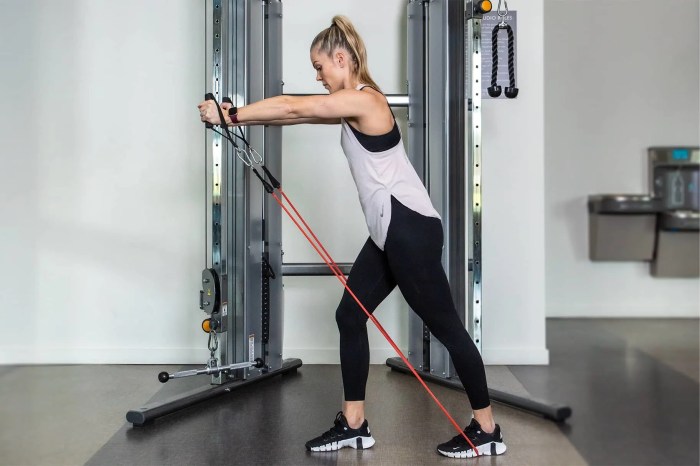
Exercises for arthritic knees are crucial for managing pain and improving mobility. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of various exercises, tailored to different levels of knee arthritis severity. We’ll explore different types of exercises, safety precautions, and how to design a personalized program to help you stay active and comfortable. From strengthening to flexibility, we cover it all, offering practical advice and illustrative examples to help you get started.
Knee arthritis can significantly impact your daily life, making even simple tasks challenging. Understanding the types of exercises that are beneficial and safe is essential for managing symptoms and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of exercise for arthritic knees, enabling you to create a personalized program that suits your specific needs and limitations.
We’ll delve into the importance of consistency, proper warm-up and cool-down routines, and the role of physical therapy in optimizing your exercise program.
Introduction to Knee Arthritis Exercises
Knee arthritis is a common condition that affects millions worldwide, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the knee joint. This condition arises from the breakdown of cartilage, the smooth tissue that cushions the joint. As cartilage deteriorates, bones rub against each other, leading to inflammation, discomfort, and difficulty with everyday activities. The impact on mobility ranges from minor limitations to significant impairments, impacting everything from walking and climbing stairs to simple tasks like getting dressed.Regular exercise plays a crucial role in managing knee arthritis symptoms.
Taking care of arthritic knees involves gentle exercises, like swimming or stationary cycling. While the focus is on managing knee pain, it’s important to consider that lung cancer survival without treatment varies significantly, as detailed in this insightful article lung cancer survival without treatment. Ultimately, consistent, low-impact exercise is key to maintaining mobility and overall well-being for those with arthritic knees.
Exercise helps maintain joint flexibility, strengthens supporting muscles, and improves overall cardiovascular health. A well-designed exercise program can help reduce pain, increase range of motion, and enhance functional abilities. This allows individuals with arthritis to maintain an active lifestyle and improve their quality of life.
General Principles of Exercise for Arthritis
Effective exercise programs for individuals with knee arthritis follow several key principles. A proper warm-up prepares the muscles and joints for activity, reducing the risk of injury. This should involve gentle movements, such as leg swings and knee circles, gradually increasing the range of motion. Cool-down exercises are equally important, helping the body return to a resting state.
These involve static stretches, holding each stretch for 15-30 seconds, targeting the muscles around the knee. Proper form is essential to avoid exacerbating pain or causing further damage to the knee joint. This involves maintaining a neutral posture and avoiding movements that put excessive stress on the knee.
Types of Knee Arthritis
Different types of arthritis can affect the knee, each with unique characteristics and treatment approaches. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for developing an appropriate exercise plan.
| Type of Arthritis | Description | Impact on Knee | Example Exercises |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteoarthritis | A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joint. | Progressive deterioration of cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone friction, pain, and stiffness. | Low-impact exercises like walking, cycling, swimming, and water aerobics. Strengthening exercises for quadriceps and hamstring muscles. |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | An autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the joints. | Inflammation of the joint lining, leading to pain, swelling, and potential joint deformity. | Gentle range-of-motion exercises, low-impact cardio. Exercises focusing on joint stability and flexibility. |
Proper diagnosis and guidance from a healthcare professional are essential for individuals with knee arthritis to develop safe and effective exercise routines.
Types of Exercises for Arthritic Knees

Knee arthritis can significantly impact daily life, but exercise plays a crucial role in managing pain and improving function. A well-rounded exercise program tailored to individual needs can help maintain joint health and mobility. Understanding the different types of exercises and their appropriate application is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.Effective exercise programs for arthritic knees often involve a combination of strengthening, flexibility, and range-of-motion exercises.
These targeted approaches help to build muscle strength around the knee, improve joint flexibility, and increase the range of motion, ultimately reducing pain and stiffness.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are essential for supporting the knee joint and reducing stress on the cartilage. These exercises target the muscles surrounding the knee, such as the quadriceps and hamstrings, enhancing stability and reducing pain. Regular strengthening exercises help improve overall knee function and prevent further deterioration.
- Quadriceps strengthening: Exercises like wall sits, leg presses, and quadriceps sets help build strength in the quadriceps muscles. These exercises can be performed with varying degrees of resistance, allowing for adaptation based on individual knee condition. For example, seated leg extensions can be used, with resistance adjusted based on the individual’s pain tolerance and strength level.
- Hamstring stretches: Hamstring stretches are crucial for maintaining flexibility and preventing tightness in the muscles behind the knee. Examples include hamstring curls and lying hamstring stretches. These stretches improve the range of motion in the knee and help alleviate stiffness.
- Glute strengthening: Exercises targeting the gluteal muscles (butt muscles) are important for hip stability and balance. This stability benefits the knee by reducing stress on the joint. Examples include glute bridges and clamshells.
Flexibility Exercises
Maintaining flexibility in the muscles surrounding the knee joint is vital for pain management and improved range of motion. Flexibility exercises help to prevent stiffness and improve the overall mobility of the knee.
- Knee flexion and extension: These exercises help to improve the range of motion in the knee joint. Gentle bending and straightening of the knee can be performed while seated or standing, keeping the range of motion gradual and controlled. Examples include bending the knee to various degrees while sitting, holding for 15-30 seconds, and repeating several times.
- Hip flexor stretches: Tight hip flexors can contribute to knee pain. Stretching these muscles can help alleviate this issue and improve overall mobility. Examples include lying hip flexor stretches and kneeling hip flexor stretches.
Range of Motion Exercises
Range of motion exercises focus on restoring and maintaining the full range of movement in the knee joint. These exercises help to increase flexibility, improve joint lubrication, and reduce stiffness.
- Stationary bike: A stationary bike is a low-impact exercise that can be beneficial for improving knee range of motion. The rhythmic pedaling motion gently moves the knee joint through its full range of motion.
- Walking: Walking is a low-impact exercise that can be gradually incorporated into a knee exercise program. It helps maintain joint mobility and cardiovascular health. Starting with short walks and gradually increasing duration and intensity is crucial.
- Gentle knee circles: Gentle knee circles can improve the range of motion in the knee joint. These movements should be performed slowly and with control, avoiding any pain or discomfort.
Comparison of Exercise Types
| Exercise Type | Description | Variations for Different Severity Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Strength Training | Builds muscle strength around the knee. | Light weights/resistance bands for mild, progressively heavier weights for moderate, and supervised, light weight exercises for severe. |
| Flexibility Exercises | Maintains and improves flexibility. | Gentle stretches for mild, moderate stretches for moderate, and assisted stretches for severe. |
| Range of Motion Exercises | Improves joint movement. | Simple range of motion exercises for mild, progressively increasing range of motion for moderate, and assisted range of motion exercises for severe. |
Low-Impact vs. High-Impact Exercises
| Exercise Type | Description | Suitability for Arthritic Knees |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Impact | Exercises that put minimal stress on the joints. | Generally suitable for individuals with arthritic knees. |
| Examples | Walking, swimming, stationary cycling, elliptical training. | |
| High-Impact | Exercises that put significant stress on the joints. | Generally not recommended for individuals with severe arthritis. |
| Examples | Running, jumping, high-impact aerobics. |
Exercise Considerations for Specific Needs: Exercises For Arthritic Knees
Knee arthritis can significantly impact daily life, and exercise plays a crucial role in managing pain, improving mobility, and maintaining overall health. However, an effective exercise program needs careful consideration of individual needs, including the severity of arthritis, pain tolerance, and physical limitations. This section delves into the importance of personalized exercise programs tailored to each arthritic knee’s unique circumstances.Effective exercise programs for arthritic knees require a comprehensive approach that goes beyond generic routines.
Understanding the specific needs of each individual, such as the degree of joint pain and stiffness, is crucial for developing a safe and effective exercise plan. This approach is best achieved through a collaborative effort between the patient and a qualified healthcare professional, like a physical therapist.
Role of Physical Therapy in Designing an Exercise Program
Physical therapists are invaluable in crafting personalized exercise plans for arthritic knees. Their expertise allows them to assess the individual’s specific needs, including the extent of joint damage, pain levels, and functional limitations. They develop a tailored program that focuses on building strength, improving flexibility, and enhancing joint stability. This personalized approach is essential to avoid exacerbating existing pain or causing further injury.
Adjusting Exercises Based on Arthritis Severity and Limitations
Exercise intensity and type must be adjusted according to the severity of arthritis. For individuals with mild arthritis, a moderate exercise program can be beneficial. However, those with severe arthritis may need to focus on low-impact exercises and gentler movements. Individual limitations, such as previous injuries or other medical conditions, should also be carefully considered when designing the exercise routine.
This personalized approach ensures that the exercises are not only effective but also safe for the individual.
Exercise Modifications Based on Pain Tolerance and Mobility
Pain tolerance and mobility levels significantly influence the type and intensity of exercises. If an exercise causes excessive pain, it should be modified or avoided altogether. Modifying exercises may involve using lighter weights, shorter durations, or changing the exercise’s form. For example, instead of full squats, partial squats or chair squats can be performed if a person experiences pain or limited mobility.
This approach prioritizes comfort and safety during exercise.
Taking care of arthritic knees requires consistent exercise, but sometimes the demands of caring for someone with a condition can lead to caregiver burnout. Finding the right balance between physical therapy and emotional well-being is key. It’s important to recognize the signs of caregiver burnout, like feeling overwhelmed or exhausted, to prioritize self-care and maintain a healthy routine for effective knee exercises.
Knowing when to seek help from support groups or professionals, like therapists, is crucial for continuing to focus on exercises that improve mobility and reduce pain in arthritic knees. signs of caregiver burnout can be a serious concern if not addressed, but remember that staying committed to knee exercises is vital for managing the condition. This will in turn allow for a better quality of life.
Importance of Proper Posture and Body Mechanics
Maintaining proper posture and body mechanics is crucial during exercises to prevent further injury or pain. This involves using correct alignment of the spine, knees, and hips, as well as engaging core muscles for support. A physical therapist can provide guidance on proper form and body mechanics for each specific exercise. This is especially important for those with arthritic knees, as maintaining correct form helps reduce stress on the joints.
“Proper posture and body mechanics are essential to prevent exacerbating joint pain and to ensure safe and effective exercise.”
Modifications Table for Knee Exercises
| Degree of Knee Pain and Stiffness | Exercise Modification Examples |
|---|---|
| Mild | Full range of motion exercises, light weights, moderate intensity |
| Moderate | Modified exercises (e.g., chair squats instead of full squats), lighter weights, shorter durations, use of assistive devices (e.g., handrails) |
| Severe | Low-impact exercises (e.g., swimming, stationary cycling), very light weights, very short durations, focus on maintaining range of motion, use of assistive devices |
Safety and Precautions
Protecting your knees during exercise is paramount, especially if you have arthritis. Proper form, mindful pacing, and recognizing potential issues are key to avoiding injury and maximizing the benefits of your workouts. Ignoring these safety measures can lead to setbacks in your recovery and potentially exacerbate your knee pain.Careful attention to safety and appropriate precautions is crucial for individuals with arthritic knees.
By understanding the potential risks and implementing preventative measures, you can ensure a safe and effective exercise routine that promotes joint health and overall well-being.
Important Safety Considerations
Proper exercise technique and mindful pacing are essential for safety. Overexertion or improper form can lead to pain, inflammation, and even further damage to the affected joint. Listen to your body and adjust the intensity or type of exercise as needed. Consistent, gradual progression is more beneficial than pushing yourself too hard too quickly.
Potential Risks and Complications
Improper exercise techniques can result in a variety of problems, including increased pain, swelling, and joint instability. For example, using poor form during squats or lunges can put undue stress on the knee joint, potentially causing cartilage damage or further deterioration of existing conditions. Sudden, jerky movements are particularly risky. Be sure to focus on controlled, smooth motions.
Recognizing and Responding to Pain, Exercises for arthritic knees
Pain is a crucial signal from your body. It indicates that you’ve reached a point where further exercise could potentially harm the knee joint. Don’t ignore pain. Adjust the exercise, rest, and consult your healthcare professional if the pain persists or worsens. Learning to distinguish between normal muscle soreness and pain originating from the joint is important.
If you experience sharp, throbbing, or persistent pain, stop the exercise immediately.
Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
Adequate warm-up and cool-down are vital components of any exercise program, especially for individuals with arthritic knees. A proper warm-up prepares the muscles and joints for the demands of exercise, reducing the risk of injury. Cool-down helps the body return to its resting state, reducing muscle stiffness and promoting recovery. Examples include gentle stretching and light cardio for 5-10 minutes before and after your workout.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
| Mistake | Corrective Action |
|---|---|
| Skipping the warm-up | Include 5-10 minutes of light cardio and dynamic stretching before each workout. |
| Using improper form | Seek guidance from a physical therapist or certified instructor to learn proper techniques for exercises. |
| Ignoring pain signals | Listen to your body. Stop the exercise immediately if you experience sharp or persistent pain. |
| Overexertion | Start with shorter durations and lower intensities, gradually increasing the duration and intensity as your strength and endurance improve. |
| Not consulting your doctor | Discuss your exercise plan with your doctor or physical therapist before starting any new routine. |
Exercise Program Design
Creating a personalized exercise program is crucial for managing knee arthritis effectively. It allows individuals to tailor their routine to their specific needs and pain levels, maximizing benefits and minimizing risk. A well-designed program should address the unique characteristics of each person’s knee condition, considering factors like the severity of arthritis, joint pain, and overall health. This personalized approach ensures that exercises are safe, effective, and sustainable.A well-structured program emphasizes gradual progression.
Rushing into intense workouts can lead to pain, injury, and discouragement. Instead, a gradual increase in exercise intensity and duration is essential for building strength, improving flexibility, and reducing pain over time. This approach allows the body to adapt and respond to the challenges presented by arthritis, promoting long-term adherence and improved quality of life.
Personalized Exercise Program Steps
Developing a personalized exercise program for managing knee arthritis involves several key steps. First, a thorough assessment of the individual’s condition is necessary, considering the severity of the arthritis, any previous injuries, and current health status. This initial evaluation forms the foundation for designing a safe and effective exercise routine. Secondly, the program should be tailored to the individual’s abilities and preferences.
Taking care of arthritic knees involves gentle exercises, like swimming or water aerobics. But, what if your diet is also contributing to joint pain? Consider what happens to your body when you eat red meat every day; what happens to your body when you eat red meat everyday might surprise you. Focusing on low-impact, regular movement, alongside a balanced diet, is key for maintaining knee health.
So, incorporating those gentle exercises into your routine is a great step toward feeling better.
Incorporating exercises that the person enjoys and finds manageable will increase the likelihood of consistent participation. Finally, a regular evaluation and modification of the program based on the individual’s progress and feedback are essential for long-term effectiveness.
Gradual Progression in Exercise Intensity and Duration
Gradual progression is a fundamental principle in designing an exercise program for knee arthritis. Starting with low-intensity activities and gradually increasing the duration and intensity of exercises is crucial for preventing pain and injury. This approach allows the body to adapt to the increased demands placed upon it. The goal is to progressively challenge the knee while maintaining comfort and avoiding overexertion.
For example, starting with 5 minutes of walking three times a week and gradually increasing the duration and frequency to 30 minutes five times a week over several weeks is a safe and effective approach. This slow, steady increase allows the body to adapt and reduces the risk of injury.
Sample Exercise Routines for Different Levels of Knee Arthritis Severity
Exercise routines should be tailored to the severity of knee arthritis. For mild cases, low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and stationary cycling can be incorporated. As the severity increases, modified versions of these activities or other exercises like gentle stretching and strengthening exercises using resistance bands or light weights can be considered. For more severe cases, aquatic exercises in a pool or specialized exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist are often recommended.
Exercise Program Durations and Frequencies
| Knee Arthritis Severity | Exercise Duration (minutes/session) | Exercise Frequency (days/week) |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 15-30 | 3-5 |
| Moderate | 20-45 | 4-6 |
| Severe | 15-30 (in conjunction with physical therapy) | 3-5 (with physical therapy sessions) |
This table provides a general guideline for exercise program durations and frequencies. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to determine the most appropriate plan for an individual’s specific needs.
Sample Weekly Exercise Plan
This sample weekly exercise plan provides a framework for managing knee arthritis. Adjustments are necessary based on individual needs and progress. Always consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program.
- Monday: Low-impact cardio, like walking on a flat surface (15 minutes), followed by gentle stretching (10 minutes).
- Tuesday: Strength training using resistance bands (15 minutes), focusing on quadriceps and hamstring exercises.
- Wednesday: Rest or light activity like chair exercises (15 minutes) to prevent stiffness.
- Thursday: Swimming or water aerobics (20 minutes) to reduce impact on the knee.
- Friday: Repeat Monday’s routine.
- Saturday: Gentle walking or cycling (20 minutes) followed by stretching.
- Sunday: Rest or light activity.
Importance of Consistency and Lifestyle
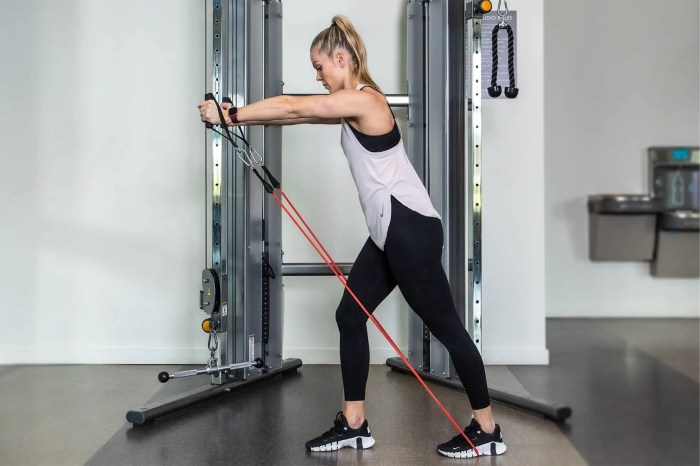

Knee arthritis can be a persistent condition, but its impact can be significantly mitigated through consistent lifestyle choices. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight play crucial roles in managing pain and improving overall knee function. This section delves into the vital connection between these lifestyle factors and long-term knee health.Adopting a consistent approach to exercise, nutrition, and weight management is not a quick fix, but rather a cornerstone of effective knee arthritis management.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance your quality of life. Consistent effort over time yields substantial benefits, and the cumulative impact of these choices is undeniable.
The Significance of Consistent Exercise
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining joint health and function. Consistent exercise helps to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improving stability and reducing stress on the joint. This support prevents further deterioration and can lessen the need for pain medication. It also boosts overall fitness, enhancing your ability to perform daily tasks and enjoy activities.
The Role of Proper Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition provides the building blocks for healthy cartilage and tissues, crucial for joint health. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein, coupled with adequate hydration, supports the body’s natural repair processes. This aids in maintaining joint health and reducing inflammation. Staying hydrated helps lubricate joints, reducing friction and pain.
The Importance of Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is paramount in reducing stress on the knees. Excess weight puts significant pressure on the joints, accelerating wear and tear. Losing even a small amount of weight can substantially lessen the strain on your knees, thereby reducing pain and improving mobility. This is particularly important for individuals who already have knee arthritis.
Suggestions for Incorporating Exercises into Daily Routines
Incorporating exercises into daily routines can be achieved through various strategies. Consider incorporating short bursts of activity throughout the day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, or taking a brisk walk during your lunch break. Scheduling specific exercise sessions into your daily calendar can make them a priority. Finding activities you enjoy will make them sustainable.
For example, a gentle yoga class, swimming, or cycling can be beneficial.
Creating a Supportive Lifestyle
A table outlining the relationship between lifestyle choices and knee arthritis management can visually represent the interconnectedness of these factors:
| Lifestyle Choice | Impact on Knee Arthritis | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Consistent Exercise | Strengthens muscles, reduces stress, improves mobility | Walking 30 minutes daily, attending a gentle yoga class twice a week |
| Proper Nutrition | Supports cartilage repair, reduces inflammation | Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein; drinking plenty of water |
| Healthy Weight Management | Reduces stress on joints, improves mobility | Maintaining a healthy BMI through a balanced diet and regular exercise |
| Hydration | Lubricates joints, reduces friction | Drinking 8 glasses of water daily |
Illustrative Examples
Putting theory into practice is crucial for effectively managing knee arthritis. This section provides specific, actionable exercises, detailed descriptions, and visual aids to guide you through proper form and technique. Understanding how to perform these exercises correctly will maximize their benefits and minimize the risk of injury.
Chair Squats
Chair squats are a fantastic exercise for strengthening the quadriceps and glutes, important muscle groups for knee stability. This exercise is particularly beneficial for those with mild to moderate knee arthritis as it reduces stress on the knee joint while still providing a strengthening effect.
Proper Form: Begin by sitting on a sturdy chair with your feet flat on the floor, shoulder-width apart. Keeping your back straight and core engaged, slowly stand up, pushing through your heels. Pause briefly at the top of the movement. Then, slowly lower yourself back down to the chair, controlling the movement. Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Benefits for Knee Arthritis: Chair squats improve quadriceps strength, which can help stabilize the knee joint and reduce pain. The controlled movement also reduces stress on the knee, making it a low-impact, effective exercise for people with arthritis.
Leg Raises (lying)
Leg raises, performed while lying down, are an excellent way to strengthen the hip flexors and quadriceps, improving knee stability and flexibility. This exercise is particularly helpful for those experiencing pain in the front of the knee joint.
Proper Form: Lie flat on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Engage your core muscles and slowly lift your legs straight up, keeping them as close to your body as possible. Pause briefly at the top of the movement, maintaining a controlled descent back to the starting position. Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Benefits for Knee Arthritis: Leg raises strengthen the muscles around the hip and knee, reducing stress on the knee joint. This can help to improve mobility and reduce pain, especially in the front of the knee.
Wall Slides
Wall slides are a low-impact exercise that gently stretches and strengthens the muscles around the knee, while improving flexibility and reducing stiffness. It’s a suitable exercise for all stages of knee arthritis, especially for those who find standing exercises challenging.
Proper Form: Stand facing a wall, placing your hands on the wall at shoulder height. Keeping your back straight and core engaged, slowly slide down the wall, bending your knees until your thighs are parallel to the floor. Pause briefly, then slowly slide back up to the starting position. Repeat for the desired number of repetitions.
Benefits for Knee Arthritis: Wall slides gently stretch the hamstrings and quadriceps, improving knee flexibility and reducing stiffness. The controlled movement minimizes stress on the knee joint, making it suitable for people with varying degrees of arthritis.
Summary Table
| Exercise | Muscle Groups Targeted | Benefits for Knee Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Chair Squats | Quadriceps, Glutes | Improved knee stability, reduced pain, enhanced quad strength |
| Leg Raises (lying) | Hip flexors, Quadriceps | Strengthened hip and knee muscles, improved mobility, reduced knee pain |
| Wall Slides | Hamstrings, Quadriceps | Improved knee flexibility, reduced stiffness, low-impact strengthening |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, managing arthritic knees through exercise requires a personalized approach that considers the severity of your condition, your pain tolerance, and your overall fitness level. Remember, consistency is key to long-term success. By incorporating the exercises and strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can significantly improve your knee health and quality of life. Listen to your body, adjust as needed, and celebrate your progress along the way.
Your journey to better knee health begins with the right knowledge and a dedicated commitment to your well-being.