How to treat cat bites and scratches is a crucial guide for anyone who shares their home with a feline friend. These seemingly minor injuries can quickly escalate if not handled properly. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to assess, manage, and prevent infections from these common occurrences. We’ll explore everything from initial first aid to long-term care, including preventative measures.
This guide details a step-by-step approach to dealing with cat bites and scratches, from immediate care to ongoing wound management. It covers different wound types, the importance of seeking medical attention when necessary, and prevention strategies. By understanding the various aspects of treatment, you can ensure a swift and safe recovery for yourself or a loved one.
Initial Assessment and First Aid
A cat bite or scratch, though seemingly minor, can lead to serious infections if not treated promptly and correctly. Understanding the initial assessment and implementing proper first aid is crucial in preventing complications and promoting healing. This section will guide you through the steps involved in evaluating and treating these wounds.Assessing the severity of a cat bite or scratch is paramount.
Factors like the depth, size, and presence of foreign objects significantly influence the appropriate treatment plan. Immediate action, including thorough cleaning, plays a vital role in minimizing the risk of infection.
Assessing the Wound
Determining the severity of the wound is the first step in providing appropriate care. This involves careful observation of the affected area. Look for signs of deep penetration, significant tissue damage, or the presence of foreign materials like dirt or debris. The depth and size of the wound, as well as the presence of puncture marks or ragged edges, all contribute to the severity assessment.
Cleaning the Wound
Prompt and thorough cleaning is essential to prevent infection. The goal is to remove any dirt, debris, or bacteria that may be present. Cleaning the wound immediately after the injury is crucial.
- Using Clean Water: Rinse the wound gently with clean, cool running water. Avoid using hot or cold water, as this can cause discomfort and potentially exacerbate the injury.
- Applying Mild Soap: A mild antibacterial soap can be used to further cleanse the wound. Apply a small amount of soap to a clean cloth or cotton ball and gently scrub the affected area. Avoid harsh scrubbing or excessive pressure, which could damage the surrounding tissue.
Comparing Cleaning Solutions
Various solutions can be used for wound cleaning, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. This table provides a comparison of common solutions.
| Solution | Description | Suitability | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Water | Simple and readily available | Excellent for initial rinsing | May not remove all contaminants |
| Mild Soap | Gentle cleanser | Effective for removing dirt and debris | Avoid harsh scrubbing |
| Saline Solution | Isotonic solution | Gentle and effective | Can be irritating if applied to deep wounds |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Oxidizing agent | Effective in removing debris | Can cause stinging and potentially damage healthy tissue; not recommended for initial cleaning |
Importance of Immediate First Aid
Immediate first aid plays a critical role in preventing infection. By removing contaminants and cleaning the wound promptly, you drastically reduce the risk of bacterial growth and subsequent complications. A clean wound allows the body’s natural healing processes to work more effectively, minimizing the chance of scarring and promoting a faster recovery. Early intervention significantly improves the outcome and prevents the potential for serious infections, like cellulitis or tetanus.
Wound Management: How To Treat Cat Bites And Scratches
Cat bites and scratches, while seemingly minor, can lead to serious infections if not treated properly. Prompt and appropriate wound management is crucial in preventing complications and promoting healing. Understanding the different types of wounds and how to manage them effectively is key to ensuring a swift and healthy recovery.Proper wound management involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing antiseptic application, bandage selection, and recognizing when professional medical attention is necessary.
This detailed guide will help you navigate the steps involved in effectively treating these injuries.
Types of Cat Bites and Scratches
Cat bites and scratches can vary significantly in severity, from superficial abrasions to deep puncture wounds. Understanding the type of wound will influence the appropriate treatment plan. Superficial scratches may only require gentle cleaning and antiseptic application, while deeper bites may necessitate professional medical attention. A deep puncture wound, especially one that penetrates the skin, may harbor bacteria that can cause significant infection.
Wound Assessment
Before beginning any treatment, thoroughly assess the wound for depth and extent of damage. Evaluate the presence of visible debris, puncture marks, or signs of infection. A deep puncture wound will likely require medical attention to ensure proper cleaning and antibiotic administration.
Antiseptic Solutions
Antiseptic solutions play a vital role in wound management. They help eliminate bacteria and promote a clean environment for healing. Selection of an antiseptic solution should consider the severity of the wound. A mild antiseptic, like diluted hydrogen peroxide, might suffice for superficial scratches. More severe wounds might require a stronger antiseptic, such as iodine or chlorhexidine gluconate.
Comparison of Antiseptic Solutions
| Antiseptic | Effectiveness | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Peroxide (diluted) | Effective against some bacteria; can be irritating to tissues. | Avoid using on deep wounds; can cause further tissue damage. |
| Povidone-Iodine | Broad-spectrum antiseptic; effective against various bacteria. | Can stain skin; avoid contact with eyes. |
| Chlorhexidine Gluconate | Highly effective antiseptic; less irritating than iodine. | May cause skin irritation in some individuals. |
Bandage Application
Proper bandage application is essential to protect the wound and promote healing. Choose a bandage appropriate for the size and type of wound. Adhesive bandages are suitable for minor scratches, while larger wounds may require gauze dressings. A bandage should be applied firmly enough to prevent movement but not so tightly as to impede blood flow.
Cleaning cat bites and scratches thoroughly with mild soap and water is crucial. Following up with a topical antibiotic can help prevent infection. However, if you’re on a prednisone regimen and considering tapering off, it’s essential to understand how prednisone tapering affects your body. Knowing if prednisone tapering minimizes withdrawal symptoms is vital for a safe transition.
For more on this, check out this resource on does prednisone tapering minimize withdrawal. Ultimately, proper wound care is key to healing cat bites and scratches quickly and preventing complications.
Types of Bandages
Using the correct bandage type is crucial for proper wound management. A simple adhesive bandage might suffice for a small, superficial scratch. For deeper or more extensive wounds, a gauze dressing provides better protection and absorption of exudate. Gauze dressings often require a secondary bandage, like a wrap, for proper support and containment. A well-fitting bandage will help prevent the wound from becoming irritated and contaminated.
Wound Care and Prevention of Complications
Maintaining a clean and dry wound is vital to prevent infection and promote healing. Change bandages regularly and monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, or pus. A timely and well-managed wound can prevent complications like cellulitis or other more serious infections. The frequency of dressing changes will depend on the type and severity of the wound.
Infection Prevention and Treatment
Preventing infection after a cat bite or scratch is crucial for a speedy and healthy recovery. Proper wound care and vigilance are key to avoiding complications. Early recognition of infection symptoms is vital for prompt treatment.Recognizing the difference between normal healing and an infection is paramount. A healthy wound will show signs of gradual improvement, while an infected wound will exhibit worsening symptoms.
This section will detail the signs of infection, common bacteria involved, and the importance of seeking medical attention.
Signs and Symptoms of Infection
Infected cat bites and scratches often display noticeable changes from a normal healing process. These changes often involve inflammation, redness, and sometimes, pus. Pay close attention to the area around the wound, not just the wound itself.
- Redness: A widening area of redness around the wound is a clear indication of inflammation. This redness can be a sign of a localized infection.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling, including the surrounding tissue, is another possible sign of infection. This is due to the body’s immune response to the bacteria.
- Pus: The presence of pus, a thick yellowish or greenish fluid, indicates a bacterial infection. Pus is a collection of dead white blood cells and bacteria.
- Increased Pain: If the pain around the wound intensifies or persists beyond a few days, it could be a sign of infection.
- Warmth: An infected wound often feels warmer than the surrounding skin due to increased blood flow.
- Fever: A systemic infection might cause a fever. If you experience a fever, consult a doctor immediately.
Common Bacteria Involved
Several types of bacteria can cause infections from cat bites and scratches. These include
- Pasteurella multocida*,
- Streptococcus*, and
- Staphylococcus*. Knowing the potential culprits can help in seeking the right medical attention.
- *Pasteurella multocida*: This is a common bacterium found in cats’ mouths. It’s a significant cause of infections in cat bites, often resulting in cellulitis.
- *Streptococcus*: This bacterium can lead to strep throat and other infections. It can also be a contributor to wound infections.
- *Staphylococcus*: This bacterium is frequently found on the skin and can cause various skin infections, including boils and abscesses, potentially related to cat scratches.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you notice any signs of infection, seeking medical advice is essential. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Early intervention can prevent complications.
A doctor can assess the severity of the infection and prescribe the most appropriate treatment. Ignoring signs of infection can lead to more serious health problems.
Distinguishing Normal Healing from Infection
It’s crucial to differentiate between normal wound healing and signs of infection. Normal healing involves gradual improvement, while an infection worsens over time.
- Normal healing: The wound gradually closes, redness and swelling subside, and the area around the wound returns to normal.
- Infection: Redness, swelling, and pain worsen, pus may appear, and the area may become warm to the touch.
Antibiotics and Topical Ointments
Antibiotics are sometimes necessary to treat bacterial infections. Your doctor will determine if antibiotics are required based on the severity and type of infection. Topical ointments can also help promote wound healing and prevent infection.
- Antibiotics: Prescription antibiotics are necessary in cases of severe or systemic infection, or when the bacteria are resistant to topical treatments.
- Topical Ointments: Topical ointments can help promote healing and reduce the risk of infection, especially in cases of minor wounds.
Summary Table
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Redness | Widening area of redness around the wound |
| Swelling | Noticeable swelling in the surrounding tissue |
| Pus | Thick yellowish or greenish fluid |
| Increased Pain | Intensified or persistent pain beyond a few days |
| Warmth | Wound feels warmer than surrounding skin |
| Fever | Systemic infection, consult a doctor immediately |
Long-Term Care and Prevention

Taking care of a wound from a cat bite or scratch extends beyond the initial first aid. Proper follow-up care is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring complete healing. This involves meticulous monitoring of the wound, diligent hygiene, and proactive measures to avoid future incidents. Understanding these factors can significantly improve the healing process and minimize potential risks.Effective long-term care hinges on consistent monitoring and proactive measures.
This includes not only the physical aspects of wound care but also preventative strategies to reduce the likelihood of future injuries. By understanding the importance of these measures, cat owners can foster a healthier and safer environment for both their feline companions and themselves.
So, you’ve got a cat scratch or bite? First, clean the wound thoroughly with mild soap and water. Then, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment. But, while you’re focusing on your pet-related injuries, you might also want to consider what happens to your body when you rely on protein bars for every meal. For example, are you getting all the nutrients your body needs?
This article delves into the long-term effects of a protein bar-heavy diet: what happens to your body when you eat a protein bar every day. Finally, remember to monitor the wound for signs of infection and see a doctor if necessary. Proper care is key for healing any injury.
Importance of Follow-up Care
Follow-up care is essential for assessing wound progress, addressing any potential complications, and ensuring optimal healing. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian can detect signs of infection or other issues early on. Prompt intervention is key to preventing long-term problems. Early detection and treatment are vital for avoiding serious complications.
Monitoring Wound Healing
Consistent monitoring is crucial for successful wound healing. This involves daily observation for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus. Careful observation for changes in the wound’s appearance is a key part of this process. This involves checking for signs of inflammation, such as redness, warmth, or swelling around the wound. The presence of pus or any unusual discharge should be reported to a veterinarian immediately.
The wound’s progression should be meticulously documented, including photographs or detailed notes. The notes should include the date, time, and any observed changes.
Cleaning a cat bite or scratch with mild soap and water is crucial, just like addressing any wound. But, what if you’re also dealing with something more concerning, like waking up with stomach pain? Waking up with stomach pain can be pretty unsettling, but if you’ve just been scratched by a cat, it’s important to follow up with a tetanus shot and keep an eye out for signs of infection, like redness, swelling, or pus.
Don’t ignore any unusual symptoms, and remember to prioritize proper wound care for those cat scratches.
Wound Hygiene: Keeping it Clean and Dry, How to treat cat bites and scratches
Maintaining a clean and dry wound environment is paramount to preventing infection. Gentle cleaning with a saline solution or a veterinarian-recommended antiseptic is recommended. Avoid using harsh soaps or rubbing alcohol, which can irritate the wound. Keeping the wound area clean and dry is vital for healing. Avoiding excessive moisture or exposure to dirt is essential to prevent further complications.
This is especially important when bathing or swimming.
Preventing Future Cat Bites and Scratches
Preventing future incidents is just as crucial as treating the current one. This involves understanding feline behavior and taking proactive steps to avoid interactions that could lead to injuries. Redirecting unwanted behaviors is often necessary to prevent future incidents. Recognizing and addressing the underlying causes of aggressive behavior can minimize the risk of future injuries. Understanding a cat’s body language and behavior cues is important for preventing conflicts.
A calm and predictable environment can also reduce stress, leading to less aggressive behavior.
Role of Vaccination in Preventing Infections
Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing infections. Some infections can be prevented by vaccinations, which can help prevent severe illnesses. Certain vaccines can protect against bacteria or viruses that can cause complications in wounds. Vaccinations against rabies and other infectious diseases are often recommended.
Preventive Measures Table
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Vet Checkups | Routine examinations can detect potential issues early. |
| Understanding Cat Behavior | Recognizing warning signs and body language. |
| Safe Handling Practices | Avoiding sudden movements or forceful interactions. |
| Proper Feeding and Enrichment | Meeting a cat’s nutritional and environmental needs. |
| Wound Care Hygiene | Keeping the wound clean and dry, following vet’s instructions. |
Common Household Items for Prevention
A variety of household items can help deter cat bites and scratches. These include:
- Protective Gloves: Wearing gloves when interacting with cats, especially during playtime or grooming.
- Distraction Toys: Providing engaging toys to redirect a cat’s attention away from potentially harmful behaviors.
- Catnip and Other Cat Toys: Utilizing toys that can provide mental stimulation and engagement.
- Scratching Posts: Providing appropriate scratching surfaces to satisfy a cat’s natural scratching instincts.
Specific Considerations
Treating cat bites and scratches requires careful attention to detail, especially considering the location and nature of the wound. Factors like the animal’s health, the individual’s immune system, and the potential for infection all influence the appropriate course of action. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective wound management and preventing complications.
Location of the Wound
The location of a cat bite or scratch significantly impacts treatment. A wound on the face, for instance, requires different care than one on the hand or arm. The proximity to sensitive areas, like eyes or joints, also warrants special consideration.
Treatment by Body Part
Different parts of the body necessitate different approaches to treatment. For example, facial wounds, especially around the eyes, require meticulous cleaning and potential referral to a physician due to the risk of infection spreading to the delicate structures of the eye. Wounds on the hands and fingers, crucial for daily activities, need particular care to minimize functional impairment and promote swift healing.
Types of Wounds and Treatments
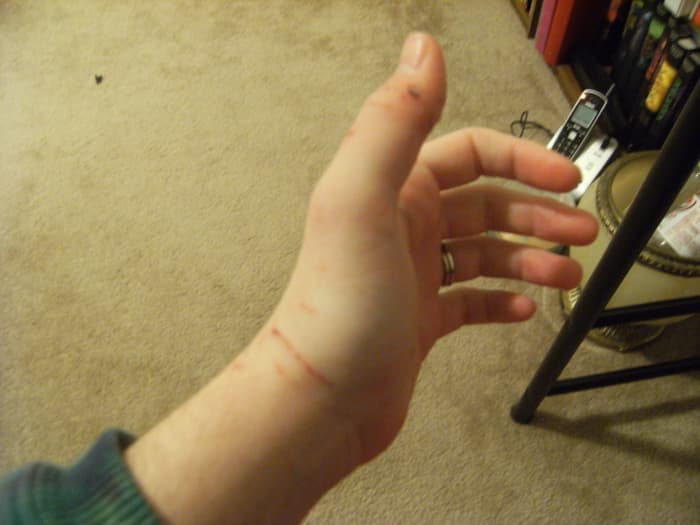
Cat bites and scratches can manifest in various forms, each requiring tailored treatment. A superficial scratch might only need cleansing and antiseptic application, while a deep puncture wound from a bite necessitates thorough cleaning and possibly antibiotics. A laceration, a cut with irregular edges, calls for careful closure and potential stitches to promote proper healing. A cat bite with visible swelling and redness, often accompanied by pain, may indicate infection and warrants immediate medical attention.
Detailed records of the wound’s characteristics, including size, depth, and presence of foreign bodies, are essential for accurate assessment and treatment planning.
Comparison of Treatment in Children and Adults
Children and adults may react differently to cat bites and scratches. Children’s skin is generally more delicate and prone to infection. Moreover, children’s immune systems might not be as developed, leading to a higher risk of complications. Adults, while possessing more robust immune systems, may still experience pain, discomfort, and potential infection. Assessing the child’s age, overall health, and the severity of the wound is critical in determining the appropriate course of action.
A child’s emotional state and the possibility of psychological trauma must also be taken into account.
Special Considerations for Vulnerable Populations
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or with chronic illnesses, are more susceptible to infection. These individuals require particularly careful wound care, and close monitoring of any signs of infection. Careful attention should be given to the potential for delayed healing and the necessity of contacting a physician for guidance and antibiotic prescription, if required.
Seeking Veterinary Advice for Animal Bites
Animal bites, especially those from cats, can transmit various diseases. Always seek veterinary advice to assess the animal’s health status and the possibility of zoonotic transmission. This is vital to prevent potential complications and to understand the appropriate course of action for both the patient and the animal. The veterinarian can provide valuable insights into the animal’s health history and any potential risks associated with the bite.
Illustrations and Visual Aids
Visual aids are crucial for understanding and effectively treating cat bites and scratches. Proper identification of the wound’s characteristics, normal healing stages, and potential infection signs helps in determining the appropriate course of action. Detailed descriptions of wound types, bandages, and antiseptic solutions provide a clear picture of the treatment process.
Wound Appearance: Normal vs. Infected
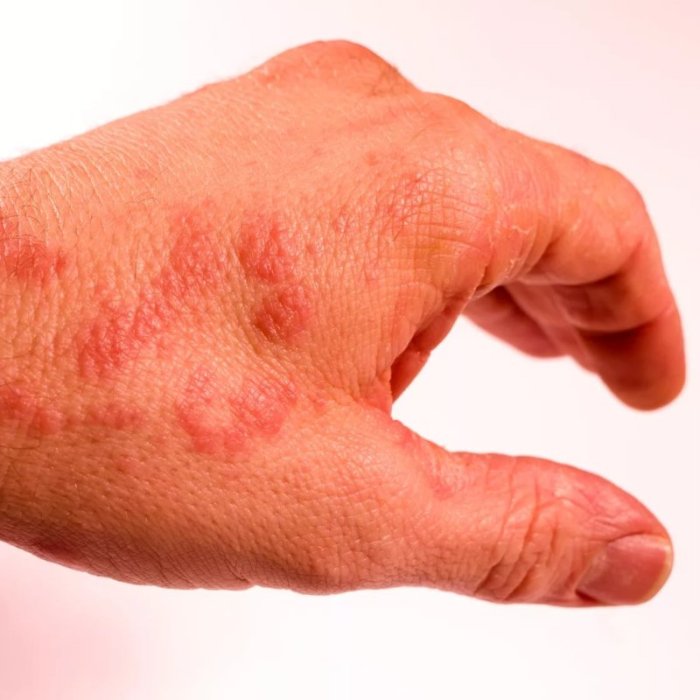
Understanding the progression of normal wound healing is essential to recognizing signs of infection. Healthy wounds typically show a gradual closure and tissue regeneration. Initial inflammation (redness, swelling, warmth) is followed by the formation of a scab. Healthy granulation tissue, a reddish-pink tissue that helps in wound closure, appears beneath the scab. A healthy wound gradually decreases in size and discomfort over time.
Infection, on the other hand, manifests with increased pain, swelling, redness, and the presence of pus or a foul odor. The wound might also appear deeper or more inflamed than expected. Visual representation of both normal healing and signs of infection is critical in guiding treatment.
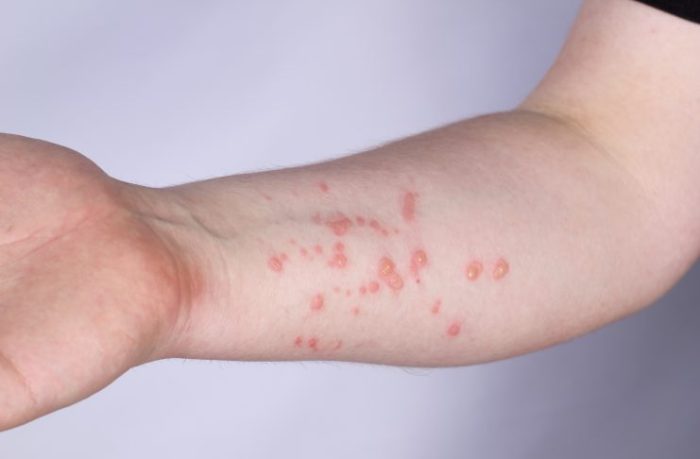
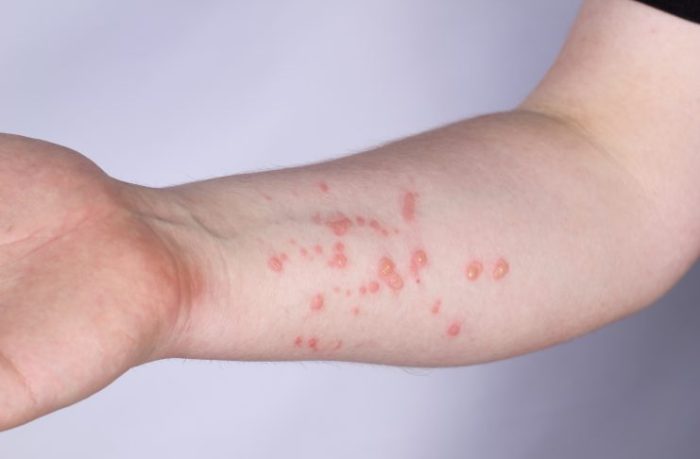
Types of Cat Bites and Scratches
Cat bites and scratches can vary significantly in appearance. A superficial scratch may present as a linear abrasion with slight bleeding, while a deeper puncture wound from a bite may have jagged edges and a deeper penetration. A bite wound often involves multiple puncture marks and can easily become infected due to the bacteria present in a cat’s mouth.
A severe bite can also show significant tissue damage, requiring more extensive treatment. Visual aids showcasing these varying types of wounds are crucial for proper assessment.
Bandages and Antiseptic Solutions
Various bandages and antiseptic solutions are used in wound care. Clean gauze dressings are commonly used for covering minor wounds. Sterile adhesive bandages are suitable for protecting superficial wounds and keeping them clean. More extensive wounds may require more substantial dressings, like non-adherent pads or hydrocolloid dressings, which promote wound healing. Antiseptic solutions, such as hydrogen peroxide or saline solutions, are used for cleaning the wound.
Illustrations demonstrating the different types of bandages and their appropriate uses are helpful for understanding the treatment process.
Cleaning a Cat Bite on the Hand
Cleaning a cat bite on the hand requires meticulous attention to detail. First, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. Then, gently clean the wound with a clean, damp gauze pad soaked in sterile saline solution. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide, as it can damage healthy tissue. Gently flush out any debris or dirt.
Ensure that you do not scrub the wound. Finally, apply an antibiotic ointment, such as bacitracin or neosporin, to the wound and cover it with a clean bandage. Visual demonstrations of this process are essential for ensuring correct technique.
Types of Bacteria Causing Infection
Various bacteria can cause infections in cat bite and scratch wounds. Pasteurella multocida is a common bacterium found in the mouths of cats. Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species are also prevalent causes of wound infections. E. coli can also be involved in certain cases. Identifying the potential bacteria is important for determining the appropriate antibiotic treatment.
Visual aids illustrating the appearance of these bacteria and their potential effects on wounds are valuable in determining treatment plans.
Outcome Summary

In conclusion, treating cat bites and scratches requires a multi-faceted approach. From immediate first aid and wound management to infection prevention and long-term care, this guide offers a comprehensive overview. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications and ensure a healthy recovery. Remember, prompt medical attention is crucial for severe wounds, and preventive measures can minimize the likelihood of future incidents.
Ultimately, this knowledge empowers you to care for yourself or others effectively.