Sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants: This comparison explores the two leading preventative dental care methods. Sealants are a popular choice, often seen as a straightforward solution. However, silver diamine fluoride (SDF) offers a unique approach, with both advantages and disadvantages. We’ll examine their application methods, efficacy, patient considerations, safety, and even delve into clinical case studies and cost-benefit analyses.
Understanding the differences between these two treatments is crucial for patients and dental professionals alike. This in-depth comparison will provide a clear picture of their effectiveness, potential side effects, and overall suitability for different situations.
Introduction to Dental Sealants and Silver Diamine Fluoride
Dental caries, or tooth decay, is a common oral health problem affecting individuals of all ages. Effective preventative measures are crucial in maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Two such preventive strategies are dental sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF). Understanding their individual applications and comparing their efficacy can help patients and dentists make informed decisions regarding oral health care.Dental sealants and silver diamine fluoride are distinct approaches to preventing cavities, each with its own mechanism of action and suitability for different situations.
Sealants are a more traditional method, while SDF has emerged as a valuable tool in recent years. This discussion will delve into the specifics of each, highlighting their similarities and differences, and offering a comparative analysis of their cost-effectiveness.
So, I’ve been researching sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants lately, and it’s a tough one. While sealants are a classic approach, sliver diamine fluoride seems like a promising alternative. Interestingly, similarly to how gaviscon antacid treatment for heartburn can provide fast relief for acid indigestion, this fluoride treatment seems to offer a quick and effective way to prevent cavities.
Ultimately, the best choice for your oral health will depend on individual needs and circumstances, but it’s certainly a compelling topic to explore further regarding sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants.
Dental Sealants: A Protective Barrier
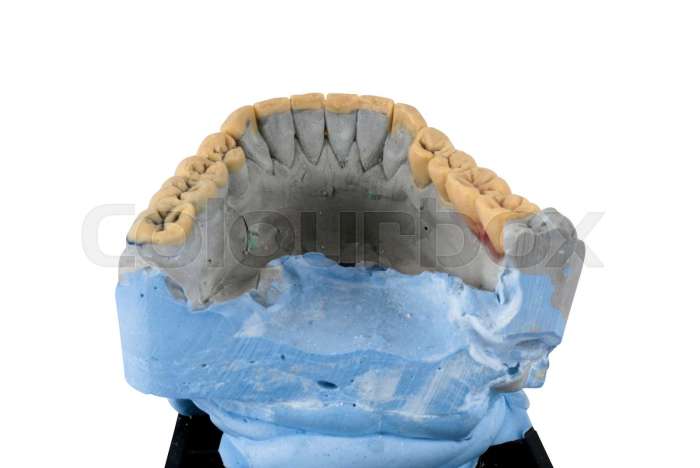
Dental sealants are thin, protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of molars and premolars. These surfaces, often rough and pitted, are prone to accumulating food particles and bacteria. The sealant acts as a barrier, preventing these particles from lodging in the grooves and fissures, thus inhibiting bacterial growth and reducing the risk of cavities. The procedure typically involves applying a tooth-colored resin material to the surface of the tooth.
This material hardens, creating a smooth, protective layer that makes it difficult for food and bacteria to adhere.
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF): A Powerful Cavity Fighter
Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is a topical liquid containing fluoride ions and silver ions. SDF works by penetrating the tooth’s surface and releasing fluoride, which strengthens tooth enamel and makes it more resistant to decay. Additionally, the silver ions in SDF inhibit bacterial growth within the tooth’s structure, further reducing the risk of cavities. SDF can be applied directly to areas affected by or at risk of cavities, including pits and fissures, and even early carious lesions.
It is often used as a minimally invasive treatment option.
Similarities and Differences in Use Cases
Both sealants and SDF aim to prevent cavities by creating a barrier against bacteria and promoting remineralization of enamel. However, they differ in their application and target areas. Sealants are typically applied to the smooth surfaces of teeth or in pits and fissures to prevent cavities from forming. SDF is used for areas already affected by decay or where decay is suspected.
SDF’s effectiveness in arresting the progression of early caries is noteworthy. Sealants, on the other hand, are highly effective in preventing cavities from developing in the first place. This makes sealants an ideal preventative measure for children and adolescents, particularly those with difficult-to-clean tooth surfaces.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
| Feature | Dental Sealants | Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Generally lower | Potentially lower, but can vary based on the complexity of the treatment. |
| Long-term cost | Potentially lower in the long run, as it prevents cavities from forming | Can be lower in the long run if it prevents more extensive dental procedures |
| Frequency of application | Typically a one-time application for a given area | May require follow-up applications |
| Treatment time | Generally short | Generally short |
| Potential for reapplication | Usually not necessary | Potentially required for areas with persistent issues |
The long-term cost-effectiveness of SDF often hinges on preventing the need for more costly dental interventions. By addressing early signs of decay, SDF may reduce the need for fillings or extractions.
The table above highlights the potential cost-effectiveness of both treatments, emphasizing that the long-term savings from preventing more extensive dental work are significant factors. Factors such as insurance coverage, treatment complexity, and individual patient needs can influence the final cost comparison.
Methods of Application: Sliver Diamine Fluoride Vs Sealants
Applying dental sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF) requires precise techniques to ensure effective treatment. Understanding the steps involved in each procedure is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes and patient comfort. This section details the typical methods for applying both materials, highlighting the differences in procedures and necessary equipment.
Dental Sealant Application
Dental sealants are a preventive measure applied to the grooves and fissures of posterior teeth to prevent the accumulation of bacteria and food particles. The process typically involves these steps:
- Tooth Preparation: The tooth surface is thoroughly cleaned and dried to remove any debris or plaque. This step is critical to ensure proper sealant adhesion. A fluoride varnish might be applied prior to sealant application to enhance the bonding process.
- Sealant Material Selection: The appropriate sealant material is chosen based on the patient’s needs and the specific tooth structure. Different types of sealants are available, with varying compositions and curing mechanisms.
- Sealant Application: The sealant is carefully placed into the grooves and fissures of the tooth using a brush or applicator. The material is typically light-cured or self-cured, according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Curing and Finishing: The sealant is cured according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper polymerization and bonding. Excess sealant is removed to create a smooth and polished surface.
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) Application
Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is a potent fluoride treatment used to arrest caries and remineralize tooth surfaces. Its application differs significantly from dental sealants.
- Patient Assessment: Before application, the dentist carefully assesses the tooth’s condition and identifies the affected areas. This includes evaluating the extent of the carious lesion and determining the appropriate concentration of SDF.
- Concentration Selection: SDF is available in different concentrations. Typically, a 38% concentration is used for carious lesions, while lower concentrations may be used for preventative purposes.
- Application Technique: SDF is carefully applied directly to the carious lesion or affected area using a small applicator. The application time varies depending on the lesion’s severity and the desired outcome. A critical aspect of SDF application is minimizing the exposure of surrounding healthy tooth tissues.
- Post-Application Care: After application, the area is monitored for any adverse reactions. No rinsing or further treatment is generally required.
Comparison of Application Techniques
The methods for applying sealants and SDF differ considerably. Sealants are applied to healthy tooth surfaces to prevent future decay, while SDF is applied to existing lesions to arrest the progression of decay. Sealants involve careful placement into grooves and fissures, whereas SDF is applied directly to the affected area. Furthermore, sealants require curing and finishing steps, which are not needed for SDF.
Equipment for Sealant and SDF Applications
The following table Artikels the equipment required for both sealant and SDF applications.
| Category | Dental Sealants | SDF |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Dental explorer, scaler, air abrasion device, polishing instruments, rubber dam (sometimes) | Dental explorer, scaler, (potentially) rubber dam |
| Application | Sealant applicator, light-curing unit, brush, sealant material, mixing materials (if needed) | Small applicator, fluoride solution (SDF), potentially cotton rolls, cotton pliers, protective eyewear (for dentist) |
| Finishing | Finishing burs, polishing materials, polishing instruments | None (typically) |
Efficacy and Effectiveness

Dental sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF) are both valuable tools in the fight against tooth decay. Understanding their effectiveness, especially in preventing cavities and arresting early caries, is crucial for making informed decisions about preventative care. This section delves into the efficacy and long-term results of both treatments.Sealants, in particular, offer a highly effective preventative measure, especially when applied to susceptible areas.
SDF, on the other hand, excels at arresting the early stages of decay and promoting remineralization. Comparing their long-term durability reveals unique strengths for each, ultimately leading to better overall oral health.
Sealant Effectiveness in Cavity Prevention
Sealants are thin, plastic coatings applied to the grooves and pits of teeth, effectively preventing bacteria from accumulating and causing cavities. Studies consistently show a significant reduction in cavities in treated areas. For example, a meta-analysis published in the Journal of Dentistry demonstrated a substantial reduction in caries rates among children who received sealant applications compared to those who did not.
This protective barrier creates a physical barrier that hinders the development of decay, especially in the hard-to-reach grooves of molars. This makes them an extremely valuable preventive measure.
SDF Efficacy in Arresting Early Caries and Remineralization
Silver diamine fluoride (SDF) is a potent agent for arresting early caries. SDF works by creating a chemical barrier on the tooth surface, which inhibits bacterial growth and promotes remineralization. Remineralization is the process of replacing lost minerals in tooth enamel, strengthening the tooth structure and slowing the progression of decay. Clinical trials have consistently demonstrated the effectiveness of SDF in arresting the progression of early caries lesions and in reversing the early stages of demineralization.
This makes it a particularly useful tool in managing early cavities and promoting a healthier oral environment.
Long-Term Results and Durability
The long-term durability of both sealants and SDF varies. Sealants, when properly placed and maintained, can offer protection for several years. However, factors like trauma, chewing habits, and oral hygiene practices can influence the longevity of sealants. SDF, while highly effective in arresting early caries, may need periodic applications to maintain its protective effect. Both treatments, however, demonstrate their worth in reducing cavities and maintaining oral health over time.
Comparative Success Rates by Age Group
| Treatment | Children (6-12 years) | Adolescents (13-18 years) | Adults (19+ years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sealants | Studies show significantly reduced caries rates in children with sealants compared to control groups. | Similar success rates in adolescents compared to children, although the exact data can vary depending on the specific study. | While less common in adults, sealants can still be effective for preventing decay in areas prone to cavities. |
| SDF | Highly effective in arresting early caries and promoting remineralization, showing significant reduction in decay progression. | Effective in arresting early caries in adolescents, offering a way to intervene early in the decay process. | SDF can effectively arrest early caries in adults, and may be a particularly useful tool in high-risk situations. |
Note: Data for success rates varies based on the study and the specific populations being analyzed. The table provides a general overview of the observed effectiveness across different age groups. Further research and specific studies on long-term efficacy are needed for a more in-depth analysis.
Patient Considerations

Choosing between dental sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF) for a patient requires careful consideration of various factors. Both methods offer preventive benefits, but their suitability depends on the individual’s specific oral health, age, and preferences. Understanding the potential advantages and disadvantages of each treatment is crucial for making an informed decision that prioritizes the patient’s well-being.A comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s oral health status, including the presence and severity of caries risk factors, is vital.
Factors like the patient’s age, dexterity, and compliance with treatment protocols also play a significant role. Ultimately, the dentist must determine the most appropriate preventive strategy for the individual.
So, I’ve been doing some research on sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants for my kids’ teeth, and it’s a bit of a minefield! While sealants are a popular option, exploring healthy alternatives to full fat dairy products like these might play a surprisingly big role in their oral health, too. Ultimately, finding the best solution for cavities prevention still comes down to a personalized approach, considering all the options carefully.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choice
The decision to use sealants or SDF hinges on various factors, primarily the patient’s oral health status and specific needs. Careful assessment is crucial for selecting the most effective approach.
- Patient Age: Sealants are generally preferred for younger patients, especially those with developing permanent molars. SDF is more suitable for older patients, adolescents, and adults, particularly when rapid treatment is required or when sealants are not feasible.
- Oral Health Conditions: Patients with extensive caries or significant risk factors for developing cavities might benefit from SDF due to its rapid action. Sealants are a better choice for patients with intact enamel and a lower risk of caries.
- Compliance and Dexterity: Sealants require cooperation from the patient to ensure the sealant material remains adhered correctly to the enamel surfaces. Patients with difficulties following instructions or those with limited dexterity may find SDF application easier.
- Accessibility and Cost: The accessibility of dental professionals experienced in both sealant and SDF application influences treatment selection. In areas with limited access to dental sealant applications, SDF can provide a viable alternative.
Suitability for Different Demographics
The selection of either sealants or SDF can vary based on the patient’s demographic and specific oral health circumstances.
- Children and Adolescents: Sealants are often the preferred choice for children and adolescents, as they protect developing permanent molars from early caries. SDF is sometimes considered for adolescents or younger adults who may not be as compliant with sealant placement or for those with limited access to routine dental care.
- Adults: Both sealants and SDF can be suitable for adults. Sealants are particularly useful for preventing caries in healthy adults, while SDF may be more appropriate for those with active caries or rapid progression of the disease.
Potential Side Effects, Sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants
Both sealants and SDF have potential side effects, although they are generally well-tolerated.
- Sealants: Allergic reactions to the sealant materials are rare. The primary potential discomfort is the temporary sensitivity experienced by some patients during the procedure.
- SDF: While generally safe, SDF application can cause mild tooth sensitivity, temporary discoloration (especially in children), and a burning sensation. Rare cases of allergic reactions or sensitivity have been reported.
Patient Experience Comparison
The patient experience can vary significantly between sealant and SDF applications.
| Feature | Sealants | SDF |
|---|---|---|
| Comfort | Generally comfortable, minimal discomfort during application. | May cause a mild burning sensation, but is usually tolerated well. |
| Discomfort | Possible temporary sensitivity. | Possible temporary sensitivity, discoloration, or burning sensation. |
| Procedure Duration | Typically shorter. | Typically shorter. |
| Frequency of Application | Typically applied once or twice for a lifetime. | Can be applied more frequently if needed, usually as a preventive measure. |
Safety and Precautions
Protecting patients and ensuring a safe dental procedure are paramount. This section details the crucial safety measures and precautions for both sealant and Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) applications, emphasizing potential hazards and mitigation strategies. Proper adherence to these guidelines is vital to prevent complications and maintain patient well-being.
Sealant Application Safety Measures
Proper preparation of the tooth surface is crucial for sealant adhesion and long-term effectiveness. This involves meticulous cleaning and etching to create a receptive surface for the sealant material. Using the correct etching agent concentration and time is vital to ensure optimal bonding. Additionally, maintaining a sterile environment throughout the procedure is essential to prevent the introduction of pathogens.
This includes using sterile instruments, gloves, and proper hand hygiene. The use of a high-volume suction system to remove saliva and debris is also important to avoid contamination.
SDF Application Safety Precautions
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) offers a unique approach to caries prevention, but potential staining is a significant consideration. Understanding the risks and implementing appropriate safety measures is critical. SDF can stain the tooth structure, particularly if it contacts the enamel for an extended period. Therefore, precise application technique is paramount. The use of appropriate isolation techniques, such as rubber dams, can help prevent unintentional contact with surrounding teeth.
Post-application rinsing and the use of a protective barrier to prevent the solution from spreading to adjacent teeth are also important steps. Care should be taken to avoid contact with the eyes and skin, using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and eyewear. Monitoring the application time closely to prevent prolonged contact is essential to minimize staining risk.
Safety Equipment and Protocols
Maintaining a safe environment during both sealant and SDF applications requires meticulous attention to detail. Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential. This includes wearing gloves, masks, and eye protection. Sterile instruments and materials are crucial to avoid cross-contamination. Adequate ventilation in the treatment area helps minimize exposure to potentially harmful chemicals.
Detailed protocols should be in place for managing potential accidents, including accidental exposure to SDF or the etching agent. These protocols should include immediate rinsing, and the use of appropriate neutralizing agents if needed.
Summary of Safety Protocols
| Procedure | Potential Hazards | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Sealant Application | Cross-contamination | Sterile instruments, gloves, hand hygiene, high-volume suction |
| Incorrect etching technique | Following manufacturer’s instructions for etching agent concentration and time | |
| Inadequate tooth preparation | Thorough cleaning and surface preparation prior to application | |
| SDF Application | Staining | Precise application technique, isolation techniques (e.g., rubber dam), prompt rinsing, protective barriers |
| Accidental contact with eyes/skin | Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), proper handling procedures | |
| Prolonged contact | Close monitoring of application time | |
| Inadequate isolation | Rubber dam isolation to prevent spillover to adjacent teeth |
Clinical Case Studies
Analyzing the efficacy of dental sealants and Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) requires examining real-world applications. Case studies offer valuable insights into the performance of these treatments, allowing dentists to make informed decisions based on observed outcomes. These studies provide practical examples that illustrate the advantages and limitations of each approach.
While researching sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants, I stumbled upon a fascinating connection. Sometimes, dental issues can mimic other health problems, like urinary tract infections. This got me thinking about how important it is to get a proper diagnosis, especially when symptoms overlap. For example, some sexually transmitted diseases ( stds that feel like uti ) can present with similar discomfort to a UTI.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of these dental treatments and potential underlying health concerns is key to making informed decisions about your oral care.
Hypothetical Case Study: Early Caries
A 10-year-old patient presents with early enamel lesions on the buccal surfaces of the maxillary molars. Visual inspection and probing confirm the presence of demineralization, indicating the early stages of caries. The patient is otherwise healthy and cooperative.
Decision-Making Process
The decision to use sealants or SDF depends on several factors. The extent of the lesion, the patient’s oral hygiene habits, and their compliance are crucial considerations. In this case, the dentist assesses the depth and size of the demineralized areas. The patient expresses a preference for a non-invasive treatment. The dentist also considers the potential for remineralization and the patient’s willingness to maintain good oral hygiene.
Managing the Patient’s Condition
- Sealants: The dentist meticulously prepares the occlusal surfaces of the molars. This includes isolating the teeth with cotton rolls and drying the surfaces. The sealant material is then applied and light-cured to form a durable barrier. Post-operative instructions emphasize the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene practices. This method prevents the entry of bacteria into the pits and fissures of the teeth.
Regular check-ups are scheduled to monitor the progression of the lesion.
- SDF: In this case, SDF application is an alternative to sealants. The dentist carefully applies a drop of SDF to the affected areas, allowing it to dwell for a few minutes. This method promotes remineralization and reduces the risk of further decay. Post-operative instructions include avoiding rinsing or eating for a short period to allow the fluoride to remain in contact with the teeth.
Follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the response and to identify any adverse reactions.
Treatment Efficacy Summary
| Treatment | Method | Outcomes | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sealants | Application of a protective coating to the occlusal surfaces of the teeth. | Significant reduction in caries progression in the majority of cases. | High, especially for preventing new caries. |
| SDF | Application of a fluoride-containing agent to the affected tooth surfaces. | Positive outcomes, often resulting in remineralization and arrested decay. | High, particularly in arresting early lesions. |
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Dental treatments, like sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF), aim to prevent cavities, a significant concern for individuals and public health. A crucial aspect of evaluating these treatments is understanding their cost-effectiveness. This involves comparing the initial costs of materials and procedures with the long-term savings from avoided dental work.Analyzing the cost-benefit ratio allows for informed decisions regarding treatment choices, particularly in public health initiatives.
Understanding the financial implications, both immediate and future, is essential for optimizing preventive strategies and maximizing the value of dental care.
Material and Procedure Costs
Initial costs vary significantly based on factors like location, dentist’s fees, and specific materials used. Sealants typically involve a one-time application cost, while SDF applications may require multiple visits for optimal results. The cost of the materials themselves also influences the overall expenditure. For instance, composite resin sealants might have a slightly higher upfront cost compared to SDF, but this could be offset by the need for fewer future treatments.
Variations in pricing often depend on the specific location and dental practice.
Long-Term Cost Implications
Preventing cavities significantly reduces the need for more expensive restorative procedures like fillings, crowns, or root canals in the long run. A cavity left untreated can escalate into complex and costly dental interventions. By preventing cavities, sealants and SDF effectively minimize the lifetime cost of dental care. The long-term cost implications extend to productivity gains and reduced pain and suffering for patients.
For example, a child avoiding multiple fillings in their formative years can positively impact their educational and social development.
Cost-Effectiveness in Public Health
Cost-effectiveness analysis becomes even more critical in public health initiatives. By preventing cavities in large populations, these treatments contribute to a healthier and more productive workforce. In areas with limited access to dental care, the long-term cost savings from preventive treatments like sealants and SDF become paramount. Reduced absenteeism from work and school due to dental pain can also have a significant economic impact.
Summary Table
| Feature | Sealants | SDF |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Material Cost | Moderate (varies with resin type) | Low (relatively inexpensive) |
| Procedure Cost | Moderate (one-time application) | Moderate (multiple applications might be needed) |
| Long-Term Cost Savings | Significant (avoidance of fillings, crowns) | Significant (avoidance of fillings, crowns) |
| Public Health Impact | Reduced dental treatment burden on the public system | Reduced dental treatment burden on the public system |
| Treatment Frequency | Single application | Multiple applications may be necessary |
| Cost-Effectiveness for Prevention | High | High |
Cost-effectiveness varies significantly based on local factors, such as material pricing and dentist fees. Local data on treatment costs and dental service utilization should be considered when comparing these approaches.
Future Trends and Research
The landscape of dental caries prevention is constantly evolving, with innovative approaches emerging to combat this persistent oral health challenge. Sealants and silver diamine fluoride (SDF) are cornerstones of modern preventive dentistry, and ongoing research is poised to further refine their efficacy and expand their application. This exploration delves into exciting future trends and research directions in both areas, highlighting potential impacts on clinical practice.Emerging research is focused on optimizing existing treatments and exploring novel strategies.
This includes investigating improved materials, application techniques, and patient selection criteria to maximize the effectiveness and longevity of both sealants and SDF.
Emerging Trends in Sealant Technology
Advancements in sealant materials are a key focus of research. Researchers are exploring new polymers and composites to enhance the durability and bonding strength of sealants. These advancements could potentially lead to sealants with improved resistance to wear and tear, prolonging their effectiveness and reducing the need for frequent replacements. Improved adhesive properties are also being explored to enhance the sealants’ bond to enamel, minimizing the risk of leakage and ensuring long-term protection.
Future Research Directions in SDF Applications
Future research into SDF is targeting more precise and targeted delivery methods. This includes exploring the potential of controlled-release formulations to provide sustained fluoride exposure within the affected tooth structure. This could lead to enhanced remineralization and improved clinical outcomes. The research is also investigating the potential for SDF to address specific types of caries or conditions, such as those occurring in particular vulnerable patient groups or those resistant to traditional treatments.
Moreover, investigation into the combined use of SDF with other preventative strategies is also a growing area of research.
Potential Impact of New Research on Sealants and SDF
New research in sealant and SDF technologies could lead to significant improvements in caries prevention. For instance, enhanced sealant durability could reduce the frequency of sealant replacements, minimizing patient discomfort and costs. More precise SDF delivery methods could potentially increase the efficacy of remineralization, especially in hard-to-reach or challenging areas. This could lead to reduced treatment time and improved patient outcomes, especially in high-risk populations.
Summary Table of Emerging Trends in Sealant and SDF Research
| Research Area | Emerging Trends | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Sealant Materials | Improved polymers and composites for enhanced durability and bonding strength | Longer-lasting protection, reduced replacement frequency |
| SDF Application | Controlled-release formulations, targeted delivery methods | Enhanced remineralization, improved clinical outcomes, especially in challenging cases |
| Combined Treatments | Integration of SDF with other preventative strategies | Synergistic effects, improved caries control |
Conclusion
Ultimately, the choice between silver diamine fluoride and dental sealants hinges on individual patient needs and circumstances. Factors like age, oral health history, and specific cavity risk play a significant role. While both methods aim to prevent cavities, SDF’s ability to remineralize teeth and its potential to address early decay makes it an intriguing alternative. Ultimately, a thorough discussion with a dental professional is key to determining the best course of action.