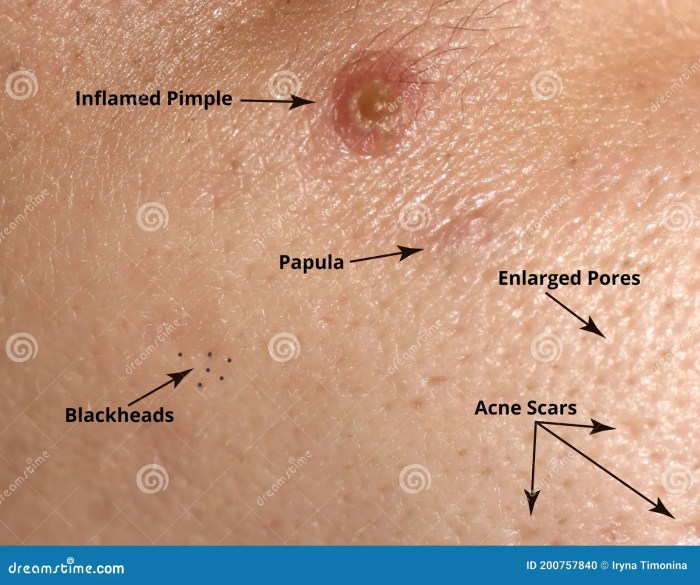
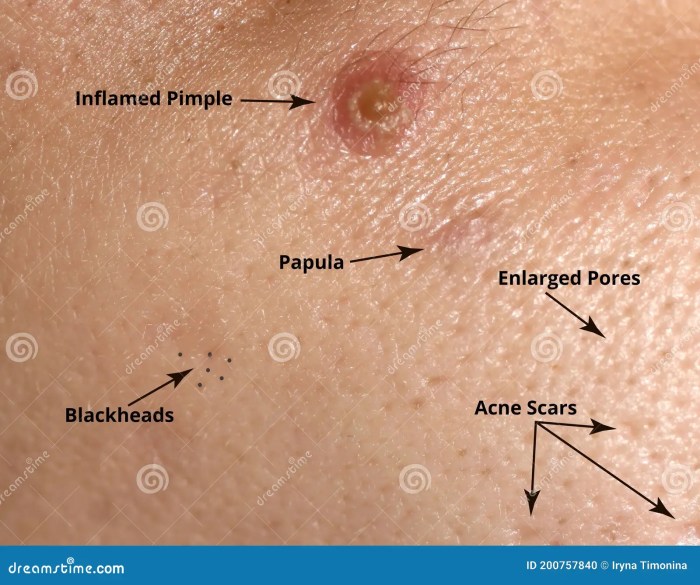
Acne and oily skin can be a real challenge, affecting self-esteem and confidence. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, types, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, home remedies, skincare routines, and even how your skin reacts to products. We’ll explore everything from hormonal imbalances and genetics to dietary choices, environmental factors, and stress levels.
We’ll cover various types of acne, from mild comedones to severe inflammation, and discuss the different characteristics of oily skin. Understanding these aspects is key to developing an effective strategy for managing your skin’s needs.
Causes of Acne and Oily Skin
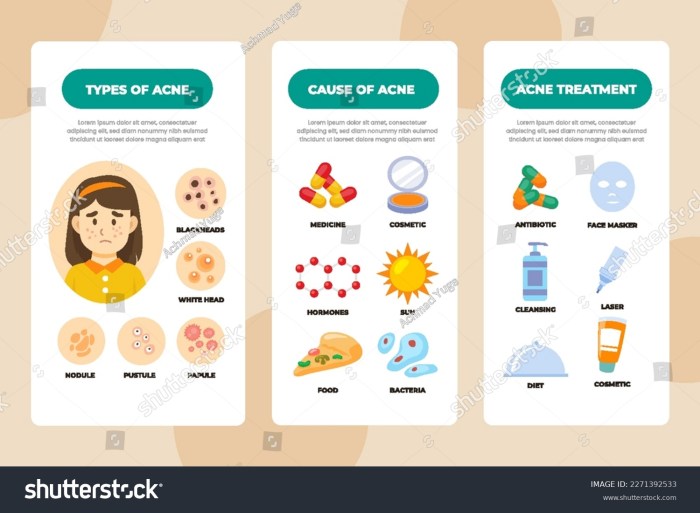
Understanding the complex interplay of factors contributing to acne and oily skin is crucial for effective management. These conditions are rarely caused by a single factor, but rather a combination of internal and external influences. This in-depth look will delve into the hormonal, genetic, dietary, environmental, and stress-related aspects of this skin issue.Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in acne and oily skin development.
The body’s production of androgens, hormones like testosterone, influences sebum production. Increased androgen levels stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to an overproduction of sebum. This excess oil can clog pores, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth, a key factor in acne formation. Similarly, fluctuating estrogen levels during menstruation or pregnancy can also affect sebum production.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal changes, particularly fluctuations in androgen levels, are a key driver of acne and oily skin. Androgens stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to increased sebum production. This excess oil can clog pores, creating an environment ideal for bacteria to thrive, which is crucial in the development of acne. Furthermore, hormonal shifts during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can also contribute to changes in skin oil production.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics significantly influences an individual’s susceptibility to acne and oily skin. Inherited traits can affect the activity of sebaceous glands, the amount of sebum produced, and the skin’s response to hormonal fluctuations. Individuals with a family history of acne or oily skin are more likely to develop these conditions. This genetic predisposition doesn’t guarantee the development of acne or oily skin, but it certainly increases the risk.
Dietary Influences
Diet, while not a direct cause, can significantly impact acne and oily skin. Certain foods may exacerbate these issues, while others might offer some protection. High-glycemic index foods, processed foods, and dairy products can potentially worsen acne and oil production. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins may contribute to healthier skin. The specific impact of different dietary choices on skin oil production is complex and varies from person to person.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as climate and exposure to pollution, can affect skin health. Hot, humid climates can exacerbate oily skin, while dry climates might lead to overcompensation and increased oil production. Similarly, pollution can irritate and inflame the skin, potentially contributing to acne development. Exposure to allergens and irritants in the environment also plays a role in skin reactions.
Stress and Acne/Oily Skin
Stress significantly impacts skin health. When stressed, the body releases hormones that can affect sebum production, increasing oiliness and potentially worsening acne. This stress response can lead to increased inflammation and worsen existing acne conditions. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle adjustments can help regulate skin oil production and improve overall skin health.
Dietary Impact on Skin Oil Production
| Dietary Choice | Impact on Skin Oil Production |
|---|---|
| High-glycemic index foods (e.g., white bread, sugary drinks) | Potentially increases skin oil production due to insulin spikes. |
| Processed foods (e.g., fast food, packaged snacks) | May exacerbate acne and oil production due to high sugar and unhealthy fats. |
| Dairy products (e.g., milk, cheese) | Potential link to increased skin oil production, but evidence is varied. |
| Fruits and vegetables | May contribute to healthier skin and potentially reduce oil production due to their antioxidant properties. |
| Lean proteins (e.g., fish, poultry) | Generally considered beneficial for skin health. |
Note: The impact of different dietary choices on skin oil production can vary significantly from individual to individual.
Types of Acne and Oily Skin
Understanding the different types of acne and oily skin is crucial for effective treatment. Knowing the specific characteristics of your skin condition allows you to tailor your approach, maximizing the likelihood of successful management. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about skincare products and professional consultations.
Acne Types
Different types of acne present with varying symptoms and severity. This understanding is essential for personalized treatment strategies. Acne types range from mild to severe, reflecting the underlying inflammation and involvement of the skin’s sebaceous glands.
- Comedonal Acne: This is the most common type of acne, characterized by the formation of blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones). These are non-inflammatory lesions, meaning there’s no significant redness or swelling. Comedones form when hair follicles become clogged with sebum and dead skin cells.
- Inflammatory Acne: This type involves inflammation of the skin. It presents with papules (small, red bumps), pustules (papules with pus), nodules (larger, deeper, and more painful bumps), and cysts (large, pus-filled, and painful lesions). Inflammatory acne typically indicates a more severe condition requiring more aggressive treatment approaches.
- Nodular Acne: A subtype of inflammatory acne, nodular acne is characterized by painful, deep-seated bumps beneath the skin’s surface. These lesions are often inflamed and cause significant discomfort. They are typically larger than papules or pustules and can persist for extended periods.
- Cystic Acne: The most severe form of inflammatory acne, cystic acne involves large, painful, and pus-filled cysts that extend deep within the skin. These lesions are often accompanied by significant inflammation, scarring, and discomfort. Cystic acne requires immediate professional medical attention.
Oily Skin Characteristics
Oily skin is often associated with acne, as excess sebum production can clog pores. Understanding the specific characteristics of your oily skin type is crucial for appropriate skincare.
- Shiny Appearance: A noticeable sheen across the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin) is a hallmark of oily skin. This is due to the overproduction of sebum.
- Large Pores: Oily skin often has visible pores, which can appear larger due to the sebum buildup.
- Prone to Breakouts: Oily skin is more susceptible to acne breakouts, particularly comedones, due to the increased sebum production and potential clogging of pores.
- Greasy Feel: Oily skin often feels greasy or slippery to the touch, especially throughout the day.
Acne Breakout Examples and Types
The type of acne breakout is closely linked to the severity of the underlying condition.
- Example 1: A person with comedonal acne might experience only blackheads and whiteheads on the nose and forehead, while an individual with inflammatory acne might experience painful red bumps, pus-filled pustules, and noticeable inflammation across the face.
- Example 2: An individual with nodular acne could develop large, deep-seated, and painful bumps, often accompanied by significant discomfort, while an individual with cystic acne might experience large, pus-filled cysts that cause severe inflammation and potentially permanent scarring.
Correlation Between Skin Type and Acne Severity
Oily skin types are more prone to acne breakouts due to the increased sebum production. The severity of the acne can vary significantly, ranging from mild comedones to severe cystic acne.
Acne Type Classification
| Acne Type | Visual Description | Treatment Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Comedonal Acne | Blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones), often on the nose, forehead, and chin. Little to no redness or inflammation. | Gentle exfoliation, salicylic acid, and spot treatments. Consider a dermatologist for more severe cases. |
| Inflammatory Acne | Papules (small red bumps), pustules (papules with pus), nodules (larger, deeper, and more painful bumps), and cysts (large, pus-filled, and painful lesions). Significant redness and inflammation. | Topical retinoids, antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, and possibly oral antibiotics. Professional consultation highly recommended. |
| Nodular Acne | Painful, deep-seated bumps beneath the skin’s surface, often inflamed and causing significant discomfort. | Combination of topical treatments for inflammatory acne, possibly including oral medications, and/or professional medical intervention. |
| Cystic Acne | Large, painful, pus-filled cysts that extend deep within the skin. Severe inflammation and discomfort, potential for permanent scarring. | Professional consultation and treatment with oral antibiotics, isotretinoin (often a last resort), and/or other advanced treatments. |
Diagnosing Acne and Oily Skin
Understanding the root causes of acne and oily skin is crucial, but accurate diagnosis is equally important for effective treatment. A proper diagnosis involves a multi-faceted approach, considering various factors beyond just visual observation. A skilled professional can pinpoint the specific type and severity of the condition, guiding the path towards personalized solutions.Diagnosing acne and oily skin requires a comprehensive evaluation.
This goes beyond simply identifying the presence of pimples or excess oil. A thorough assessment considers the patient’s medical history, lifestyle factors, and physical examination findings to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. Skin analysis tools can provide objective data that aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of the condition’s progression.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
A proper diagnosis of acne and oily skin conditions hinges on careful consideration of various factors. The process involves a detailed evaluation of the patient’s skin, medical history, and lifestyle. This comprehensive approach helps determine the underlying causes and tailor appropriate treatments.
Role of Skin Examinations
Visual examination of the skin is a cornerstone of diagnosis. The dermatologist meticulously assesses the distribution, type, and severity of acne lesions, looking for patterns indicative of different types of acne. Careful observation of skin texture, including the presence of enlarged pores, shine, or inflammation, aids in identifying oily skin conditions. The evaluation also takes into account the overall skin tone and any visible signs of irritation or dryness, which could be related or contributing factors.
Importance of Medical History
A detailed medical history provides valuable insights into potential contributing factors. The dermatologist inquires about the patient’s lifestyle, including diet, stress levels, and use of medications or cosmetics. Information on family history of acne or skin conditions can also provide clues about potential genetic predispositions. Previous treatments, their effectiveness, and any adverse reactions to medications are crucial for determining the best course of action.
Use of Skin Analysis Tools
Advanced skin analysis tools offer objective data to aid in diagnosis and treatment monitoring. These tools measure sebum production, pore size, and skin hydration levels, providing quantitative data that can be used to personalize treatment plans. For instance, a high sebum production reading might indicate a need for targeted therapies to control oil production. Similarly, low hydration levels might point to a need for moisturizers or treatments to restore skin moisture balance.
Diagnostic Procedures Table
| Diagnostic Procedure | Tools Used | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Skin Examination | Dermatoscope, Magnifying Glass | Identifying lesion type, distribution, severity, and associated signs of inflammation or dryness. Assessment of skin texture and shine. |
| Medical History Review | Patient Interview | Identifying potential contributing factors like diet, stress, medications, cosmetics, and family history of skin conditions. |
| Skin Analysis | Corneometer, Sebumeter, Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL) meter | Quantifying sebum production, hydration levels, pore size, and other skin characteristics to provide objective data for personalized treatment plans. |
Treatment Options for Acne and Oily Skin

Managing acne and oily skin requires a multifaceted approach, combining topical treatments, oral medications, lifestyle adjustments, and professional skincare. This section delves into the various strategies available, providing insights into their mechanisms, potential benefits, and drawbacks.Effective acne and oily skin management involves a combination of targeted treatments and consistent lifestyle changes. Understanding the nuances of each approach is crucial for developing a personalized plan tailored to individual needs and skin type.
Topical Treatments for Acne and Oily Skin
Topical treatments directly target the skin, offering localized solutions for acne and oil production. These treatments often come in various forms, including lotions, gels, creams, and pads, offering diverse applications and benefits.
- Salicylic Acid: A beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) that exfoliates the skin, unclogging pores and reducing inflammation. It’s effective against blackheads and whiteheads, often used in concentrations ranging from 0.5% to 2%. Potential side effects include skin irritation, redness, and dryness, especially at higher concentrations. Salicylic acid is a common ingredient in acne treatments due to its ability to penetrate the skin and effectively exfoliate.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: An antibacterial agent that kills bacteria responsible for acne formation. It also has comedolytic properties, meaning it can unclog pores. Benzoyl peroxide is available in various concentrations, and higher concentrations can lead to more significant benefits but also greater irritation. Side effects include skin dryness, redness, and irritation. It’s important to start with a low concentration and gradually increase it as tolerated.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids promote cell turnover, reduce inflammation, and unclog pores. Topical retinoids are effective in treating acne and promoting healthy skin texture. Side effects include dryness, redness, and peeling, often described as skin irritation, which typically improves over time with continued use. Starting with a lower concentration and gradually increasing it can help mitigate these side effects.
- Sulfur: A keratolytic agent that helps exfoliate the skin and reduce the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads). Sulfur also possesses antibacterial properties, helping to control acne-causing bacteria. It is commonly used in combination with other topical treatments. Side effects include skin irritation and dryness. A low concentration is usually used initially, and the treatment should be adjusted based on skin tolerance.
Oral Medications for Acne and Oily Skin
Oral medications offer a systemic approach to acne and oily skin treatment. They act on the body as a whole, often impacting hormone levels or bacterial activity to manage acne.
- Antibiotics: These medications target bacteria associated with acne formation. They can be prescribed for short-term or long-term use, depending on the severity and response to treatment. Potential side effects include antibiotic resistance and gastrointestinal issues. Antibiotics are typically prescribed in conjunction with topical treatments to enhance efficacy.
- Hormonal Medications: These medications, such as birth control pills, can regulate hormone levels, reducing the production of sebum and the inflammatory response associated with acne. They are often prescribed for women experiencing hormonal acne. Potential side effects include changes in menstrual cycles, mood swings, and other hormonal imbalances. The selection of hormonal medications should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle Changes for Acne and Oily Skin Management
Lifestyle changes are integral to acne and oily skin management, impacting the overall health of the skin.
Dealing with acne and oily skin can be frustrating. Sometimes, seemingly unrelated factors can contribute, like sleep apnea. If you suspect your CPAP machine isn’t working properly, check out this helpful guide on signs your cpap is not working. Addressing potential CPAP issues could potentially resolve some of those skin problems. In the end, understanding your health holistically is key to tackling acne and oily skin effectively.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can contribute to healthier skin. Reducing sugar and processed foods might also be beneficial, as these can sometimes exacerbate acne. There is no scientific consensus on whether certain foods directly cause acne, but reducing processed food and sugar intake can contribute to better overall health, which might have a positive effect on skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress can influence hormone levels and exacerbate acne. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as exercise, yoga, or meditation can contribute to better overall skin health.
- Hygiene Practices: Maintaining proper hygiene, including gentle cleansing and avoiding harsh scrubbing, is important to prevent clogged pores. Over-washing can also be detrimental. Using appropriate skin care products, and avoiding excessive scrubbing, are important steps.
Professional Skincare Treatments for Acne and Oily Skin
Professional treatments provide more intensive approaches to managing acne and oily skin.
- Chemical Peels: These treatments use chemical solutions to exfoliate the skin, removing dead skin cells and promoting cell turnover. They can help improve acne scarring and refine skin texture. Chemical peels can vary in intensity and should be performed by a qualified professional.
- Extractions: These treatments involve removing blackheads and whiteheads by physically extracting them from the pores. Professional extractions can be more effective than home remedies. Extractions should only be performed by a qualified professional to minimize the risk of infection and skin damage.
- Laser Treatments: Laser treatments can target acne lesions and reduce inflammation. They are typically used for more severe acne cases or acne scarring. Laser treatments should be performed by a qualified dermatologist.
Specific Skincare Products for Acne-Prone and Oily Skin
Choosing appropriate skincare products is essential for managing acne and oily skin. Look for products formulated for acne-prone and oily skin types. These products often contain ingredients like salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or retinoids.
Table of Topical Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Salicylic Acid | Exfoliates skin, unclogs pores | Skin irritation, redness, dryness |
| Benzoyl Peroxide | Kills acne-causing bacteria, unclogs pores | Skin dryness, redness, irritation |
| Retinoids | Promotes cell turnover, reduces inflammation, unclogs pores | Dryness, redness, peeling |
| Sulfur | Exfoliates skin, reduces comedones, antibacterial | Skin irritation, dryness |
Preventing Acne and Oily Skin
Preventing acne and oily skin involves a multifaceted approach that goes beyond just topical treatments. A proactive strategy focusing on lifestyle choices and consistent skincare routines can significantly reduce the likelihood of breakouts and excess oil production. This proactive approach emphasizes long-term well-being, not just short-term fixes.Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, stress management, and appropriate skincare, plays a crucial role in preventing acne and oily skin.
Understanding the interplay of these factors empowers individuals to take control of their skin health and achieve a clearer, more balanced complexion.
Dietary Habits for Acne Prevention
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can contribute to healthier skin. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive consumption of greasy or fried foods can minimize the production of excess oil. A diet rich in antioxidants can also help protect skin cells from damage.
- Fruits and vegetables are excellent sources of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, promoting overall health and skin health.
- Lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, and beans, provide essential nutrients for skin repair and regeneration.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive consumption of greasy or fried foods, as these can trigger oil production and inflammation.
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water supports overall bodily functions, including skin health.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress can exacerbate acne and oily skin. Stress triggers hormonal imbalances that can lead to increased sebum production. Incorporating stress-reducing activities into daily routines can significantly contribute to skin health.
Dealing with acne and oily skin can be frustrating. Sometimes, a new product or ingredient can trigger an allergic reaction, which can manifest in similar ways to acne. Understanding how long an allergic reaction lasts is key to managing the symptoms and figuring out what’s causing the problem. For example, if your breakout persists longer than expected, you might want to check out this helpful resource on how long does an allergic reaction last.
Ultimately, identifying the root cause of the acne and oily skin is crucial for effective long-term management.
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help regulate stress levels and promote emotional well-being.
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as exercise or yoga, releases endorphins and reduces stress hormones.
- Prioritizing sufficient sleep allows the body to repair and recover, reducing stress and promoting healthy skin.
- Taking time for hobbies and relaxation activities helps to de-stress and improve overall well-being.
Effective Skincare Routines
A tailored skincare routine is essential for managing acne and oily skin. This routine should include gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing to maintain a balanced skin microbiome. The choice of products should be carefully considered to avoid further irritation or inflammation.
- Cleansing the skin twice daily with a gentle, oil-free cleanser removes excess oil and impurities without stripping the skin’s natural oils.
- Exfoliation, done regularly but gently, helps to remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and improve skin texture.
- Moisturizing with a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer helps to hydrate the skin without adding excess oil.
- Using spot treatments targeted at acne can help reduce breakouts and inflammation.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Consulting a dermatologist can provide personalized advice and tailored treatment plans. A dermatologist can assess individual skin conditions and recommend the most appropriate preventative strategies. They can also provide guidance on product selection and usage.
- Dermatologists can accurately diagnose the type and severity of acne and oily skin.
- They can recommend the most suitable skincare products and routines for optimal results.
- Dermatologists can provide personalized guidance on stress management and lifestyle adjustments.
- Regular check-ups with a dermatologist are crucial for maintaining long-term skin health.
Preventive Measures by Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: Prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive consumption of greasy or fried foods.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing activities into daily routines. These can include mindfulness, exercise, sufficient sleep, and hobbies.
- Skincare: Use a gentle, oil-free cleanser, consider exfoliation, and moisturize with a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer. Spot treatments can help manage breakouts.
- Professional Guidance: Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and a tailored treatment plan. Regular check-ups can maintain long-term skin health.
Home Remedies for Acne and Oily Skin
Many people turn to home remedies for acne and oily skin before resorting to expensive treatments. These remedies often involve natural ingredients and may offer a gentler approach. However, it’s crucial to remember that home remedies are not always a substitute for professional medical advice, especially for severe or persistent acne. Consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan if your condition doesn’t improve.While some home remedies show promise in managing mild acne and oily skin, their effectiveness can vary significantly depending on individual factors.
The safety and efficacy of these methods are not always rigorously tested or proven in clinical trials. Always be cautious and patch test any new home remedy before applying it to your entire face.
Natural Ingredients Used in Home Remedies, Acne and oily skin
Home remedies for acne and oily skin frequently utilize natural ingredients like honey, lemon juice, aloe vera, tea tree oil, and various fruits and vegetables. These ingredients are often touted for their antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties, which can potentially help control acne and reduce oil production. However, the effectiveness of these ingredients varies and depends on individual skin types and sensitivities.
Effectiveness and Safety of Home Remedies
The effectiveness of home remedies for acne and oily skin is often anecdotal, based on personal experiences rather than rigorous scientific studies. While some individuals may experience improvement, others may not see any noticeable change. Furthermore, the safety of certain home remedies is not always guaranteed. Some ingredients can cause irritation, allergic reactions, or skin discoloration if not used correctly.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Home Remedies
The potential benefits of home remedies often lie in their gentle nature and affordability. They may be less harsh than conventional treatments, minimizing the risk of side effects. However, a potential drawback is their lack of proven effectiveness for severe acne cases. Always proceed cautiously, prioritizing a consultation with a dermatologist if you’re experiencing severe or persistent acne or if you have sensitive skin.
Use of Natural Ingredients in Home Remedies
Natural ingredients like honey, known for its antibacterial properties, can be used as a mask. Lemon juice, with its astringent properties, can help reduce oil production. Aloe vera gel, renowned for its soothing properties, can calm irritated skin. Tea tree oil, an effective antimicrobial agent, is often incorporated into spot treatments. It’s crucial to understand that while these ingredients are natural, they can still cause irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
Comparison of Home Remedies and Conventional Treatments
| Feature | Home Remedies | Conventional Treatments |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Honey, lemon juice, aloe vera, tea tree oil | Topical retinoids, antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, oral medications |
| Application Methods | Masks, spot treatments, topical applications | Prescribed creams, gels, pills, and procedures |
| Potential Drawbacks | Varying effectiveness, potential for skin irritation, allergic reactions, lack of scientific backing | Side effects from medication, high cost, potential for dependence |
| Effectiveness | Generally mild to moderate, depending on individual response | Can be highly effective for severe acne, but requires professional guidance |
Note: This table is a simplified comparison and does not encompass all potential home remedies and conventional treatments. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Skincare Routine for Acne-Prone and Oily Skin
Acne-prone and oily skin requires a targeted skincare routine that addresses both excess sebum production and potential breakouts. This routine focuses on gentle cleansing, exfoliation, hydration, and targeted treatments to manage these issues effectively. A personalized approach is key, so tailoring the routine to your specific skin needs is crucial for optimal results.
Cleansing
Effective cleansing is the cornerstone of any skincare routine, especially for acne-prone and oily skin. It removes excess oil, dirt, and makeup that can clog pores and lead to breakouts. Choosing the right cleanser is vital. Harsh cleansers can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation, while gentle cleansers effectively remove impurities without disrupting the skin’s barrier.
- Morning Cleansing: A gentle, foaming cleanser is ideal for removing overnight buildup. Apply a small amount to damp skin, massage gently, and rinse thoroughly. This step helps to prepare the skin for the day ahead, removing any excess oil or makeup that may have accumulated overnight.
- Evening Cleansing: A slightly more thorough cleanse is beneficial in the evening. This removes the day’s pollutants, makeup, and sebum, preventing clogged pores and encouraging a healthy skin renewal process. Double cleansing with an oil-based cleanser followed by a water-based cleanser can be beneficial for removing stubborn makeup or sunscreen.
- Frequency: Twice daily, morning and evening.
- Duration: 30-60 seconds per cleanse.
Exfoliation
Gentle exfoliation helps to remove dead skin cells, unclog pores, and improve skin texture. Over-exfoliation can irritate the skin, so it’s important to find a balance. Chemical exfoliants are often preferred for their targeted action, while physical exfoliants should be used sparingly and with caution.
- Frequency: 1-2 times per week, depending on skin sensitivity.
- Duration: Keep the exfoliation time brief to avoid irritation. Aim for 1-2 minutes.
- Product Recommendation: A chemical exfoliant containing AHAs (alpha-hydroxy acids) or BHAs (beta-hydroxy acids) can gently remove dead skin cells without harsh scrubbing.
Hydration
Hydration is important for all skin types, but particularly for acne-prone and oily skin. A lightweight, oil-free moisturizer can hydrate the skin without contributing to excess oil production. Look for non-comedogenic formulas to prevent clogging pores.
Dealing with acne and oily skin can be frustrating, especially during allergy season. My skin tends to get extra greasy when my nose is running, and I’ve found that addressing seasonal allergies can actually help. Check out this guide on how to get rid of seasonal allergies for tips on managing symptoms, which in turn can reduce inflammation and oil production, leading to less acne.
It’s all about finding the right balance to keep my skin clear and healthy!
- Frequency: Twice daily, after cleansing.
- Duration: Apply a small amount to the face and gently pat in.
- Product Recommendation: Choose a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer specifically formulated for acne-prone and oily skin.
Treatment
Spot treatments or topical medications can target specific acne issues, like breakouts or inflammation. These should be used in conjunction with a comprehensive skincare routine.
- Frequency: As needed, based on acne severity.
- Duration: Follow the product instructions for application and frequency.
- Product Recommendation: A topical retinoid, salicylic acid, or benzoyl peroxide can help control acne.
Additional Tips
Tailoring your routine to your specific skin needs is crucial. If you experience dryness, adjust the frequency of exfoliation. If breakouts are persistent, increase the frequency of spot treatments. Monitoring your skin’s response to different products and adjusting your routine accordingly is essential for long-term success.
| Step | Product Recommendations | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Morning Cleansing | Gentle foaming cleanser | Removes overnight buildup, prepares skin for the day. |
| Evening Cleansing | Gentle foaming cleanser or double cleansing (oil-based + water-based) | Removes day’s pollutants, makeup, and sebum, prevents clogging. |
| Exfoliation | Chemical exfoliant (AHAs/BHAs) | Removes dead skin cells, unclogs pores, improves texture. |
| Hydration | Lightweight, oil-free moisturizer | Hydrates skin without contributing to excess oil. |
| Treatment | Topical retinoid, salicylic acid, or benzoyl peroxide | Targets specific acne issues. |
Understanding Skin’s Response to Products
Knowing how your skin reacts to different skincare products is crucial for effective and safe treatment. This understanding allows you to tailor your routine to your specific needs, preventing potential irritations and maximizing the benefits of your chosen products. A personalized approach to skincare is essential for achieving healthy, radiant skin.Different skin types react to skincare products in various ways.
Acne-prone and oily skin, for instance, often require products formulated with specific ingredients to control oil production and manage breakouts. Understanding these reactions allows for a more targeted approach to skincare.
Product Formulation Effects on Acne and Oily Skin
Various product formulations have distinct effects on acne-prone and oily skin. Oily skin often benefits from products containing ingredients like salicylic acid, which can exfoliate and help control oil production. Conversely, products with overly rich or heavy formulations can potentially clog pores and worsen acne.
Potential Side Effects of Skincare Products
Certain skincare products can have adverse effects on acne-prone and oily skin. Harsh cleansers, for example, can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness, irritation, and potentially increased oil production. Similarly, products containing high concentrations of certain ingredients like fragrance or alcohol can trigger allergic reactions or inflame the skin, exacerbating acne.
Identifying Potential Allergens and Irritants
Careful consideration of product ingredients is paramount for identifying potential allergens and irritants. Common allergens in skincare include fragrances, certain essential oils, and preservatives. Irritants such as harsh detergents or exfoliating agents can also cause skin reactions. Thorough reading of ingredient lists and patch testing are crucial steps in determining product suitability for your skin type.
Comparison of Skincare Product Ingredients
| Ingredient | Potential Impact on Acne-Prone/Oily Skin |
|---|---|
| Salicylic Acid | Exfoliates, controls oil production, helps unclog pores. Can cause dryness or irritation if used in high concentrations. |
| Benzoyl Peroxide | Effective against acne-causing bacteria, can help reduce inflammation. May cause skin dryness, redness, or sensitivity. |
| Vitamin A (Retinoids) | Reduces inflammation, helps with acne, improves skin texture. Can cause dryness, peeling, and increased sensitivity, especially at the beginning of use. |
| Hyaluronic Acid | Hydrates the skin, can be beneficial for dryness caused by acne treatments. Generally well-tolerated. |
| Alcohol | Can dry out the skin and potentially irritate. Avoid if you have sensitive or acne-prone skin. |
| Fragrances | May cause allergic reactions or irritation in sensitive individuals. Look for fragrance-free options. |
| Comedogenic Oils (e.g., Coconut Oil, Mineral Oil) | Can clog pores and worsen acne. Choose oil-free or water-based products. |
This table provides a general overview. Individual reactions may vary. Always conduct thorough research and patch testing before incorporating new products into your routine.
Ending Remarks: Acne And Oily Skin
In conclusion, managing acne and oily skin requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond just applying topical treatments. This guide has highlighted the interplay of genetics, diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Remember, consistency and a personalized approach are crucial for achieving healthy, clear skin. Consult with a dermatologist for tailored advice, and don’t hesitate to explore home remedies as complementary options.
Ultimately, understanding your skin’s unique response to various products and lifestyle choices will lead to long-term success.