Identifying insect bites and stings is crucial for prompt and appropriate treatment. This guide delves into the differences between bites and stings, explores common symptoms, and details assessment procedures, first aid, prevention, and specific insect types. From recognizing the subtle variations in bite marks to understanding potential allergic reactions, this comprehensive resource will equip you…
Tag: allergies
Can Allergies Cause a Fever? Understanding the Link
Can allergies cause a fever? This question delves into the intricate relationship between allergic reactions and elevated body temperature. Allergies, encompassing a spectrum of immune responses to foreign substances, often manifest as uncomfortable symptoms like sneezing, itching, and rashes. However, the connection to fever is less straightforward. While a fever is frequently associated with infections,…
Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema A Deep Dive
Atopic dermatitis vs eczema – are they the same thing? This exploration delves into the similarities and differences between these skin conditions, highlighting their often-overlapping nature. We’ll uncover the historical understanding, examine the underlying causes, and explore the nuances of diagnosis and management. Understanding these distinctions is key to providing the best possible care for…
First Aid Allergies Anaphylaxis A Guide
First aid allergies anaphylaxis is a critical topic demanding immediate attention. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and appropriate response is crucial for saving lives. This guide will walk you through recognizing various allergic reactions, progressing to anaphylaxis, and the crucial first aid steps to take in each scenario. From mild reactions to severe anaphylactic episodes, we’ll…
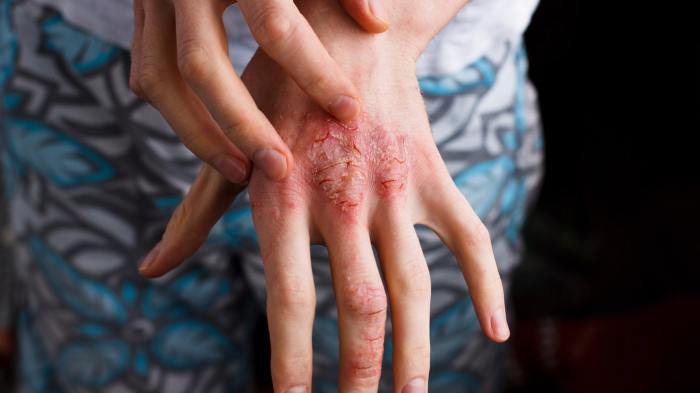
Itchy Hands and Feet Causes and Solutions
Itchy hands and feet can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience. This comprehensive guide delves into the various potential causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures for this common ailment. Understanding the nuances of itchy hands and feet is key to finding relief and restoring comfort. From skin conditions to allergies and underlying health…
Outdoor Allergic Asthma Triggers A Comprehensive Guide
Outdoor allergic asthma triggers, a significant concern for many, encompass a range of environmental factors that can induce allergic reactions in asthmatics. Understanding these triggers, their mechanisms, and how to manage exposure is crucial for effective asthma management. This guide explores the various types of outdoor allergens, their seasonal patterns, and the environmental conditions that…