Pros and cons of IUD: This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of intrauterine devices (IUDs), exploring their various types, advantages, potential drawbacks, and crucial factors to consider before choosing one. We’ll examine the effectiveness, convenience, and potential side effects, equipping you with the knowledge to make an informed decision about your reproductive health.
From understanding the different types of IUDs – hormonal and copper – to exploring their mechanisms of action, we’ll unravel the complexities behind this popular birth control method. We’ll also discuss the potential complications, risks, and essential steps involved in insertion and removal, ensuring you’re well-versed in all aspects of IUD use.
Introduction to Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
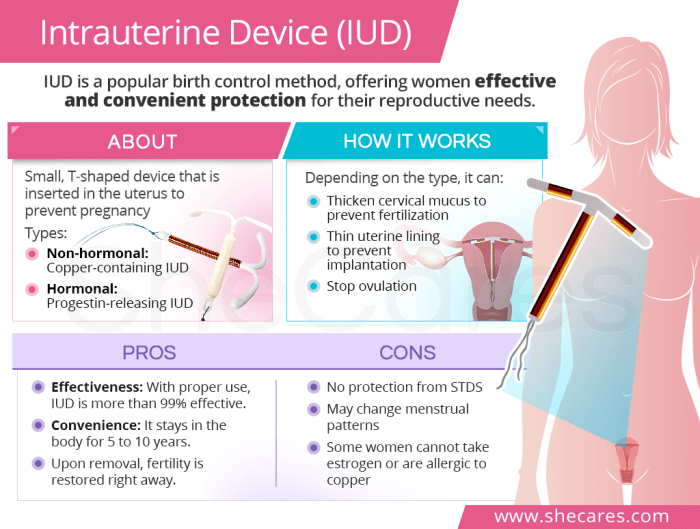
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are small, T-shaped devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. They are a highly effective and long-lasting form of birth control, offering significant advantages over other methods. The mechanism of action varies depending on the specific type of IUD, but they all work by creating a hostile environment for sperm or preventing the implantation of a fertilized egg.Understanding the different types of IUDs and their mechanisms is crucial for making informed decisions about contraception.
Choosing the right IUD can depend on individual needs and preferences, and consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for determining the most suitable option.
Types of Intrauterine Devices
Various IUDs are available, each with unique characteristics and mechanisms of action. The most common types are hormonal and copper IUDs.
Hormonal IUDs
Hormonal IUDs, such as the Mirena and Liletta, release a small amount of progestin hormone into the uterus. This hormone thickens the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. It also thins the uterine lining, reducing the likelihood of implantation. This continuous release of hormones is a key factor in their long-term effectiveness.
Copper IUDs
Copper IUDs, like the ParaGard, contain copper within their structure. The copper ions released by the device create a hostile environment for sperm, preventing fertilization. They do not contain hormones, making them a suitable option for individuals who prefer non-hormonal methods.
Comparison of IUD Types
| Characteristic | Hormonal IUD (e.g., Mirena) | Copper IUD (e.g., ParaGard) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Releases progestin hormone, thickens cervical mucus, thins uterine lining. | Releases copper ions, creating a hostile environment for sperm. |
| Effectiveness | >99% effective at preventing pregnancy. | >99% effective at preventing pregnancy. |
| Side Effects | Possible side effects include irregular periods, spotting, or cramping in the initial weeks. Some users may experience mood changes or breast tenderness. | Possible side effects include heavier or more frequent periods, cramping, and spotting. |
| Duration | Effective for 5-7 years. | Effective for 10 years. |
Advantages of Using IUDs
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) offer a highly effective and convenient method of contraception for many women. Their long-term effectiveness, coupled with their low maintenance, makes them a popular choice for those seeking reliable birth control. This section delves into the specific advantages of IUDs, exploring their long-term efficacy, ease of use, and overall impact on reproductive health.IUDs are designed to prevent pregnancy by creating a hostile environment for sperm and/or by preventing implantation.
Their sustained action offers a significant advantage over other methods that require daily or monthly attention. This prolonged protection makes them a highly practical choice for women who value ease and reliability in their contraceptive regimen.
Long-Term Effectiveness as a Contraceptive
IUDs are remarkably effective at preventing pregnancy over extended periods. They provide continuous protection, often for several years, without the need for daily reminders or the risk of user error associated with other methods. This sustained effectiveness is a key advantage for women who desire a reliable contraceptive option with minimal intervention. A properly inserted and functioning IUD is highly effective, with failure rates significantly lower than other methods.
For example, the copper IUD has a failure rate of less than 1% over a 10-year period. This consistent efficacy is a significant draw for women who prioritize long-term reliability.
Convenience and Low Maintenance
One of the most significant advantages of IUDs is their convenience. Once inserted by a healthcare professional, the IUD requires minimal ongoing effort from the user. This contrasts sharply with other methods that necessitate daily or weekly actions, such as taking pills or using condoms. Users do not need to remember to take a pill every day or worry about remembering to use protection each time they engage in sexual activity.
Thinking about an IUD? Weighing the pros and cons is key. While some women experience fewer periods and reduced cramping, others might face complications. It’s important to consider your overall health, including potential links to other conditions. For instance, understanding how ear infections and COVID-19 can be connected, as discussed in this article ear infection and covid 19 , can help you make informed decisions.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual circumstances and what feels right for you.
This low maintenance factor significantly enhances the user experience, making it a time-saving and convenient option. This aspect of ease is a substantial advantage for busy individuals who value convenience.
Reduced Risk of Pregnancy Compared to Other Methods
The effectiveness of IUDs results in a dramatically reduced risk of pregnancy compared to many other birth control methods. Factors such as user error and inconsistent use can significantly impact the effectiveness of methods like birth control pills or condoms. IUDs, on the other hand, provide a consistent barrier to pregnancy without the need for daily or regular actions.
This predictable efficacy is critical for women who want to be assured of their contraceptive protection. For instance, IUDs have a significantly lower failure rate than birth control pills or barrier methods like condoms, particularly when considering long-term use.
Potential Benefits for Women Using IUDs
IUDs offer a range of potential benefits beyond their contraceptive function. Some women report a reduction in menstrual cramps and a decrease in the amount of menstrual bleeding. This can improve overall comfort and well-being. Additionally, some IUDs can be left in place for several years, significantly reducing the need for repeated visits to a healthcare provider for new prescriptions or methods.
Thinking about an IUD? Weighing the pros and cons is key. While they’re generally a very effective and convenient birth control option, like any medical device, there are potential side effects. Interestingly, a recent study on intermittent fasting, specifically the 4:3 method ( 4 3 intermittent fasting outperforms daily calorie restriction in weight loss study ), highlights how different approaches to weight management can impact health.
Ultimately, the best choice for birth control always depends on your individual needs and health status, making careful consideration of the pros and cons of IUDs even more crucial.
This consistency can also offer a level of financial savings for women.
- Reduced menstrual cramps: Some women experience a reduction in the intensity and frequency of menstrual cramps with IUD use.
- Decreased menstrual bleeding: Some women report a decrease in the amount of menstrual blood flow with IUD use.
- Long-term convenience: IUDs can be left in place for several years, minimizing the need for frequent follow-up appointments and reducing the need for ongoing purchases of birth control.
- Reduced risk of pregnancy: The high effectiveness of IUDs significantly lowers the chances of unintended pregnancy compared to other methods.
Comparison of Effectiveness Over Time
| Birth Control Method | Typical Use Failure Rate (Annual Percentage) | Perfect Use Failure Rate (Annual Percentage) |
|---|---|---|
| IUD (Hormonal) | 0.2 – 0.8 | 0.0 |
| IUD (Copper) | 0.8 – 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Birth Control Pills | 9.0 | 0.3 |
| Condoms | 15.0 | 2.0 |
Note: Failure rates represent the probability of pregnancy per 100 women using the method over one year. The failure rates for IUDs are exceptionally low, demonstrating their reliability and long-term effectiveness.
Disadvantages of Using IUDs
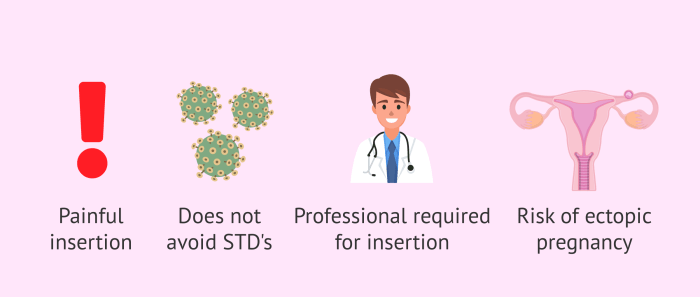
While intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a highly effective form of contraception, they are not without potential drawbacks. Understanding the potential side effects and complications is crucial for making an informed decision about whether an IUD is the right choice for you. Careful consideration of these aspects can help ensure a positive experience and minimize potential issues.
Potential Side Effects
IUDs can sometimes cause discomfort or changes in normal bodily functions. These side effects are generally temporary and often manageable with proper care and communication with your healthcare provider. It’s important to remember that individual experiences can vary greatly.
- Pain and Cramping: Some women experience pain or cramping, especially during the first few weeks after insertion. This is often related to the IUD’s placement and your body’s adjustment to the foreign object. Over-the-counter pain relievers may help manage this discomfort.
- Bleeding Irregularities: Changes in menstrual bleeding patterns, such as heavier or more frequent periods, are possible. This can sometimes be a temporary adjustment, but in some cases, it might persist. Consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or severe pelvic pain unrelated to menstruation could signal a potential complication. It’s essential to report any such pain to your doctor immediately.
Expulsion and Perforation
IUDs, though generally safe, have a small risk of expulsion or perforation. Expulsion means the IUD comes out of the uterus, rendering it ineffective as contraception. Perforation is a puncture of the uterus wall, which is a rare but serious complication.
- Expulsion: Risk factors for expulsion include improper insertion technique, certain physical characteristics, or excessive physical activity shortly after insertion. Symptoms of potential expulsion may include unusual cramping, bleeding, or feeling the IUD. Frequent check-ups are crucial for early detection and appropriate management.
- Perforation: This is a rare but serious complication that requires immediate medical attention. Perforation can occur during IUD insertion. Factors like anatomical variations or improper technique can contribute to the risk. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential to prevent severe complications.
Potential Complications During Insertion and Removal
While IUD insertion and removal are typically safe procedures, potential complications can arise. These complications are usually mild and resolved with prompt medical attention.
- Insertion Complications: During insertion, there’s a slight risk of infection or injury to surrounding tissues. These complications are often short-lived and easily managed.
- Removal Complications: Difficulties in removing the IUD can arise. This may be due to improper positioning or the IUD becoming embedded. Proper technique during removal can minimize these risks.
Infections and Other Health Issues
Although rare, infections or other health issues can potentially be associated with IUD use. These complications are usually mild and treatable. However, prompt medical attention is important for early intervention.
- Infections: The risk of infection, like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is slightly increased in the initial period after IUD insertion. However, PID is not common, and early treatment can prevent serious complications. Following your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding hygiene is vital.
- Other Health Issues: Some women might experience unusual symptoms or changes in health after IUD insertion. It is crucial to communicate any concerns or unusual symptoms with your doctor promptly.
Frequency of Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Pain and Cramping (first few weeks) | Common |
| Bleeding Irregularities | Possible |
| Pelvic Pain (unrelated to menstruation) | Uncommon |
| Expulsion | Rare |
| Perforation | Extremely Rare |
| Insertion Complications | Rare |
| Removal Complications | Rare |
| Infections (e.g., PID) | Rare |
| Other Health Issues | Rare |
Factors to Consider Before Choosing an IUD
Choosing the right intrauterine device (IUD) is a significant decision, requiring careful consideration of various factors. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution, and understanding your individual circumstances is crucial for a successful and comfortable experience. Ultimately, a personalized approach, guided by your healthcare provider, is key to ensuring the IUD is the best contraceptive option for you.Before committing to an IUD, a thorough evaluation of your medical history, lifestyle, and preferences is essential.
This proactive approach helps in determining the suitability of the IUD for your specific needs. It’s also important to understand the potential impact of various medical conditions on the IUD’s effectiveness and safety.
Medical History
Understanding your medical history is fundamental to assessing the appropriateness of an IUD. Certain conditions may influence the suitability of an IUD. For example, a history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) may require careful consideration. A history of uterine abnormalities, such as fibroids or polyps, might also necessitate a more in-depth discussion with your healthcare provider.
Other conditions, like bleeding disorders, may also affect the choice of IUD and the monitoring process.
Lifestyle Factors
Your lifestyle plays a significant role in determining the best IUD for you. Factors such as frequency of sexual activity, desire for future pregnancies, and general health concerns all influence the decision-making process. For example, if you have a demanding career or travel frequently, the convenience and reliability of the IUD are important considerations. Conversely, if you are considering future pregnancies, the reversibility of different IUD types becomes crucial.
Individual Preferences
Individual preferences are vital to consider when choosing an IUD. Factors such as the type of IUD (hormonal or copper), the level of comfort with potential side effects, and the desired length of contraception influence the decision. For example, some women may prefer the convenience of a long-term method, while others might be more comfortable with a shorter-term solution.
Different women have different levels of comfort with potential side effects, such as cramping or bleeding irregularities.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
A crucial aspect of choosing an IUD is consulting with a healthcare provider. A healthcare provider can evaluate your medical history, lifestyle, and preferences to provide personalized advice. They can discuss the potential benefits and risks of different IUD types and address any concerns you may have. A thorough discussion is essential to ensure the IUD is the most suitable choice for your health and well-being.
Table: Factors to Consider Before Choosing an IUD
| Factor | Description | How it Affects IUD Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Medical History | Past conditions like PID, STIs, or uterine abnormalities. | Certain conditions may require a more cautious approach to IUD selection and monitoring. |
| Lifestyle | Frequency of sexual activity, travel, and career demands. | Lifestyle factors impact the convenience and reliability of the IUD. |
| Preferences | Comfort level with potential side effects, desired duration of contraception, and IUD type. | Preferences directly influence the selection of the most comfortable and suitable IUD. |
| Healthcare Provider Consultation | Personalized assessment of medical history, lifestyle, and preferences. | Provides crucial insights and recommendations for the best IUD choice. |
Comparison of IUD Types
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) come in various forms, each with its unique hormonal or copper composition. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision about which IUD type might best suit your individual needs and preferences. Different IUDs can have varying effects on menstrual cycles, overall health, and duration of effectiveness. This section will delve into the specifics of each type, highlighting key considerations.
Hormonal IUDs
Hormonal IUDs release a small amount of progestin hormone into the uterus. This hormone works to prevent pregnancy by thickening the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. It also thins the uterine lining, further reducing the likelihood of implantation. This consistent release of hormones leads to significant changes in menstrual cycles and can impact overall health in different ways.
- Reduced bleeding: Hormonal IUDs are often associated with significantly lighter or even absent periods. This can be a significant benefit for some women, reducing discomfort and potential iron deficiency.
- Potential side effects: While reduced bleeding is a common benefit, some women experience spotting or other changes in their menstrual flow. Other potential side effects may include headaches, mood changes, or breast tenderness. These effects are usually mild and temporary.
- Duration of effectiveness: Hormonal IUDs typically offer protection for three to seven years, depending on the specific type. This extended protection eliminates the need for frequent replacements.
- Potential long-term implications: Long-term use of hormonal IUDs has not been linked to major health risks. However, some women may experience changes in their menstrual cycle patterns, or experience other side effects.
Copper IUDs
Copper IUDs, unlike hormonal IUDs, do not contain hormones. Instead, they rely on the copper component to prevent pregnancy. The copper creates an inhospitable environment for sperm, inhibiting their ability to fertilize an egg.
- No hormonal effects: This is a significant advantage for women who prefer not to use hormonal methods or have experienced negative reactions to hormones.
- Menstrual cycle changes: Copper IUDs can sometimes lead to heavier or more prolonged periods, along with more cramping in the first few months. However, the experience can vary significantly between individuals.
- Duration of effectiveness: Copper IUDs provide protection for up to 10 years. This longer duration is a considerable advantage in terms of convenience and cost.
- Potential long-term implications: Studies have not revealed major health risks associated with long-term use of copper IUDs. However, some women may experience prolonged or intense menstrual cramping, requiring a doctor’s consultation if symptoms become severe.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Hormonal IUD | Copper IUD |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal Content | Yes (Progestin) | No |
| Mechanism of Action | Thickens cervical mucus, thins uterine lining | Creates inhospitable environment for sperm |
| Menstrual Cycle Effects | Reduced or absent bleeding; potential spotting | Heavier or prolonged periods; potential cramping |
| Duration of Effectiveness | 3-7 years | 10 years |
| Potential Side Effects | Spotting, headaches, mood changes | Heavier bleeding, cramping |
Insertion and Removal Procedures
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) offer a long-term, effective method of contraception. Understanding the insertion and removal procedures is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Proper technique ensures the device’s effectiveness and minimizes potential discomfort.The procedures for inserting and removing an IUD are typically performed by a healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or nurse practitioner. The specific steps and sensations may vary slightly depending on the type of IUD and the individual’s anatomy.
A thorough understanding of these procedures can help alleviate anxiety and promote a positive experience.
Weighing the pros and cons of an IUD can be a big decision, and it’s definitely something to think about carefully. While some women find it incredibly convenient and effective, others might experience side effects. For example, if you’re exploring ways to manage your health, consider how changing your diet might help treat psoriasis. Changing your diet to cure psoriasis could be a holistic approach, but it’s important to remember that IUDs offer a different kind of birth control solution and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
IUD Insertion Procedure
The insertion process typically involves several steps designed to ensure the IUD’s proper placement and minimize discomfort. Careful preparation and communication with the healthcare provider are essential for a smooth experience.
The insertion process is generally quick, taking between 5-10 minutes.
- Preparation: The healthcare provider will typically conduct a pelvic exam to assess the cervix and uterus. They may use a speculum to visualize the cervix and apply a local anesthetic to reduce discomfort.
- Measuring and Positioning: The provider will measure the length and position of the uterine cavity to ensure proper IUD placement. A sterile lubricant may be used to help with insertion.
- Insertion: The provider will carefully introduce the IUD through the cervix and into the uterus. They will then use specialized tools to expand and position the device correctly. There may be cramping or mild discomfort during this stage.
- Post-Insertion Check: Once the IUD is in place, the provider will verify its correct position using ultrasound or other imaging techniques. This is crucial to ensure the device is functioning correctly.
IUD Removal Procedure
Removing an IUD is a relatively straightforward procedure, usually taking only a few minutes. The process is often similar to insertion, but focuses on dislodging the device.
- Preparation: The healthcare provider will conduct a pelvic exam to locate the IUD. A speculum will be used to visualize the cervix.
- Grasping and Removal: Using specialized instruments, the provider will carefully grasp the IUD’s strings and gently remove it from the uterus. There may be some mild cramping or discomfort as the device is withdrawn.
- Post-Removal Check: The provider will confirm the IUD has been completely removed. This step ensures the device is not lodged in the uterus.
Potential Discomfort and Pain
Both IUD insertion and removal can cause some degree of discomfort or cramping. The intensity of the pain varies from person to person.
Some women experience mild cramping, while others may experience more significant pain. Factors such as the individual’s pain tolerance and the type of IUD can influence the level of discomfort.
Many healthcare providers use local anesthesia to minimize pain during insertion and removal. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen, can also help manage any discomfort.
Recovery Time
The recovery time after IUD insertion or removal is typically short. Most women can resume normal activities within a few hours.
Slight cramping or spotting may occur for a few days following the procedure. Resting and taking over-the-counter pain medication can help manage any discomfort.
The typical recovery time is usually a few hours to a day or two, but some women may experience longer recovery periods.
Potential Complications and Risks
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are generally safe and effective methods of contraception. However, like any medical procedure, they carry potential complications and risks. Understanding these potential issues, their associated risk factors, and the importance of regular check-ups can help women make informed decisions about using IUDs.While rare, complications can occur. Factors such as individual health history, the specific type of IUD used, and adherence to follow-up appointments all play a role in the likelihood of experiencing a complication.
This section delves into the potential complications, outlining their causes, frequencies, and how proactive monitoring can minimize risks.
Infection
IUD insertion can introduce a small risk of infection. This risk is generally low, but factors like existing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or poor hygiene practices can increase the likelihood of infection. The frequency of IUD-related infections is relatively low, with studies showing it occurring in a small percentage of cases.
Expulsion
IUD expulsion, where the IUD shifts or completely leaves the uterus, is a possible complication. This can occur more frequently in women who have had multiple pregnancies or in those with a history of pelvic inflammatory disease or abnormalities in the uterine cavity. While expulsion is not a significant health risk, it renders the IUD ineffective as contraception.
The frequency of expulsion varies depending on the type of IUD and the individual woman’s anatomy and medical history.
Perforation
Perforation, where the IUD punctures the uterine wall, is a rare but serious complication. Factors that can increase the risk include a smaller uterine cavity, anatomical variations, or improper insertion technique. The incidence of perforation is quite low, and proper training and technique for insertion play a significant role in reducing the risk. It’s crucial for both the healthcare provider and the patient to understand the procedure’s nuances to minimize this risk.
Other Potential Complications
Other less frequent complications include heavier or more painful periods, cramping, and bleeding between periods.
These issues are usually temporary and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or other methods as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for women using IUDs. These appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor the IUD’s position, assess for any signs of infection or other complications, and address any concerns the woman may have. Early detection and intervention can often prevent potential problems from escalating.
Table of Potential Complications and Risks
| Potential Complication | Associated Risk Factors | Frequency (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Existing PID, poor hygiene, other infections | Low |
| Expulsion | Multiple pregnancies, PID, uterine abnormalities | Variable, depends on IUD type |
| Perforation | Small uterine cavity, anatomical variations, improper insertion | Very low |
| Other (e.g., heavier bleeding) | Individual variations, IUD type | Variable, often temporary |
Long-Term Effects and Maintenance: Pros And Cons Of Iud
The long-term use of an intrauterine device (IUD) can significantly impact a woman’s menstrual cycle and overall well-being. Understanding these effects and the importance of regular check-ups are crucial for ensuring the IUD’s continued effectiveness and safety. Proper maintenance and prompt attention to any unusual symptoms are vital for a positive experience.
Long-Term Effects on Menstrual Cycles
IUDs can alter menstrual patterns in various ways. Some women experience lighter bleeding or spotting between periods, while others may experience heavier bleeding during their periods. These changes are often temporary and typically normalize within a few months of insertion. However, persistent or significant changes warrant a discussion with your healthcare provider.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring the IUD’s position and ensuring its continued effectiveness. These appointments allow your healthcare provider to assess the IUD’s placement, detect any signs of complications, and address any concerns you may have.
Frequency of Check-ups
The recommended frequency of check-ups varies depending on the specific IUD and individual circumstances. For instance, some IUDs might require yearly check-ups, while others might have a different schedule. Your healthcare provider will discuss the appropriate frequency based on your individual needs.
Situations Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Certain situations require immediate medical attention. These include severe abdominal pain, fever, unusual vaginal discharge, heavy bleeding, and persistent pain or discomfort. Any of these symptoms should prompt an immediate call to your healthcare provider.
Recommended Follow-up Schedules, Pros and cons of iud
| IUD Type | Initial Check-up | Follow-up Appointments (Frequency) |
|---|---|---|
| Hormonal IUD (e.g., Mirena) | Within 4-6 weeks post-insertion | Annually, or sooner if needed |
| Copper IUD (e.g., ParaGard) | Within 4-6 weeks post-insertion | Annually, or sooner if needed |
| Other IUD Types | Within 4-6 weeks post-insertion | Follow your healthcare provider’s specific recommendations |
Note: This table provides general guidelines. Your specific follow-up schedule will depend on your individual circumstances and the type of IUD used. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, while IUDs offer a highly effective and convenient long-term birth control option, it’s crucial to weigh the advantages against potential disadvantages and consider individual factors before making a decision. Thorough research, consultations with healthcare providers, and careful consideration of personal circumstances are paramount. This guide aims to provide a balanced perspective, enabling you to navigate the decision-making process with confidence and make an informed choice that aligns with your needs and well-being.