HAART highly active antiretroviral therapy has revolutionized HIV treatment, dramatically altering the course of the disease. This comprehensive look explores the science behind HAART, from its historical development and key components to its impact on patients’ lives. We’ll delve into the mechanisms of action, different treatment regimens, potential side effects, and the critical role of adherence.
Understanding HAART is crucial for anyone affected by or interested in HIV/AIDS. This blog post will cover the essential aspects of HAART, including its complex interplay with the virus and the patient’s overall health.
Introduction to HAART
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) is a life-saving combination of antiviral drugs used to treat HIV infection. It significantly slows the progression of the disease by reducing the viral load in the body. This allows the immune system to recover and function more effectively. HAART is not a cure for HIV, but it dramatically improves the quality of life for those living with the virus.The development of HAART was a monumental achievement in medical science.
Prior to the 1990s, HIV infection was often a death sentence. The virus gradually weakened the immune system, leading to opportunistic infections and eventually AIDS. Researchers relentlessly pursued strategies to combat the virus, ultimately leading to the discovery and combination of drugs that effectively suppressed HIV replication.
Key Components of a Typical HAART Regimen
A typical HAART regimen comprises three or more drugs from different classes, targeting various stages of the HIV life cycle. This multi-drug approach significantly reduces the risk of drug resistance developing.
Drug Classes in HAART
| Drug Class | Example Drug | Mechanism of Action | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs) | Zidovudine (AZT) | These drugs interfere with the HIV enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is essential for the virus to replicate. They do so by mimicking the natural building blocks of DNA, which are incorporated into the viral DNA, rendering it non-functional. | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, peripheral neuropathy, lactic acidosis, lipodystrophy (body shape changes). |
| Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs) | Efavirenz | These drugs bind to and inhibit the reverse transcriptase enzyme, thus preventing the virus from replicating. | Rash, headache, dizziness, insomnia, nightmares, liver problems. |
| Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | Ritonavir | These drugs block the HIV protease enzyme, preventing the virus from assembling new viral particles. | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, increased blood sugar, fat redistribution (lipodystrophy), kidney problems. |
| Integrase Inhibitors | Raltegravir | These drugs prevent the integration of viral genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, thus stopping the virus from replicating. | Headache, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, insomnia, rash, increased liver enzymes. |
| Entry Inhibitors | Maraviroc | These drugs prevent the virus from entering the host cell. | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, skin rash, cough, and some respiratory issues. |
Mechanisms of Action
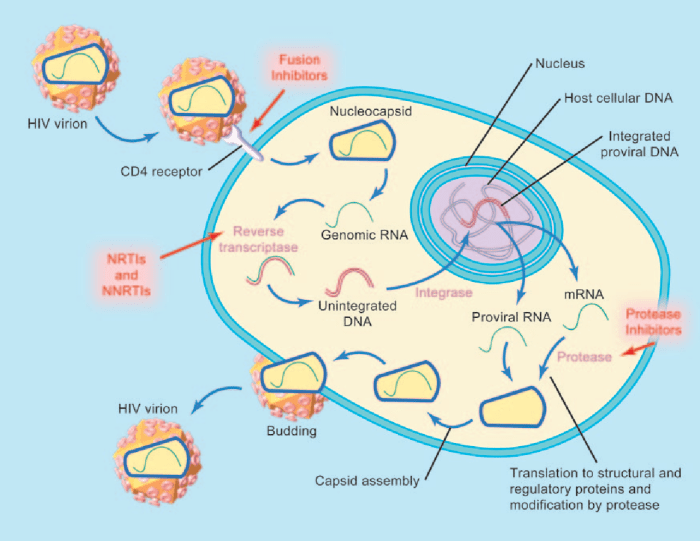
HAART, or highly active antiretroviral therapy, is a powerful arsenal against HIV, effectively controlling the virus by targeting different stages of its life cycle. Understanding the specific mechanisms of action of the various drugs within HAART is crucial for comprehending their collective impact on viral replication and disease progression. This section delves into how these drugs inhibit viral replication, comparing and contrasting their actions, and highlighting the role of each drug class in suppressing viral load.The core strategy of HAART is to inhibit HIV’s replication at multiple points.
This multifaceted approach significantly reduces the viral load, allowing the immune system to recover and function more effectively. By targeting different steps in the viral life cycle, HAART prevents the virus from replicating and spreading throughout the body.
Drug Classes and Their Mechanisms
Different drug classes within HAART target specific steps in the HIV replication cycle. These drugs act in various ways to block viral replication.
- Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs): These drugs are structurally similar to the building blocks of DNA, but they lack the 3′-hydroxyl group essential for chain elongation. They become incorporated into the growing DNA chain, halting further replication. Examples include zidovudine (AZT), lamivudine (3TC), and tenofovir. NRTIs are critical for suppressing the viral load by preventing the virus from producing its own DNA copy.
- Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs): These drugs bind to and directly inhibit reverse transcriptase, the enzyme responsible for converting viral RNA into DNA. This prevents the synthesis of viral DNA, thus halting viral replication. Examples include efavirenz and nevirapine. NNRTIs, like NRTIs, contribute to the overall suppression of viral load by interrupting the early stages of viral replication.
- Protease Inhibitors (PIs): HIV protease is essential for processing viral proteins into functional components. PIs bind to and inhibit this enzyme, preventing the maturation of new viral particles. This results in the production of non-infectious virus particles. Examples include ritonavir, lopinavir, and atazanavir. PIs significantly reduce the amount of infectious virus released by infected cells, which in turn reduces viral load.
- Integrase Inhibitors (INSTIs): These drugs interfere with the viral enzyme integrase, which is responsible for integrating the viral DNA into the host cell’s DNA. By inhibiting this step, the virus cannot establish a persistent infection. Examples include raltegravir and dolutegravir. INSTIs are a crucial component of HAART, preventing the virus from establishing itself within the host’s genetic material.
Impact on Viral Load
Each drug class contributes to the overall reduction in viral load by targeting a specific stage in the HIV replication cycle. The combined effect of these drugs is highly potent, allowing for significant viral suppression and improved health outcomes. The effectiveness of HAART is often measured by the viral load, which is the amount of HIV RNA in a patient’s blood.
A suppressed viral load, ideally undetectable, is a key indicator of successful HAART treatment.
Stages of Viral Replication and HAART Intervention
| Stage of Viral Replication | Description | How HAART Drugs Interfere |
|---|---|---|
| Binding and Entry | HIV binds to the CD4 receptor and other co-receptors on the host cell surface and enters the cell. | NRTIs, NNRTIs, and some fusion inhibitors can interfere with this process. |
| Reverse Transcription | Viral RNA is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase. | NRTIs and NNRTIs inhibit reverse transcriptase. |
| Integration | Viral DNA is integrated into the host cell’s DNA. | Integrase inhibitors block this step. |
| Translation and Assembly | Viral proteins are produced, and new viral particles are assembled. | Protease inhibitors prevent the maturation of new viral particles. |
| Release | Newly assembled viral particles are released from the host cell. | Some drugs may also affect release, but primarily focus on earlier steps. |
Types of HAART Regimens: Haart Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy
HAART, or highly active antiretroviral therapy, has revolutionized HIV treatment, dramatically improving the lives of millions. A key component of this success is the careful selection of HAART regimens. Understanding the various types and their applications is crucial for both healthcare providers and individuals living with HIV.Different HAART regimens are tailored to specific circumstances, from initial treatment to managing treatment failure.
This approach acknowledges the diverse nature of HIV and the unique needs of each patient.
Common HAART Regimens in Initial Treatment
Choosing the right initial HAART regimen is paramount for viral suppression and preventing drug resistance. Factors like patient preferences, comorbidities, and potential drug interactions play significant roles in the selection process. The goal is to select a regimen that is well-tolerated, effective, and minimizes the risk of adverse effects.
- A common initial regimen often includes two nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) and a protease inhibitor (PI) or a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI). This combination provides a potent and broad-spectrum approach to viral suppression. For instance, a regimen of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) plus darunavir (DRV) is a widely used and effective option.
- Integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) have emerged as a crucial component of many modern HAART regimens, often replacing PIs or NNRTIs in some initial treatment plans. Regimens containing INSTIs like dolutegravir (DTG) have demonstrated high efficacy and a favorable safety profile. The combination of TDF/FTC and DTG is a common and highly effective choice.
Regimens for Treatment Failure
When an initial HAART regimen fails to adequately suppress the virus, a change in therapy is necessary. This involves careful assessment of the reasons for failure, such as drug resistance or poor adherence.
- Regimens used in cases of treatment failure often incorporate different drug classes to circumvent the developed resistance. For example, if resistance develops to a PI, the regimen may be switched to include an INSTI or an NNRTI. This strategy aims to maintain potent viral suppression and prevent further resistance development. A regimen using a different PI, or switching to a regimen containing an INSTI, such as DTG, can be effective in these cases.
- Additional factors, such as comorbidities and the patient’s history of previous treatments, are crucial in selecting a new regimen. A thorough evaluation, including resistance testing, is essential for effective management of treatment failure.
Factors Considered in Regimen Selection
Numerous factors influence the selection of a HAART regimen. This decision-making process requires careful consideration of the patient’s individual characteristics and clinical context.
HAART, or highly active antiretroviral therapy, is crucial for managing HIV. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, is vital for overall well-being, and this includes knowing which foods to avoid when taking medications like Ozempic. For example, certain foods might interact negatively with Ozempic, potentially impacting its effectiveness or causing side effects. Check out this helpful guide on foods to avoid on ozempic to learn more.
Ultimately, a good understanding of dietary considerations, like those for Ozempic, can be just as important as the HAART regimen itself for managing HIV.
- Patient factors such as age, overall health, and previous treatment history are essential to consider. A patient’s preferences and understanding of the treatment plan are also crucial for successful adherence.
- Drug interactions are another important aspect. The regimen should be carefully chosen to minimize interactions with other medications the patient might be taking. Drug interactions can impact the effectiveness and safety of HAART.
- The presence of comorbidities, such as liver disease or kidney issues, can influence the choice of drugs in the regimen. The selection process needs to be adapted to accommodate these additional health concerns.
Comparison of HAART Regimens
| Regimen | Drug Components | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| TDF/FTC + DRV | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine, Darunavir | High efficacy, well-tolerated | Potential for drug interactions, some side effects |
| TDF/FTC + DTG | Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine, Dolutegravir | High efficacy, good safety profile, fewer side effects | Potential for drug interactions, less experience compared to other regimens |
| Alternative Regimen A | (List drugs) | (List advantages) | (List disadvantages) |
| Alternative Regimen B | (List drugs) | (List advantages) | (List disadvantages) |
Side Effects and Management
HAART, while revolutionizing HIV treatment, isn’t without potential side effects. Understanding these effects and how to manage them is crucial for patients’ overall well-being and adherence to therapy. These side effects, while often manageable, can range from mild discomfort to more serious complications. Effective communication with healthcare providers is essential to address concerns and develop tailored strategies for each individual.The diverse range of drugs in HAART regimens can lead to a spectrum of side effects.
Some are relatively common, while others are less frequent. The severity of side effects can vary significantly, influenced by individual factors like genetics, overall health, and the specific HAART regimen prescribed. Careful monitoring and proactive management are key to mitigating potential problems.
Common Side Effects
A significant number of patients experience common side effects during HAART. These typically develop early in treatment and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue. These symptoms can often be managed effectively with lifestyle adjustments and medication.
- Nausea and Vomiting: This is a frequent side effect, often linked to specific drugs in the regimen. Small, frequent meals, avoiding greasy or rich foods, and taking medication with food can help alleviate symptoms.
- Diarrhea: Similarly, diarrhea can be a common consequence of HAART. Maintaining a balanced diet, increasing fiber intake gradually, and possibly using anti-diarrheal medication (under medical supervision) are strategies for managing this side effect.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness is another common complaint. Ensuring adequate sleep, incorporating regular exercise (with medical approval), and stress management techniques can help combat this symptom.
- Headaches: Headaches, often mild to moderate, can be a result of HAART medications. Pain relievers can be helpful, but consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
Potential Long-Term Side Effects
While many side effects are temporary, HAART can potentially lead to long-term complications. These can affect various organ systems, including the liver, kidneys, and cardiovascular system.
- Metabolic Complications: HAART can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to conditions like insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol), and elevated blood sugar levels. These issues can increase the risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Careful monitoring of blood sugar, cholesterol, and other metabolic markers is essential for prevention and early intervention.
- Liver and Kidney Dysfunction: Certain HAART components can put a strain on the liver and kidneys. Regular monitoring of liver function tests (LFTs) and kidney function tests (KFTs) is vital for detecting any potential damage. Adjusting the regimen or using supportive medications may be necessary to mitigate these effects.
- Bone Loss: HAART can sometimes lead to bone density loss, increasing the risk of fractures. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation, along with regular exercise, are crucial to maintaining bone health.
- Cardiovascular Issues: Long-term use of some HAART drugs has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart disease and stroke. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, controlling blood pressure, and monitoring cholesterol levels are critical to mitigating these risks.
Management Strategies, Haart highly active antiretroviral therapy
Effective management of HAART side effects requires a collaborative approach between the patient and healthcare team.
- Communication and Monitoring: Open communication with the healthcare provider about any side effects, no matter how minor, is paramount. Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood tests are crucial for detecting and managing potential issues.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help mitigate some side effects. This often involves working with a registered dietitian and a physical therapist for personalized guidance.
- Medication Adjustments: In some cases, the healthcare provider may adjust the HAART regimen to minimize side effects or switch to a different medication if necessary. These adjustments are tailored to the individual patient and their specific needs.
- Supportive Therapies: Supplements, such as vitamin D and calcium, may be recommended to address specific side effects like bone loss. Other supportive therapies, such as counseling and support groups, can help manage the emotional and psychological aspects of living with HIV.
Common Side Effects Table
| Side Effect | Severity | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea/Vomiting | Mild to Moderate | Small, frequent meals; avoid greasy foods; take medication with food; anti-nausea medication (as prescribed) |
| Diarrhea | Mild to Moderate | Balanced diet; increased fiber intake (gradually); anti-diarrheal medication (as prescribed) |
| Fatigue | Mild to Moderate | Adequate sleep; regular exercise (with medical approval); stress management techniques |
| Headaches | Mild to Moderate | Pain relievers (as needed); consult healthcare provider |
| Metabolic Complications | Moderate to Severe | Regular blood sugar and cholesterol monitoring; lifestyle changes; medication adjustments |
| Liver/Kidney Dysfunction | Moderate to Severe | Regular LFTs and KFTs; medication adjustments; supportive medications |
| Bone Loss | Moderate | Calcium and vitamin D supplements; regular exercise |
| Cardiovascular Issues | Moderate to Severe | Healthy lifestyle; blood pressure control; cholesterol monitoring |
HAART and Treatment Adherence
Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is crucial for effective HIV management. Consistent and correct medication intake is essential for suppressing viral load, preventing disease progression, and improving overall health outcomes. Without proper adherence, the virus can develop resistance to the drugs, rendering them ineffective and potentially leading to a resurgence of the disease.
Importance of Adherence
Consistent HAART use significantly reduces the viral load, thereby preventing the progression of HIV to AIDS. This suppression also helps prevent opportunistic infections, which are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in individuals with advanced HIV. Adherence to the regimen minimizes the risk of drug resistance, ensuring the continued efficacy of the medications over time. Maintaining a suppressed viral load also positively impacts the immune system, allowing it to function more effectively.
This in turn reduces the risk of complications and promotes overall well-being.
Challenges in Adherence
Numerous factors contribute to challenges in adhering to HAART regimens. These include the complexity of the medication schedule, side effects, financial constraints, social stigma, and psychological factors like depression, anxiety, or denial about the illness. Patients may also experience difficulty remembering to take their medication at the prescribed times, particularly if the regimen involves multiple pills taken at different intervals throughout the day.
The long-term nature of HAART, requiring lifelong commitment, can be mentally challenging for some individuals. Moreover, the presence of other health conditions or social issues can further complicate adherence.
Strategies for Improving Adherence
Improving treatment adherence requires a multi-faceted approach involving both the healthcare provider and the patient. Simplified medication regimens with fewer pills are often helpful. Regular follow-up appointments, providing clear instructions, and building a strong doctor-patient relationship can help address concerns and provide emotional support. Patient education regarding the importance of adherence, potential side effects, and strategies for managing them is crucial.
The development of support groups and peer counseling programs can empower patients and provide a sense of community. Additionally, addressing any underlying mental health concerns, social determinants of health, or financial barriers can significantly improve adherence rates.
Impact of Poor Adherence
Poor adherence to HAART regimens can lead to a resurgence of the virus, often resulting in drug resistance. This resistance can render existing medications ineffective, making it difficult to find alternative treatments. The lack of viral suppression can also lead to a more rapid progression of HIV to AIDS, increasing the risk of opportunistic infections. The potential for these complications is significant, and poor adherence can lead to a decrease in quality of life and a higher risk of premature death.
Patient Support Systems
Effective patient support systems are essential for successful HAART adherence.
- Healthcare Providers: Dedicated healthcare providers who understand the patient’s needs and address concerns effectively are paramount. This includes ongoing monitoring, support, and open communication. Regular follow-up appointments and clear explanations about the treatment plan help patients feel confident and informed.
- Support Groups: Peer support groups provide a valuable platform for patients to connect with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences, offering encouragement, and providing emotional support can significantly enhance adherence.
- Family and Friends: The support of family and friends can be crucial in maintaining motivation and encouraging adherence to the treatment plan. Understanding the importance of consistent medication intake and providing encouragement can be vital.
- Mental Health Professionals: Addressing any underlying mental health conditions like depression or anxiety is crucial. Therapists and counselors can help patients cope with the emotional challenges of living with HIV and develop strategies for maintaining adherence.
- Social Workers: Social workers can help navigate social and economic barriers, such as housing instability or financial difficulties, that may affect adherence. They can connect patients with resources and support services.
- Community Organizations: Local organizations dedicated to HIV/AIDS care and support can offer various resources and services, including transportation, nutrition assistance, and educational programs. These resources can facilitate access to care and support systems.
HAART and Resistance
HIV, unfortunately, isn’t static. It constantly evolves, and this evolution plays a significant role in how effective HAART therapy can be. This adaptability is a key feature of the virus, and understanding how it develops resistance is crucial for optimizing treatment strategies and preventing the progression of the disease. HAART, while highly effective, can face challenges when the virus mutates to evade the drugs’ actions.HIV’s genetic makeup is prone to errors during replication.
These errors, called mutations, can alter the virus’s structure and function. If a mutation confers resistance to a drug in HAART, the virus with that mutation will be more likely to replicate and spread, potentially leading to a treatment failure. This highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and adjusting treatment regimens to maintain viral suppression.
Mechanisms of HIV Resistance Development
HIV’s RNA genome undergoes frequent mutations during replication. These mutations can arise spontaneously or be induced by the drugs themselves. These mutations can occur in specific genes within the virus’s genome, such as the reverse transcriptase and protease genes, which are directly targeted by the HAART drugs. Mutations in these genes can alter the virus’s ability to be inhibited by the drugs.
HAART, or highly active antiretroviral therapy, is crucial for managing HIV. Regular health checks are vital, and a prenuvo full body MRI scan, for example, can provide comprehensive insights into overall health, aiding in the ongoing management of HAART’s effectiveness. Understanding how HAART affects the body is key, and such scans can contribute to a more thorough understanding of the patient’s health status, which is critical for HAART treatment success.
Significance of Drug Resistance Mutations
Drug resistance mutations are critical because they can render HAART ineffective. If the virus develops resistance to multiple drugs within a regimen, treatment options become severely limited. This can lead to treatment failure, potentially allowing the virus to replicate unchecked, increasing the risk of opportunistic infections and disease progression. The emergence of resistance is a significant concern in the management of HIV, emphasizing the importance of careful monitoring and strategic treatment adjustments.
Monitoring Drug Resistance
Monitoring drug resistance is essential for adapting treatment strategies to maintain viral suppression. Methods for monitoring include genetic testing of the virus, which identifies specific mutations associated with drug resistance. Viral load tests are also important, helping to measure the amount of virus in the body. A combination of these tests, along with clinical assessments, allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment regimens proactively and effectively.
HAART, highly active antiretroviral therapy, is crucial for managing HIV, but it can sometimes impact cardiovascular health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular cardiovascular exercise, is vital for managing potential side effects and overall well-being. This is particularly important in those with conditions like diabetes, where the benefits of cardiovascular exercise and diabetes are well-documented.
Ultimately, a balanced approach to managing HAART side effects, coupled with a focus on overall health and exercise, is key to long-term success.
Common Drug Resistance Mutations and Their Impact
| Drug | Common Mutation(s) | Impact on Treatment Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| NRTIs (Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) | M184V, K65R, T215Y/F | Significant reduction in efficacy against some NRTIs. |
| NNRTIs (Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) | K103N, Y181C | Reduced susceptibility to most NNRTIs. |
| Protease Inhibitors (PIs) | I54V, L90M, I84V | Decreased susceptibility to certain PIs. |
Note: This table is not exhaustive and provides only a few examples of common resistance mutations. The specific mutations and their impact on treatment can vary depending on the specific drug and the patient. Continuous research and updates on mutation patterns are crucial for effective HAART management.
HAART and Other Health Considerations
Living with HIV and undergoing HAART therapy requires careful consideration of its impact on overall health. This section delves into the effects of HAART on other health conditions, potential drug interactions, and the crucial role of routine monitoring. Understanding these aspects is vital for managing the complexities of HIV treatment and ensuring optimal well-being.
Effect of HAART on Other Health Conditions
HAART can influence various health conditions. For example, some individuals may experience changes in lipid profiles, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Careful monitoring and lifestyle adjustments can mitigate these risks. Similarly, HAART can affect bone health, potentially leading to osteoporosis. This highlights the importance of proactive management and appropriate supplementation if necessary.
Additionally, HAART’s impact on kidney function requires vigilance, as some medications can increase the risk of kidney problems.
Interaction of HAART with Other Medications
Drug interactions are a significant concern during HAART. Many HIV medications can interact with other drugs, potentially reducing the effectiveness of one or both medications. This is crucial to consider when taking any additional prescription or over-the-counter medication. Interactions can also cause adverse side effects, ranging from mild discomfort to serious complications.
Importance of Routine Monitoring during HAART
Regular monitoring is essential for managing HAART effectively and identifying potential complications early. Blood tests are vital for assessing the levels of HIV in the blood, the function of various organs (liver, kidneys, and blood cells), and for tracking potential side effects of the medication. These tests allow healthcare providers to adjust treatment regimens as needed and ensure the patient’s health is optimized.
Consistent monitoring is also crucial for identifying any changes in the body that might indicate a developing issue related to the treatment.
Potential Interactions Between HAART and Other Medications
Understanding potential drug interactions is crucial. This table provides a glimpse into possible interactions, but it is not exhaustive. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication while on HAART.
| HAART Medication | Potential Interacting Medication | Potential Interaction Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Tenofovir | Certain diuretics | Increased risk of kidney problems |
| Ritonavir | Many medications | Increased or decreased effectiveness of the interacting medication; potential for side effects |
| Efavirenz | Certain antidepressants | Increased risk of drug-drug interaction and side effects |
| Nevirapine | Certain medications for epilepsy | Increased risk of liver toxicity |
Future Directions of HAART
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) has revolutionized the treatment of HIV, significantly improving the lives of those affected. As research continues, the future of HAART holds immense promise, focusing on enhancing efficacy, minimizing side effects, and addressing emerging challenges. This evolution hinges on innovative approaches and a deeper understanding of the virus’s complex interactions with the human immune system.
Ongoing Research in HAART
Current research in HAART explores novel strategies beyond the existing regimens. Researchers are investigating new drug classes and mechanisms of action to overcome resistance and enhance viral suppression. This involves scrutinizing the viral lifecycle to identify vulnerabilities not yet targeted by existing drugs. The goal is to develop therapies that are more effective, safer, and easier to adhere to, thereby improving long-term health outcomes.
Potential New Approaches and Drug Targets
One promising avenue is the development of drugs targeting viral reservoirs, the hidden sanctuaries where HIV can persist despite antiretroviral treatment. These reservoirs pose a significant obstacle to achieving a functional cure. Scientists are also investigating drugs that can bolster the immune system’s ability to fight the virus, thereby enhancing the body’s natural defenses. Furthermore, research is focused on developing therapies that can directly eliminate the viral reservoirs.
Future HAART Regimens and Strategies
Future HAART regimens may involve the combination of drugs targeting multiple viral pathways. This approach could enhance efficacy and reduce the risk of drug resistance. Scientists are also exploring strategies to tailor HAART regimens to individual patients based on their genetic profiles and viral characteristics. Personalized medicine promises more effective and safer treatment plans, potentially minimizing adverse effects and optimizing treatment outcomes.
This approach is expected to become more commonplace in the future, as it is already being adopted in other medical fields.
Emerging Advancements in HAART
- Development of drugs targeting viral reservoirs: Researchers are exploring drugs that can reach and eliminate HIV hidden within immune cells, potentially leading to a functional cure. This represents a crucial step towards eradicating the virus completely.
- Immune system-boosting therapies: New approaches focus on enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight HIV, thus reducing reliance on antiretrovirals. These therapies could improve long-term health outcomes and minimize the need for continuous treatment.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring HAART regimens to individual patient characteristics, including genetic makeup and viral mutations, may improve efficacy and reduce side effects. This could lead to more effective treatment plans that are specifically designed for each patient.
- Combination therapies: Future regimens may incorporate drugs targeting multiple stages of the viral life cycle. This multi-pronged approach could enhance viral suppression and reduce the risk of drug resistance.
Conclusive Thoughts

In conclusion, HAART highly active antiretroviral therapy has transformed HIV treatment, offering a path toward managing the virus and improving the quality of life for countless individuals. While challenges remain, the ongoing research and development surrounding HAART are promising, hinting at even more effective and personalized treatments in the future. Adherence, patient support, and ongoing monitoring are crucial to successful outcomes.