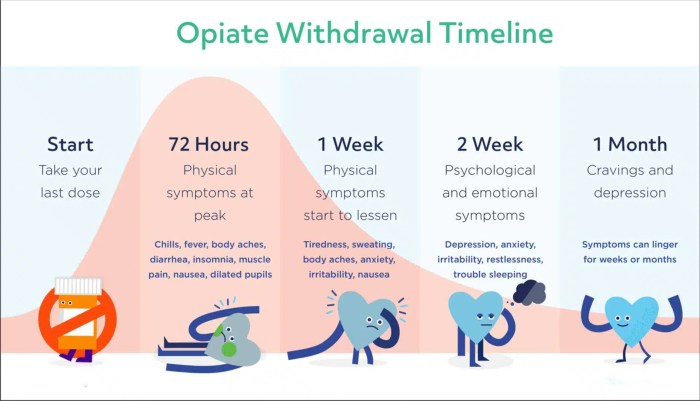
Painkiller withdrawal chronic pain sets the stage for this exploration, delving into the complex interplay of chronic pain, opioid use, and the challenges of withdrawal. This journey navigates the science behind chronic pain, from its various types and causes to the physiological effects of painkillers. We’ll also examine the often-overlooked aspects of withdrawal, from the…
Author: Lonzo Howell
Gluten Intolerance vs Celiac A Deep Dive
Gluten intolerance vs celiac sets the stage for a detailed exploration of two related but distinct conditions. Understanding the nuances between them is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. This exploration will delve into the differences in their nature, mechanisms, and the impact they have on daily life. This comprehensive guide will cover the defining…
What Causes Heat Rash A Deep Dive
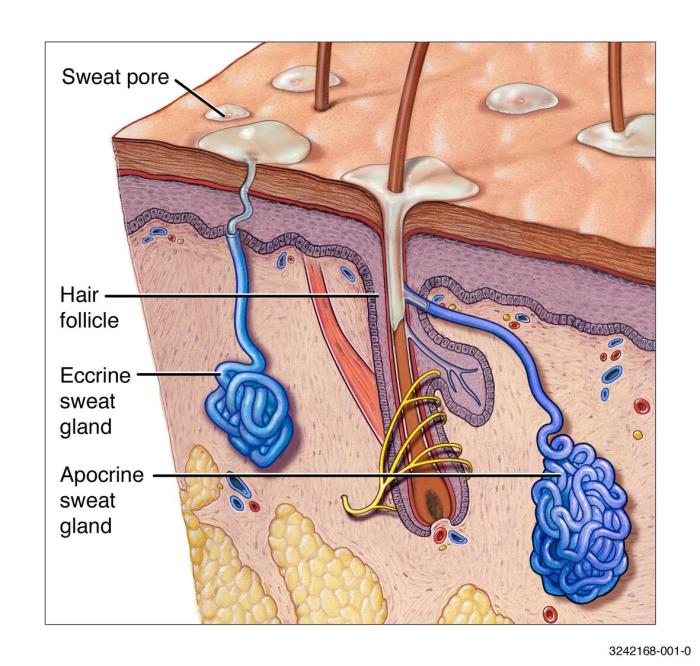
What causes heat rash? This common skin condition, often mistaken for other skin problems, is more than just a summer nuisance. Understanding the underlying factors behind heat rash is key to preventing and effectively managing this uncomfortable issue. From the role of humidity to the impact of clothing, we’ll explore the environmental and personal factors…
How Long Does Aspirin Stay in Your System?
How long does aspirin stay in your system? This question is crucial for understanding aspirin’s impact on the body and its interaction with other medications. The answer isn’t straightforward, as numerous factors influence how quickly aspirin is metabolized and eliminated. This exploration dives into the intricate processes involved, from the biochemical pathways to individual variations…
Why Am I Getting Headaches Every Day All of a Sudden?
Why am I getting headaches every day all of a sudden? This perplexing question plagues many, and understanding the potential causes is crucial for finding relief. Headaches can stem from various factors, ranging from simple lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. This exploration delves into the possible physical, lifestyle, environmental, and medical contributors to this…
Fear of People Anthropophobia Explained
Fear of people anthropophobia – Fear of people, anthropophobia, is a specific phobia characterized by an intense and persistent fear of other people. It’s different from general social anxiety, often focusing on a broad range of social situations rather than a specific fear of interaction. This fear can vary in severity, from mild discomfort to…
How to Treat Bed Bug Bites A Comprehensive Guide
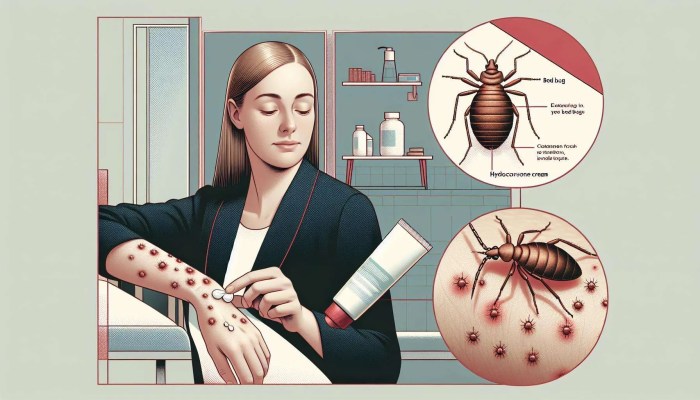
How to treat bed bug bites effectively and safely is a crucial step in managing the discomfort and potential complications associated with these tiny pests. This guide provides a detailed look at identifying bed bug bites, immediate actions, home remedies, over-the-counter treatments, professional options, preventing future bites, and managing symptoms. We’ll cover everything from recognizing…
Dry Eyes in Kids A Comprehensive Guide
Dry eyes in kids sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This condition, while sometimes overlooked, can significantly impact a child’s well-being and vision. Understanding the nuances of dry eye syndrome in children, from its symptoms…
Wake vs Visitation Unveiling the Differences
Wake vs visitation whats the difference – Wake vs visitation: what’s the difference? This question delves into the nuances of these distinct rituals, exploring how cultures across the globe honor their departed. A wake often involves a lively gathering, with shared stories and memories, while a visitation might focus on quiet reflection and personal remembrance….
Medications for Crohns Disease A Comprehensive Guide
Medications for crohns disease – Medications for Crohn’s disease are a crucial aspect of treatment, and understanding the various options available can be empowering for patients. This guide delves into the different types of medications used, their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and important considerations for selection. We’ll explore everything from the basics of…