Does high blood sugar make you tired? This exploration delves into the fascinating link between elevated blood sugar and persistent fatigue. We’ll unravel the physiological mechanisms, examine symptoms, and discuss effective management strategies. Understanding this connection is key to optimizing your well-being. High blood sugar, often associated with conditions like diabetes, can disrupt the body’s…
Category: Health and Wellness
High Blood Pressure and Erectile Dysfunction A Deep Dive
High blood pressure and erectile dysfunction are often linked, and understanding this connection is crucial for proactive health management. This exploration delves into the physiological mechanisms behind this association, examining the prevalence of both conditions and the factors that contribute to their development. We’ll also cover diagnosis, management strategies, potential complications, and ultimately, preventative measures….
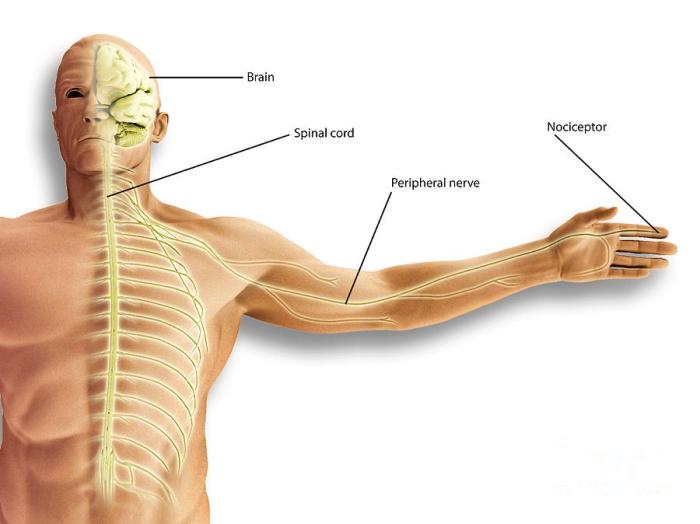
What is Nociceptive Pain A Deep Dive
What is nociceptive pain? It’s pain originating from actual or potential tissue damage. This isn’t just a fleeting discomfort; it’s a complex physiological response triggered by various stimuli. From a simple burn to a persistent muscle strain, understanding the mechanisms behind nociceptive pain is crucial for effective pain management. This exploration delves into the science…
EGCG Supplement Benefits and Safety A Deep Dive
EGCG supplement benefits and safety are a complex topic. This exploration delves into the chemical makeup, potential health advantages, safety considerations, and factors specific to different groups. We’ll cover everything from the various forms of EGCG supplements to their potential interactions with other substances, and even examine historical uses. Getting informed is key to making…
What is Iron Overload? A Deep Dive
What is iron overload? This fascinating condition involves an excess of iron in the body, disrupting normal physiological processes. Iron, crucial for various bodily functions, is absorbed and stored. But when the body absorbs more iron than it needs, it can lead to a buildup that damages vital organs. This buildup contrasts sharply with iron…
Fixing Low Iron Thyroid A Comprehensive Guide
Fixing low iron thyroid is crucial for overall health. This guide dives deep into the intricate connection between iron deficiency and thyroid function, exploring the diagnostic process, treatment strategies, dietary considerations, and vital monitoring steps. We’ll uncover how these two seemingly separate conditions can influence each other, potentially masking symptoms and complicating diagnosis. Get ready…
Fatigue Symptoms Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Fatigue symptoms causes diagnosis and treatment is a complex issue affecting many people. This in-depth exploration dives into the various facets of fatigue, from its different forms and potential causes to effective diagnostic methods and treatment strategies. Understanding the nuances of fatigue, including its physiological and psychological roots, is crucial. This article will explore the…
Why Do I Sweat So Easily? Understanding the Causes
Why do I sweat so easily? This question plagues many, leading to discomfort and concern. Understanding the underlying reasons for excessive sweating is crucial for finding relief and improving overall well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the medical conditions, lifestyle factors, and physiological mechanisms that contribute to excessive perspiration, providing insights into diagnosis, treatment, and prevention…
Does Iron Cause Constipation? A Deep Dive
Does iron cause constipation? This exploration delves into the complex relationship between iron intake and digestive health. Understanding the role of iron in the body, the various forms of iron, and their absorption processes is crucial to comprehending this connection. We’ll also examine how individual differences, diet, and medications might influence this relationship. Iron, an…
Does Milk Make You Taller? Unveiling the Truth
Does milk make you taller? This age-old question sparks curiosity and debate. We’ll delve into the intricate relationship between milk consumption and height, exploring the science behind growth and development, the nutritional value of various milk types, and the evidence from scientific studies. This exploration promises to shed light on whether that glass of milk…