Sebaceous hyperplasia causes symptoms and treatments are explored in detail. This comprehensive guide dives into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for sebaceous hyperplasia, a common skin condition. We’ll examine the underlying reasons for its development, the visible signs it presents, and the different approaches to managing it. Understanding this condition empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Sebaceous hyperplasia, often appearing as small, yellowish bumps on the face, neck, or upper chest, is frequently misunderstood. This condition, often benign and not requiring immediate medical attention, can be easily confused with other skin issues. However, a thorough understanding of its characteristics, causes, and potential treatments is crucial for appropriate management.
Introduction to Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a common, benign skin condition characterized by the overgrowth of sebaceous glands. These glands, responsible for producing sebum (oil), become enlarged and form small, often flesh-colored or yellowish bumps on the skin. Understanding this condition is crucial for differentiating it from other skin issues with similar appearances and for managing patient concerns.
Definition of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign (non-cancerous) proliferation of sebaceous glands, typically occurring in middle-aged and older adults. It’s a common finding, often appearing as small, raised bumps on the skin.
Locations of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia commonly appears on areas of the body with a high concentration of sebaceous glands. These locations include the face (especially the nose, cheeks, and forehead), chest, back, and shoulders. The distribution often mirrors areas with higher sebum production.
Appearance of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia typically presents as small, smooth, flesh-colored or yellowish papules (small, solid bumps). They are usually less than 5 millimeters in diameter and may appear slightly raised above the skin surface. The bumps often have a pearly or waxy texture. Their appearance can vary from subtle to more noticeable, depending on the individual and the affected area.
Comparison to Other Skin Conditions
| Condition | Typical Appearance | Location | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sebaceous Hyperplasia | Small, smooth, flesh-colored or yellowish papules, less than 5 mm in diameter | Face, chest, back, shoulders | Benign, often multiple, typically asymptomatic. |
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | Small, pearly, translucent, or reddish papules or nodules; may have a slightly crusted or ulcerated surface | Face, ears, neck, scalp | Can be cancerous; often has a non-healing or bleeding characteristic; may have a rolled or pearly border |
| Moles (Melanocytic Nevi) | Various colors, shapes, and sizes; typically dark brown or black | Anywhere on the skin | May have irregular borders; can be raised or flat; a change in size, shape, or color can be a warning sign. |
| Acne | Red, inflamed papules, pustules, or nodules; often accompanied by blackheads or whiteheads | Face, back, chest | Often accompanied by inflammation and pain; commonly seen in adolescents and young adults |
Risk Factors for Sebaceous Hyperplasia
| Risk Factor | Description | Potential Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Increased incidence with advancing age | Higher probability of developing sebaceous hyperplasia as one ages. | Numerous studies show a correlation between age and prevalence. |
| Genetics | Family history of sebaceous hyperplasia | Genetic predisposition may increase the risk of developing the condition. | Family history studies suggest a potential genetic component. |
| Hormonal changes | Hormonal fluctuations (e.g., during puberty or pregnancy) | Possible influence on sebaceous gland activity. | Limited direct evidence, but hormonal fluctuations are known to affect skin conditions. |
| Sun exposure | Prolonged or intense exposure to sunlight | No direct evidence linking sun exposure to the development of sebaceous hyperplasia. Other skin conditions can be affected by sun exposure. | Data is inconclusive. The condition itself is not directly sun-related. |
Causes of Sebaceous Hyperplasia: Sebaceous Hyperplasia Causes Symptoms And Treatments
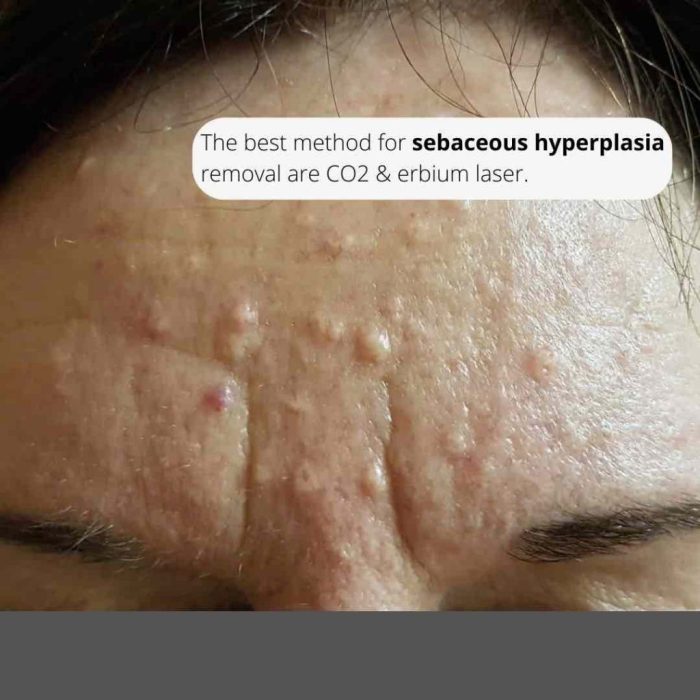
Sebaceous hyperplasia, benign skin growths, often appear as small, yellowish bumps, particularly on the face, chest, and back. While their exact cause remains somewhat elusive, researchers are uncovering crucial insights into the factors that contribute to their development. Understanding these factors is vital for both diagnosis and management strategies.The underlying causes of sebaceous hyperplasia are complex and not fully understood.
Current research suggests a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental influences. This interplay is likely the driving force behind the formation of these common skin lesions.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of sebaceous hyperplasia. Family history often reveals a pattern of these lesions. Inherited variations in genes related to skin cell growth and function might increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing these bumps. Studies on large families with a high prevalence of sebaceous hyperplasia have identified potential candidate genes, although definitive links are still being investigated.
The exact mechanisms through which these genetic variations influence sebaceous hyperplasia remain a subject of ongoing research.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors may also contribute to the development or exacerbation of sebaceous hyperplasia. Exposure to certain irritants or chronic inflammation could potentially trigger the growth of these benign lesions. Hormonal fluctuations, especially in individuals with hormonal imbalances, could also influence the proliferation of sebaceous glands. For instance, individuals experiencing significant hormonal shifts during puberty or pregnancy may see an increase in sebaceous hyperplasia lesions.
Comparison of Theories
Different theories exist regarding the precise cause of sebaceous hyperplasia. One prominent theory emphasizes the role of genetic predisposition, suggesting that individuals with a specific genetic makeup are more prone to developing these lesions, irrespective of environmental factors. Another theory highlights the importance of environmental factors, suggesting that prolonged exposure to specific irritants or chronic inflammation could trigger or exacerbate sebaceous hyperplasia in genetically susceptible individuals.
These theories aren’t mutually exclusive, and a more accurate explanation likely involves an interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental triggers.
Triggers for Exacerbation
While the exact causes of sebaceous hyperplasia are not fully understood, several factors could potentially exacerbate the growth or appearance of existing lesions. For example, irritation from frequent rubbing or pressure on the affected area might lead to inflammation and a visible increase in lesion size. Likewise, individuals with sensitive skin might experience flare-ups when exposed to harsh skincare products.
The effects of prolonged sun exposure on sebaceous hyperplasia lesions are also a potential factor, although further research is needed to determine the extent of this effect.
Hypotheses on Triggers
| Hypothesis | Description | Supporting Evidence | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genetic Predisposition | Individuals inherit a predisposition to develop sebaceous hyperplasia due to specific gene variations. | Family history studies show clustering of cases in families. Candidate genes have been identified, although definitive links remain to be established. | Doesn’t explain all cases; environmental factors likely play a role. The specific genes and their interactions are still under investigation. |
| Chronic Inflammation | Chronic skin irritation or inflammation may trigger or exacerbate the development of sebaceous hyperplasia. | Some studies suggest a correlation between chronic inflammation and sebaceous hyperplasia. Irritants like certain cosmetics or friction could contribute. | Difficult to isolate inflammation as the sole cause; genetic predisposition likely plays a significant role. Studies on the specific inflammatory pathways are limited. |
| Hormonal Fluctuations | Changes in hormone levels, especially in puberty or pregnancy, could influence sebaceous gland activity and hyperplasia. | Observations of increased lesions during hormonal shifts in some individuals suggest a potential link. | Correlation does not equal causation; other factors may contribute. More rigorous studies are needed to assess the precise hormonal impact. |
| Environmental Irritants | Prolonged exposure to specific irritants or chemicals could contribute to the development or exacerbation of sebaceous hyperplasia. | Certain cosmetics or products may trigger inflammation. Friction or pressure on the affected area could also exacerbate the condition. | Identifying specific triggers and quantifying their impact on sebaceous hyperplasia remains challenging. Individual responses to irritants vary significantly. |
Symptoms of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia, a common benign skin condition, often presents with subtle changes that can be easily overlooked. Understanding the typical symptoms is crucial for distinguishing it from other skin issues and for appropriate management. While generally harmless, it’s important to recognize any unusual developments.
Common Symptoms
Sebaceous hyperplasia is typically characterized by small, raised, and yellowish or flesh-colored bumps. These lesions are usually smooth and round, and they vary in size, often ranging from a few millimeters to a few millimeters in diameter. They are frequently found on the face, particularly on the cheeks, nose, and forehead, but can also appear on the chest, back, and shoulders.
These lesions are typically painless and do not cause any discomfort. Their appearance can be subtle, with the bumps sometimes being so small they may be barely noticeable.
Distinguishing Features
Several key features help differentiate sebaceous hyperplasia from other skin conditions. Unlike skin cancers, sebaceous hyperplasia lesions are usually well-defined and do not have irregular borders. They tend to appear in clusters, rather than scattered individually. They are often associated with areas of increased sebum production, a factor that can be noted in some cases. It is important to note that sebaceous hyperplasia typically does not cause itching, bleeding, or pain.
Potential Complications
While sebaceous hyperplasia is generally benign, potential complications are rare. The following table Artikels some possibilities and their associated symptoms.
| Complication | Description | Symptoms | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammation | Localized redness, swelling, and tenderness around the lesion. | Pain, warmth, redness, potential swelling, discomfort. | Mild to moderate. Often resolves with time. |
| Secondary Infection | Bacterial or fungal infection of the lesion. | Pus-filled sores, increased redness, pain, fever. | Moderate to severe. Requires medical intervention. |
| Cosmetic Concerns | Patient dissatisfaction with the appearance of lesions. | Psychological distress, desire for treatment, concerns about social interaction. | Mild to moderate. Management varies based on patient preference. |
| Accidental Trauma | Injury or damage to the lesion from external factors. | Bleeding, broken skin, pain. | Mild to severe depending on the extent of injury. |
Variations in Symptoms
The appearance and extent of symptoms can vary depending on the location and extent of the sebaceous hyperplasia. Lesions on sun-exposed areas may be slightly darker in color. Larger clusters of lesions may cause a noticeable thickening of the skin in the affected area. In cases where the lesions are numerous and widespread, the appearance may be more noticeable.
Individual variations in skin tone and texture can also affect the overall visual impression of the lesions.
Sebaceous hyperplasia, a common skin condition, often presents with small, yellowish bumps, typically on the face and chest. While usually harmless, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is important. Interestingly, some research suggests a potential link between certain medications, like NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which can sometimes complicate the picture. For a deeper dive into the relationship between NSAIDs and IBD, check out this informative article: nsaids non steroidal anti inflammatories and ibd.
Fortunately, various treatment options exist for sebaceous hyperplasia, ranging from topical creams to surgical removal, depending on the severity and location of the lesions.
Treatments for Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia, while typically harmless, can be cosmetically bothersome for some individuals. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to address the lesions and improve appearance. The best approach depends on factors such as the size, number, and location of the lesions, as well as individual preferences and potential risks.Effective treatment strategies aim to reduce the size, flatten the surface, or remove the sebaceous hyperplasia lesions, restoring a more even skin tone.
The decision of whether or not to pursue treatment is a personal one and should be made in consultation with a dermatologist.
Treatment Options
Several treatment options exist for sebaceous hyperplasia, each with varying degrees of effectiveness and potential side effects. The choice of treatment often depends on the severity and location of the lesions, as well as the patient’s individual preferences.
Surgical Removal
Surgical removal is a definitive treatment option for sebaceous hyperplasia. This procedure involves excising the lesions under local anesthesia. Surgical removal is generally effective in eliminating the lesions and can provide a very satisfactory aesthetic outcome. However, it carries a risk of scarring, which can be more noticeable on certain areas of the body. The extent of scarring depends on the size of the lesion, the surgical technique, and the individual’s skin characteristics.
This treatment is often considered for larger or more numerous lesions, particularly those on areas of the body where scarring might be less noticeable, such as the back or chest.
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy involves freezing the sebaceous hyperplasia lesion using liquid nitrogen. This method is generally effective in reducing the size and appearance of the lesions. It is often a less invasive approach compared to surgical removal, with a lower risk of scarring. However, it may not be as effective for larger lesions and may take multiple treatments for optimal results.
Side effects include temporary skin discoloration and discomfort, and, in rare cases, blistering. This treatment is well-suited for smaller lesions on less sensitive skin areas.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy uses focused light beams to target and destroy the sebaceous hyperplasia lesions. Different types of lasers can be used, each with varying effectiveness and potential side effects. Laser therapy can be highly effective in treating sebaceous hyperplasia, leading to a significant reduction in lesion size and improved skin texture. Potential side effects include redness, swelling, and temporary skin discoloration.
The choice of laser therapy will depend on the type of laser and the individual patient’s skin characteristics. It is often a viable option for treating multiple lesions, especially those on visible areas, and can offer a more precise approach compared to cryotherapy.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels can be used to treat sebaceous hyperplasia, although their effectiveness may vary depending on the concentration and type of chemical used. The treatment involves applying a chemical solution to the skin to remove the top layers, potentially causing the sebaceous hyperplasia lesions to become less noticeable. Chemical peels can be effective in treating sebaceous hyperplasia, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments.
Side effects can include temporary redness, swelling, and skin sensitivity. This treatment is often considered for less severe cases or in combination with other methods.
Comparison Table
| Treatment | Description | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Removal | Excision of lesions under local anesthesia | Generally very effective | Scarring possible, depending on location and technique |
| Cryotherapy | Freezing lesions with liquid nitrogen | Effective for smaller lesions, multiple treatments may be needed | Temporary discoloration, discomfort, possible blistering |
| Laser Therapy | Using focused light beams to target lesions | Highly effective, often precise | Redness, swelling, temporary discoloration |
| Chemical Peels | Applying chemical solution to remove skin layers | Variable effectiveness, often used in combination | Temporary redness, swelling, skin sensitivity |
Spontaneous Resolution
In some cases, sebaceous hyperplasia lesions may spontaneously resolve without any treatment. However, this is not a reliable outcome and the time it takes for resolution is unpredictable. The likelihood of spontaneous resolution varies depending on factors such as the size, location, and individual characteristics of the lesions.
Diagnosis of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
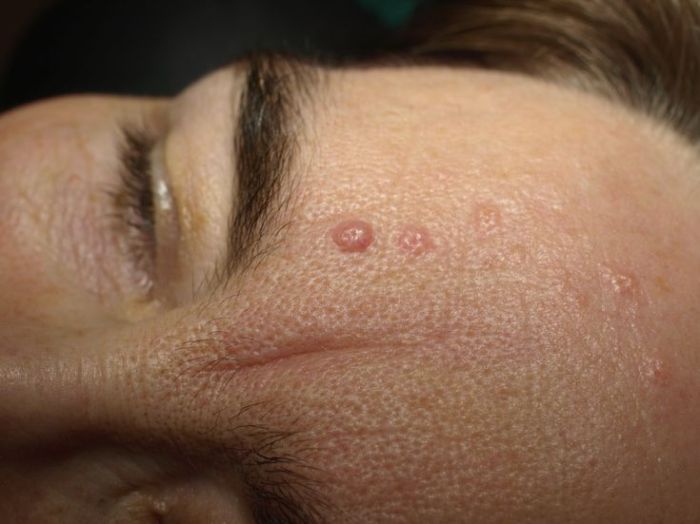
Sebaceous hyperplasia, while often benign and easily recognizable, requires a proper diagnosis to rule out similar skin conditions. Accurate identification is crucial for appropriate management and to ensure patients receive the right treatment. This process typically involves a combination of visual assessment and, sometimes, additional diagnostic tools.Proper diagnosis of sebaceous hyperplasia is vital to differentiate it from other skin lesions that may mimic its appearance.
This distinction helps guide treatment and avoid unnecessary interventions. The process often begins with a detailed physical examination, focusing on the characteristics of the lesions.
Sebaceous hyperplasia, those little bumps on your skin, are usually harmless and often caused by aging or hormones. While some remedies suggest turmeric for potential benefits, it’s important to understand how much turmeric is too much, as with any supplement. This page will give you more details on the safe dosage of turmeric. Ultimately, proper medical advice from a dermatologist remains the best approach for addressing sebaceous hyperplasia causes, symptoms, and effective treatments.
Physical Examination, Sebaceous hyperplasia causes symptoms and treatments
A thorough physical examination plays a key role in diagnosing sebaceous hyperplasia. Clinicians visually inspect the skin lesions, paying close attention to their size, shape, color, and distribution. The presence of multiple, well-defined, yellowish or flesh-colored papules or plaques, often clustered together, is a strong indicator. The location of the lesions, typically on the face, neck, chest, or back, can also provide valuable clues.
Careful observation of the surrounding skin and the absence of any alarming symptoms like inflammation or ulceration further support the diagnosis.
Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating sebaceous hyperplasia from other skin conditions is crucial. Similar-appearing lesions, such as basal cell carcinoma, seborrheic keratosis, or other benign growths, can require further investigation. The clinician must carefully assess the characteristics of the lesion to rule out these potential alternatives. Features like irregular borders, ulceration, rapid growth, or bleeding strongly suggest the need for additional tests.
Diagnostic Criteria
Careful evaluation of diagnostic criteria is critical to confirm a diagnosis of sebaceous hyperplasia. This systematic approach helps clinicians determine if the lesion meets the criteria for sebaceous hyperplasia.
| Criterion | Description | Diagnostic Method | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Well-defined, yellowish or flesh-colored papules or plaques, often clustered together. | Visual inspection during physical examination. | Suggests the presence of sebaceous hyperplasia. |
| Location | Typically found on the face, neck, chest, or back. | Physical examination. | Provides additional context and supports the diagnosis. |
| Size | Usually small, ranging from a few millimeters to a few centimeters in diameter. | Physical examination. | Helps differentiate from larger, potentially concerning lesions. |
| Consistency | Soft and slightly raised; often with a smooth surface. | Palpation during physical examination. | Assists in distinguishing from other lesions with different consistencies. |
Imaging Techniques
While not always necessary, imaging techniques can aid in the diagnosis, particularly when differential diagnoses are suspected. Dermoscopy, a non-invasive technique that uses a specialized microscope to examine the skin’s surface, can provide detailed images of the lesion’s structure and characteristics. This can be useful in differentiating sebaceous hyperplasia from other skin conditions with similar appearances. In cases of doubt, a biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination.
This is the definitive diagnostic method, confirming the presence and nature of the lesion.
Sebaceous hyperplasia, those little bumps on your skin, often have simple causes like genetics or aging. Understanding the different types of carbs, like good vs bad carbs , might not directly impact the condition, but a balanced diet can certainly contribute to overall health and potentially influence skin health. Treatments range from topical creams to laser procedures, depending on the severity and location of the hyperplasia.
Prevention of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia, while typically harmless, can be bothersome due to its appearance. Unfortunately, there are no definitive preventive measures currently available to stop the development of these benign skin growths. Understanding the factors that might increase the risk, however, can help in managing potential triggers.Currently, the primary focus in managing sebaceous hyperplasia is on symptom management and treatment when necessary, rather than on prevention.
This is because the exact causes of the condition are not fully understood. Research continues, but for now, there’s no proven method to prevent their formation.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Development
Several lifestyle factors could potentially influence the likelihood of developing sebaceous hyperplasia. These factors, however, are not definitive causes, and further research is needed to establish clear links. It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list and more research is necessary to determine the complete picture.
- Genetics: A family history of sebaceous hyperplasia might increase a person’s predisposition to developing the condition. However, this doesn’t guarantee development, and many individuals with a family history do not experience it.
- Age: Sebaceous hyperplasia typically appears in middle-aged and older adults. This suggests an association with aging, but it doesn’t mean younger individuals are immune. The exact mechanisms behind this correlation are still under investigation.
- Hormonal Changes: While not fully understood, hormonal fluctuations might play a role. However, there’s no conclusive evidence to support this theory, and further studies are needed to establish a definite link.
Managing Potential Risk Factors
While definitive prevention is not yet possible, managing potential risk factors can help in reducing the likelihood of developing sebaceous hyperplasia. These approaches focus on general health and well-being rather than on targeting the specific causes.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may contribute to overall health and well-being. This may indirectly influence the body’s response to factors that might contribute to sebaceous hyperplasia.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can contribute to a healthier lifestyle, which might help in managing potential risk factors. The exact impact on sebaceous hyperplasia development is not yet fully understood.
- Stress Management: Managing stress effectively through techniques like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can have positive effects on overall health. There is some evidence linking stress to skin conditions, but further research is needed to explore its relationship with sebaceous hyperplasia.
Potential Effectiveness of Preventive Measures
The effectiveness of these preventive measures is difficult to assess due to the lack of definitive research on the causes of sebaceous hyperplasia. While adopting a healthy lifestyle can improve overall health, there’s no guarantee it will prevent the development of sebaceous hyperplasia. The current understanding is that these strategies contribute to general well-being, which might indirectly influence the development of various skin conditions.
However, further research is crucial to determine a definitive link between lifestyle choices and the prevention of sebaceous hyperplasia.
Illustrations and Visual Aids
Visual aids are crucial for understanding and recognizing sebaceous hyperplasia. They allow for a clear comparison with other skin conditions and facilitate the identification of various stages and locations of the lesions. This section provides detailed visual representations of sebaceous hyperplasia in different contexts.Visual representations are a valuable tool for learning about the nuances of sebaceous hyperplasia. By visualizing the different stages of development, locations, microscopic structures, and comparisons with other skin conditions, one can gain a deeper understanding of this benign skin lesion.
Detailed Visual Representation of Sebaceous Hyperplasia in Various Stages
Sebaceous hyperplasia typically presents as small, yellowish or flesh-colored bumps. Early-stage lesions appear as slightly raised, smooth papules. As the lesions mature, they can become more prominent, slightly larger, and potentially develop a slightly rough or slightly pearly texture. The color might vary slightly, but generally remains in the yellowish or flesh-colored range. Advanced stages may show slightly more noticeable enlargement and a slight increase in the number of lesions.
These visual representations help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, particularly important for medical professionals.
Graphic Illustration of Common Locations
Sebaceous hyperplasia frequently appears on the face, particularly on the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. It can also appear on the back, chest, and shoulders. A visual representation of these common locations would show the distribution patterns on different areas of the body. The illustrations would highlight the clustering tendency of these lesions in certain areas, providing context for potential misdiagnosis.
For example, a cluster of lesions on the nose might be mistaken for another skin condition.
Microscopic Structure of Sebaceous Hyperplasia
A microscopic view of sebaceous hyperplasia reveals an accumulation of sebaceous glands. These glands are often enlarged and appear as clusters of cells, with a slightly irregular arrangement. The cells within the glands might show some degree of atypia but generally maintain a benign appearance. The surrounding skin tissue usually appears normal, lacking significant inflammation or other cellular abnormalities.
A clear visual comparison with a normal sebaceous gland would be valuable for educational purposes.
Visual Comparison with Other Skin Conditions
Differentiating sebaceous hyperplasia from other skin conditions, like basal cell carcinoma or acne, can be crucial. A visual comparison chart, including images of each condition, would highlight the key differences. Sebaceous hyperplasia often presents as a more rounded, slightly raised bump, while basal cell carcinoma might have a slightly ulcerated or pearly appearance. Acne lesions, in contrast, might be inflamed and have a pustular or papular appearance.
Accurate visual representations help medical professionals make informed diagnoses.
Recognizing Sebaceous Hyperplasia: A Detailed Illustration
A detailed illustration should guide the viewer through the process of identifying sebaceous hyperplasia. The illustration could begin with a general overview of the appearance of the lesion, progressing to close-up views showing the characteristic features. Specific details, such as the size, shape, color, and consistency of the lesions, should be highlighted. This visual representation could be combined with a key identifying the key characteristics to aid in diagnosis.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, sebaceous hyperplasia, while generally harmless, warrants careful consideration. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to managing this condition effectively. This discussion highlights the importance of accurate diagnosis and the various approaches available to address sebaceous hyperplasia, from watchful waiting to more interventionist treatments. Remember, consulting a dermatologist is crucial for personalized guidance and effective management.

