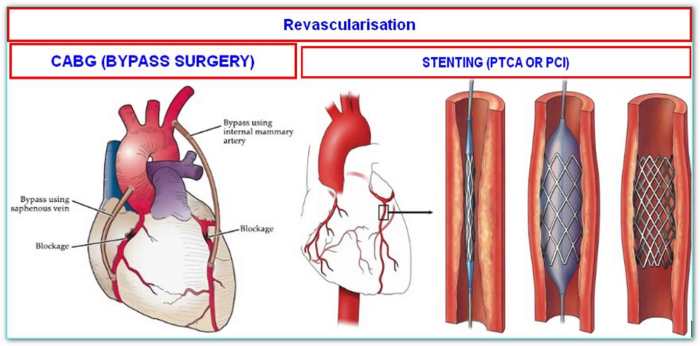
What is a double bypass heart surgery? This procedure, a significant step in cardiovascular care, aims to improve blood flow to the heart. It involves rerouting blood flow around blocked coronary arteries, often caused by atherosclerosis. Understanding the historical context, different types of bypasses, and the meticulous preparation and recovery process is crucial for patients and their families.
This guide delves into the details, from the initial evaluation to long-term implications, ensuring a clear picture of this complex surgical intervention.
The surgical process itself involves carefully assessing the patient’s condition and identifying the most appropriate approach for the double bypass. Different types of bypasses cater to various anatomical areas affected by blockages, and the selection process considers the specific needs of each patient. This detailed examination of the procedure also encompasses the critical pre-operative and post-operative phases, including patient counseling, recovery timelines, and potential complications.
Furthermore, the potential alternatives and long-term outcomes are thoroughly explored, equipping the reader with a complete picture of this life-altering surgery.
Introduction to Double Bypass Heart Surgery
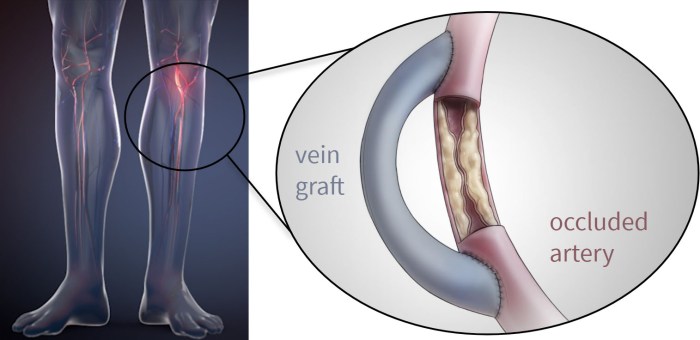
A double bypass heart surgery is a complex cardiovascular procedure where two blocked coronary arteries are treated by rerouting blood flow around the blockages. This is achieved by using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body to create new pathways for blood to reach the heart muscle. Essentially, the surgeon creates detours for blood to bypass the obstructed areas, ensuring a continuous and adequate blood supply to the heart.
The primary goal is to restore normal blood flow and prevent further damage to the heart.The fundamental purpose of a double bypass heart surgery is to address coronary artery disease (CAD). CAD occurs when plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. This buildup narrows the arteries, reducing blood flow and potentially leading to a heart attack.
A double bypass heart surgery reroutes blood flow around blocked arteries, improving heart function. While the focus is on heart health, it’s important to consider the impact of serious illnesses like ALS, Lou Gehrig’s disease, on life expectancy. Understanding life expectancy in cases like this can help patients and families make informed decisions about treatment options, such as a double bypass surgery, als lou gehrigs disease life expectancy.
Ultimately, the surgery aims to enhance the quality of life for patients by improving their cardiovascular health.
By creating new pathways for blood, the surgery aims to alleviate the blockage and improve blood flow to the heart muscle. This prevents further damage and improves the patient’s overall health.The overall goal of the surgery is to improve the patient’s quality of life and prevent serious complications from heart disease. This means a significant reduction in chest pain (angina), improvement in energy levels, and the ability to perform daily activities without discomfort.
Ultimately, the surgery aims to extend the patient’s lifespan and prevent life-threatening events such as heart attacks and strokes.The historical context of this surgical technique is rooted in the evolution of cardiovascular surgery. Early attempts at coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) emerged in the mid-20th century. Dr. Robert Goetz is often credited with pioneering this technique. Over time, surgical techniques and materials have significantly improved, leading to greater success rates and lower complication rates for patients.
Improvements in anesthesia and post-operative care also played crucial roles in enhancing the safety and efficacy of the procedure.
A double bypass heart surgery essentially reroutes blood flow around blocked arteries in the heart. It’s a significant procedure, often necessary for serious heart conditions. Interestingly, the age of onset for certain neurological conditions, like ALS, can sometimes be a factor in considering treatment options, such as als age of onset , alongside the patient’s overall health and the severity of the heart blockage.
Ultimately, the decision for a double bypass is a complex one, involving careful evaluation by medical professionals.
Surgical Procedure Details
A detailed understanding of the procedure itself helps to understand the procedure better. This section will explore the steps involved in a double bypass heart surgery. It will also provide insight into the various considerations for choosing this type of procedure.
| Procedure Name | Description | Benefits | Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Double Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) | The surgeon uses healthy blood vessels (typically from the leg or chest) to create new pathways for blood to flow around blocked sections of the coronary arteries. | Improved blood flow to the heart muscle, reduced chest pain, and reduced risk of heart attack or stroke. | Bleeding, infection, stroke, blood clots, and damage to surrounding tissues. |
Types of Double Bypass Procedures
Double bypass heart surgery, while fundamentally aimed at improving blood flow to the heart, can be tailored to specific patient needs and anatomical variations. Different approaches exist, each with unique considerations for the surgeon and the patient. Understanding these variations is crucial for both informed decision-making and successful outcomes.
Different Types of Double Bypass Procedures, What is a double bypass heart surgery
Various approaches exist for double bypass procedures, each targeting specific coronary arteries. These differences in targeting specific arteries directly impact the surgical complexity, recovery time, and potential complications. The surgeon’s expertise and assessment of the patient’s particular artery blockage patterns are crucial in selecting the optimal technique.
- Left Anterior Descending (LAD) and Right Coronary Artery (RCA) Bypass: This is a common and often preferred approach. The LAD artery, responsible for supplying blood to the front and left side of the heart, and the RCA, supplying blood to the right side, are the primary targets. This approach directly addresses two major blood flow limitations, typically improving overall heart function significantly. The surgeon aims to restore blood flow by creating new pathways to these blocked arteries.
- Left Main Coronary Artery (LMCA) and Left Circumflex Artery (LCX) Bypass: This approach is used when the left main coronary artery (LMCA) or the LCX, responsible for blood supply to the left side of the heart, is severely obstructed. This more complex technique may involve greater surgical time and potential risks, but it is often essential for ensuring adequate blood flow when major blockages exist in these critical vessels.
It typically involves grafting a healthy blood vessel to the LMCA and/or the LCX, bypassing the blocked area.
- Multiple Vessel Bypass (Involving LAD, RCA, and LCX): This approach is a more comprehensive procedure that addresses blockages in multiple coronary arteries simultaneously. This might involve grafting to the LAD, RCA, and LCX, or a combination of these, potentially increasing the complexity of the surgery but often offering a more extensive and long-term solution for improved blood flow. The selection of these additional bypasses is predicated on the extent of blockage in the affected vessels.
This approach is most often indicated for patients with extensive coronary artery disease.
Selection Criteria for Double Bypass Procedures
The choice of the specific double bypass procedure is not arbitrary. Several factors influence the surgeon’s decision, ultimately aiming for the best possible outcome for the patient. The extent of the blockage, the location of the blockages, and the overall health of the patient are all carefully considered.
- Extent of Blockage: The severity and location of blockages in the coronary arteries play a crucial role. For example, a total occlusion (complete blockage) of a major artery necessitates a bypass, whereas a partial blockage may be managed with other interventions. The surgeon must carefully assess the extent of blockage to determine the appropriate type of bypass and the number of vessels that need to be addressed.
- Patient’s Overall Health: Factors such as age, other medical conditions, and overall health status are considered. For instance, a patient with severe lung or kidney issues might require a more cautious approach. This holistic assessment helps the surgeon tailor the procedure to the patient’s specific needs and risks.
- Location of Blockage: The specific location of the blockage in the coronary arteries directly impacts the surgical approach. The complexity of accessing certain arteries may influence the choice of technique and potential complications. Surgeons must be mindful of anatomical variations and factors that may influence access to specific areas.
Comparison of Double Bypass Techniques
The different double bypass procedures vary in their complexity and the specific anatomical areas targeted. Careful consideration of these differences is vital for determining the best possible surgical approach for each individual patient.
| Procedure Type | Targeted Arteries | Complexity | Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| LAD and RCA Bypass | LAD and RCA | Moderate | Partial or significant blockages in LAD and RCA |
| LMCA and LCX Bypass | LMCA and LCX | High | Severe blockages in LMCA or LCX |
| Multiple Vessel Bypass | LAD, RCA, LCX, or others | High | Extensive blockages in multiple coronary arteries |
Pre-Operative Considerations and Preparation
Before undergoing a double bypass heart surgery, a meticulous pre-operative evaluation and preparation process is critical. This process ensures the patient is as healthy as possible to withstand the procedure and optimize the chances of a successful outcome. Careful consideration of potential risks and thorough patient counseling are integral parts of this preparation.
Pre-Operative Evaluation Process
The pre-operative evaluation process involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s overall health. This assessment aims to identify any underlying conditions that might complicate the surgery or increase the risk of complications. A thorough medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests are used to determine the patient’s suitability for the procedure and to tailor the surgical approach.
Tests and Assessments Performed Before Surgery
Numerous tests and assessments are performed to evaluate the patient’s cardiovascular health, overall physical condition, and potential risks. These include but are not limited to: blood tests (complete blood count, coagulation studies, and electrolytes), chest X-rays, electrocardiograms (ECGs), echocardiograms, stress tests, and potentially cardiac catheterization. These tests provide critical data about the heart’s function, the extent of coronary artery disease, and the patient’s overall health.
Potential Risks to Consider Before the Procedure
While double bypass surgery is a life-saving procedure, it carries inherent risks. Potential risks include but are not limited to: bleeding, infection, stroke, blood clots, heart attack, kidney failure, and respiratory complications. A thorough discussion of these potential risks with the patient and their family is crucial for informed decision-making. The surgical team will thoroughly discuss these risks and their likelihood, along with the benefits of the surgery.
Patient Preparation Process
The patient preparation process extends beyond the immediate pre-operative period. It involves a series of instructions and recommendations to prepare the body for the surgery. This includes medication adjustments, dietary restrictions, and avoidance of smoking and alcohol. The specific preparation steps are tailored to each patient’s individual needs and health status.
Patient Counseling
Patient counseling is a cornerstone of pre-operative preparation. It involves educating the patient about the procedure, potential risks and benefits, expected recovery process, and post-operative care. The surgical team will provide clear, concise, and understandable information to ensure the patient is fully informed and prepared for the surgical experience. Open communication and addressing any concerns are essential elements of effective patient counseling.
Summary of Pre-Operative Preparation Steps
| Step | Timeline | Required Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed Medical History | Weeks before surgery | Patient’s medical records, previous test results |
| Physical Examination | Weeks before surgery | Physician’s notes, vital signs |
| Diagnostic Tests | Weeks before surgery | Lab reports, ECG results, echocardiogram reports, stress test results |
| Medication Review and Adjustments | Weeks before surgery | Medication list, physician’s recommendations |
| Dietary Restrictions | Days before surgery | Physician’s instructions on diet |
| Smoking Cessation (if applicable) | Weeks before surgery | Documentation of smoking cessation plan |
| Alcohol Restriction (if applicable) | Days before surgery | Physician’s instructions on alcohol intake |
| Patient Counseling | Days before surgery | Signed consent form, documented discussion of risks and benefits |
| Pre-operative Medications | Day before surgery | Administered pre-operative medications |
Surgical Procedure Details: What Is A Double Bypass Heart Surgery
The surgical procedure for a double bypass involves a series of precise steps to redirect blood flow around blocked coronary arteries. This intricate process requires meticulous attention to detail and advanced surgical techniques. Understanding the steps, instruments, and anatomical landmarks involved provides a deeper insight into the complexity of this life-saving procedure.
Surgical Steps Overview
A double bypass operation involves grafting healthy blood vessels to reroute blood flow around blocked coronary arteries. This bypass allows improved blood supply to the heart muscle, alleviating the effects of ischemia. The steps are carefully orchestrated to minimize trauma and maximize effectiveness.
- Incision and Exposure: A small incision is made in the chest, typically on the left side, allowing access to the heart and major vessels. The surgeon carefully dissects the chest wall and surrounding tissues to expose the heart and the targeted coronary arteries.
- Identification of Blocked Arteries: The surgeon meticulously identifies the blocked coronary arteries that require bypass. Advanced imaging techniques may be used to confirm the location and extent of the blockages.
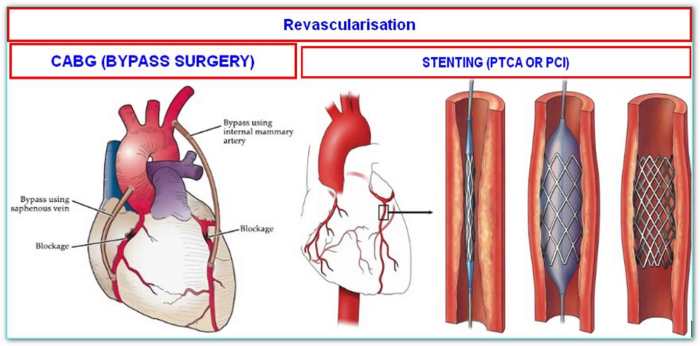
- Graft Selection and Preparation: A healthy blood vessel, either from the patient’s leg (saphenous vein) or from a section of the chest wall (internal mammary artery), is selected as a graft. The chosen vessel is carefully prepared and measured to ensure a proper fit with the target coronary arteries.
- Graft Anastomosis: The prepared graft is connected to the healthy section of the blocked artery using sutures or surgical staples. This connection, or anastomosis, ensures that blood can flow from the graft into the coronary artery, bypassing the blockage.
- Closure and Drainage: Once all bypasses are completed, the surgeon carefully closes the chest incision. Drainage tubes are placed to collect any excess fluid from the surgical site.
Instruments and Tools Used
A wide array of instruments and tools are essential for the precision and safety of the procedure. These tools include scalpels, surgical scissors, surgical staplers, sutures, and various types of clamps to control bleeding. Advanced monitoring equipment is also critical to continuously assess the patient’s vital signs and cardiac function throughout the operation.
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass Machine: This sophisticated machine takes over the function of the heart and lungs during the surgery, allowing the surgeon to work on the heart without interruption.
- Surgical Staplers: These instruments rapidly and precisely seal blood vessels, minimizing bleeding and tissue damage.
- Microsurgical Instruments: These highly precise tools are used for the delicate anastomosis of the graft to the coronary artery.
- Sutures and Needles: Various types of sutures are used to close tissues and connect the graft to the coronary arteries.
Anatomical Landmarks and Structures
The surgeon must accurately identify and manipulate several key anatomical structures during the procedure. This includes the coronary arteries, the aorta, and the various valves of the heart. A clear understanding of the heart’s anatomy is essential to prevent complications.
Procedure Phases
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Incision | A small incision is made in the chest, and the chest wall is carefully opened to expose the heart and major vessels. |
| Graft Placement | The selected graft (e.g., saphenous vein or internal mammary artery) is prepared and connected to the coronary artery using precise surgical techniques. |
| Vessel Repair | The blocked section of the coronary artery is bypassed by connecting the graft to the healthy portion of the artery. |
| Closure | The chest incision is closed, and drainage tubes are placed to manage any potential fluid buildup. |
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Following a double bypass heart surgery, a meticulous post-operative care plan is crucial for a smooth recovery. Patients are closely monitored for any complications, and a supportive environment is essential for healing. This phase focuses on managing pain, monitoring vital signs, and gradually resuming daily activities. Proper adherence to the prescribed care plan significantly influences the overall outcome and the speed of recovery.
Post-Operative Care Plan
The post-operative care plan is tailored to each individual patient’s needs and condition. It involves a multidisciplinary approach, with input from surgeons, nurses, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals. The plan typically includes regular monitoring of vital signs, pain management, and gradually increasing activity levels as tolerated.
Typical Recovery Process
The typical recovery period following a double bypass surgery can vary. Early days focus on stabilizing vital signs, managing pain, and preventing complications. As the patient progresses, activity levels are gradually increased under medical supervision. This gradual progression is vital to avoid undue strain on the heart and ensure a safe and effective recovery. Patients often experience fatigue, but with consistent care and adherence to the prescribed plan, recovery typically takes several weeks to months.
Potential Complications and Their Management
While double bypass surgery is generally safe, potential complications can arise. These can include, but are not limited to, infection, bleeding, blood clots, and heart rhythm problems. Early detection and appropriate management are crucial. The healthcare team employs various strategies, such as antibiotics for infection, blood thinners for clots, and medications for heart rhythm disturbances, to address and mitigate these risks.
List of Potential Complications
Potential complications following double bypass surgery can include: infection at the incision site, excessive bleeding, blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), difficulty breathing, heart rhythm disturbances, stroke, kidney failure, and wound complications. These are not exhaustive, but highlight the importance of close monitoring.
- Infection: Infection at the incision site is a possibility. Prompt treatment with antibiotics and careful wound care can help manage this.
- Bleeding: Post-operative bleeding can occur. Close monitoring of vital signs and blood tests are crucial for early detection and management.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots, particularly deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE), can develop. Medications like blood thinners and compression stockings help prevent these.
- Heart Rhythm Problems: Changes in heart rhythm can occur. Monitoring heart rate and rhythm, and using medications as prescribed, are essential to manage these.
- Wound Complications: Wound complications such as dehiscence (opening of the wound) or seromas (fluid buildup) are possible. Appropriate wound care and dressings are vital to manage these issues.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain management is a key aspect of post-operative care. Pain medications, including both opioid and non-opioid options, are typically prescribed. The approach is individualized, considering the patient’s pain tolerance and response to different medications. Non-pharmacological methods, such as physical therapy and relaxation techniques, are also often incorporated to enhance pain management.
A double bypass heart surgery reroutes blood flow around blocked arteries in the heart. Navigating health conversations, especially when dealing with conditions like psoriasis, can be tricky. For example, sometimes it’s hard to find the right words to talk about your experience with a condition like psoriasis, and the best way to approach that topic is a topic for another blog post, like conversation issues discussing psoriasis.
Ultimately, a double bypass is a serious procedure with significant recovery periods, and careful planning is essential.
Monitoring Vital Signs Post-Operation
Regular monitoring of vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, and oxygen saturation) is crucial to detect any potential complications early. This allows for prompt intervention if needed. The frequency of monitoring depends on the patient’s condition and response to the surgery.
Post-Operative Activity Schedule
| Day | Activity | Care |
|---|---|---|
| Days 1-3 | Light activity, such as sitting up in bed, getting out of bed with assistance. | Monitoring vital signs every 2-4 hours. Pain management as prescribed. Deep breathing exercises encouraged. |
| Days 3-7 | Gradually increasing activity levels, short walks, and assisted ambulation. | Monitoring vital signs every 4-6 hours. Wound care as directed. Blood pressure and pulse checks. |
| Days 7-14 | Increasing activity levels, including stairs and more complex activities. | Monitoring vital signs every 6-8 hours. Physical therapy sessions. Reviewing medication adjustments. |
| Days 14+ | Returning to normal activities gradually, with physical limitations. | Monitoring vital signs as needed. Follow-up appointments with the surgeon. |
Risks and Complications
While double bypass heart surgery is a life-saving procedure, it’s important to acknowledge the potential risks and complications that can arise. Understanding these potential issues allows patients and their families to make informed decisions and prepare for the possibility of encountering these challenges during the recovery process.
Potential Short-Term Complications
Short-term complications, which typically manifest within the first few days or weeks following surgery, encompass a range of issues. These can include but are not limited to cardiac complications, respiratory issues, and blood clots. Recognizing these complications and their potential severity is crucial for prompt intervention and optimal recovery.
- Cardiac Complications: Problems with the heart’s rhythm (arrhythmias), such as atrial fibrillation or heart block, are possible. These can range from mild and manageable to severe, requiring further interventions like pacemakers. Post-operative heart failure is another possibility, especially in patients with pre-existing heart conditions. The severity depends on factors like the patient’s overall health and the extent of the surgery.
- Respiratory Complications: Patients may experience difficulties with breathing, including pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). These complications often require additional treatment, such as mechanical ventilation. The risk of respiratory complications is influenced by the patient’s pre-existing lung conditions and the nature of the surgery.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are serious blood clot complications that can develop in the legs or lungs after surgery. These clots can block blood flow, leading to severe pain, shortness of breath, and even death. Early mobilization and appropriate anticoagulant therapy are crucial preventative measures.
Potential Long-Term Complications
Long-term complications, which may appear months or even years after surgery, can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. These complications often stem from the impact of the surgery on the heart and surrounding tissues. Examples include chronic pain, chronic heart failure, and a potential need for additional surgeries. Managing expectations and understanding the long-term implications are crucial.
- Chronic Pain: Some patients experience persistent chest pain or pain in the surgical area, impacting their daily activities. Factors influencing pain severity include the extent of the surgical intervention and individual patient responses.
- Chronic Heart Failure: In some cases, the heart may not function optimally long-term, requiring ongoing management with medication and lifestyle adjustments. This can be influenced by pre-existing heart conditions and the complexity of the bypass procedure.
- Need for Additional Surgeries: Further surgical interventions may be required to address complications arising from the initial procedure or due to long-term issues, including valve problems or further coronary artery disease.
Minimizing Complications and Preventative Measures
Various strategies and preventative measures can minimize the risks associated with double bypass heart surgery. These include meticulous pre-operative assessments, meticulous surgical techniques, and aggressive post-operative care.
- Pre-operative Risk Assessment: Comprehensive assessments of the patient’s health, including cardiovascular, respiratory, and coagulation status, help identify potential risk factors. This assessment enables personalized strategies to mitigate risks.
- Surgical Techniques: Minimally invasive surgical techniques and careful surgical planning can reduce the extent of tissue damage, potentially minimizing complications.
- Post-operative Care: Aggressive post-operative care, including close monitoring, pain management, and prompt treatment of any complications, is essential to promote recovery and reduce risks.
Risk Factor Comparison Table
| Risk Factor | Description | Possible Outcomes | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-existing heart conditions | Presence of prior heart diseases | Increased risk of heart failure, arrhythmias, and other complications | High |
| Diabetes | High blood sugar levels | Increased risk of infection and delayed recovery | Medium |
| Smoking | Active smoking habit | Increased risk of blood clots and respiratory complications | Medium-High |
| Age | Older age | Increased risk of complications due to physiological changes | Medium-High |
Alternatives to Double Bypass Heart Surgery
A double bypass, while a crucial procedure for many, isn’t always the best option. Sometimes, less invasive or more targeted approaches can achieve similar results with fewer risks and a quicker recovery. Understanding these alternatives is vital for patients and healthcare professionals alike. Choosing the right procedure depends on the specifics of the individual’s condition.Considering alternatives to double bypass surgery is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes.
Factors such as the extent of the blockage, the patient’s overall health, and potential risks need careful evaluation. A thorough assessment by a team of medical professionals, including cardiologists, surgeons, and other specialists, is paramount in selecting the most appropriate treatment strategy.
Alternative Procedures
Several procedures can be considered as alternatives to a double bypass. These procedures often address specific areas of blockage and may offer a less extensive approach than a full double bypass.
- Percutaneous Coronary Interventions (PCI): PCI, commonly known as angioplasty, involves inserting a catheter with a balloon to open narrowed arteries. Stents are often placed to maintain the artery’s patency. This minimally invasive procedure is often suitable for patients with single-vessel or limited multi-vessel disease. PCI avoids the need for open-heart surgery, resulting in a quicker recovery time and less scarring.
- Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (MICS CABG): MICS CABG utilizes smaller incisions than traditional CABG, minimizing trauma to surrounding tissues. This technique, similar to a traditional bypass, uses grafts to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries. It often results in less pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery, but may not be suitable for all cases of severe blockage.
- Off-pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (OPCABG): OPCABG is a surgical procedure that involves bypassing blocked arteries without using a heart-lung machine. This method reduces the risk of complications associated with the use of the heart-lung machine, but it might be less suitable for patients with extensive blockages.
- Valve Repair or Replacement: If valve disease is contributing to the heart’s workload, valve repair or replacement may be necessary. This approach targets the underlying cause of the heart’s stress, potentially improving overall function and reducing the need for a bypass.
Reasons for Choosing an Alternative
Patients may opt for an alternative to a double bypass due to various factors. These alternatives often reduce the overall invasiveness of the procedure, potentially leading to shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, and a reduced risk of complications. The specific situation, including the extent of the blockage, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s assessment, are crucial in determining the best course of action.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Procedures
Choosing the right procedure involves weighing the benefits and drawbacks of each alternative. For instance, PCI is a less invasive procedure, resulting in a quicker recovery, but it may not be sufficient for extensive blockages. MICS CABG offers a less extensive approach compared to traditional CABG but might not be suitable for all cases of severe blockages. The risks of each procedure vary, and the decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Conditions Requiring Alternative Approaches
Certain conditions may necessitate alternative surgical approaches to a double bypass. For instance, patients with limited access to the vessels or those with a history of multiple prior surgeries may be better served with PCI or MICS CABG. The extent of the blockage, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of any other underlying conditions are all crucial factors in making the decision.
Comparison Table
| Alternative Procedure | Success Rate (Approximate) | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Percutaneous Coronary Interventions (PCI) | High (90-95%) | Bleeding, stroke, stent thrombosis, restenosis |
| Minimally Invasive Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (MICS CABG) | High (90-95%) | Bleeding, infection, stroke, graft failure |
| Off-pump Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (OPCABG) | High (90-95%) | Bleeding, infection, stroke, arrhythmias |
| Valve Repair or Replacement | High (95%+ for repairs) | Bleeding, infection, stroke, complications related to the specific valve procedure |
Patient Outcomes and Long-Term Implications
A double bypass heart surgery, while often a life-saving procedure, carries long-term implications for patients. Understanding these implications, including potential quality of life improvements and challenges, is crucial for both patients and their healthcare teams. The success of the surgery hinges on a combination of factors, from pre-operative health to post-operative adherence to medical recommendations. Ultimately, the long-term well-being of patients is significantly influenced by their proactive participation in their own recovery and adherence to ongoing care.Long-term outcomes for patients who undergo a double bypass vary significantly, depending on several factors.
These factors include the patient’s overall health, the severity of the underlying heart condition, the skill of the surgical team, and the patient’s commitment to lifestyle changes and follow-up care. Success is often measured not only by survival but also by improvements in quality of life and the ability to maintain an active lifestyle.
Long-Term Survival Rates
Post-operative survival rates for double bypass surgery are generally high. Data from reputable medical institutions indicate a significant improvement in survival compared to patients with similar conditions who do not undergo surgery. While survival rates are generally positive, individual results can vary based on pre-existing conditions and patient factors. Long-term follow-up care is essential to monitor for potential complications and ensure optimal outcomes.
Quality of Life Improvements
Double bypass surgery can dramatically improve the quality of life for many patients. Patients often report a significant reduction in chest pain, improved exercise tolerance, and an overall sense of well-being. They are better able to engage in activities they enjoyed before their heart condition worsened. The ability to return to work and daily activities is frequently enhanced.
However, it’s important to remember that individual experiences can vary.
Factors Influencing Surgical Success
Several factors can influence the success of a double bypass surgery. Pre-operative health, the severity of the heart condition, and the surgical technique all play a role. Patient adherence to post-operative recommendations, including medication, diet, and exercise, is crucial. Furthermore, a strong support system and proactive engagement in follow-up care significantly contribute to positive long-term outcomes.
Importance of Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring and follow-up care are critical for optimizing the long-term outcomes of double bypass surgery. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and adherence to prescribed medications are vital for detecting and addressing any potential complications early. This proactive approach allows healthcare professionals to intervene promptly, potentially preventing future health issues. Regular cardiac rehabilitation programs can also greatly improve long-term outcomes by helping patients develop healthy lifestyle habits.
Long-Term Effects and Impact
| Aspect | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Activity | Increased ability to perform daily activities and exercise | Potential for fatigue or limitations in physical activity, especially in the early post-operative period. |
| Work Capacity | Improved ability to return to work or engage in desired occupations. | Potential limitations in work capacity, especially if the job requires strenuous activity. |
| Emotional Well-being | Increased confidence and improved overall mental health | Potential for anxiety, depression, or emotional distress related to the surgery and recovery process. |
| Social Interactions | Improved ability to participate in social activities | Potential for social isolation or reduced social interaction due to physical limitations. |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Improved lifestyle choices (diet, exercise) | Need to make long-term dietary and lifestyle changes to manage health conditions. |
Last Word
In conclusion, a double bypass heart surgery is a complex procedure with potential risks and benefits. Thorough preparation, meticulous surgical execution, and diligent post-operative care are crucial for optimal outcomes. While the surgery can significantly improve a patient’s quality of life, understanding the various factors involved is essential for informed decision-making. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the procedure, allowing readers to gain a deeper understanding of this critical medical intervention.