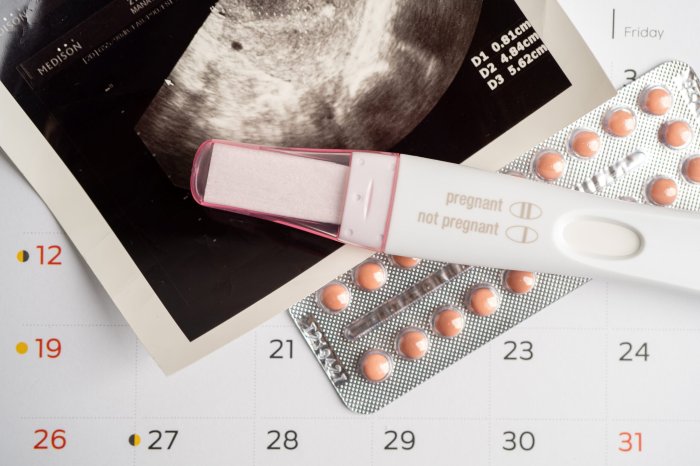
Fertility when are your most fertile days – Fertility: When are your most fertile days? Understanding your menstrual cycle and fertile window is key to optimizing your chances of conception. This comprehensive guide explores everything from the intricacies of your monthly cycle to the various methods for pinpointing your fertile days, including the calendar method, basal body temperature tracking, and cervical mucus observation. We’ll also delve into factors affecting fertility, from lifestyle choices to underlying health conditions, and how to effectively track your cycle using apps and resources.
We’ll examine the male side of fertility, discussing male reproductive health and factors influencing sperm quality. Furthermore, we’ll explore strategies for optimizing fertility for couples, including communication, support, and addressing potential obstacles. Finally, we’ll equip you with practical tips for improving your overall fertility health, from dietary recommendations to stress management techniques. Let’s uncover the secrets to maximizing your chances of conception!
Understanding the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a complex biological process that governs a woman’s reproductive health. Understanding its phases, hormonal fluctuations, and potential influences is crucial for optimizing fertility and overall well-being. This intricate cycle is a testament to the remarkable coordination within the female body.The menstrual cycle is a recurring cycle of hormonal changes that prepare the uterus for potential pregnancy.
It’s a fundamental aspect of female reproductive health, impacting not only fertility but also general well-being. The length and regularity of the cycle can vary significantly between individuals, and understanding these variations is key to comprehending individual fertility patterns.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is typically divided into four distinct phases: menstruation, the follicular phase, ovulation, and the luteal phase. Each phase is characterized by specific hormonal changes that contribute to the overall process.
Hormonal Fluctuations During the Cycle
Hormones play a pivotal role in regulating the menstrual cycle. The interplay between follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen, and progesterone orchestrates the events of each phase. These hormones are responsible for the cyclical changes in the uterine lining and the maturation of an egg.
| Phase | Duration (average) | Key Hormonal Changes | Uterine Lining Changes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Menstruation | 3-7 days | Estrogen and progesterone levels are low. | The uterine lining sheds, resulting in bleeding. |
| Follicular Phase | 7-10 days | FSH stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries, which produce estrogen. | The uterine lining begins to thicken. |
| Ovulation | 1-2 days | LH surge triggers the release of the mature egg. | The egg is released from the ovary. |
| Luteal Phase | 10-14 days | Progesterone levels rise, preparing the uterus for potential implantation. | The uterine lining continues to thicken. |
Role of Ovulation in Fertility
Ovulation is the pivotal event in the menstrual cycle for fertility. It’s the release of a mature egg from the ovary, which is ready for fertilization. The timeframe for ovulation typically occurs mid-cycle, approximately 14 days before the next expected period. This precise timing is critical for successful conception.
Indicators of Ovulation
Various indicators can signal the approaching ovulation. Changes in cervical mucus, basal body temperature, and ovulation tests can help identify the fertile window.
- Cervical Mucus Changes: Cervical mucus becomes clear, stretchy, and abundant, resembling egg white. This change facilitates sperm movement. A significant increase in the amount and consistency of cervical mucus often occurs a few days before ovulation.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): BBT charts track slight temperature fluctuations throughout the cycle. A rise in BBT typically occurs after ovulation, signaling the beginning of the luteal phase. This can be a helpful indicator of when ovulation has occurred.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): These kits detect the surge in LH hormone, which signals the impending release of the egg. Positive results on the OPK typically occur within 24-48 hours of ovulation.
Factors Influencing Menstrual Cycle Regularity
Numerous factors can impact the regularity of the menstrual cycle, including stress, diet, exercise, and underlying medical conditions. Significant changes in these areas can disrupt the hormonal balance, affecting cycle length and regularity.
- Stress: Significant stress can disrupt the hormonal balance, leading to irregular cycles. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help maintain cycle regularity.
- Diet and Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance and supporting a regular menstrual cycle. Nutrient deficiencies or extreme dietary changes can affect the cycle.
- Exercise: Excessive or intense exercise can disrupt the hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods. A moderate exercise routine is recommended for optimal reproductive health.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can affect the menstrual cycle, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.
Identifying Fertile Days
Pinpointing your fertile window is crucial for optimizing your chances of conception. Understanding the rhythm of your menstrual cycle is a first step, but identifying the precise days when you’re most likely to conceive requires further investigation. This section dives into various methods for calculating fertile days, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Different Methods for Calculating Fertile Days
Various methods exist to help you identify your fertile window, each with its own strengths and limitations. The accuracy of these methods can vary, so it’s often helpful to combine them for a more comprehensive understanding of your cycle.
- The Calendar Method: This method relies on tracking the length of your menstrual cycles over several months to predict future fertile periods. Understanding your typical cycle length is key, as it helps to identify the approximate time of ovulation. For example, if your average cycle is 28 days, ovulation would typically occur around day 14. Knowing this baseline allows you to anticipate your fertile window.
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Tracking: BBT tracking involves recording your body temperature first thing in the morning, before any activity. Ovulation causes a slight increase in body temperature, which you can monitor. This method is particularly useful in conjunction with cervical mucus observation, as the temperature shift typically follows ovulation. For example, a woman with a 28-day cycle might notice a rise in BBT around day 14-15, signaling the fertile window.
- Cervical Mucus Observation: This method focuses on changes in cervical mucus, which becomes clearer, wetter, and more stretchy around ovulation. This “egg white” consistency is a key indicator of ovulation. Tracking cervical mucus alongside other methods can significantly enhance accuracy. For example, a woman might notice a noticeable increase in cervical mucus around day 12-14 of a 28-day cycle, signifying her fertile window.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): OPKs are urine tests that detect luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, which typically occur just before ovulation. These kits provide a convenient way to identify the peak fertile period. Results are usually positive 24-48 hours before ovulation, allowing for targeted timing of intercourse. For example, a positive OPK result would indicate a very high probability of ovulation in the next 24-48 hours, suggesting a fertile period.
Figuring out when you’re most fertile can be tricky, but understanding your cycle is key. Knowing your body’s rhythm is important for many reasons, including timing those precious moments. While we’re on the topic of biological rhythms, did you know that ear mites can sometimes affect human health? It’s a fascinating area of study, and you can learn more about ear mites in humans here.
Ultimately, understanding your fertile window is crucial for those hoping to conceive, so let’s dive back into the specifics of those fertile days!
Accuracy and Reliability of Methods
The accuracy of each method varies. The calendar method, while simple, can be less accurate for irregular cycles. BBT tracking requires diligence and attention to detail, but it can be quite precise. Cervical mucus observation is highly sensitive but can be subjective. OPKs provide a relatively objective measure, but they don’t indicate the quality of the egg or the health of the reproductive system.
Step-by-Step Guide: Calendar Method
- Track the length of your menstrual cycles for at least three months. Record the first day of your period each month.
- Calculate the approximate length of your average cycle by averaging the lengths of the cycles tracked.
- Determine your estimated ovulation date by subtracting 14 days from the length of your average cycle. For example, if your average cycle is 28 days, ovulation is expected around day 14.
- Your fertile window typically extends for a few days around the estimated ovulation date. This typically includes the day before and the day of ovulation, plus a day or two after. For example, if ovulation is expected on day 14, the fertile window might be days 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16.
- Repeat this process each month, using your average cycle length as a prediction tool.
Potential Limitations and Inaccuracies
Factors such as stress, illness, medications, and lifestyle changes can affect cycle regularity. The calendar method is less reliable for women with irregular cycles. BBT tracking can be affected by factors like sleep disturbances. Cervical mucus observation requires practice and awareness. OPKs can produce false positives or negatives due to variations in hormone levels.
Comparison Table: Pros and Cons of Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Calendar Method | Simple, inexpensive, and easy to use. | Less accurate for irregular cycles, doesn’t account for individual variations. |
| BBT Tracking | Highly accurate, tracks ovulation, and helps understand overall cycle health. | Requires diligence, can be affected by factors like illness or sleep disturbances. |
| Cervical Mucus Observation | Relatively inexpensive, highly sensitive, and allows for detailed cycle understanding. | Requires practice and can be subjective, can be affected by vaginal infections or medications. |
| OPKs | Convenient, objective measure of LH surge, easy to use. | Can be expensive, doesn’t account for individual hormonal variations, doesn’t show egg quality. |
Factors Affecting Fertility

Understanding your fertile window is crucial, but it’s not the sole determinant of your ability to conceive. Many other factors, both internal and external, can impact your fertility. This section will explore the diverse influences on reproductive health, including lifestyle choices, age-related changes, underlying health conditions, and the effects of certain medications.
Lifestyle Factors and Fertility
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in overall health, and fertility is no exception. A balanced approach to diet, exercise, and stress management can positively impact your reproductive potential. Conversely, unhealthy habits can hinder your ability to conceive.
- Diet: A nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein supports overall health, including reproductive function. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods, saturated fats, and sugary drinks can negatively affect hormone balance and ovulation, potentially reducing fertility.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and promoting hormonal balance. However, extreme or excessive exercise can disrupt menstrual cycles and ovulation, impacting fertility. Finding a balance between physical activity and rest is key.
- Stress Levels: Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone production and disrupt the delicate balance needed for ovulation and fertilization. Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or meditation, can help mitigate these effects.
Age and Fertility
Age is a significant factor in fertility for both men and women. As we age, our reproductive systems undergo natural changes that can affect our ability to conceive.
- Women: Female fertility naturally declines with age. Ovarian reserve, the number of eggs available for fertilization, decreases significantly after the age of 35. This decrease in egg quality and quantity leads to a higher risk of infertility as women age. For example, a 35-year-old woman might experience a longer time to conceive compared to a younger woman, and the chances of having a healthy pregnancy might be slightly reduced.
Figuring out when you’re most fertile can be tricky, but understanding your cycle is key. Knowing your body’s rhythm can help you pinpoint those precious few days. While focusing on your fertility, it’s also important to be aware of conditions that can impact reproductive health. For example, familial dysautonomia, a rare genetic disorder, can have significant effects on the body’s systems, potentially affecting fertility.
Learning more about this condition, including its causes and symptoms, can be invaluable. an overview of familial dysautonomia offers valuable insight. Ultimately, understanding your own body and seeking appropriate medical advice are essential for optimal reproductive health and fertility awareness.
- Men: Male fertility also declines with age. Sperm quality and quantity can decrease, and the ability to produce healthy sperm can diminish. While male fertility tends to decline more gradually than female fertility, age is still a factor to consider. For example, a 40-year-old man may require more time to conceive compared to a younger man.
Underlying Health Conditions and Medical Treatments
Certain health conditions and medical treatments can impact fertility. These conditions can affect hormone production, ovulation, or sperm production.
- Examples of conditions: Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, endometriosis, and certain autoimmune diseases can significantly affect fertility. For example, PCOS can disrupt ovulation, making it difficult to conceive. Medical interventions such as surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy can also negatively impact fertility.
- Role of medical treatments: Specific medications, such as certain chemotherapy drugs or some hormonal treatments, can negatively affect reproductive health. For example, some medications can reduce sperm count or disrupt ovulation. It is important to discuss potential fertility implications with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Medications and Fertility
Certain medications can influence fertility, either positively or negatively. Understanding these effects is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Potential effects: Some medications can interfere with hormone production or ovulation, potentially impacting fertility. Conversely, some medications may support fertility, but this requires careful monitoring and medical advice.
Table: Lifestyle Factors and Fertility
| Lifestyle Factor | Potential Impact on Fertility |
|---|---|
| Unhealthy Diet | Reduced hormone balance, irregular ovulation, lower sperm quality |
| Lack of Exercise | Weight gain, hormonal imbalances, irregular periods |
| Chronic Stress | Disrupted hormone production, irregular ovulation, reduced sperm count |
| Excessive Exercise | Disrupted menstrual cycles, hormonal imbalances, decreased ovulation |
Tracking Fertility
Knowing your fertile window is crucial for optimizing your chances of conception. This involves diligently tracking your menstrual cycle and identifying the specific days when you are most likely to get pregnant. Accurate tracking allows you to plan sexual activity strategically and increase your chances of success.
Tools and Resources for Cycle Tracking
Effective cycle tracking relies on utilizing various tools and resources. These tools help you understand your body’s rhythms and predict your fertile window with greater precision. This section details different options available for cycle monitoring.
- Calendar Method: A basic approach involves manually noting the start and end dates of your periods on a calendar. This method can help you identify general patterns in your cycle length. However, it’s less precise than other methods, as it doesn’t consider the variability that can occur in cycle length from month to month. It also doesn’t factor in the fluctuations in your fertile window.
- Fertility Tracking Apps: Mobile apps dedicated to fertility tracking offer comprehensive features for monitoring your cycle and identifying fertile days. These apps often incorporate advanced algorithms to predict ovulation based on your cycle history and other factors. They can track multiple cycles, provide visual representations of your cycle data, and provide insights into your individual patterns. This approach is more accurate and detailed than the calendar method, offering more information and support in planning for conception.
- Fertility Monitors: These devices measure various physiological parameters, such as basal body temperature (BBT), cervical mucus consistency, and hormone levels. Based on these measurements, they predict your fertile window. They often provide more data than apps alone and are increasingly popular due to their ability to capture subtle changes in your body.
Examples of Cycle Tracking Apps
A range of apps are available to assist in cycle tracking. Each app offers varying features and levels of sophistication. Some popular options include:
- Clue: Known for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive data tracking, Clue offers insights into your cycle and possible ovulation dates. It also incorporates features for managing your health data.
- Flo: A popular choice, Flo provides a broad range of information and tools related to women’s health, including tracking cycles, managing medications, and providing information about fertility and pregnancy.
- Ovia: A well-regarded app for pregnancy planning, Ovia also offers robust cycle tracking capabilities. It provides educational resources and insights into potential pregnancy outcomes.
- Kindara: Focused specifically on fertility, Kindara provides highly detailed cycle tracking and personalized insights into your fertile window. It also provides information about pregnancy and preconception health.
Using a Fertility Tracking App
Using a fertility tracking app effectively involves several steps:
- Download and Install: Download the chosen app from your device’s app store.
- Input Data: Enter the start date of your period and any relevant details, such as cycle length, symptoms, or previous pregnancies.
- Monitor Data: Observe the app’s predictions and insights into your fertile window.
- Record Observations: Add any other relevant observations to the app’s data entry sections.
- Review Patterns: Regularly review the data to understand your cycle patterns and identify trends.
Interpreting Tracking Tool Data
Interpreting the data from these tools involves analyzing the trends and patterns in your cycle data. The app should highlight your fertile window, which typically encompasses a few days around ovulation. Look for consistent patterns in your cycle length and ovulation timing to predict future cycles. By closely monitoring these patterns, you can anticipate your fertile days with greater accuracy.
Figuring out when you’re most fertile can be tricky, but knowing your body’s cycle is key. While factors like stress and environmental toxins can affect your overall health, including potential impacts on fertility, understanding your ovulation window is crucial. Did you know that the EPA recently set new limits on PFAS in drinking water? epa pfas limits drinking water can significantly impact reproductive health.
This means clean water is more important than ever, especially when trying to conceive. Knowing your fertile window and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are still vital for optimizing your chances of getting pregnant.
Comparison of Fertility Tracking Apps
| App | Features | Cost | User Reviews |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clue | User-friendly interface, comprehensive data tracking, health insights | Free with in-app purchases | Generally positive, praised for its ease of use |
| Flo | Wide range of women’s health information, cycle tracking | Free with in-app purchases | Positive feedback on its breadth of information, mixed on the quality of fertility prediction |
| Ovia | Pregnancy planning, cycle tracking, educational resources | Free with in-app purchases | Positive user reviews, noted for comprehensive pregnancy information |
| Kindara | Focused on fertility, detailed cycle tracking, personalized insights | Subscription based | Generally positive, praised for its accuracy in fertility prediction |
Optimizing Fertility
Embarking on a journey to conceive requires a holistic approach, recognizing that fertility is a multifaceted process influenced by numerous factors. Beyond understanding your cycle and identifying fertile windows, optimizing your overall health plays a pivotal role in enhancing your chances of conception. This involves mindful choices regarding diet, exercise, and stress management. A comprehensive strategy addresses the interplay of these factors to create a supportive environment for conception.Optimizing fertility extends beyond just the fertile window; it encompasses a lifestyle that promotes overall well-being.
A balanced approach to nutrition, regular physical activity, and effective stress management are crucial components for achieving optimal reproductive health.
Dietary Recommendations for Fertility
A healthy diet is fundamental for both male and female fertility. Proper nutrition provides the building blocks for healthy reproductive organs and ensures optimal hormone function. Nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact fertility.
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. This ensures adequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants crucial for reproductive health.
- Prioritize foods rich in folate, vitamin D, and iron. These nutrients are vital for the development of a healthy embryo and the prevention of certain birth defects. For example, leafy greens, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals are excellent sources of folate. Fatty fish, fortified foods, and sunlight exposure are key sources of vitamin D. Red meat, beans, and leafy greens are good sources of iron.
- Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated and trans fats. These dietary choices can negatively impact hormone balance and overall health, which directly affects fertility.
Sample Meal Plan for Fertility Support
This sample meal plan is designed to provide a framework for incorporating fertility-boosting foods into your daily diet. Adjust portions and specific foods to fit your individual needs and preferences.
| Meal | Description |
|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with berries and nuts, or a protein smoothie with spinach and banana. |
| Lunch | Salad with grilled chicken or fish, quinoa, and a variety of vegetables. |
| Dinner | Baked salmon with roasted vegetables (broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes) and brown rice. |
| Snacks | Fruits (apples, bananas, oranges), vegetables with hummus, or a handful of almonds. |
Exercise for Fertility
Regular physical activity is vital for overall health and fertility. Moderate-intensity exercise promotes hormone balance, reduces stress, and supports healthy weight management.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise most days of the week. Examples include brisk walking, swimming, cycling, or dancing.
- Incorporate strength training exercises 2-3 times a week. These exercises help build muscle mass and support overall health.
- Avoid overly intense or strenuous exercise that can negatively impact hormone balance and menstrual cycles. Listen to your body and adjust your routine as needed.
Stress Management Techniques for Fertility
Chronic stress can negatively impact hormone production and menstrual regularity, potentially affecting fertility. Effective stress management techniques can mitigate these negative impacts.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. These practices can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
- Prioritize sufficient sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night to support hormonal balance and overall well-being.
- Engage in activities you enjoy. Making time for hobbies and interests can provide a healthy outlet for stress and promote emotional well-being.
Understanding Male Fertility
The journey to parenthood often involves a shared responsibility, and understanding both male and female fertility is crucial for a successful conception. This section delves into the intricacies of male fertility, exploring the male reproductive system, factors that impact it, and common issues. A healthy understanding of male fertility empowers couples to make informed decisions and potentially address any concerns proactively.The male reproductive system is responsible for producing and delivering sperm, the male gametes, essential for fertilization.
This complex process involves a delicate interplay of organs, hormones, and physiological functions. Understanding this system and the factors that influence it can significantly contribute to a deeper understanding of male fertility.
The Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system encompasses various organs that work in concert to produce, store, and transport sperm. The testes are the primary organs, responsible for sperm production. Spermatogenesis, the process of sperm development, takes place within the seminiferous tubules of the testes. The testes also produce testosterone, a crucial hormone for male sexual development and function. Ejaculation, the release of semen, involves the coordinated activity of various ducts and glands, including the epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands.
These glands produce fluids that nourish and protect the sperm, creating semen.
Factors Affecting Male Fertility
Numerous factors can influence male fertility. Lifestyle choices play a significant role. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use can negatively impact sperm production and quality. Obesity and a lack of physical activity can also affect fertility. Age is another critical factor.
As men age, their sperm count and motility may decline. Certain health conditions, including hormonal imbalances, infections, and genetic disorders, can also contribute to infertility. Varicocele, a condition involving enlarged veins in the scrotum, is a common cause of infertility.
Common Male Infertility Issues
Several factors can lead to male infertility. Low sperm count, poor sperm motility (the ability of sperm to move), and abnormal sperm morphology (shape) are common causes. Varicocele, as previously mentioned, can hinder sperm production and maturation. Other conditions, such as testicular cancer, undescended testicles, and infections, can also affect fertility. The impact of lifestyle factors, like smoking and obesity, can also be significant in contributing to infertility.
Sperm Health and Motility
Sperm health and motility are essential for fertilization. Sperm count, motility, and morphology are crucial indicators of sperm quality. Sperm motility refers to the ability of sperm to move towards the egg. Abnormal sperm morphology, where the shape of the sperm is abnormal, can hinder the sperm’s ability to penetrate the egg. Sperm count is another key indicator, as a low sperm count can make fertilization less likely.
A complete semen analysis can provide detailed information about sperm parameters.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle for Male Fertility
Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding excessive heat exposure are crucial for male fertility. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is vital. Excessive body fat can disrupt hormonal balance, potentially impacting sperm production. Similarly, prolonged exposure to high temperatures, such as from saunas or hot tubs, can damage sperm. Minimizing these exposures can significantly contribute to healthy sperm production and quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the male reproductive system and the factors that affect male fertility is essential for proactive health management. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and seeking medical attention when necessary, men can take steps to optimize their fertility and improve their chances of conceiving.
Couple’s Fertility: Fertility When Are Your Most Fertile Days

Conception is a journey often shared by two people. Understanding that fertility is a collaborative process, where both partners’ health and well-being play crucial roles, is essential for optimizing chances of a successful pregnancy. This shared responsibility extends beyond the physical aspects, encompassing emotional support, open communication, and a willingness to address potential obstacles together.
The Importance of Partner Health
Optimal fertility hinges on the health of both partners. Conditions such as PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) in women and varicocele in men can significantly impact reproductive health. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are vital for early detection and management of any underlying conditions that may hinder fertility.
Strategies for Couples to Improve Their Chances of Conception
Working together is key. A collaborative approach involves shared responsibility for lifestyle choices that affect fertility. This encompasses a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful substances like tobacco and excessive alcohol.
Communication and Support within a Couple Regarding Fertility Concerns, Fertility when are your most fertile days
Open communication is paramount. Discussing concerns, anxieties, and expectations regarding the conception process is crucial. Creating a supportive environment where both partners feel comfortable expressing their needs and fears can foster a healthy relationship and navigate the challenges that may arise.
Potential Obstacles Encountered During the Conception Process
Obstacles can range from lifestyle factors to underlying health issues. Stress, anxiety, and relationship conflicts can all affect hormone levels and overall well-being, making conception more challenging. Additionally, age-related decline in fertility, both in men and women, can be a significant factor. Sometimes, couples may require professional guidance and support from fertility specialists. In some cases, unexplained infertility might require further investigation and potential interventions.
Communication Strategies for Couples Facing Fertility Challenges
| Communication Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Listening | Paying close attention to what the other person is saying, asking clarifying questions, and reflecting back their feelings to ensure understanding. |
| Empathy and Validation | Understanding and acknowledging the emotions and feelings of the other person, even if they are difficult to comprehend. |
| Honest and Open Dialogue | Expressing concerns and anxieties openly and honestly, without judgment or blame. |
| Seeking Professional Help Together | Consulting with fertility specialists or therapists to address challenges and develop strategies together. |
| Setting Realistic Expectations | Acknowledging that the conception process can be unpredictable and may take time. |
| Celebrating Small Victories | Recognizing and appreciating progress made, no matter how small, and maintaining hope. |
Last Word
In conclusion, understanding fertility and your most fertile days involves a deep dive into your menstrual cycle, the different methods for identifying fertile windows, and the various factors that influence both male and female fertility. We’ve explored methods for tracking cycles, lifestyle considerations, and strategies for optimizing your fertility journey. Remember, a holistic approach encompassing both physical and emotional well-being is key.
This guide is meant to empower you with the knowledge to navigate this journey and make informed decisions about your reproductive health.