Lump under skin causes and when to worry about it is a crucial topic for anyone experiencing such a concern. Skin lumps can arise from a variety of factors, ranging from harmless cysts to more serious conditions. Understanding the potential causes and knowing when to seek medical attention can be vital for a quick diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
This post explores the different types of skin lumps, common causes, and the signs that suggest you should consult a doctor. We’ll cover everything from benign growths to potential indicators of more serious issues. Armed with knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to navigate this potentially unsettling experience.
Introduction to Skin Lumps
Skin lumps, also known as skin lesions, are abnormal growths or swellings that appear on the surface of the skin. They can vary significantly in size, shape, and texture, and their appearance can be a clue to their underlying cause. Understanding the characteristics of skin lumps, including their location, appearance, and potential causes, is crucial for determining whether further medical evaluation is necessary.Skin lumps can arise from a multitude of causes, ranging from harmless, benign conditions to more serious, potentially cancerous ones.
Recognizing the different types of skin lumps and their potential implications is essential for appropriate action. This section will Artikel the common types of skin lumps, their characteristics, and when it’s important to seek professional medical advice.
Lumps under the skin can be a real worry, but often they’re completely harmless. They can stem from a variety of things, like cysts, infections, or even just a buildup of fluid. However, if you’re concerned, it’s always best to see a doctor. Knowing the potential risks of imaging tests like CT scans is also important; for example, the potential cancer risks associated with CT scans are something you should be aware of, especially if they are frequently used.
ct scan cancer risk is a factor to consider alongside other potential causes when evaluating a lump. Ultimately, the best way to determine the cause of a lump and decide if you need to be concerned is to consult with a healthcare professional.
Types of Skin Lumps
Skin lumps can be broadly categorized into benign, malignant, and inflammatory types. Benign lumps are typically harmless and do not spread to other parts of the body. Malignant lumps, conversely, are cancerous and can metastasize. Inflammatory lumps are caused by an underlying inflammatory process. The precise classification of a lump often requires a thorough examination and possibly a biopsy.
Common Locations of Skin Lumps
Skin lumps can appear virtually anywhere on the body. Common locations include the face, neck, back, chest, arms, legs, and scalp. The location of the lump can offer clues to the potential cause. For example, lumps on the scalp might be related to hair follicle issues, while those on the legs could be related to subcutaneous fat deposits or other factors.
Appearance and Texture of Skin Lumps
The appearance and texture of a skin lump can provide valuable clues about its potential nature. Some common characteristics include:
- Size and Shape: Lumps can range from tiny bumps to larger masses. The shape can be round, oval, irregular, or nodular.
- Color: Skin lumps can be the same color as the surrounding skin, or they might appear red, pink, brown, black, or even bluish.
- Texture: The texture can vary from smooth and soft to firm, hard, or even bumpy.
- Pain: Some lumps may be painless, while others may be tender or cause discomfort.
- Mobility: The mobility of a lump, meaning how easily it can be moved under the skin, can provide information about its depth and potential nature.
Table of Common Skin Lumps
This table summarizes different types of skin lumps, their appearance, potential causes, and when medical attention is recommended.
| Lump Type | Appearance | Common Causes | When to Seek Medical Attention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign Cyst | Smooth, firm, or soft, often round, typically painless. | Blocked hair follicles, sebaceous glands, or other fluid-filled sacs. | If the lump is rapidly growing, painful, or causing significant discomfort. |
| Skin Tag | Small, fleshy, and often stalk-like, usually painless. | Skin folds, friction, or aging. | If the skin tag is causing irritation or bleeding. |
| Moles (Melanocytic Nevi) | Various colors, often flat or raised, can be small or large, usually painless. | Genetic predisposition, sun exposure. | If the mole changes in size, shape, color, or texture, or if it bleeds or itches. |
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | Often pearly or waxy, with a slightly raised border, sometimes with a central ulcer. | Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. | Immediately if the lump appears to be growing or changing. |
Potential Causes of Skin Lumps
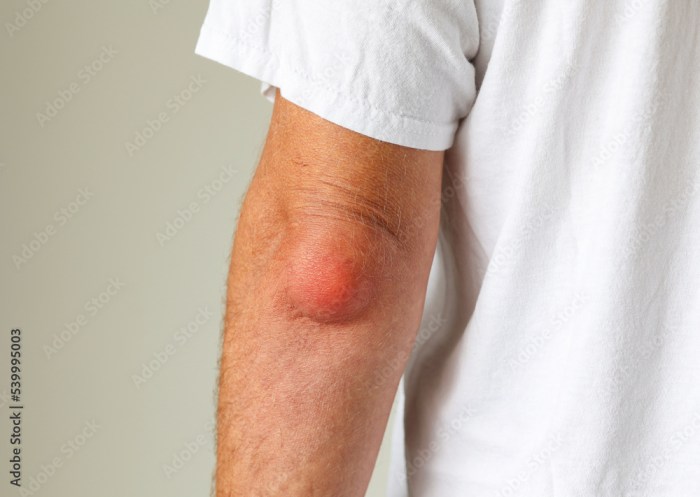
Skin lumps, while often benign, can sometimes signal underlying health concerns. Understanding the potential causes, ranging from common, harmless conditions to more serious possibilities, is crucial for appropriate evaluation and treatment. This section delves into the diverse factors contributing to skin lump formation.Identifying the cause of a skin lump is essential for determining the appropriate course of action.
Accurate diagnosis requires a comprehensive evaluation, considering the lump’s characteristics (size, shape, color, location, and any associated symptoms) and the individual’s medical history.
Common Benign Causes
Many skin lumps are harmless and result from benign conditions. These conditions typically do not pose a significant health risk. Examples include:
- Epidermal Cysts: These are common, fluid-filled cysts that develop beneath the skin’s surface. They are typically painless and slow-growing, often appearing as a small, firm bump. They are usually caused by trapped skin cells.
- Sebaceous Cysts: These cysts are formed from blocked sebaceous glands, which produce oil for the skin. They typically present as a soft, fluctuating lump, often filled with a cheesy material.
- Lipomas: These are benign fatty tumors that often develop beneath the skin. They are usually soft, painless, and movable. They are frequently found in the arms, shoulders, and back.
- Skin Tags: These are small, benign growths that hang from the skin by a stalk. They are typically flesh-colored and painless. Skin tags often develop in areas with friction, such as the neck, armpits, or groin.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammation can lead to various skin lumps. These conditions often present with redness, warmth, and tenderness around the affected area.
- Acne: While often associated with bumps and pimples, severe acne can result in inflamed lumps under the skin. These lumps can be painful and may require treatment to resolve.
- Cellulitis: This bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues can cause painful, red, and swollen lumps. Cellulitis requires prompt medical attention.
- Contact Dermatitis: An allergic reaction to an irritant or allergen can cause inflamed lumps and bumps on the skin. The affected area may be itchy and painful.
- Insect Bites/Stings: A localized reaction to insect bites or stings can cause inflamed lumps, often with itching and swelling.
Cysts
Cysts are sac-like structures that can contain various substances, including fluid, air, or solid material. Different types of cysts can lead to skin lumps.
- Dermoid Cysts: These cysts contain various tissues, such as hair follicles and teeth. They are often found in the face or scalp and are slow-growing.
- Pilar Cysts: These cysts develop from hair follicles and appear as small, firm lumps, usually painless and slow-growing.
- Galactoceles: These are cysts that develop in the milk ducts, particularly in women who have recently given birth or are breastfeeding.
Infections
Infections, particularly bacterial or fungal infections, can lead to skin lumps.
- Furuncles (Boils): These are localized bacterial infections that cause painful, pus-filled lumps. They are commonly found on the skin’s surface.
- Abscesses: Deeper skin infections that can result in pus-filled lumps that may need drainage.
- Skin infections caused by certain fungi: Some fungal infections can lead to inflamed lumps and bumps, often with itching and scaling.
Comparison of Benign and Malignant Skin Lump Causes
| Characteristic | Benign Causes | Malignant Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Slow and gradual | Can be rapid |
| Pain | Often painless | May be painful |
| Appearance | Smooth, firm, or soft | Irregular, ulcerated, or bleeding |
| Texture | Typically firm or soft | Can be hard and irregular |
| Mobility | Usually movable | Often fixed |
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain underlying medical conditions can contribute to skin lump formation.
- Lupus: This autoimmune disorder can manifest with skin lumps and rashes. Lupus symptoms vary significantly.
- Sarcoidosis: This inflammatory condition can cause lumps in various parts of the body, including the skin.
- Certain types of cancer: While less common, certain cancers can cause skin lumps. Skin cancer is characterized by specific patterns.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Spotting a lump on your skin can be unsettling. While many skin lumps are harmless, some can signal underlying health concerns. Understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Knowing the potential warning signs can empower you to take proactive steps towards your well-being.Knowing when to seek medical attention for a skin lump is vital.
Ignoring potentially serious signs could delay appropriate care, potentially affecting the outcome. Factors like the lump’s growth rate, appearance, and location can all contribute to the need for professional evaluation.
Symptoms Warranting Immediate Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention is essential for certain skin lump characteristics. Rapid growth, significant pain, changes in the skin around the lump, and unusual bleeding or discharge are all cause for concern. These symptoms may indicate an infection, a cancerous growth, or another underlying medical condition. If you notice any of these immediate warning signs, it’s crucial to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare professional.
Factors Increasing the Risk of a Serious Skin Lump, Lump under skin causes and when to worry
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of a skin lump being a cause for concern. A history of skin cancer in the family, a weakened immune system, or exposure to excessive sunlight or harmful substances can heighten the risk. Furthermore, lumps that appear in unusual locations, such as the armpit or groin, may require more immediate evaluation. Knowing these factors can help you determine if a skin lump requires more immediate attention.
Tracking Changes in Lump Characteristics
Regularly monitoring a skin lump’s size, shape, and appearance is vital. Note any changes, such as increasing size, altered borders, or color variations. Changes in the lump’s texture or the surrounding skin, such as redness, inflammation, or tenderness, should also be documented. These observations can aid in determining if the lump is progressing or potentially becoming more serious.
Detailed records can be crucial for communication with your healthcare provider.
Location-Specific Concerns
The location of a skin lump can also be a factor in determining the need for medical evaluation. Lumps appearing on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, or hands might warrant closer examination due to their increased risk of being a skin cancer. Lumps located near joints or areas prone to injury might suggest a different underlying cause.
Understanding the location’s potential significance can help guide your approach.
Table of Key Characteristics Requiring Immediate Medical Evaluation
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid Growth | A noticeable increase in size within a short period. |
| Significant Pain | Persistent or intense pain associated with the lump. |
| Change in Skin Around the Lump | Redness, inflammation, or other changes in the skin surrounding the lump. |
| Bleeding or Discharge | Uncommon bleeding or discharge from the lump. |
| Unusual Location | Appearance in unusual areas like the armpits, groin, or on sun-exposed skin. |
| Family History of Skin Cancer | Presence of a family history of skin cancer. |
Diagnostic Methods for Skin Lumps
Understanding the cause of a skin lump is crucial for appropriate treatment. Accurate diagnosis relies on a combination of methods, from a simple physical examination to more sophisticated imaging techniques and biopsies. This process helps determine the nature of the lump, its potential impact on health, and the most effective course of action.
Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is the first step in assessing a skin lump. This involves careful observation of the lump’s size, shape, color, consistency, location, and any associated symptoms. The dermatologist or physician will look for signs such as tenderness, bleeding, or ulceration. The location of the lump, for example, near a joint or in an area with increased sun exposure, can provide valuable clues about potential underlying conditions.
The examination also assesses the surrounding skin for any abnormalities or changes in texture.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a significant role in evaluating skin lumps, particularly when physical examination alone isn’t sufficient to determine the nature of the lesion. Dermatologists and other specialists often use techniques like ultrasound and dermatoscopic imaging to obtain detailed visual information about the lump’s structure and depth.Ultrasound, a non-invasive method, uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal structures.
It’s particularly helpful in distinguishing between solid and cystic masses and assessing the size and depth of the lump. Dermatoscopic imaging uses a specialized microscope to magnify and analyze the skin’s surface, allowing for the identification of subtle features that might be missed during a routine examination. This is especially useful for assessing pigmented lesions, which could indicate skin cancer.
Computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans might be employed in certain cases to obtain a more detailed cross-sectional view of the skin and surrounding tissues.
Biopsies
Biopsies are a critical step in diagnosing skin lumps, especially when the physical examination and imaging findings are inconclusive. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of the lump tissue for microscopic examination by a pathologist. This allows for a definitive diagnosis of the type of cell present in the lump and can identify conditions such as benign tumors, skin cancers, infections, or inflammatory processes.The type of biopsy performed depends on the size, location, and suspected nature of the lump.
Excisional biopsies involve removing the entire lump, while incisional biopsies remove only a portion of it. The choice between these two types depends on the clinical judgment of the physician.
Summary of Diagnostic Methods
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual inspection, palpation, assessment of size, shape, color, and location. | Initial assessment, identifying suspicious features, guiding further investigations. |
| Imaging Techniques (e.g., Ultrasound, Dermatoscopy) | Non-invasive methods to visualize internal structures and skin surface details. | Assessing the structure and depth of the lump, aiding in distinguishing between solid and cystic masses, evaluating pigmented lesions. |
| Biopsy (e.g., Excisional, Incisional) | Removal of a tissue sample for microscopic examination. | Providing a definitive diagnosis when other methods are inconclusive, identifying the type of cells present. |
Treatment Options for Skin Lumps: Lump Under Skin Causes And When To Worry
Treating skin lumps requires careful consideration of their underlying cause and potential for harm. A thorough evaluation by a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare professional is crucial to determine the most appropriate course of action. Different types of skin lumps necessitate different treatment strategies, ranging from simple observation to surgical intervention.Effective treatment plans aim to address the underlying issue, whether it’s a benign growth, an infection, or a more serious condition.
Factors such as the lump’s size, location, and potential for growth or spread influence the chosen treatment. It’s essential to understand that self-treating skin lumps can be risky and potentially worsen the condition.
Common Treatments for Benign Skin Lumps
Benign skin lumps, which are typically harmless, often require less aggressive treatment options. These options aim to either remove the lump or manage its symptoms.
A lump under the skin can be concerning, but often benign. Sometimes, it’s just a harmless cyst. However, if you’re experiencing chest congestion, trying some soothing home remedies like those found in this helpful guide on home remedies for chest congestion might help. But if the lump is growing rapidly, painful, or accompanied by other symptoms, it’s always best to see a doctor to rule out anything more serious.
- Excision: Surgical removal is a common method for benign skin lumps. The procedure involves cutting out the lump and surrounding tissue. Excision is often used for skin tags, moles, and other benign tumors. The specific technique used depends on the size and location of the lump, and the surgeon’s preference. For example, a small, superficial skin tag might be removed with a simple scalpel incision, while a larger, deeper lesion might require a more extensive surgical approach.
- Cryotherapy: This non-surgical technique involves freezing the skin lump to destroy it. Liquid nitrogen is typically used for this purpose. Cryotherapy is often effective for treating certain types of warts and small skin lesions. Potential side effects include temporary skin discoloration or discomfort.
- Electrocautery: This method uses heat to destroy the skin lump. A heated instrument, often an electric needle, is used to burn away the abnormal tissue. Electrocautery is a useful technique for treating small, superficial skin lesions. Possible complications include scarring.
- Laser therapy: Laser surgery uses a highly focused beam of light to vaporize or remove the skin lump. This approach is particularly useful for treating skin lesions that are difficult to access or remove with other methods. Laser therapy often results in minimal scarring and is effective for various skin conditions.
Treatment Approaches Based on Underlying Causes
The chosen treatment strategy for a skin lump often depends on the underlying cause. For example, an infected skin lump might require antibiotic treatment, while a cancerous lump might necessitate more aggressive therapies.
- Infections: Infected skin lumps may respond to antibiotic therapy. The specific antibiotic and duration of treatment will depend on the causative organism. Antibiotics may be taken orally or applied topically.
- Inflammation: Inflammation-related skin lumps may be treated with anti-inflammatory medications or topical creams. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and cause of the inflammation.
- Cancerous Lumps: Cancerous skin lumps require specialized treatments like chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery. These treatments are often part of a broader cancer treatment plan and are determined by the type, stage, and location of the cancer.
Surgical Procedures for Removing Skin Lumps
Surgical removal is a common treatment option for skin lumps. The specific surgical technique used depends on the type, size, and location of the lump.
- Simple excision: This is a straightforward procedure involving the removal of the lump and a small margin of surrounding tissue. It’s often used for benign skin lesions.
- Mohs surgery: This specialized surgical technique is used for skin cancers. Thin layers of tissue are removed and examined under a microscope until no cancerous cells are detected. It’s a precise approach that aims to minimize the removal of healthy tissue.
- Curettage and electrodessication: This involves scraping away the lump with a curette and then using an electric current to destroy the remaining tissue. It’s often used for superficial skin lesions.
Role of Medication in Managing Skin Lumps
Medication can play a significant role in managing certain skin lumps, particularly those related to infections or inflammation.
Lumps under the skin can stem from various things, like cysts or infections. But sometimes, a lump could be a sign of something more serious, like a tumor. For instance, a lump in the pelvic area, especially in men, might warrant further investigation, particularly if it’s accompanied by other symptoms. It’s crucial to consider more serious conditions like metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer, which, in some cases, can manifest as a lump.
If you’re concerned about a lump, it’s always best to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and to rule out any potential underlying health issues. Remember, early detection is key when it comes to lumps under the skin. metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat infections that cause skin lumps. The choice of antibiotic depends on the specific bacteria causing the infection.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation associated with certain skin lumps. The dosage and type of medication are determined by the healthcare professional.
Treatment Options Table
| Treatment Option | Suitability | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Excision | Benign lumps, some cancers | Bleeding, infection, scarring |
| Cryotherapy | Small, superficial lumps | Discomfort, temporary skin discoloration |
| Electrocautery | Small, superficial lumps | Scarring, pain |
| Laser therapy | Various skin lesions, difficult-to-reach lumps | Pain, temporary redness, scarring |
| Antibiotics | Infected skin lumps | Allergic reactions, digestive upset |
| Anti-inflammatory medications | Inflammation-related lumps | Stomach upset, headache, other side effects |
Prevention Strategies for Skin Lumps
Skin lumps, while sometimes benign, can be a source of concern. Proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing them. Implementing healthy lifestyle choices and practicing regular self-examination are crucial steps in this preventative approach.Early detection and prompt treatment are key to managing skin lumps effectively. A preventative approach focuses on minimizing risk factors and promoting overall skin health, leading to a lower likelihood of developing skin abnormalities.
Lifestyle Factors to Reduce Skin Lump Risk
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a vital role in overall well-being and can reduce the risk of various skin conditions, including the development of skin lumps. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for healthy skin tissue repair and function. Regular exercise promotes blood circulation, supporting skin health and immune function. Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also contribute to a healthier skin environment.
Importance of Regular Skin Checks and Self-Examinations
Regular skin checks are crucial for early detection of skin changes. This includes both professional examinations by dermatologists and self-examinations performed at home. Self-exams are simple yet effective tools for identifying potential problems early on. By regularly checking your skin, you can detect any unusual growths, changes in existing moles, or other irregularities that might signal a developing skin lump.
This early detection allows for prompt medical intervention and treatment if necessary.
Sun Protection in Preventing Skin Lumps
Protecting your skin from excessive sun exposure is paramount in preventing various skin conditions, including skin lumps. The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a significant risk factor for skin cancer, a leading cause of skin lumps. Sun protection measures include using broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
Regular use of sunscreen, along with other protective measures, helps significantly reduce the risk of skin damage and subsequent skin lump development.
Managing Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing skin lumps. For example, individuals with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to various skin infections and growths. Individuals with autoimmune diseases might experience skin manifestations as part of their condition. Managing underlying medical conditions effectively can help minimize the risk of skin lumps. This may involve adhering to prescribed medications, attending regular checkups, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Preventative Measures
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for skin health, promoting repair and function.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes blood circulation, supporting skin health and immune function.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation or yoga can create a healthier skin environment.
- Regular Skin Checks: Self-exams and professional dermatological examinations are crucial for early detection of skin changes.
- Sun Protection: Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wear protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sun hours.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Adhering to medical treatments, regular checkups, and a healthy lifestyle are vital for minimizing risks associated with pre-existing conditions.
Last Point
In conclusion, dealing with a lump under the skin can be concerning, but a proactive approach is key. By understanding the possible causes, recognizing warning signs, and knowing when to seek medical help, you can effectively manage the situation. Remember, early detection and proper diagnosis are paramount to ensuring the best possible outcome. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.