinal health and oral well-being. This exploration delves into the specifics of this connection, examining the common oral health concerns associated with AS, the underlying mechanisms, and effective management strategies. This comprehensive guide will cover various aspects of oral health in individuals…
Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Neck Understanding the Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis in the neck can significantly impact your quality of life, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Understanding the specific ways RA affects the cervical spine, along with its symptoms and treatment options, is crucial for effective management. This guide delves into the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis in the neck, providing a comprehensive overview…
Alternatives to Hip Replacement Exploring Options
Alternatives to hip replacement are gaining traction as people seek less invasive and potentially quicker recovery methods. This exploration delves into various approaches, from non-surgical therapies to minimally invasive procedures and even alternative treatments. Understanding the limitations of traditional hip replacement and the diverse range of options available is crucial for informed decision-making. We’ll examine…
Rheumatoid Arthritis Back Pain Understanding the Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis back pain is a complex condition that significantly impacts a person’s life. It’s not just about aches and stiffness; it’s about understanding the underlying mechanisms, the various symptoms, and the available treatment options. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of RA back pain, providing a detailed overview of its causes, diagnosis, and…
Finger Locking Why Do My Fingers Lock Up?
Why do my fingers lock up? This frustrating issue can range from a simple, temporary discomfort to a chronic condition requiring medical attention. Understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options is key to finding relief and maintaining healthy hands. This guide delves into the complexities of finger locking, offering insights into various medical…