Eczema on face treatment is a crucial aspect of managing this common skin condition. This guide delves into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options, from simple home remedies to professional medical interventions. We’ll explore everything from understanding different types of facial eczema to managing flare-ups and preventing recurrence.
Facial eczema can be frustrating and impact daily life. Understanding its diverse triggers and effective treatment strategies is key to finding relief and maintaining healthy skin. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to take control of your eczema.
Introduction to Eczema on the Face
Facial eczema, a common skin condition, presents as inflamed, itchy, and sometimes painful patches on the face. It’s a chronic skin disorder, meaning it tends to persist over time, often recurring with periods of remission. Understanding its various forms and triggers is crucial for effective management.The causes of facial eczema are multifaceted. Underlying factors, such as a weakened skin barrier, can make individuals more susceptible.
Allergic reactions to environmental factors like pollen or certain chemicals, and even stress, can trigger or worsen facial eczema outbreaks. Genetics also plays a significant role in some cases.
Types of Facial Eczema
Different types of eczema can manifest on the face, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding the specific type helps tailor treatment strategies effectively. Atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis are common forms that affect the face.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition. It’s characterized by dry, itchy skin, often with red, inflamed patches. These patches may be accompanied by blisters, weeping sores, and scaling. The inflammation can vary in severity from mild to severe. Atopic dermatitis often occurs in individuals with a family history of allergies or asthma.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a skin reaction triggered by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. Common triggers include soaps, detergents, fragrances, certain metals, and even certain types of jewelry. The reaction typically appears within hours or days of contact and manifests as redness, itching, and sometimes blisters or oozing sores at the contact site. This type of eczema is more localized and often responds well to avoidance of the trigger.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas with oil glands, like the face, scalp, and chest. It’s characterized by flaky, yellowish-white patches, often with redness and itching. The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is still under investigation, but it’s believed to involve a combination of factors, including yeast overgrowth and an immune response.
Comparison of Facial Eczema Types, Eczema on face treatment
| Type of Eczema | Symptoms | Triggers | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Dry, itchy skin, red, inflamed patches, blisters, scaling | Family history, allergies, stress, environmental factors | Moisturizing, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines, avoiding triggers |
| Contact Dermatitis | Redness, itching, blisters, oozing sores at contact site | Irritants or allergens (e.g., soaps, metals, fragrances) | Identifying and avoiding triggers, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Flaky, yellowish-white patches, redness, itching | Yeast overgrowth, immune response, possibly hormonal factors | Anti-fungal treatments, topical corticosteroids, medicated shampoos |
Understanding the Causes of Facial Eczema
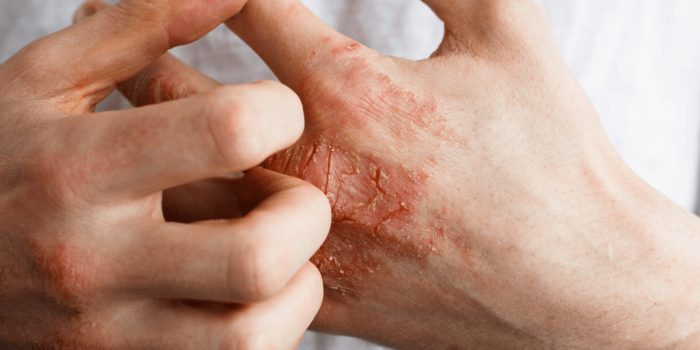
Facial eczema, a common skin condition, isn’t just about itchy patches; it’s a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective management and preventing flare-ups. From genetics to lifestyle, various elements contribute to the development and persistence of facial eczema.While the exact cause of eczema isn’t fully understood, research points towards a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers.
This means that even if you have a family history of eczema, environmental factors can still play a critical role in whether or not you experience symptoms.
Genetic Factors
Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of atopic dermatitis (a type of eczema) are more likely to develop facial eczema. This genetic predisposition involves variations in genes that regulate the skin’s barrier function, making the skin more susceptible to irritants and allergens. Studies have shown specific gene variations linked to a higher risk of developing eczema.
This genetic tendency doesn’t automatically mean you’ll get eczema, but it increases the likelihood.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors are frequently implicated in eczema flare-ups. These triggers can be broadly categorized as allergens and irritants.
Allergens
Allergens are substances that can trigger an immune response in susceptible individuals. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold spores, and certain foods. Exposure to these allergens can lead to inflammation and itching, exacerbating facial eczema. For instance, someone with a genetic predisposition to eczema might experience a flare-up after exposure to pollen during a spring allergy season.
Irritants
Irritants, unlike allergens, don’t trigger an immune response but can still cause inflammation and irritation of the skin. These can include harsh soaps, detergents, strong perfumes, and certain fabrics. Even seemingly innocuous substances can become irritants for individuals with sensitive skin. A common example is using harsh facial cleansers that dry out the skin, leading to eczema flare-ups.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact eczema development and severity. Stress, for example, is a known trigger for many inflammatory conditions, including eczema. Chronic stress can weaken the skin’s barrier function, making it more vulnerable to irritants and allergens. Furthermore, poor sleep, a poor diet, and inadequate hydration can also contribute to eczema development. Maintaining a balanced lifestyle, including stress management techniques, a healthy diet, and sufficient sleep, can help manage eczema symptoms.
Stress
Stress plays a significant role in exacerbating eczema. The body’s response to stress can increase inflammation throughout the body, potentially affecting the skin. Stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, may be beneficial for managing eczema symptoms.
Diet
While not a direct cause, certain dietary factors can influence eczema. A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats might worsen inflammation. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids might help maintain skin health.
Summary Table of Common Triggers for Facial Eczema
| Category | Triggers | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | Family history of atopic dermatitis | Having a parent or sibling with eczema |
| Allergens | Substances triggering immune response | Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods |
| Irritants | Substances directly irritating the skin | Harsh soaps, detergents, strong perfumes, certain fabrics |
| Lifestyle | Stress, sleep, diet, hydration | Chronic stress, poor sleep, poor diet, dehydration |
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
Many people with mild facial eczema find relief with natural remedies and home care techniques. These methods can often reduce inflammation and itching, and when combined with a good skincare routine, can significantly improve the overall appearance and comfort of the skin. However, it’s crucial to remember that these remedies are not a substitute for professional medical advice.
If your eczema is severe or doesn’t improve with home remedies, consult a dermatologist.Natural ingredients, when used correctly, can be powerful allies in managing facial eczema. Applying gentle, soothing treatments can help reduce dryness and irritation, which are common triggers for flare-ups. Consistency is key, and patience is needed to see results.
Finding the right eczema treatment for your face can be a real challenge, and sometimes it’s not just about topical creams. Did you know that what you eat can actually impact your skin health? For example, some studies suggest that excessive consumption of artificial sweeteners could be a factor in kidney issues, which might, in turn, affect skin conditions like eczema.
Understanding the potential effects of artificial sweeteners on the kidneys is crucial for overall well-being, and finding resources like artificial sweeteners effects on the kidneys can help you make informed choices. Ultimately, a holistic approach to eczema treatment, including diet considerations, is key for effective management.
Effectiveness of Home Remedies
Home remedies for mild facial eczema can be effective in managing symptoms, particularly when used as part of a comprehensive skincare routine. The efficacy of these remedies varies depending on individual factors, such as the severity of the eczema, the specific triggers, and the individual’s skin type. Consistency and patience are essential for seeing results.
Natural Ingredients and Their Potential Benefits
A range of natural ingredients are often used in home remedies for facial eczema. These ingredients typically offer soothing, anti-inflammatory, and moisturizing properties.
- Oatmeal: Oatmeal is known for its gentle exfoliating and anti-inflammatory properties. Colloidal oatmeal, a finely ground form of oatmeal, can create a soothing paste or bath, which can calm irritated skin and reduce itching. The avenanthramides in oatmeal are thought to help modulate the immune response, potentially lessening the inflammatory reactions that contribute to eczema.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel is widely used for its soothing and moisturizing properties. It can help reduce inflammation and irritation, and its moisturizing qualities can help keep the skin hydrated. The gel’s cooling effect can also provide temporary relief from itching.
- Honey: Honey is a humectant, meaning it draws moisture to the skin. It can also have antimicrobial properties. However, some people may be allergic to honey, so caution is advised.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer that can help hydrate the skin and soothe dryness. Its antimicrobial properties may also help prevent infections.
Gentle Cleansing and Moisturizing Techniques
Maintaining a gentle skincare routine is crucial for managing facial eczema. Harsh cleansers and scrubbing can further irritate the skin, exacerbating the condition.
- Cleansing: Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser specifically formulated for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh scrubbing or rubbing. Gently massage the cleanser into the skin, and rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water.
- Moisturizing: Moisturize your face regularly, especially after cleansing. Use a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer that’s suitable for sensitive skin. Apply a thin layer of moisturizer to damp skin to help lock in moisture.
Home Remedies Table
The following table provides a summary of common home remedies for facial eczema, their potential benefits, and potential side effects.
| Home Remedy | Potential Benefits | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Oatmeal | Soothing, anti-inflammatory, gentle exfoliation | Possible allergic reaction in sensitive individuals |
| Aloe Vera | Soothing, moisturizing, anti-inflammatory | Possible allergic reaction in sensitive individuals |
| Honey | Moisturizing, antimicrobial | Possible allergic reaction |
| Coconut Oil | Moisturizing, antimicrobial | May cause skin irritation in some individuals |
Topical Treatments for Facial Eczema
Treating facial eczema often involves a multi-pronged approach, and topical medications play a crucial role. These treatments work directly on the affected skin, aiming to soothe inflammation, reduce dryness, and prevent further irritation. Choosing the right topical treatment is essential, as improper use can worsen the condition.Understanding the different types of topical treatments and their mechanisms of action is key to effective eczema management.
This includes recognizing the potential benefits and risks associated with each medication. A balanced approach that combines topical treatments with a proper skincare routine and lifestyle modifications is often the most successful strategy for managing facial eczema.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are potent anti-inflammatory medications frequently used for treating eczema. They work by suppressing the immune response, reducing inflammation and itching. Short-term use of low-potency corticosteroids is generally well-tolerated, and can be effective in managing flares. However, long-term use of high-potency corticosteroids may lead to skin thinning, striae (stretch marks), and other adverse effects.
Moisturizers
Moisturizers are essential for maintaining skin hydration and preventing dryness, a common trigger for eczema flares. They create a protective barrier on the skin, preventing moisture loss and providing a soothing effect. Choosing a fragrance-free and hypoallergenic moisturizer is crucial, as fragrances and certain ingredients can irritate the skin and worsen eczema. A consistent moisturizing routine is key to maintaining skin health and preventing flare-ups.
Other Topical Treatments
Several other topical medications, including calcineurin inhibitors and topical immunomodulators, are available for managing facial eczema. These treatments work by targeting specific pathways involved in the inflammatory response. Their efficacy and safety profiles vary, and consultation with a dermatologist is essential for determining the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Importance of Fragrance-Free and Hypoallergenic Skincare
Facial eczema often responds well to a simplified skincare routine. Using fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products is paramount. Fragrances, dyes, and harsh chemicals in skincare products can trigger allergic reactions and worsen eczema symptoms. Prioritizing products formulated for sensitive skin can significantly improve comfort and reduce irritation.
Potential Side Effects of Topical Treatments
Topical treatments, while beneficial, can have potential side effects. These side effects can range from mild to severe and depend on the specific medication, potency, and duration of use. Common side effects include skin irritation, redness, burning, and dryness. More serious side effects, such as skin thinning or increased risk of infection, are less common but can occur with prolonged use of high-potency corticosteroids.
Comparison of Topical Treatments
| Treatment | Mechanism of Action | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Corticosteroids | Suppress inflammation by reducing immune response. | Skin thinning, striae, irritation, redness, burning, increased risk of infection (with high potency and long-term use). |
| Moisturizers | Maintain skin hydration, create a protective barrier. | Possible allergic reactions to certain ingredients (if not hypoallergenic). |
| Calcineurin Inhibitors | Target specific inflammatory pathways. | Skin irritation, burning, infection (in some cases). |
| Topical Immunomodulators | Modify immune response. | Skin irritation, burning, itching, and other allergic reactions (in some cases). |
Professional Medical Treatments
Dealing with facial eczema can be frustrating, and sometimes, home remedies and topical treatments aren’t enough. Fortunately, professional medical interventions can provide significant relief and address the underlying causes of the condition in severe cases. A dermatologist, with their specialized knowledge and experience, can provide tailored treatment plans that target the specific needs of your skin.Seeking expert medical advice is crucial for effective eczema management.
Dermatologists can accurately diagnose the type of eczema, assess the severity of the condition, and recommend the most appropriate treatment strategy. They can differentiate between different types of facial eczema and tailor treatment plans accordingly, which is essential for successful long-term management.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy utilizes controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light to reduce inflammation and control eczema symptoms. This treatment is often effective in reducing itching and promoting skin healing. Different types of UV light, such as UVB and UVA, can be used, with specific wavelengths tailored to the individual’s needs and skin type. This method can be particularly beneficial for persistent cases where other treatments have not been successful.
Important note: Phototherapy requires careful monitoring by a dermatologist to avoid potential skin damage or complications.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators are medications that help regulate the immune system’s response to inflammation. These drugs can be effective in managing chronic eczema, especially in cases where inflammation is a significant factor. They work by reducing the overactive immune response that contributes to the eczema flare-ups. Examples of immunomodulators include topical corticosteroids and oral medications like cyclosporine. These medications can have side effects, so close monitoring by a dermatologist is vital to manage any potential complications.
Prescription Medications
Prescription medications play a crucial role in managing severe cases of facial eczema that don’t respond to other treatments. These medications can help control inflammation, reduce itching, and prevent further skin damage. They may include stronger corticosteroids, immunomodulators, or even biologics in extreme situations. It’s important to understand that prescription medications are not a one-size-fits-all solution and should only be considered under the guidance of a dermatologist.
They can significantly improve the quality of life for those struggling with severe eczema.
Summary of Medical Treatments
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Phototherapy | Generally effective in reducing inflammation and itching, often showing good results in persistent cases. | Potential for skin damage if not monitored properly, risk of sunburn. |
| Immunomodulators | Can effectively manage chronic eczema, especially when inflammation is a significant factor. | Potential side effects, ranging from mild to more severe, depending on the specific medication. Close monitoring is crucial. |
| Prescription Medications (Severe Cases) | Can significantly control inflammation and prevent further skin damage in severe cases not responding to other treatments. | Potential for significant side effects, requiring careful monitoring. Only considered under the guidance of a dermatologist. |
Managing Flare-Ups and Preventing Recurrence
Facial eczema, while manageable, can be frustrating due to unpredictable flare-ups. Understanding how to recognize and respond to these episodes, combined with proactive measures to prevent future outbreaks, significantly improves quality of life. This section delves into practical strategies for controlling flare-ups and establishing a long-term, preventative skincare routine.Effective eczema management involves a multifaceted approach, recognizing that triggers and individual responses vary.
By learning to identify and avoid triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, and implementing preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of future flare-ups and enjoy more comfortable skin.
Strategies for Managing Facial Eczema Flare-Ups
Identifying the specific triggers and reactions associated with facial eczema flare-ups is crucial for effective management. Pay close attention to the timing of flare-ups, considering potential environmental factors, dietary changes, or new skincare products. Documenting these observations in a journal can provide valuable insights into patterns and contributing factors.
Dealing with eczema on my face has been a real challenge, and I’ve tried countless remedies. While researching different treatments, I stumbled across the concept of cardiac resynchronization therapy CRT, a procedure that helps regulate heart function. It got me thinking about how interconnected our body systems can be. Ultimately, though, focusing back on eczema, I’m still on the hunt for the perfect solution to soothe my skin and reduce the inflammation.
cardiac resynchronization therapy crt is a fascinating area, but my main priority is finding a solution for my facial eczema.
Importance of Avoiding Known Triggers
Avoiding known triggers is paramount in preventing eczema flare-ups. This includes identifying potential allergens such as certain cosmetics, fragrances, soaps, or fabrics. If you suspect a particular ingredient or substance triggers your eczema, consider eliminating it from your routine to observe the impact. Keep a close watch on your skin’s response to new products or changes in your environment.
Finding the right eczema treatment for my face has been a journey! I’ve been exploring different natural remedies, and one that caught my eye was mugwort. Learning about its potential benefits, side effects, dosage, and interactions is crucial before using it, and this resource offers a comprehensive guide on mugwort benefits side effects dosage and interactions.
While mugwort might hold promise, I’m still prioritizing gentle, dermatologist-approved options for my facial eczema. More research is needed to see if it works for me. Hopefully, I’ll find a solution soon!
For example, if a new skincare product seems to worsen your eczema, discontinue its use immediately.
Significance of Maintaining a Consistent Skincare Routine
Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, tailored to your skin type and eczema tendencies, plays a pivotal role in preventing flare-ups. This includes using gentle cleansers, fragrance-free moisturizers, and avoiding harsh scrubbing or excessive washing. This consistency provides a stable environment for your skin and minimizes potential irritants. Using a routine that includes gentle cleansers, suitable moisturizers, and sun protection will be beneficial for long-term management.
Practical Tips for Preventing Future Flare-Ups
Implementing practical preventative measures is key to long-term eczema control. These tips will help you establish a routine that reduces the risk of flare-ups:
- Identify and Eliminate Triggers: Keep a detailed log of potential triggers, noting any coincidences between exposure to specific substances and the onset of eczema flare-ups. This detailed record will help you pinpoint and eliminate specific allergens or irritants that could be contributing to your condition. Examples of potential triggers include certain foods, cosmetics, or environmental factors.
- Choose Gentle Skincare Products: Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic skincare products. Look for products specifically formulated for sensitive skin or those with known eczema-friendly ingredients. Consider a skincare routine designed for sensitive skin to maintain a healthy moisture balance and minimize irritation. Products containing harsh chemicals, fragrances, or dyes should be avoided.
- Moisturize Regularly: Maintaining adequate hydration is crucial. Apply moisturizer to your face immediately after cleansing and throughout the day, especially after showering or bathing. This helps maintain a protective barrier against irritants and dryness.
- Manage Stress Levels: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature into your routine. This practice can contribute to reducing stress and minimizing its impact on your skin condition.
- Protect Your Skin from the Sun: Sun exposure can aggravate eczema. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from harmful UV rays, especially during peak sun hours. This practice helps prevent further skin irritation and damage.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options. They can provide tailored recommendations for your specific needs and ensure that your approach aligns with best practices.
Illustrations and Visual Aids
Visual aids are crucial for understanding and managing facial eczema. Illustrations and comparisons can help visualize the differences between healthy skin and skin affected by eczema, making it easier to identify the condition and track its progression. Detailed depictions of lesions and stages of development are also important for effective self-care and communication with healthcare professionals.
Visualizing Facial Eczema Lesions
Facial eczema lesions can vary significantly in appearance, size, and distribution. Understanding these characteristics is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Typical lesions manifest as red, inflamed patches. The skin may be dry, rough, or cracked, and often exhibits small, raised bumps or blisters. In some cases, the affected area might ooze or crust over.
The color and texture can change depending on the severity and stage of the eczema.
Stages of Eczema Development
Eczema development often progresses through distinct stages. Early stages are characterized by mild dryness, redness, and minor irritation. As the condition worsens, the inflammation intensifies, leading to the formation of visible lesions, itching, and potentially, secondary skin infections. Chronic eczema can cause thickened, leathery skin and permanent discoloration. Identifying these stages can help tailor treatment strategies for optimal results.
Skin Barrier Function in Eczema
The skin barrier plays a crucial role in protecting the body from environmental factors. In eczema, this barrier is compromised, leading to increased water loss and susceptibility to irritants. A visual illustration would show a healthy skin barrier as a strong, intact wall, effectively preventing water loss and protecting against irritants. Conversely, a compromised skin barrier in eczema would be depicted as a weakened or damaged wall, allowing for excessive water loss and increased susceptibility to irritants and allergens.
This illustration emphasizes the importance of maintaining the skin barrier’s integrity in managing eczema.
Comparison of Normal Skin and Eczema-Affected Skin
A detailed illustration comparing normal skin to skin with eczema would highlight the significant differences in appearance and texture. Normal skin would be depicted as smooth, even-toned, and hydrated. The illustration would contrast this with eczema-affected skin, which would appear red, inflamed, dry, and potentially covered with lesions, blisters, or cracks. This visual comparison would aid in recognizing the distinctive characteristics of eczema.
Such an illustration could include labels that clearly distinguish the affected area and the presence of inflammatory cells or other key indicators associated with the condition.
Lifestyle Considerations for Eczema Management: Eczema On Face Treatment

Managing facial eczema extends beyond topical treatments. Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in controlling flare-ups and preventing future outbreaks. Understanding how diet, stress, sleep, and hydration impact your skin’s health is essential for long-term eczema management.Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly improve your skin’s overall health and resilience against eczema triggers. By incorporating these elements into your daily routine, you can effectively minimize the severity and frequency of eczema flare-ups.
Consistent effort in these areas is often key to sustained improvement.
Impact of Diet on Facial Eczema
Diet’s influence on eczema is a complex area. While a specific “eczema diet” isn’t universally recognized, certain foods may exacerbate inflammation and trigger flare-ups in susceptible individuals. Identifying potential triggers through a food diary and consulting a registered dietitian can help pinpoint problematic foods.Certain foods, like processed foods, sugary drinks, and dairy products, are sometimes associated with increased inflammation.
However, individual responses vary greatly, and a personalized approach is crucial. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with adequate hydration, can support overall skin health.
Stress Management Techniques for Eczema
Stress can significantly impact eczema. Chronic stress can increase inflammation throughout the body, potentially leading to flare-ups. Implementing stress-reducing techniques can be beneficial in managing eczema symptoms.Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels. These techniques promote relaxation and can reduce the body’s inflammatory response.
Consistent practice of stress-reducing techniques can become an essential tool for eczema management.
Importance of Adequate Sleep and Hydration
Adequate sleep and hydration are essential for overall health, including skin health. Sleep deprivation and dehydration can disrupt the skin’s natural barrier function, making it more susceptible to irritation and eczema flare-ups.Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to allow the body to repair and regenerate. Staying properly hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps maintain skin moisture, preventing dryness and irritation.
Sufficient sleep and hydration support the skin’s natural healing processes.
Summary of Lifestyle Choices and Their Impact on Eczema
| Lifestyle Choice | Impact on Eczema | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Certain foods may trigger flare-ups; a balanced diet supports skin health. | Reducing processed foods, sugary drinks, and dairy. |
| Stress Management | Chronic stress can worsen eczema; stress-reducing techniques can help. | Practicing yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. |
| Sleep | Adequate sleep aids in skin repair; insufficient sleep can trigger flare-ups. | Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. |
| Hydration | Drinking plenty of water maintains skin moisture; dehydration can exacerbate eczema. | Carrying a water bottle and drinking water throughout the day. |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, managing eczema on the face requires a multifaceted approach. Combining home remedies with appropriate topical and professional treatments, while addressing lifestyle factors, can significantly improve skin health and well-being. Remember that consistency and a personalized approach are crucial for long-term eczema management. Consult with a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.

