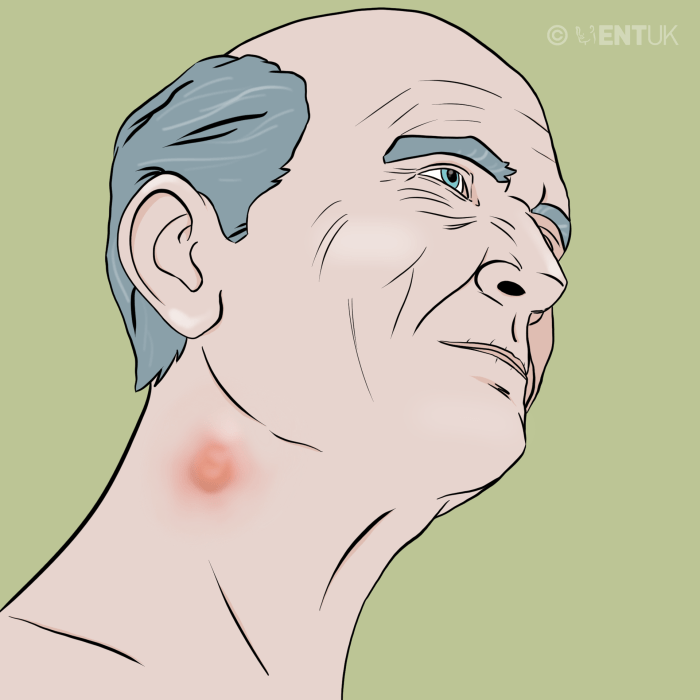
Is there a link between sneezing and migraines? This question delves into the fascinating intersection of two seemingly disparate bodily responses. Sneezing, a reflex triggered by irritants in the nasal passages, involves a complex chain of physiological events. Migraines, on the other hand, are debilitating headaches characterized by throbbing pain, often accompanied by nausea and…
Category: Health & Wellness
Worst Blood Pressure Drugs A Critical Look
Worst blood pressure drugs are a concern for many. This article dives deep into common complaints, potential risks, alternative treatments, patient experiences, and specific drug examples. We’ll examine the side effects, potential long-term consequences, and the importance of open communication with healthcare providers. Understanding the potential downsides of blood pressure medications is crucial for informed…
Yeast Infection vs UTI Understanding the Differences
Yeast infection vs UTI: This guide delves into the often-confused conditions of yeast infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs). We’ll explore their distinct symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches, helping you understand the key differences and how to approach diagnosis and care. Knowing the specifics is crucial for getting the right treatment. From common symptoms like…
Lump Under Skin Causes & When to Worry
Lump under skin causes and when to worry about it is a crucial topic for anyone experiencing such a concern. Skin lumps can arise from a variety of factors, ranging from harmless cysts to more serious conditions. Understanding the potential causes and knowing when to seek medical attention can be vital for a quick diagnosis…
Supplements for Acid Reflux Your Guide
Supplements for acid reflux can be a helpful tool in managing this common digestive issue. This comprehensive guide explores the world of supplements, from understanding the basics of acid reflux to exploring different types of supplements, their effectiveness, and safety concerns. We’ll also delve into supplement interactions, recommendations, and how to integrate them into your…
Ask an Expert Self-Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis
Ask an expert self diagnose atopic dermatitis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of atopic dermatitis (AD), providing a crucial understanding of its symptoms, triggers, and the limitations of self-diagnosis. We’ll explore the crucial difference between self-assessment and a professional diagnosis, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health. From…
Ask an Expert Creative Psoriasis Management
Ask an expert creative ways to manage psoriasis: This comprehensive guide delves into a wide range of strategies, from understanding the nuances of psoriasis to exploring innovative lifestyle modifications and cutting-edge treatments. We’ll explore everything from the basics of psoriasis, its diverse types, and contributing factors, to the latest in topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic…
Ask an Expert Breast Cancer Patient Resources
Ask an expert breast cancer patient resources is your guide to navigating the complex world of support and information. This comprehensive resource dives deep into various types of support, from in-person groups to online communities, and explains how medical professionals can help connect patients with the right resources. We’ll explore the healthcare system, online support,…
Foods to Ease Constipation A Guide
Foods to ease constipation are key to a healthy digestive system. Constipation, a common ailment, can be frustrating and uncomfortable. Fortunately, dietary changes can make a world of difference. This guide explores various fiber-rich foods, fruits, and vegetables that promote regularity, and even delves into other important dietary considerations for optimal bowel health. Understanding the…
Treating Lingering Coughs A Comprehensive Guide
Treatments for lingering cough – Treating lingering coughs: This comprehensive guide explores various aspects of persistent coughs, from understanding their causes to effective treatments and preventive measures. We’ll delve into the nuances of different cough types, diagnostic procedures, and a range of home remedies and medical treatments. Learn what constitutes a lingering cough, how to…