Kid friendly wet wraps for eczema – Kid-friendly wet wraps for eczema are a potential treatment option for children. This guide dives into the world of wet wraps, exploring their benefits, drawbacks, and important considerations for parents and caregivers. We’ll cover different types, materials, application techniques, and safety precautions, ensuring you’re well-informed to make the best decision for your child.
Understanding the potential benefits and drawbacks of using wet wraps for eczema in children is crucial. This detailed guide provides comprehensive information to help you navigate the process safely and effectively. From selecting the right materials to applying the wraps correctly and maintaining their moisture, we’ll equip you with the knowledge you need.
Introduction to Wet Wraps for Eczema in Children
Wet wraps are a therapeutic technique used to manage eczema in children. They involve applying a damp, cool cloth or compress to the affected skin areas. The dampness helps to soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. This method can be particularly helpful in managing flare-ups, though it’s important to understand the process and potential benefits and drawbacks before implementation.The goal of wet wraps is to create a moist environment that reduces itching and inflammation.
The moisture helps to hydrate the skin, allowing the skin to retain moisture and reduce the dryness and scaling that often accompany eczema. This can lead to a reduction in the need for topical steroids and other treatments in some cases. However, it’s essential to use the technique correctly and understand its limitations.
Potential Benefits of Wet Wraps
Wet wraps offer several potential benefits for children with eczema. They can provide temporary relief from itching and discomfort, reduce inflammation, and promote skin hydration. This can lead to a more comfortable experience for the child and potentially reduce the need for other treatments, such as topical steroids, though this should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Potential Drawbacks of Wet Wraps
While wet wraps can be helpful, they also have potential drawbacks. These include the possibility of skin irritation if the wraps are not applied correctly, the potential for skin infections if hygiene is not maintained, and the need for careful monitoring of the skin condition. The frequency and duration of application also need to be carefully managed.
Common Misconceptions About Wet Wraps
A common misconception is that wet wraps are a cure-all for eczema. They are a supportive treatment, not a cure. They can help manage symptoms, but they should be used as part of a broader eczema management plan, which may include other treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Another misconception is that wet wraps can be used without guidance from a healthcare professional.
It’s crucial to consult with a pediatrician or dermatologist before using wet wraps, especially in children. Proper technique and monitoring are essential to avoid complications.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before implementing wet wraps for a child with eczema, consulting a healthcare professional is paramount. A healthcare provider can assess the child’s specific needs, determine the appropriate wrap type and frequency, and monitor the child’s response to treatment. They can also identify potential complications and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Self-treating with wet wraps can be risky and potentially harmful.
Different Types of Wet Wraps
Understanding the different types of wet wraps can help determine the best approach for a child’s eczema. Different types of wraps have different materials and potential benefits.
| Wrap Type | Materials | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cool Compress | Soft, absorbent cloth (like a washcloth or soft cotton gauze) soaked in cool water | Gentle, effective for mild eczema flare-ups, relatively inexpensive | May not be as effective for severe eczema, requires frequent reapplication |
| Wet Wrap with Ointment/Cream | Dampened cloth with a thin layer of prescribed eczema ointment or cream applied before wrapping | Provides extra moisture and anti-inflammatory benefits, can be effective for more severe eczema | Requires careful application to avoid skin irritation, may need to be applied multiple times per day |
| Plastic Wrap | A thin layer of plastic wrap placed over a wet cloth or compress | Helps retain moisture and promotes healing, potentially speeds up the process | Can trap heat and increase the risk of skin irritation or infection if not used correctly, needs to be removed regularly |
| Hydrocolloid Dressings | Specialized medical dressings | Often provide moisture and protection, can accelerate healing, and provide a barrier | Can be expensive, may not be suitable for all skin types, and requires careful monitoring |
Different Types of Wet Wraps for Eczema: Kid Friendly Wet Wraps For Eczema
Wet wraps are a crucial part of managing eczema in children. They help soothe irritated skin, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Different types of wet wraps offer varying levels of comfort, absorbency, and breathability, making it essential to choose the right one for your child’s specific needs. This section will delve into the various types of wet wraps, examining their effectiveness, suitability, and key differences.
Gauze Wraps
Gauze wraps are a popular choice for wet wraps due to their soft texture and excellent absorbency. They are typically made from a thin, breathable material, which allows air to circulate around the affected area. This is particularly important for preventing skin infections. The absorbency of gauze helps to draw moisture away from the skin, which can reduce itching and inflammation.
However, gauze can be less effective at maintaining moisture compared to other types of wraps.
Cloth Wraps
Cloth wraps are another common option. They come in various fabrics, such as cotton, flannel, or bamboo. Cotton is a classic choice for its softness and absorbency. Flannel provides a bit more warmth and can be beneficial for keeping the moisture on the skin. Bamboo, known for its natural properties, is also a suitable choice for its softness and breathability.
The type of cloth used significantly impacts the wrap’s breathability and absorbency.
Cotton-Based Wraps
Cotton-based wraps, often in the form of soft t-shirts or cotton cloths, are widely accessible and affordable. Their softness and absorbency make them suitable for mild to moderate eczema cases. The breathability of cotton can be a consideration, as it may not be ideal for very hot climates or for children who sweat easily. Cotton is known for its affordability and availability.
Other Wrap Materials
There are other wrap materials, such as thin towels or even specialized eczema wraps. These often provide a balance between absorbency and breathability, depending on the material. These specialized wraps can be a good option for managing eczema on more extensive areas of the body. The specific properties of each material will impact its performance in terms of breathability and absorbency.
Comparison Table of Wrap Types
| Wrap Type | Fabric Type | Breathability | Absorbency | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauze | Cotton or synthetic | High | Medium | Mild to moderate eczema, younger children |
| Cloth (Cotton) | Cotton | Medium | High | Mild to moderate eczema, all ages |
| Cloth (Flannel) | Flannel | Low | High | Mild to moderate eczema, colder climates, may retain more moisture |
| Cloth (Bamboo) | Bamboo | High | Medium | Mild to moderate eczema, sensitive skin, all ages |
| Specialized Eczema Wraps | Various breathable fabrics | Variable | Variable | Moderate to severe eczema, larger affected areas |
Materials and Preparation for Wet Wraps
Creating a soothing and effective wet wrap for a child with eczema requires careful selection and preparation of materials. The right materials can significantly improve comfort and reduce irritation, while improper preparation can lead to discomfort and potential skin reactions. This section will guide you through choosing the right materials and preparing them for a successful and safe application.The key to a comfortable and effective wet wrap lies in selecting the right materials and following a meticulous preparation process.
Gentle, breathable fabrics are crucial to prevent further irritation, while proper preparation ensures the wrap is both soothing and supportive.
Appropriate Materials for Wet Wraps
Selecting the right materials is essential for a successful wet wrap application. The goal is to create a breathable, supportive, and gentle barrier for the affected skin. A few key materials include:
- Soft, absorbent fabrics: Choose fabrics like 100% cotton, bamboo, or flannel. These materials are gentle on the skin and readily absorb moisture, promoting a cool and comfortable environment for the affected area.
- Soft towels: Consider thin, soft washcloths or small towels for the wrap. These should be absorbent and easily washable to maintain hygiene and prevent bacteria buildup.
- Hypoallergenic bandages: Some hypoallergenic bandages or gauze can provide a thin, protective layer. These can be a useful addition for sensitive skin.
- Soft, breathable wraps: Look for thin, breathable fabrics or pre-made eczema wraps designed for moisture management. These are often ideal for maintaining a consistent moisture level.
Preparing the Materials
Proper preparation of the materials is crucial for the safety and effectiveness of the wet wrap. The process ensures a gentle application and reduces the risk of irritation.
- Washing and sterilizing materials: Thoroughly wash and sterilize all materials, including the fabric and towels. Sterilization methods like boiling or using a sterilizing solution will eliminate any potential contaminants and ensure a clean and hygienic application.
- Cutting and shaping: Cut the chosen fabric into appropriate sizes to cover the affected area. Avoid using scissors or sharp objects that could cause further irritation or injury. Consider pre-cut, ready-to-use bandages or eczema wraps for convenience and consistent sizing.
- Soaking the material: Soak the chosen fabric or towels in lukewarm water. Ensure the water temperature is not too hot or too cold to avoid discomfort or irritation. The water should be comfortably warm to the touch, ensuring the child is not exposed to extreme temperatures.
Applying the Wet Wrap
Applying the wet wrap requires a gentle and careful approach. Following the steps below can help ensure the wrap is applied correctly and comfortably.
- Pat the skin dry: Gently pat the affected area dry with a soft towel or washcloth, avoiding harsh rubbing.
- Applying the wet wrap: Carefully place the wet and cooled fabric over the affected area, ensuring the wrap is snug but not tight.
- Securing the wrap: Use soft, hypoallergenic bandages or wrap the fabric securely around the affected area to maintain moisture and comfort.
- Checking for comfort: Regularly check the child for any signs of discomfort, such as redness, itching, or pain. Adjust the wrap as needed to maintain comfort and support.
Importance of Hypoallergenic Materials
Using gentle, hypoallergenic materials is essential for children with eczema. These materials minimize the risk of allergic reactions and irritation, allowing the skin to heal and regenerate effectively. Using materials with known sensitivities (like wool or certain synthetic fabrics) can worsen symptoms and cause additional discomfort. Choose fabrics known to be hypoallergenic to ensure the comfort and well-being of the child.
Application and Maintenance of Wet Wraps
Wet wraps, a crucial part of eczema management for children, require meticulous application and consistent maintenance to be effective. Proper technique ensures the wraps remain moist for the recommended time, promoting healing and minimizing discomfort. Maintaining moisture and cleanliness is key to preventing infections and ensuring optimal results.Applying wet wraps correctly is essential for maximum benefit. The wraps must be applied with care and precision to avoid irritating the skin further.
Maintaining moisture and cleanliness throughout the treatment period is equally vital.
Applying Wet Wraps
The application process involves several key steps. First, clean the affected area thoroughly with a mild, fragrance-free cleanser. Pat the skin dry, avoiding harsh rubbing. Next, carefully apply a thin layer of a hypoallergenic, fragrance-free moisturizer. This step is crucial to protect the skin and avoid further irritation.
Then, immerse a soft, clean cloth or gauze in cool water, ensuring it is not too hot or too cold. Gently wring out the excess water. Avoid soaking the skin directly in water. Apply the damp cloth or gauze to the affected area, ensuring it covers the entire area. Then, gently secure the damp cloth or gauze with a soft, breathable bandage.
Finding gentle, kid-friendly wet wraps for eczema can be tricky, but thankfully there are some great options out there. While researching different remedies, I stumbled upon some fascinating information about non hormonal birth control options, which surprisingly, dovetailed nicely with the research I was doing on eczema treatments. This deeper dive into alternative solutions, like natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments, has helped me better understand the importance of gentle, holistic approaches, and I’m excited to see how these insights will further improve my eczema-friendly wet wrap selections for my little one.
Ensure the bandage is not too tight, as this could restrict blood flow and cause discomfort.
Maintaining Moisture
Maintaining the moisture of the wet wrap is essential for its efficacy. Frequent checks are needed to ensure the wrap remains adequately damp. To keep the wrap moist, periodically re-soak the cloth or gauze in cool water and gently squeeze out the excess water. Avoid using excessively hot or cold water. If the wrap dries out, the treatment’s effectiveness can be compromised.
Maintaining Cleanliness
Maintaining cleanliness is critical to prevent infections and skin irritation. Change the wet wrap as often as recommended by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. Use fresh, clean cloths or gauze each time. Proper disposal of used materials is crucial to avoid cross-contamination. Always ensure the affected area is clean and dry before re-applying the wet wrap.
Finding kid-friendly wet wraps for eczema can be a real challenge, but they’re often a lifesaver. While researching different eczema treatments, I stumbled across an interesting discussion about whether tomatoes are good or bad for gout, which I found fascinating. This led me to check out this article on are tomatoes bad for gout. Ultimately, the focus is back on finding the best wet wrap options for my little one’s eczema; it’s a constant process of trial and error.
Frequency and Duration of Applications
The frequency and duration of wet wrap applications are determined by the severity of the eczema and the response of the child’s skin. Consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for personalized recommendations. Typical application times range from several hours to overnight, depending on the specific situation. It’s important to adhere to the prescribed schedule for optimal results.
Comparison of Application Methods
| Application Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Cloth or Gauze Wrap | Affordable, readily available, and generally comfortable | Requires frequent re-soaking and changing, potentially causing discomfort if not applied correctly |
| Pre-made Eczema Wraps | Convenient, often pre-moistened, and designed for ease of use | Can be more expensive than cloth wraps, may not be suitable for all skin types |
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Wet wraps can be a highly effective eczema treatment for children, but safety is paramount. Understanding potential risks and how to mitigate them is crucial for ensuring a positive experience and optimal results. Careful monitoring and prompt action in case of any adverse reaction are vital components of successful wet wrap therapy.Wet wraps, while generally safe, can pose some risks if not managed properly.
It’s essential to be aware of these potential complications and to take precautions to minimize them. Knowing how to recognize and address any adverse reactions is equally important. This section will detail potential risks, precautions, and when to seek medical attention.
Potential Risks and Complications
Wet wraps, though effective, can sometimes lead to complications if not carefully managed. Skin irritation, increased dryness, and infection are potential concerns. Furthermore, improper application or maintenance can result in discomfort or hinder the treatment process. The goal is to minimize these risks by adhering to proper procedures and monitoring the child’s response closely.
Precautions to Minimize Risks
Proper preparation and application are essential to minimizing risks. Always ensure the skin is clean and free of any existing wounds or infections before applying the wet wrap. The temperature of the water should be lukewarm, never hot or cold. The wrap material should be soft, absorbent, and free of any harsh chemicals or irritants. Frequent checks for skin reactions and any signs of discomfort are crucial.
A close watch on the affected area, paying attention to any changes in skin appearance, is vital.
Recognizing Adverse Reactions
It’s crucial to be able to recognize adverse reactions to wet wraps. These can manifest in various ways, such as redness, swelling, intense itching, blistering, or oozing. Any unusual changes in the affected area or surrounding skin warrant immediate attention. A noticeable increase in discomfort or pain should also be addressed promptly.
When to Discontinue Use and Seek Medical Attention
If any signs of infection, severe irritation, or worsening eczema are observed, discontinue use immediately and consult a doctor. Persistent redness, blistering, or significant swelling are all reasons to seek medical attention. A fever, difficulty breathing, or any systemic signs of illness are also cause for immediate medical intervention.
Table of Potential Side Effects and Corresponding Actions
| Potential Side Effect | Corresponding Action |
|---|---|
| Mild redness or itching | Continue monitoring. Adjust the wrap application or material if necessary. |
| Increased dryness or cracking of the skin | Increase the frequency of moisturizing the skin, and potentially adjust the wrap application or duration. Consult a doctor if the condition worsens. |
| Oozing or weeping sores | Immediately discontinue use and seek medical attention. |
| Significant swelling or blistering | Immediately discontinue use and seek medical attention. |
| Fever, difficulty breathing, or other systemic symptoms | Immediately seek emergency medical attention. |
Addressing Specific Needs and Concerns
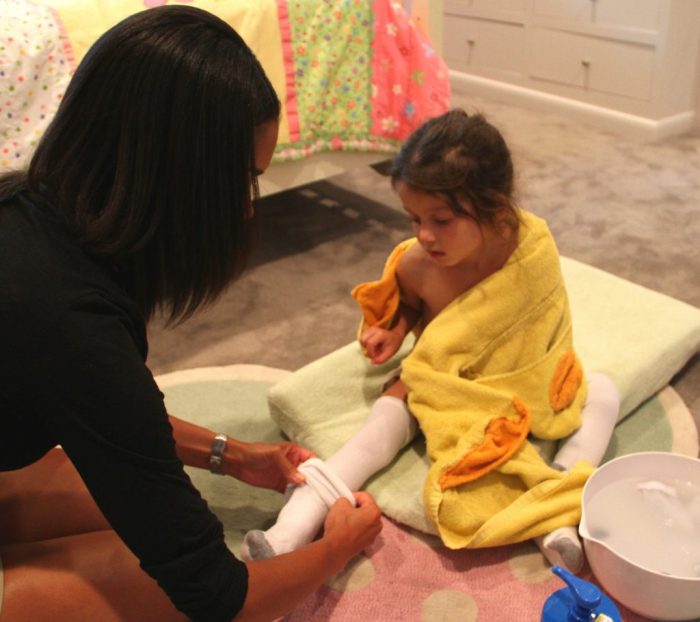
Wet wraps, while generally beneficial for eczema, require careful consideration for individual needs. Children with eczema experience diverse symptoms, and sensitivity levels vary significantly. Adjustments to the wet wrap technique are often necessary to ensure comfort and effectiveness. This section delves into adapting wet wraps for different eczema types, sensitivities, and specific skin conditions.
Eczema Types and Wet Wrap Variations
Different types of eczema respond to wet wraps in slightly different ways. Atopic dermatitis, the most common type, often benefits from the moisture-retaining properties of wet wraps. However, in cases of irritant contact dermatitis, where skin irritation is triggered by external factors, wet wraps should be applied cautiously, and the potential irritant must be identified and removed to avoid exacerbating the condition.
The skin’s response to a particular type of eczema will influence the frequency and duration of wet wrap application.
Adapting Wet Wraps for Different Sensitivities
Children with sensitive skin require a more gentle approach. The temperature of the water used for the wraps should be lukewarm, not hot, to prevent further irritation. The duration of the wrap should also be shorter for children with heightened sensitivity. A gentle, non-abrasive fabric should be used to minimize skin friction. For extremely sensitive skin, a thin layer of a hypoallergenic moisturizer can be added to the skin before applying the wet wrap.
Finding kid-friendly wet wraps for eczema can be tricky, but it’s so important for soothing those little irritated spots. Sometimes, dealing with eczema flare-ups can be overwhelming, especially when combined with other health concerns. Understanding potential withdrawal symptoms, like those detailed in withdrawal types symptoms treatment , is crucial for a holistic approach. Ultimately, the best strategy for managing eczema in kids involves a combination of effective treatments and careful monitoring, making sure you choose kid-friendly wet wraps that work for your child.
This will further protect and soothe the skin.
Wet Wraps for Additional Skin Conditions
While primarily used for eczema, wet wraps can also offer relief for other skin conditions. In cases of diaper rash, the cooling and moisturizing effects of a wet wrap can help soothe the inflamed skin. However, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist or pediatrician for proper diagnosis and treatment. Wet wraps are not a cure for all skin conditions and should be used as part of a broader treatment plan.
Comparison with Other Eczema Treatments
Wet wraps are a valuable tool in managing eczema, but their effectiveness may vary compared to other treatments. Topical corticosteroids are often used for short-term relief, while emollients provide long-term moisture. Wet wraps complement these treatments by providing a controlled, moist environment for the skin to heal and regenerate. In some cases, wet wraps may be more effective at reducing inflammation and promoting healing, especially for mild to moderate eczema.
Wet Wrap Application for Different Body Parts
The application of wet wraps varies depending on the body part. For the face, a thin layer of a wet cloth or gauze should be applied to prevent irritation. For extremities, such as hands and feet, the wraps can be applied more liberally. The wrap should be secured with a soft, breathable bandage to maintain its position and prevent discomfort.
It is crucial to ensure proper coverage and support, while avoiding pressure points or constrictions.
Visual Representation of Wet Wraps
Wet wraps for eczema in children can be a powerful tool in managing flare-ups. Understanding how these wraps should look on different parts of the body is crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and comfort. Proper application is key to maximizing their therapeutic benefits while minimizing discomfort.Visualizing a properly applied wet wrap allows parents and caregivers to quickly assess if the wrap is positioned correctly and if any adjustments are needed.
This visual guide will help you understand the appearance and texture of different wrap types and how they should look on various body parts.
Appearance of Different Wet Wrap Types, Kid friendly wet wraps for eczema
Different types of wet wraps, tailored for different body parts and needs, will have varied appearances. Understanding these differences will help you ensure proper application.
- Simple, single-layer wraps: These are often used for smaller areas, like a rash on the hand or foot. The wet compress should be smooth and even, conforming closely to the skin. It should be moist, not dripping, and held securely in place with a bandage or wrap. For example, a wet washcloth applied to a child’s ankle should be a uniform, moist layer without wrinkles or excessive moisture.
- Multi-layered wraps: These are frequently used for larger affected areas, such as the legs or torso. The multiple layers of moist fabric provide more coverage and support. The layers should be layered smoothly and consistently, ensuring even moisture distribution without creating excessive pressure points. For example, a multi-layered wrap on the thigh should have all layers evenly moist and conforming closely to the skin.
The texture will feel like multiple damp cloth layers.
- Wraps using gauze or soft fabric: These wraps are known for their gentle feel on the skin and their ability to absorb excess moisture. The wrap should have a soft, pliable texture. The gauze should not be so thick that it restricts movement or causes excessive pressure. For instance, a gauze wrap on the arm should be soft and conforming to the shape of the arm without pulling or bunching up.
The damp gauze should be visibly moist but not dripping.
Proper Application and Body Part Considerations
Proper application is paramount to the effectiveness and comfort of wet wraps. The way a wrap is applied directly impacts its ability to soothe and heal.
- Limbs (arms, legs, feet): The wrap should conform closely to the limb, avoiding wrinkles or creases. The wrap should cover the entire affected area, keeping it moist but not excessively wet. For example, a wrap around the lower leg should be smooth and flat, without wrinkles, allowing for full mobility. The wet compress should adhere gently to the skin.
- Body trunk (torso): The wrap should cover the affected area completely, allowing for optimal moisture contact with the skin. For example, a wrap covering the stomach should be smooth and even, adhering to the skin’s contours. It should not be too tight or too loose. The wrap should allow for comfortable movement.
- Face and neck: Applying wet wraps to the face and neck requires extra care to avoid irritation and discomfort. A thin layer of soft fabric, like gauze or a thin washcloth, is best. For example, a wet wrap on the face should be extremely thin, ensuring the skin remains visible and the wrap does not constrict breathing or cause pressure. The moisture should be minimal, but consistent.
Texture and Appearance of the Wraps
The texture and appearance of the wet wrap should indicate that it is properly applied and functioning as intended.
“A properly applied wet wrap should feel soft, pliable, and conforming to the skin’s contours without creating wrinkles or creases.”
“The wrap should appear moist but not dripping wet. It should be a uniform consistency across the affected area.”
“Different wrap types will have varying textures and appearances, but a crucial aspect is a smooth, even surface without excessive bunching or unevenness.”
Comparison with Other Eczema Treatments

Wet wraps offer a unique approach to managing eczema, distinct from traditional topical treatments like creams and ointments. While creams and ointments aim to soothe and moisturize the skin, wet wraps actively address inflammation and promote healing through a different mechanism. Understanding how wet wraps compare to other eczema treatments is crucial for parents to make informed decisions about their child’s care plan.
Different Treatment Approaches
Wet wraps, often used in conjunction with other eczema treatments, can be a powerful tool in managing the condition. They work by creating a moist environment that can help reduce inflammation and itching. This differs from topical creams and ointments, which primarily focus on moisturizing and providing a protective barrier. For example, a topical steroid cream might reduce inflammation, but a wet wrap can enhance that effect by keeping the skin hydrated and reducing scratching.
By combining approaches, parents can optimize their child’s eczema care.
Suitability for Different Eczema Stages
The suitability of wet wraps for different stages of eczema depends on the severity and type of eczema. For mild eczema, wet wraps might be used as a supplementary treatment alongside other moisturizers. For moderate to severe eczema, wet wraps can be a more prominent part of the treatment regimen, potentially used more frequently to manage inflammation. The crucial aspect is to consult a dermatologist or pediatrician to determine the most appropriate approach for each child’s specific needs and eczema stage.
Comparison Table
| Treatment Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Wet Wraps |
|
|
| Topical Creams/Ointments |
|
|
| Other Eczema Treatments (e.g., Phototherapy, Immunomodulators) |
|
|
Using Wet Wraps with Other Treatments
Wet wraps can be used in conjunction with other eczema treatments, such as topical creams or ointments. For example, applying a moisturizer after a wet wrap session can enhance the moisturizing effect and protect the skin. However, it’s crucial to understand that wet wraps can enhance the effect of other treatments, and to carefully coordinate the application and timing of different products.
Consulting with a dermatologist or pediatrician is essential to ensure the most effective and safe approach.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, while wet wraps can be a helpful tool for managing eczema in children, it’s essential to approach them with caution and a thorough understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks. Consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended before starting any new treatment, especially for young children. This comprehensive guide provides a starting point, but remember, individualized care tailored to your child’s specific needs is paramount.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.




